ML_note1
Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, we are given a data set and already know what our correct output should look like, having the idea that there is a relationship between the input and the output.
Supervised learning problems are categorized into "regression" and "classification" problems. In a regression problem, we are trying to predict results within a continuous output, meaning that we are trying to map input variables to some continuous function. In a classification problem, we are instead trying to predict results in a discrete output. In other words, we are trying to map input variables into discrete categories.
Example 1:
Given data about the size of houses on the real estate market, try to predict their price. Price as a function of size is a continuous output, so this is a regression problem.
We could turn this example into a classification problem by instead making our output about whether the house "sells for more or less than the asking price." Here we are classifying the houses based on price into two discrete categories.
Example 2:
(a) Regression - Given a picture of a person, we have to predict their age on the basis of the given picture
(b) Classification - Given a patient with a tumor, we have to predict whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning allows us to approach problems with little or no idea what our results should look like. We can derive structure from data where we don't necessarily know the effect of the variables.
We can derive this structure by clustering the data based on relationships among the variables in the data.
With unsupervised learning there is no feedback based on the prediction results.
Example:
Clustering: Take a collection of 1,000,000 different genes, and find a way to automatically group these genes into groups that are somehow similar or related by different variables, such as lifespan, location, roles, and so on.
Non-clustering: The "Cocktail Party Algorithm", allows you to find structure in a chaotic environment. (i.e. identifying individual voices and music from a mesh of sounds at a cocktail party).
Cost Function
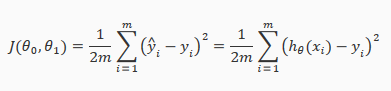
This function is otherwise called the "Squared error function", or "Mean squared error".
ML_note1的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- PHP学习笔记之数组篇
摘要:其实PHP中的数组和JavaScript中的数组很相似,就是一系列键值对的集合.... 转载请注明来源:PHP学习笔记之数组篇 一.如何定义数组:在PHP中创建数组主要有两种方式,下面就让我 ...
- Django之路:QuerySet API,后台和表单
一.Django QuerySet API Django模型中我们学习了一些基本的创建和查询.这里专门讲以下数据库接口相关的接口(QuerySet API),当然你也可以选择暂时跳过这节.如果以后用到 ...
- MapReduce常见算法
1.单词计数 2.数据去重 3.排序 4.Top K(求数据中的最大值) 5.选择 6.投影 7.分组 8.多表连接 9.单表关联
- 解决phpmyadmin上传文件大小限制的配置方法(转)
phpmyadmin导入SQL文件时涉及到phpmyadmin上传文件大小限制问题,默认phpmyadmin上传文件大小为2M,如果想要 phpmyadmin上传超过2M大文件,就需要修改phpmya ...
- JSP内置对象--web安全性及config对象的使用 (了解即可)
tomcat服务器配置的时候,在虚拟目录中必须存在一个WEB-INF文件夹,但是访问的时候并不能发现这个文件夹.改成WEB-INFs就可以看到. 所以WEB-INF文件夹不轻易让用户看到,那么其安全性 ...
- java删除文件夹 Java中实现复制文件或文件夹
删除文件夹 import java.io.File; public class DeleteDir { /** * @param args */ public static void main(Str ...
- 单词接龙(dragon)
单词接龙(dragon) 题目描述 单词接龙是一个与我们经常玩的成语接龙相类似的游戏,现在我们已知一组单词,且给定一个开头的字母,要求出以这个字母开头的最长的“龙”(每个单词都最多在“龙”中出现两次) ...
- drawRect 进阶
iOS的绘图操作是在UIView类的drawRect方法中完成的,所以如果我们要想在一个UIView中绘图,需要写一个扩展UIView 的类,并重写drawRect方法,在这里进行绘图操作,程序会自动 ...
- CABasicAnimation 基础
一.CABasicAnimation CAPropertyAnimation的子类 属性解析: fromValue:keyPath相应属性的初始值 toValue:keyPath相应属性的结束值 随着 ...
- ural1439 Battle with You-Know-Who
Battle with You-Know-Who Time limit: 2.0 secondMemory limit: 64 MB Rooms of the Ministry of Magic ar ...
