leetcode -- 二进制
leetcode -- 二进制
在学习编程语言的运算符时,大部分语言都会有与,或等二进制运算符,我在初期学习这些运算符的时候,并没有重点留意这些运算符,并且在后续的业务代码中也没有频繁的使用过,直到后来的一些算法题目和源码中经常遇到它们的身影,这些二进制运算符相比普通的运算符具有更快的效率,比如hashMap的源码就是将%替换成了&。我们在日常的很多需求都是可以转化为二进制运算符来完成的,这篇文章整理我在刷leetcode的时候遇到的一些二进制题目,对于很多问题,其实我们是没有意识来用这些二进制运算符。本文中的代码都在我的github。
公共子串
查找俩个二进制数中的公共部分,可以直接使用位与操作&,因为其中最重要的是确认哪些位置上是1,但是如果查找范围内数的公共子串呢?每个数进行位与操作就会超时,因此必须要考虑使用特殊的思想。
leetcode, 第201题,Bitwise AND of Numbers Range
Given two integers
leftandrightthat represent the range[left, right], return the bitwise AND of all numbers in this range, inclusive.Example 1:
Input: left = 5, right = 7
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: left = 0, right = 0
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: left = 1, right = 2147483647
Output: 0
Constraints:
0 <= left <= right <= 231 - 1
此题目是计算一个区间内所有数的位与结果,这道题咋看很简单,既然要范围内的所有数字都进行位与操作,那么直接使用迭代位与。
// 直接所有数字进行位与
public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int left, int right) {
if(left == right) return left;
int sum = left;
for(int index = left + 1; index <= right; ++index) {
sum &= index;
}
return sum;
}
但是这种写法是超时的,如果范围是1到2147483647,那么程序是无法通过的。
暴力解法看来不可取,只能从数据中找规律了,我们来看位与这种运算
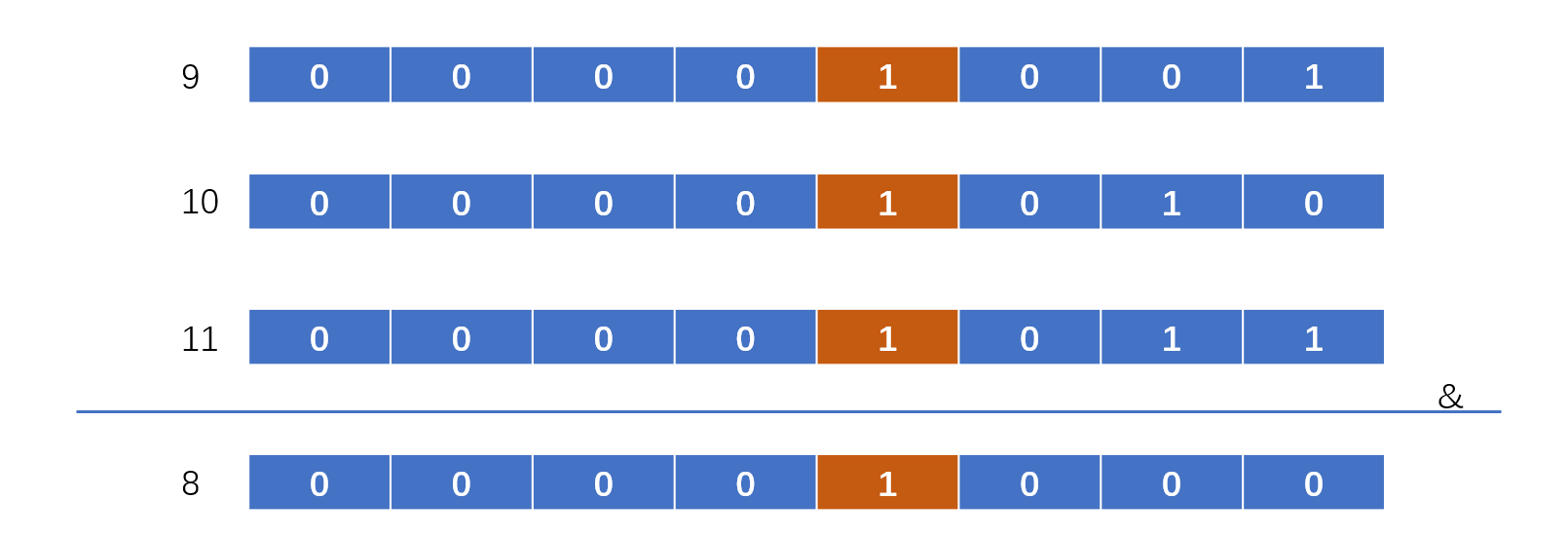
可以从图中看出,最后的结果是所有数字都是1的部分,也就是所有数的公共子串,问题就变成了找所有数的公共子串,那么如何找到所有数的公共子串呢?我们思考一下,一个数大于另一个数在二进制上的表现是什么,比如10>9,那么10的二进制数,从右数的话,第二位是1,大于了9的第二位0,同时9和10的后面的数字都是0000 10XX,也就是说一个数大于另一个数,也就是在某位上的值突然变化了,而我们所求的区间是连续的,也就是这里面所有的数都是按照顺序变化的,既然是按照顺序变化的,我们只要找出顺序中变化最大的那个就可以了。
什么是变化最大的?也就是最小数与最大数之间的变化,我们只要找到这俩个数的公共子串即可,上面我们说一个数大于另一个数,二进制表现是某位上的值突然从0变成1,那么问题在于如何找到这个变化的位数,我们可以看9和10,如果我们能把右边的01和10切掉就好了,切掉的话就是公共子串了,切掉可以表现为移位操作,也就是不断的往后移位,一直到公共部分,到公共部分具体变现为什么呢?也就是俩个数相等。
从上面的分析我们知道了解题思路,移位操作,将最大和最小的俩个值进行移位,一直到俩个数相等,再将这个数后面全变成0,还是移动,只不过方向是往左移位。
// 找出公共子串,移位操作
public int rangeBitwiseAnd_1(int left, int right) {
int shift = 0;
while(left < right) {
left >>>= 1;
right >>>= 1;
++shift;
}
return left << shift;
}
但是上面这个解法的用时只能击败leetcode中24%的人,内存只能击败41%的人,那帮人整天就以压榨性能为乐。如何才能再次提升呢?
上面的算法其实说白了就是将特定位后面的1全部变成0,清除右边的所有1,Brian Kernighan算法就是用来清除二进制当中的1,具体操作就是将n和n-1进行位与运算。
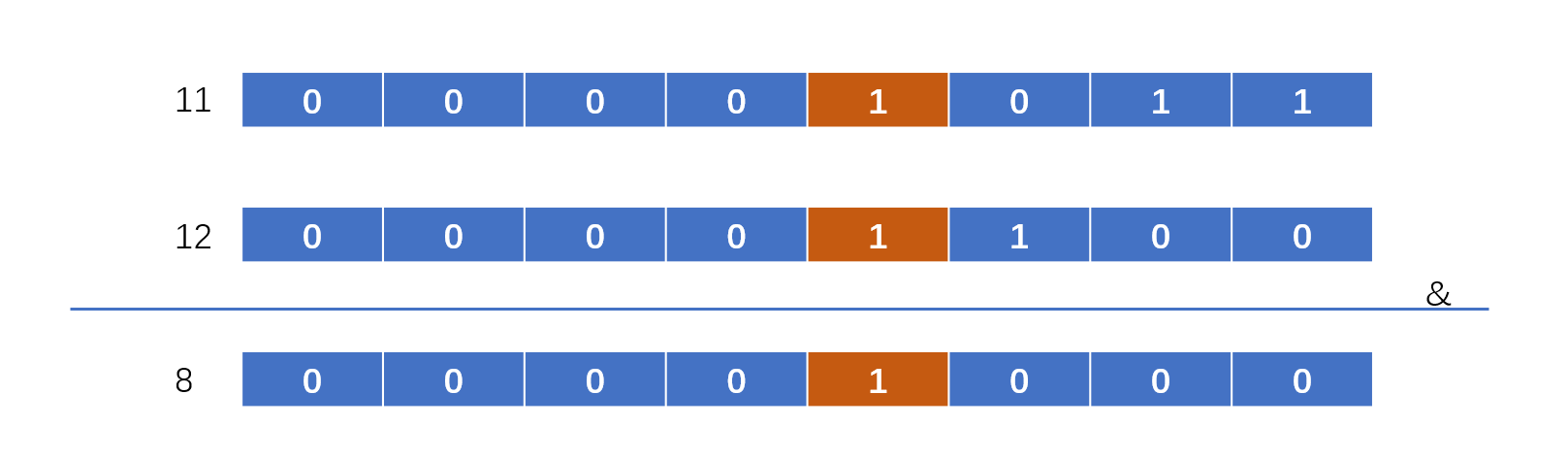
我们需要迭代计算n与n-1,直到m和n相等即可。有的时候我会想,直接将最小值和最大值进行位与操作呢?我们可以看5,6,7
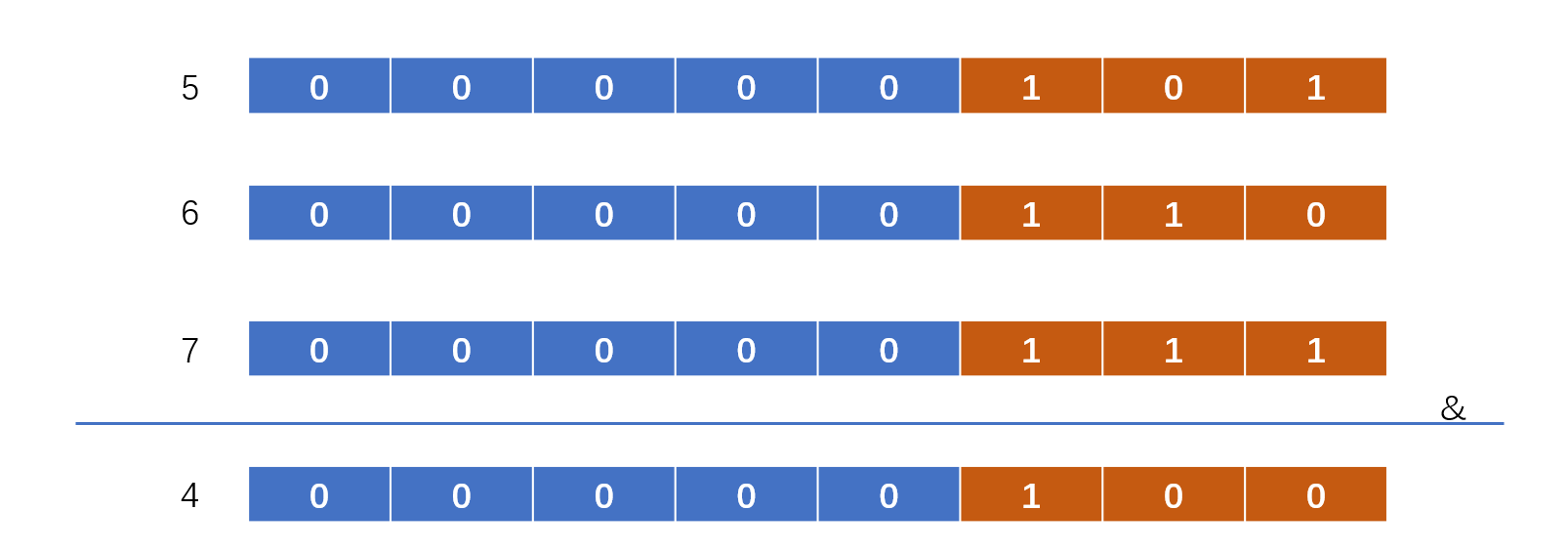
如果将5和7进行位与,发现是错误的,毕竟右边第一位二者都是相同的1,因此相邻数做位与操作
// Brian Kernighan算法结合
public int rangeBitwiseAnd_2(int left, int right) {
while(left < right) {
// 这种操作会增加内存操作
//right &= (right - 1);
right = right & (right - 1);
}
return right;
}
&=和=&,我以前一直以为二者只是写法不同,没有区别,虽然二者的运行时间相同,但是二者的内存消耗却不同,=&操作的内存消耗只有37.5MB,&=却有37.9MB的内存消耗。
反转操作
反转在多个问题中都有出现,如何反转二进制数呢?可以提取移位,也可以分而治之操作。
leetcode, 第190题,Reverse Bits
Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer.
Note:
- Note that in some languages such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, both input and output will be given as a signed integer type. They should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
- In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 2 above, the input represents the signed integer
-3and the output represents the signed integer-1073741825.Follow up:
If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
Example 1:
Input: n = 00000010100101000001111010011100
Output: 964176192 (00111001011110000010100101000000)
Explanation: The input binary string 00000010100101000001111010011100 represents the unsigned integer 43261596, so return 964176192 which its binary representation is 00111001011110000010100101000000.
Example 2:
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 3221225471 (10111111111111111111111111111111)
Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 represents the unsigned integer 4294967293, so return 3221225471 which its binary representation is 10111111111111111111111111111111.
Constraints:
- The input must be a binary string of length
32
此题是将二进制进行反转,这个反转问题在什么地方都存在,整数反转、链表反转,字符串反转等等,而且回文字有时也是反转问题。最容易想到的就是一个一个的进行颠倒位置就可以,主要是二进制的颠倒如何来做?

我们可以使用1与这个数进行位与运算,这个位与操作提取出反转数的最低位,之后将最低位进行移位,移位之后将之加到之前的值上即可。
// 逐位颠倒
public int reverseBits(int n) {
int result = 0;
for(int index = 0; index < 32; ++index) {
result |= (n & 1) << (31 - index);
// 这里的位或与相加差不多
// result += (n & 1) << (31 - index);
n >>= 1;
}
return result;
}
其实上面的实现还有一种写法,我们可以看出要是最后一位是0的话,那么其实就不用相加,这个时候使用位异或或者位或将之前的计算结果保存下来就可以了。
// 反转
public int reverseBits_1(int n) {
int result = 0;
for(int index = 0; index < 32; ++index) {
result ^= ((n >> index) & 1) == 1 ? (1 << (31-index)):0;
}
return result;
}
反转是将其中的每一位进行颠倒,那么能不能扩大想一下,将其中的每两位颠倒,将其中的每四位颠倒,将其中的每八位颠倒,将其中的每十六位颠倒,那么就简单了,我们按照这种分而治之的思路来看
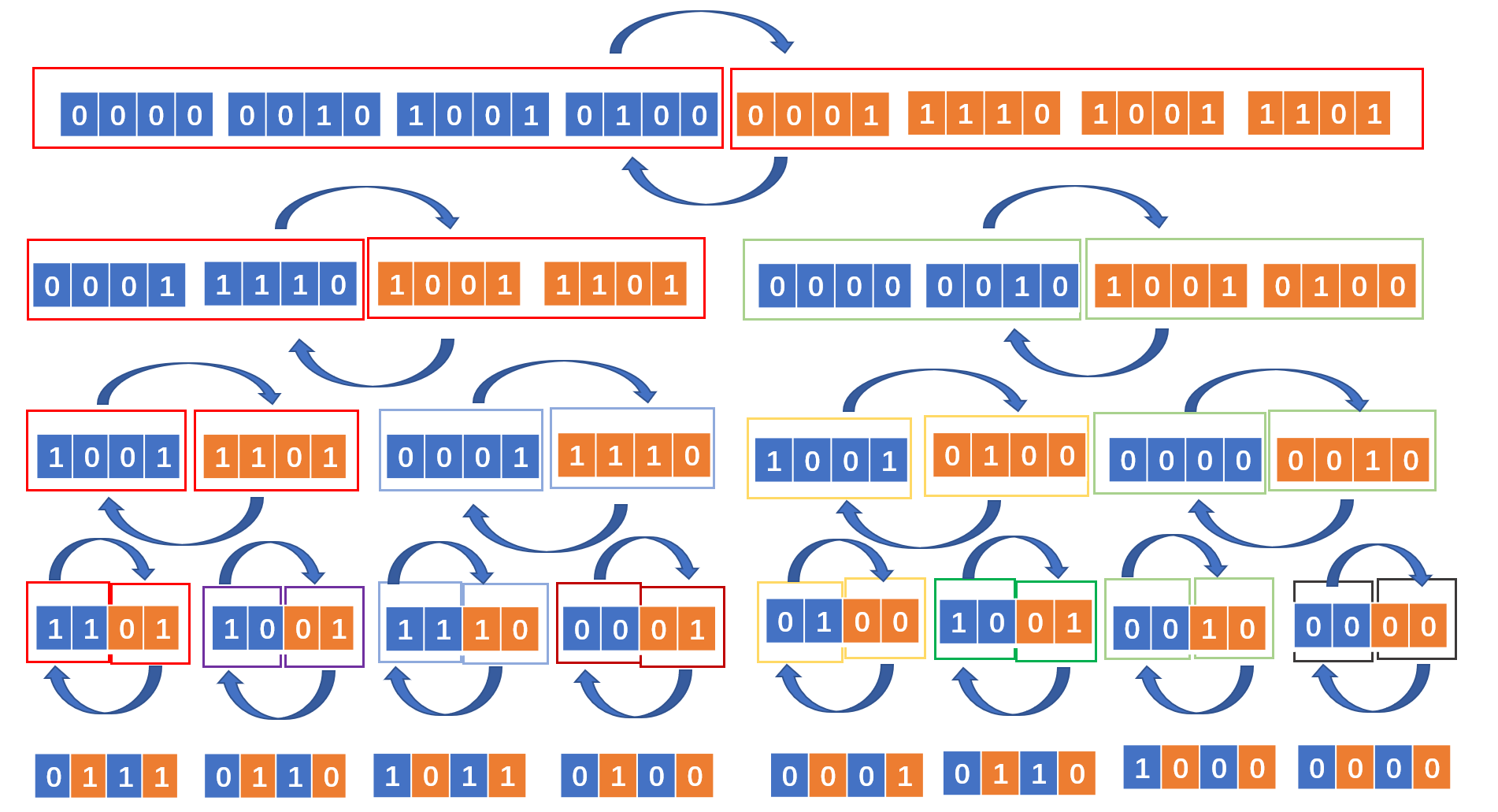
分别对之进行16位,8位,4位,2位,1位的颠倒处理,16位颠倒如何实现呢?将这个数分别右移16位,之后左移16位,二者位或合并即可,那么8位颠倒呢?如果直接右移8位和直接左移8位,那么中间还存在一段1001 1101没有被移出去,直接位或合并的话,就会产生干扰,最好的办法是右移8位的时候,将俩边靠左边的八位数提取出去,之后再进行右移8位。
那么如何才能提取呢,参照上面俩种算法中将数与1进行&提取出第一个数,我们也可以这样做,在8位颠倒的时候,右移操作需要使用1111 1111 0000 0000 1111 1111 0000 0000 进行&提取出左边八位数,在左移操作需要使用0000 0000 1111 1111 0000 0000 1111 1111进行&提取右边八位数,4位、2位、1位都是如此操作。
// 分而治之合并,这是因为它是固定的32位
public int reverseBits_2(int n) {
n = (n >>> 16) | (n << 16);
n = ((n & 0xff00ff00) >>> 8) | ((n & 0x00ff00ff) << 8);
n = ((n & 0xf0f0f0f0) >>> 4) | ((n & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4);
n = ((n & 0xcccccccc) >>> 2) | ((n & 0x33333333)<< 2);
n = ((n & 0xaaaaaaaa) >>> 1) | ((n & 0x55555555) << 1);
return n;
}
这种分而治之的思路非常的巧妙,个人感觉直接写不出这样的代码来,在java语言中,也有反转的实现,那么其中的实现原理是否可以参照一二,从源代码中来看,它也是分而治之,不过它进行了很多优化,它是从1位,2位,4位,最后将8位中的四部分分别进行颠倒,那么就少了一步16位颠倒了。
// 和上面的一样,不过写法优化了,这也是java中的Integer.reverse(int i)的源代码
public int reverseBits_3(int n) {
n = ((n & 0x55555555) << 1) | ((n >>> 1) & 0x55555555);
n = ((n & 0x33333333) << 2) | ((n >>> 2) & 0x33333333);
n = ((n & 0x0f0f0f0f) << 4) | ((n >>> 4) & 0x0f0f0f0f);
n = (n << 24) | ((n & 0xff00) << 8) | ((n >>> 8) & 0xff00) | (n >>> 24);
return n;
}
统计问题
leetcode,第338题,Counting Bits
Given an integer
n, return an arrayansof lengthn + 1such that for eachi(0 <= i <= n),ans[i]is the number of1's in the binary representation ofi.Example 1:
Input: n = 2
Output: [0,1,1]
Explanation:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
Example 2:
Input: n = 5
Output: [0,1,1,2,1,2]
Explanation:
0 --> 0
1 --> 1
2 --> 10
3 --> 11
4 --> 100
5 --> 101
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 105Follow up:
- It is very easy to come up with a solution with a runtime of
O(n log n). Can you do it in linear timeO(n)and possibly in a single pass?- Can you do it without using any built-in function (i.e., like
__builtin_popcountin C++)?
此问题主要是讨论范围0 - n,每个二进制数中1的个数,听到这个范围内每个数的统计问题,我最先想到的是动态规划,更有可能的方向是前后数是有关系的。关键是如何找出前后数之间的关系呢?数都会有进位的操作,在没进位之前,只需要在前面的基础上+1即可,但是进位之后就需要重新开始,那么这个只需要+1的范围数是哪些呢?这些范围有多大?我们可以将十进制数先转化为二进制数
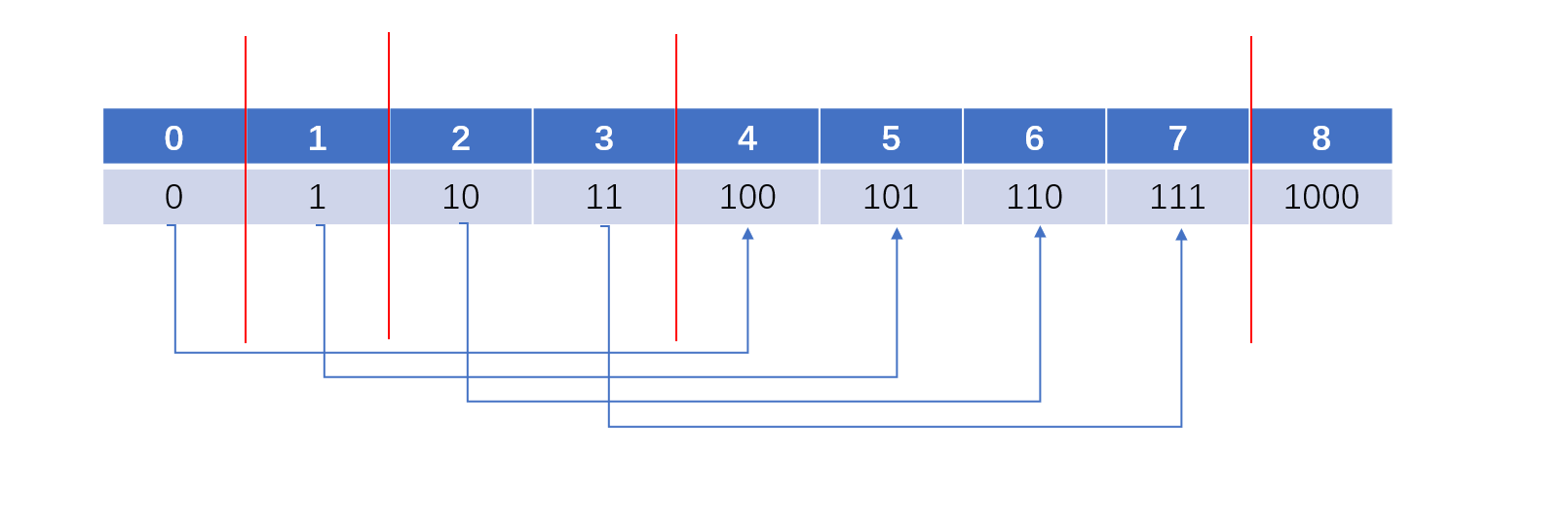
从上面我们发现2就是0前面加上了1,3就是1前面加上了1,从图中也可以看出4,5,6,7都是0,1,2,3前面加了一个1而已,也就是说范围就是2的幂次方,这样的话,我们就需要俩个变量b和start,一个是2的幂次方,一个就是用来遍历的。
// 最高有效位
public int[] countBits_1(int n) {
int[] results = new int[n+1];
if(n == 0) return results;
// 范围内的数
int start = 0;
// 最大范围
int b = 1;
while(b <= n) {
// 对范围内的数进行遍历,每次+1即可
while(start < b && start + b <= n) {
results[start + b] = results[start] + 1;
++start;
}
start = 0;
// 范围都是2的幂次方,直接移位
b <<= 1;
}
return results;
}
此方法时间和空间复杂度都很低,这是需要其中需要大量的遍历循环,并且还多出了几个变量。
那么我们能不能将这个最高有效位的写法改进一下,变成二进制的用法,我们知道每次只需要找到对应的数+1即可,但是有个转折就是2,4,8这些数是进位的数,我们可以看到2和1如果位与就是0,4和3位与也是0,8和7位与也是0,这是因为它们进位了,因此要判断是否在转折点,只需要判断x&(x-1)是否为0,只要为0,那么就得到进位了,最高有效位已经发生了改变,后面的数就需要根据这个最高有效位进行计算。
// 最高有效位
public int[] countBits_2(int n) {
int[] results = new int[n+1];
int max_bit = 0;
for(int index = 1; index <= n; ++index) {
// 判断最高有效位是否发生了改变
if((index & (index - 1)) == 0) {
max_bit = index;
}
results[index] = results[index - max_bit] + 1;
}
return results;
}
此写法的时间和空间效率都很高。
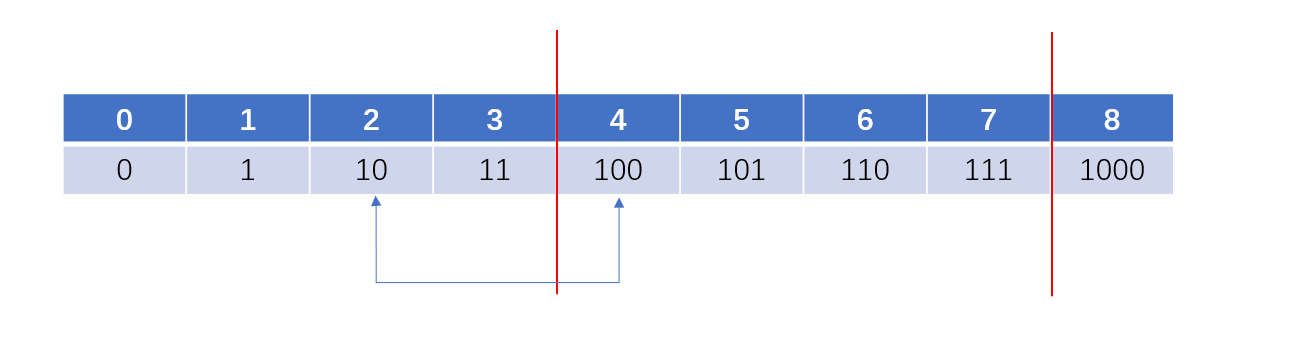
我们再来看这些二进制数,2右移一位就是1,3右移一位是1的二进制+1,4右移一位就是2,5右移一位就是2,偶数的右移是不减少1的个数的,但是奇数的右移是减少了1的个数。这样也是前后数之后的关系了。
// 最低有效位
public int[] countBits_3(int n) {
int[] results = new int[n+1];
if(n == 0) return results;
for(int index = 1; index <= n; ++index) {
// index & 1查看是否是有效位
results[index] = results[index >> 1] + (index & 1);
}
return results;
}
Brian Kernighan算法原理:对于任意整数,其中x&(x-1),就是将x的二进制数中最后一个1变成0的操作。
根据这个Brian Kernighan,就可以用来数清楚1的个数,根据这个思想来看的话有俩种方法:
- 不断的循环操作直到这个数变成0。
- Brian kernighan算法让前后数之间有了关系,这是因为x&(x-1)这个数肯定小于x,在x之前就已经计算出来了,并且它与x只相差一个1,因此x = x & (x - 1) + 1。
我们直接写第二种方法,这种方法直接设置每一个位运算的结果推导,也被称为最低设置位
// 最低设置位
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] results = new int[n+1];
if(n == 0) return results;
for(int index = 1; index <= n; ++index) {
results[index] = 1 + results[index&(index - 1)];
}
return results;
}
此题可以根据数的规律来找到二进制中1的个数,最高有效位的俩种方法和最低有效位的一种方法,还可以利用Brian Kernighan算法原理来做的。
leetcode,第191题,Number of 1 Bits
Share
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Note:
- Note that in some languages, such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
- In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 3, the input represents the signed integer.
-3.Example 1:
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
Output: 3
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
Example 2:
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
Output: 1
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
Example 3:
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 31
Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty one '1' bits.
Constraints:
- The input must be a binary string of length
32.Follow up: If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
此题也是统计一个二进制中1的个数,当然程序的入口直接输入32位的字符串而是int类型的变量。
首先想到的思路就是循环移位判断,一位一位的判断是否为1,如果为1,那么+1,如果不为1,那么直接移位判断下一步。当然这里要注意的是移位是无符号右移还是有符号右移,不过这里的位数是确定的32位,因此无论是否有符号,只要循环32次即可
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
if(n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
int num = 0;
// 循环32位判断
for(int index = 0; index < 32; ++index) {
// 判断是否为1
if((n & 1) == 1) {
++num;
}
// 移位到下一位进行判断
n >>= 1;
}
return num;
}
在上一题中有Brian Kernighan算法思想,这个就是将1变成0的操作,我们只要一直做这个操作,看要做多少次才会让数变成0,那么这个次数就是1的个数。
public int hammingWeight_1(int n) {
if(n == 0 || n == 1) return n;
int num = 0;
// 判断是否已经为0
while(n != 0) {
++num;
n = n & (n - 1);
}
return num;
}
查找问题
leetcode,第136题,Single Number
Given a non-empty array of integers
nums, every element appears twice except for one. Find that single one.You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,2,1]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,1,2,1,2]
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104-3 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 104- Each element in the array appears twice except for one element which appears only once.
此题说明一个数组中所有的数都是出现过俩次的,只有一个数会出现一次,找出这个出现一次的数。
题目说明数组中的所有数都会出现俩次,但只有一个数会出现一次,那么如果我们将数组进行排序,那些所有的数都是有次序的,这样的话只要查看前后数是否相同即可。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(len == 1) return nums[0];
int one_num = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Arrays.sort(nums);
// 因为所有的数都是俩个,只有一个数是一个,因此长度必定为奇数
for(int index = 0; index < len - 1; index += 2) {
if(nums[index] != nums[index + 1]) {
one_num = nums[index];
break;
}
}
// 如果上述的循环无法找出,那么单数就在数组的最后一个
if(one_num == Integer.MAX_VALUE) one_num = nums[len - 1];
return one_num;
}
上述的方法思想很简单,但是时间和空间都很高,这其中包含了排序,我们需要换一种思路来看待这个问题。
题目中说明所有的数都是俩个,如果有一个运算能像消消乐那样,俩个俩个的消除就好了,全部消除之后剩下的那个就是我们所查找的单数,在二进制运算中可以使用异或运算符,异或运算就可以将相同的俩个数变成0,如果俩个数不同,那么先将俩个数结合起来,这个在HashMap的hash运算中前16与后16位结合一样,之后碰到双数的时候还可以消去结合的那个数。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1) return nums[0];
for(int index = 1; index < nums.length; ++index) {
// 使用异或运算符
nums[0] ^= nums[index];
}
return nums[0];
}
leetcode,第137题,Single Number II
Given an integer array
numswhere every element appears three times except for one, which appears exactly once. Find the single element and return it.You must implement a solution with a linear runtime complexity and use only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,2]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1,0,1,0,1,99]
Output: 99
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1- Each element in
numsappears exactly three times except for one element which appears once.
此题是上一题的拓展,此题是所有的数都会出现三次,只有一个数出现一次,一个小小的改动,让上一题中所有的思想都无法使用,需要重新来思考此题目。当然最简单的可以使用哈希表来一个一个的查找。
如果不用哈希表来解决这个问题的话,这个问题就很难思考出来了。既然我们无法从十进制数下手,那么看看这些数的二进制
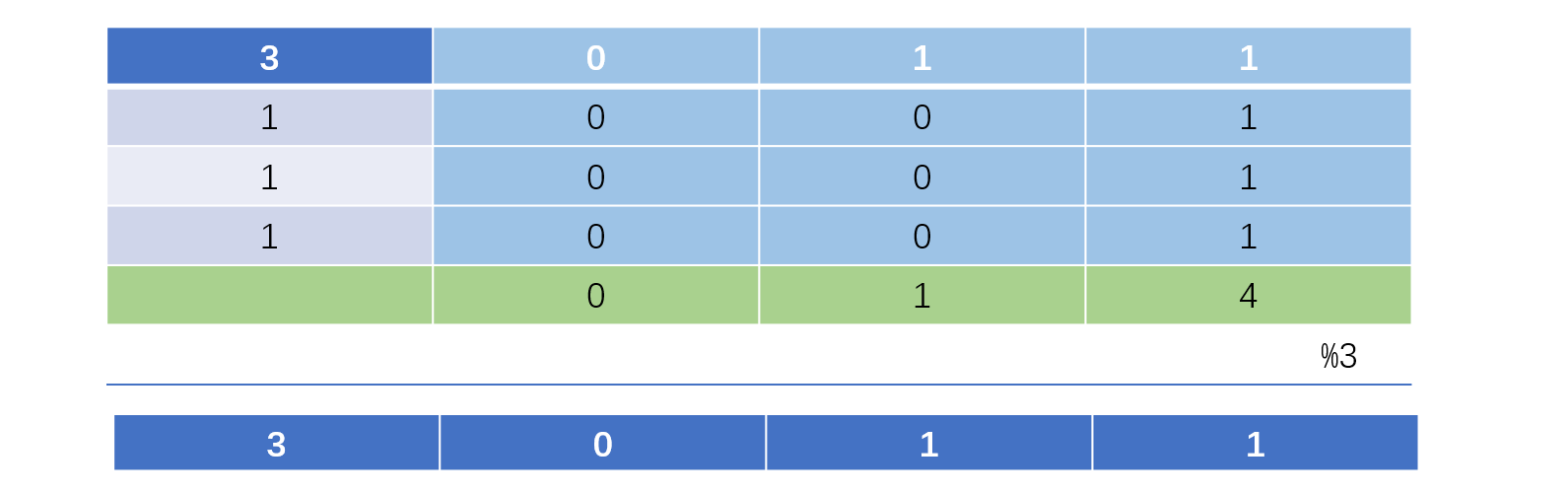
我们从图中可以看出如果我们将每一位相加之后对3取余就可以得到出现过一次的数了,我们依次确定每一个二进制位,因为对于出现了三次的数来说,对应的二进制上肯定是三个0或者三个1,无论是哪种情况,它们都是3的倍数,我们使用3取余正好就去除了出现过三次的数。
当然在实现的过程中,还需要考虑如何对每个二进制数进行相加取余,之后放入到对应的二进制位上,可以使用移位运算。
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
// 这里的32,是因为int类型的二进制位有32位,
for(int index = 0; index < 32; ++index) {
int sum = 0;
for(int num:nums) {
sum += (num >> index) & 1;
}
// 对3取余还需要进行移位操作
res |= (sum % 3) << index;
}
return res;
}
上述这种思路的效率都不高,虽然它的思路很难想到。
如果我们能用一个变量记录下出现过一次one的数就好了,当然在循环数组的时候,也会碰到出现俩次two、三次three的数,我们使用三个数来表示表示数组中数出现的情况,当然如何使用三个int类型的数来统计查找出现过一次的数才是最难,需要考虑其中的操作到底该如何设计?two是与one相关的,只有出现过一次之后再出现一次才能被记录到two中,而three是one和two同时组合才能得到的,当然其中最重要的就是one的值。
- one,值与one进行异或,这里的异或是为了考虑three的值,
- two,one与值进行位与,之后进行位或。位与判断是否俩个数相同,位或是将结果赋值给two,
- three,one与two进行位与,因为数出现俩次的时候,one是0,数出现一次的时候two是0,因此这样可以得到three值。
当一个数出现了三次了,one和two中的值如何进行纠正?就是如何将one和two中关于此数的影响进行去除,可以将one和two都位与three相反数。
对于上述思路的第一个问题
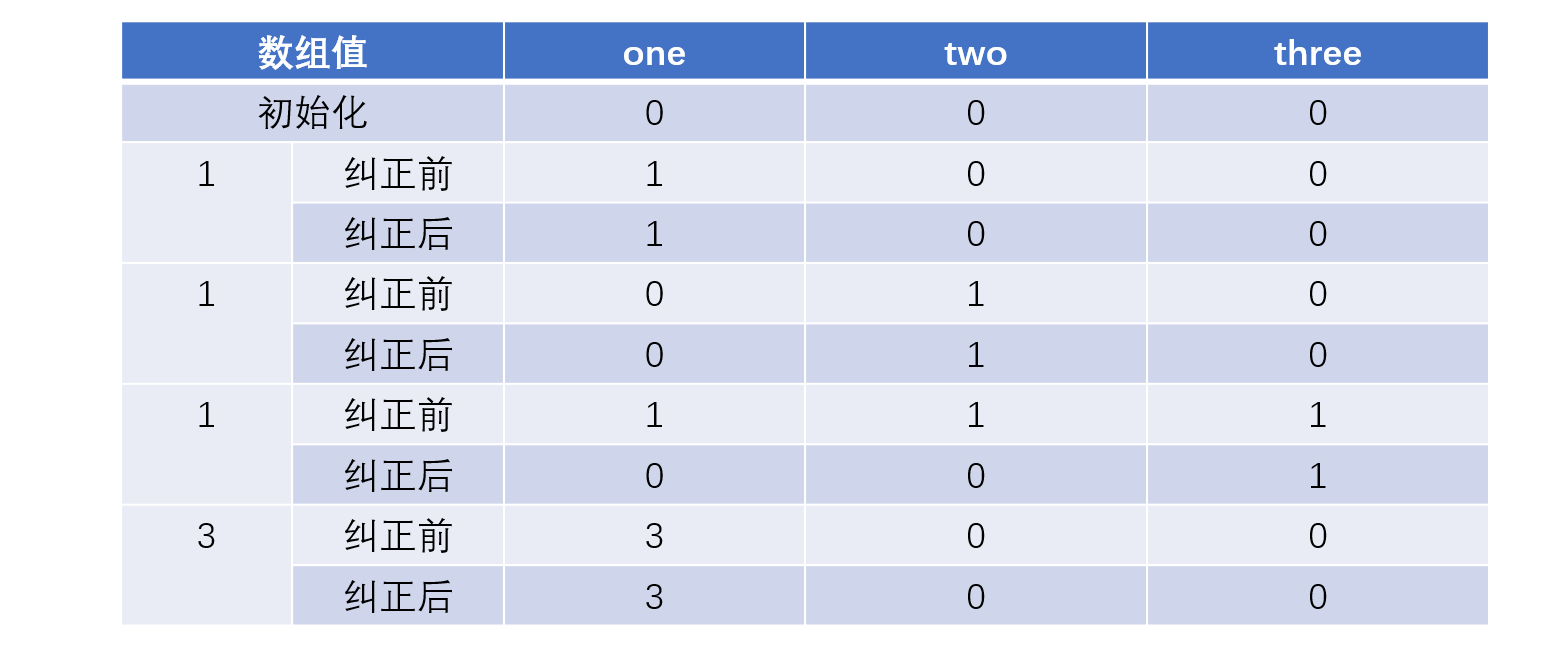
数组中数的顺序是否影响结果,比如1,1,1,3的时候,是否会按照我们预想中的执行,纠正的效果如何呢?从下图我们看出基本还是能够完成基本的功能的,虽然到达3的时候,three变成了0,并没有记录好1,但是只要one记录完成即可。
那么如何顺序变化为1,1,3,1的时候呢?
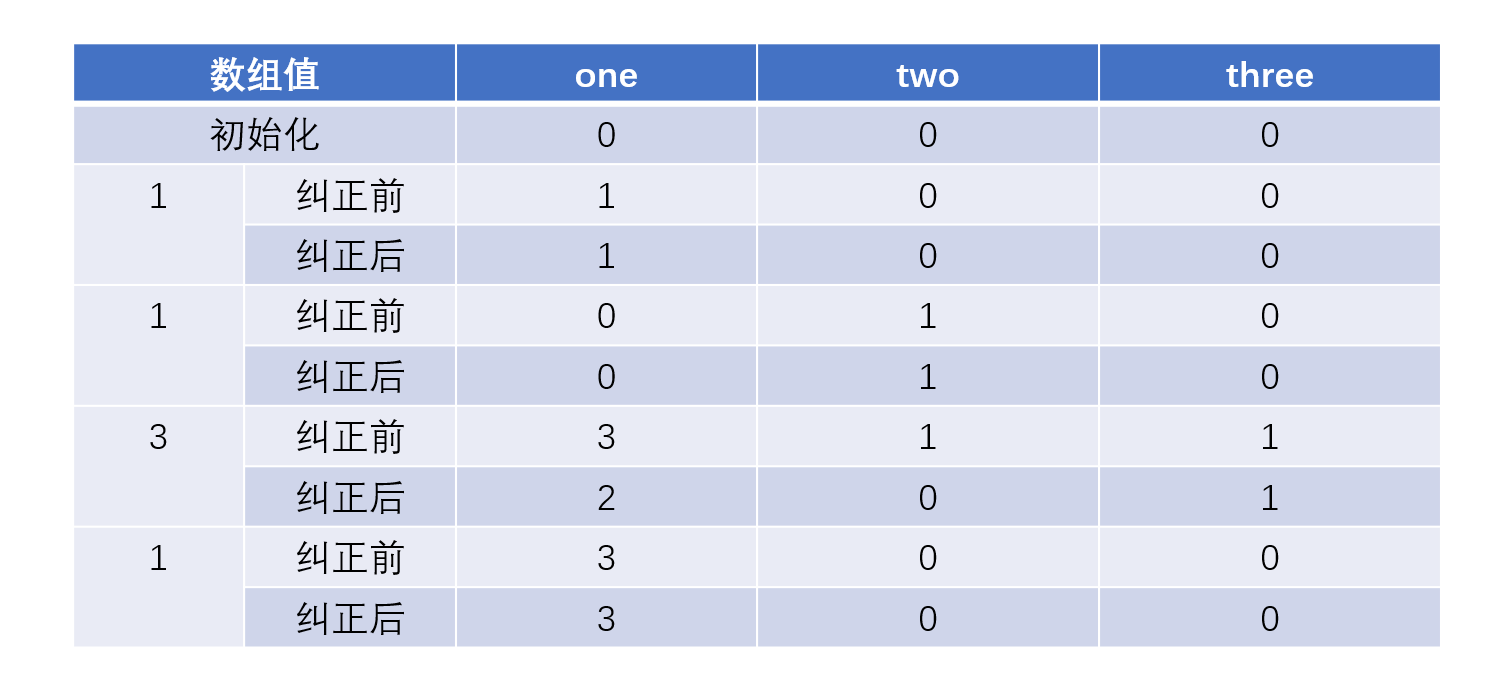
我们发现虽然中间过程3的时候并没有如我们预想那般完美,这时候因为one和two都有值,one是3,two是1,three自然也就有值了,但是在值变成1的时候,one还是能够得到的。
public int singleNumber_1(int[] nums) {
int one = 0, two = 0, three = 0;
for(int num:nums) {
// 首先更新的是第二个数
two |= one & num;
one ^= num;
three = one & two;
// 纠正
one &= ~three;
two &= ~three;
}
return one;
}
其实我们思考一下,这些解法都是通过记录状态、状态转换来实现,上面的方法使用one、two、three三个变量来记录,状态转换则是通过各种特殊的位运算实现。one、two、three记录状态过于平白,在二进制中,俩位就可以实现四种变化了,00,01,10,11。而此题其实只是需要三种变化,正如所有数都有俩个,当数达到俩个的时候就会转化为最初状态了,这里是数达到三个的时候就转化为最初状态。想法是可以做的,但是这个状态转换如何实现呢?这是每一个思路上的大问题,因为状态转换的运算设计必须是精巧的并且满足全部要求,这里的second first来表示俩位,first的更新通过first与值进行异或之后与second的反运算进行位与,second的运算也是类似的,这样在更新的时候就考虑俩位了。
- 第一次遇到,first先更新为1,使用异或运算,second此时为0,因此将second的反运算与之进行位与,first^num不管是什么都会通过的。而second更新的时候,first的反运算会让结果保持在0。second first = 0X
- 第二次遇到,firstnum成为了0,因此first也就是0了,此时secondnum则是完全通过,那么second first = X0
- 第三次遇到,first^num与second就相同了,second的反运算与之位与将first变成了0,之后second与num相同,那么二者异或就是0,那么second也会被更新为0,那么second first = 00
当然上面的只是一种理想的表述,因为如果中间出现了其他数就会进行状态叠加,此时就会发生变化,比如2,2,3,2
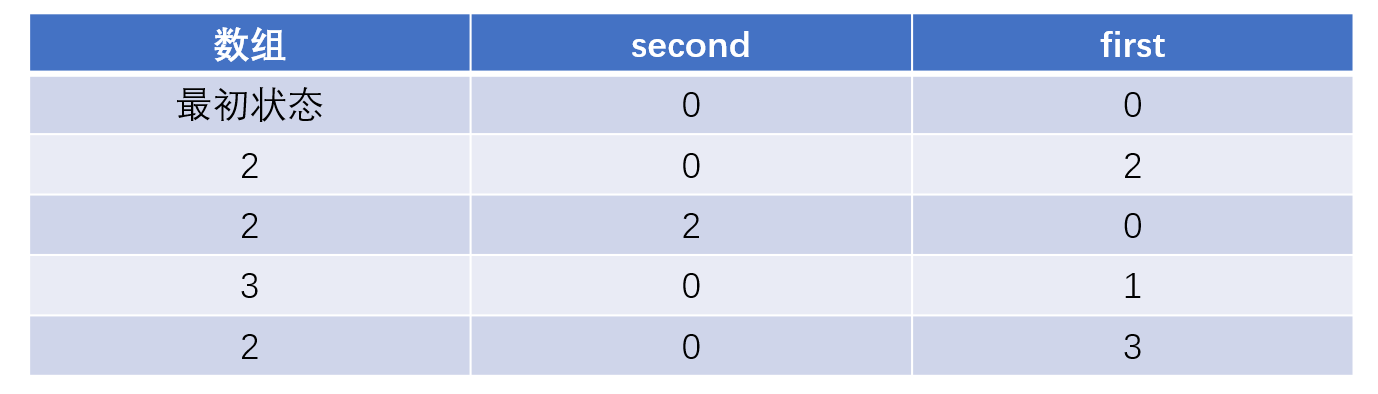
前面的俩个2,2都没有问题,按照上面的思路来实现的,之后遇到3之后就变成了01,这个其实更像是一种状态的叠加,之后再遇到2,就可以消去这种2的状态。
public int singleNumber_2(int[] nums) {
int first = 0, second = 0;
for(int num:nums) {
// 状态进行了转化
first = ~second & (first ^num);
second = ~first & (second ^num);
}
return first;
}
代码非常的简单,但是这种思路确实无法想到,如何使用位运算设计出状态转换操作也是本题一个非常大的难点。
leetcode,第260题,Single Number III
Given an integer array
nums, in which exactly two elements appear only once and all the other elements appear exactly twice. Find the two elements that appear only once. You can return the answer in any order.You must write an algorithm that runs in linear runtime complexity and uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,1,3,2,5]
Output: [3,5]
Explanation: [5, 3] is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1,0]
Output: [-1,0]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [0,1]
Output: [1,0]
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1- Each integer in
numswill appear twice, only two integers will appear once.
题目说明数组中只有俩个数是只出现过一次,其他数都出现了俩次,找出出现过一次的数。与前面一样都是明确了数量,不同于前面的就是它需要找出俩个数。但是前面的思路还是可以用的,我们可以将之先排序,这样整个数组就变得有规律了,之后进行循环前后对比,如果相同则比较下一组,如果不同,那么将之保存起来,之后比较下一个数。整体的思路基本不变,就是一些细节是需要改动一下变得符合题意的。
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1 || (nums.length == 2 && nums[0] != nums[1])) return nums;
// 进行排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] result = new int[2];
int index = 0;
int result_index = 0;
// 循环比较
for(; index < nums.length - 1;) {
if(nums[index] == nums[index + 1]) {
index += 2;
}else {
result[result_index] = nums[index];
++index;
++result_index;
}
}
if(index == nums.length - 1) result[result_index] = nums[index];
return result;
}
现在思考一下,数组全部进行异或是否能解决这个问题呢?当然不能,之前那个只有一个,因此可以,但是这里是俩个,如果全部异或,那么异或的结果就是俩个数的不同位。知道了俩个数不同位能做什么呢?似乎啥都做不了,啊哈哈。
以前我们做题的时候总会先把大问题转化为小问题,把陌生的问题转化为熟悉的问题,这里似乎也可以,是不是可以将俩个转化为一个呢?我们可以将这个大的数组进行分组,分组的要求就是
- 俩个只出现一次的数应该在不同的组中,
- 相同的数被分到相同的组中。
之前我们说全部异或的结果就是知道了俩个数不同位,当此位为1的时候,就代表这俩个数在这个对应位上是不同的,那么这个位就可以用来分组了,因为如果俩个数相同,那么这俩个数肯定也会被分到相同的组中,这一下就满足了上面俩个条件。那么整个算法过程可以分成三步
- 先将数组中所有的数进行异或,得到异或结果,
- 之后找出位为1的位置,这个位置也就是不同之处,
- 利用不同之处将数组进行分组,并且通过异或得到不同的数
public int[] singleNumber_1(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 1 || (nums.length == 2 && nums[0] != nums[1])) return nums;
int[] result = new int[2];
int sum_all = 0;
int differ_pos = 1;
// 先将数组中所有的数进行异或
for(int num:nums) {
sum_all ^= num;
}
// 之后找出sum_all为1的位置,这个位置也就是不同之处
while((sum_all & differ_pos) == 0) {
differ_pos = differ_pos << 1;
}
// 将数组进行分组,并且通过异或得到不同的数
for(int num:nums) {
if((num & differ_pos) == 0) {
result[0] ^= num;
}else {
result[1] ^= num;
}
}
return result;
}
这是一个绝妙的思路,它的时间空间效率都很好。
进制转化
在很多场景都需要进制转化和格式转化,其中最频繁出现的肯定就是十进制转化为二进制,这个在计算机组成原理就可以提及到,第一个想到的方法肯定就是除基取余法,就是将数除以2,之后记下余数,再用商除以2,一直这样除下去,记录所有的余数,直到商为0,之后把之前记录下来的余数倒着排放在一起,就是转化后的二进制数,
// 十进制转化为二进制,除基取余法
public void getResult(int num){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(num > 0) {
// 每次都要%2
sb.insert(0, num % 2);
num /= 2;
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
当然我们知道java中有很多操作二进制的运算符,其中我们就可以使用移位运算符,每次移位,之后输出0或者1,这里的只要使用位与1即可,此方法非常的方便的。
public void getResult_1(int num){
for(int index = 31; index >= 0; --index) {
System.out.print((num >> index) & 1);
}
}
总结
二进制运算符的使用在很多时候都有妙用,这些用法可以让我们的代码看起来更加的成熟,不至于很小白,啊哈哈。异或的公平用于hashMap中,也可用于消除相同元素中,hashMap的扩容使用了移位,移位更加的方便,也可用于遍历整个数的情况,位与可用于判断相同数中,找出公共点,当然也可用于判断奇偶或者1这些需求。一个需求可以实现的很巧妙,也可以实现的很朴素,这还是取决于程序员的功力。
leetcode -- 二进制的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 二进制问题
338. Counting Bits(计算小于n的各个数值对应的二进制1的个数) 思路:通过奇偶判断,if i是偶数,a[i]=a[i/2],if i是奇数,a[i]=a[i-1]+1. class ...
- leetcode 二进制求和 python
class Solution: def addBinary(self, a, b): """ :type a: str :type b: str :rtype: str ...
- [LeetCode] Prime Number of Set Bits in Binary Representation 二进制表示中的非零位个数为质数
Given two integers L and R, find the count of numbers in the range [L, R] (inclusive) having a prime ...
- [LeetCode] Special Binary String 特殊的二进制字符串
Special binary strings are binary strings with the following two properties: The number of 0's is eq ...
- [LeetCode] Count Binary Substrings 统计二进制子字符串
Give a string s, count the number of non-empty (contiguous) substrings that have the same number of ...
- [LeetCode] Binary Gap 二进制间隙
Given a positive integer N, find and return the longest distance between two consecutive 1's in the ...
- 【leetcode 简单】 第九十三题 二进制手表
二进制手表顶部有 4 个 LED 代表小时(0-11),底部的 6 个 LED 代表分钟(0-59). 每个 LED 代表一个 0 或 1,最低位在右侧. 例如,上面的二进制手表读取 “3:25”. ...
- LeetCode:二进制手表【401】
LeetCode:二进制手表[401] 题目描述 二进制手表顶部有 4 个 LED 代表小时(0-11),底部的 6 个 LED 代表分钟(0-59). 每个 LED 代表一个 0 或 1,最低位在右 ...
- LeetCode:二进制求和【67】
LeetCode:二进制求和[67] 题目描述 给定两个二进制字符串,返回他们的和(用二进制表示). 输入为非空字符串且只包含数字 1 和 0. 示例 1: 输入: a = "11" ...
随机推荐
- JAVAEE_Servlet_13_HttpServlet
HttpServlet 因为每次执行前端请求,都需要获取前端的请求方式,都需判断前端的请求方式和后端是否一致,随意这段代码就可以封装起来. 写一个HttpServlet类去继承GenericServl ...
- 一致性哈希做负载均衡,基于dubbo的简化版本,超级简单容易理解!!!
一致性哈希算法原理以及做分布式存储.一定先看:一致性哈希算法 dubbo提供了四种负载均衡实现:权重随机算法,最少活跃调用数算法,一致性哈希算法,加权轮询算法. 本文基于开源项目:guide-rpc- ...
- Linux(CentOS7)安装与卸载MySQL8.0图文详解
Mysql数据库的安装对于开发者来说,是我们必然会面对的问题,它的安装过程其实并不复杂,并且网络上的安装教程也非常多,但是对于新手来说,各种不同形式的安装教程,又给新手们带来了要选择哪种方式进行安装的 ...
- 06- Linux Ubuntu下sublime下载与使用与安装包
我有Linux下全套的安装包,如sublime,pycharm等.不用再苦逼的下软件了.需要的加我微信:chimu sublime text 3文本编辑器 启动命令:Linux命令行输入subl 或者 ...
- AliCrackme_2题的分析
作者:Fly2015 AliCrackme_2.apk运行起来的注册界面,如图. 首先使用Android反编译利器Jeb对AliCrackme_2.apk的Java层代码进行分析. 很幸运,就找到了该 ...
- CString,string,char数组的转换
来源:http://ticktick.blog.51cto.com/823160/317550 //----------------ANSI字符串转换为UNICODE字符串-------------- ...
- node-redis基本操作
//npm install redis var redis = require("redis"), client = redis.createClient(); client.se ...
- C++基于文件流和armadillo读取mnist
发现网上大把都是用python读取mnist的,用C++大都是用opencv读取的,但我不怎么用opencv,因此自己摸索了个使用文件流读取mnist的方法,armadillo仅作为储存矩阵的一种方式 ...
- 【python】Leetcode每日一题-颠倒二进制位
[python]Leetcode每日一题-颠倒二进制位 [题目描述] 颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位. 示例1: 输入: 00000010100101000001111010011100 输 ...
- Servlet三大域对象
Servlet三大域对象的应用 request.session.application(ServletContext) ServletContext是一个全局的储存信息的空间,服务器开始就存在,服务器 ...
