Kmeans在MapReduce中的实现
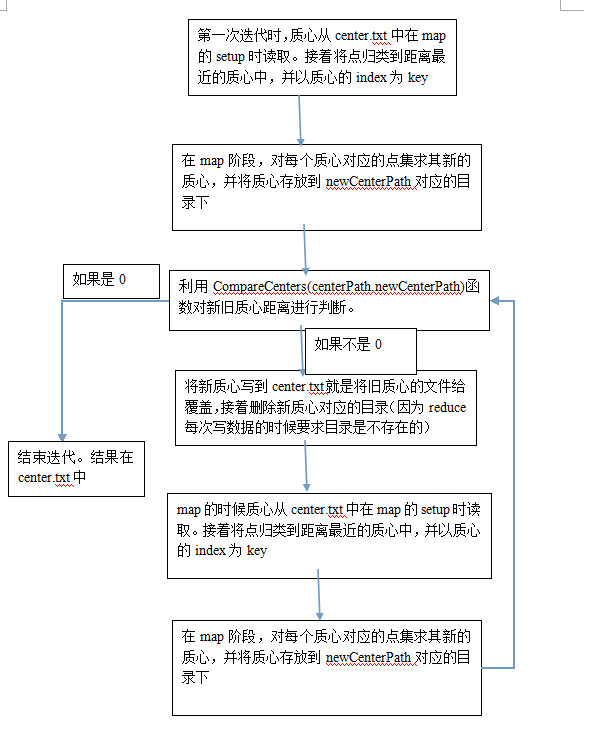
kmeans基本思想就是在一个点集中随机选取k个点作为初始的质心,然后在以这K个点求点集中其他点和这质心的距离,并且按照最近的原则,将这个点集分成k个类,接着在这k个类中求其质心,接着便是迭代,一直到质心不变或者SSE小于某个阈值或者达到指定的迭代次数。不过这样的Kmeans有几个缺点1 我们如何确定K值,2初始的质心选取很重要。基于此,可以用二分kmeans(似乎是叫这个),如果有时间可以写一下。
while(true ){
run(centerPath,dataPath,newCenterPath,true);
System. out.println(" " );
System. out.println("The " + ++count+"th time's compution is completed");
System. out.println(" " );
if(Utils.CompareCenters(centerPath,newCenterPath)){
Utils. deleteDir(newCenterPath);
break;
}
}
package hadoop.MachineLearning.kmeans; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class Kmeans { public static void run(String centerPath,String dataPath,String newCenterPath,boolean runReduce) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException{
Configuration conf =new Configuration(); conf.set("centerPath",centerPath);
Job job=Job.getInstance(conf,"Kmeans");
job.setJarByClass(hadoop.MachineLearning.kmeans.Kmeans.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
if(runReduce){
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
} FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(dataPath));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(newCenterPath));
System.out.println(job.waitForCompletion(true)); } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String centerPath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/Kmeans_input/center_input/centers.txt";
String dataPath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/Kmeans_input/data_input/data.txt";
String newCenterPath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/Kmeans_output/newCenter";
int count=0; while(true){
run(centerPath,dataPath,newCenterPath,true);
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("The "+ ++count+"th time's compution is completed");
System.out.println(" ");
if(Utils.CompareCenters(centerPath,newCenterPath)){
Utils.deleteDir(newCenterPath);
break; } } } }
package hadoop.MachineLearning.kmeans; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; public class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text> {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> centerList=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>>(); public void setup(Context context) throws IOException{
Configuration conf=context.getConfiguration();
String centerPath=conf.get("centerPath");
centerList=Utils.GetCenterFromHDFS(centerPath,false); } public void map(LongWritable ikey, Text ivalue, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ArrayList<Double> point=Utils.TextToArray(ivalue);
// int size=point.size();
double distance=0.0;
double mindis=9999.0;
int index=-1; for(int i=0;i<centerList.size();i++){
double currentDistance=0;
for(int j=1;j<point.size();j++){//原文是j=0
double centerPoint = Math.abs(centerList.get(i).get(j));
double filed = Math.abs(point.get(j));
currentDistance += Math.pow((centerPoint - filed) / (centerPoint + filed), 2); }
if(currentDistance<mindis){
mindis=currentDistance;
index=i;
}
} /*
for(int i=0;i<centerList.size();i++){
distance=Utils.getDistance(centerList.get(i),point);
if(distance<mindis){
mindis=distance;
index=i+1;
}
}
*/
// String value=""; context.write(new IntWritable(index+1),ivalue); } }
package hadoop.MachineLearning.kmeans; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; public class MyReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, Text, Text, Text> { public void reduce(IntWritable _key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// process values
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> pointList=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>>();
for (Text val : values) {
ArrayList<Double> point=Utils.TextToArray(val);
pointList.add(point);
}
int row=pointList.size();
int col=pointList.get(0).size();
double[] avg=new double[col];
for(int i=1;i<col;i++){//原文是i=0
double sum=0;
for(int j=0;j<row;j++){
sum+=pointList.get(j).get(i);
}
avg[i]=sum/row;
}
context.write(new Text("") , new Text(Arrays.toString(avg).replace("[", "").replace("]", "")));
} }
package hadoop.MachineLearning.kmeans; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.LineReader; public class Utils { /**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static ArrayList<Double> TextToArray(Text text){
ArrayList<Double> centers=new ArrayList<Double>();
String[] line=text.toString().split(",");
for(int i=0;i<line.length;i++){
double center=Double.parseDouble(line[i]);
centers.add(center);
}
return centers;
} public static ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> GetCenterFromHDFS(String centerPath,boolean isDirectory) throws IOException{
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
Path path=new Path(centerPath);
FileSystem fs=path.getFileSystem(conf); ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> result=new ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>>(); if(isDirectory){
FileStatus[] fileStatus=fs.listStatus(path);
for(int i=0;i<fileStatus.length;i++){
if(fileStatus[i].isFile()){
result.addAll(GetCenterFromHDFS(fileStatus[i].getPath().toString(),false));
}
}
return result;
}
FSDataInputStream infs=fs.open(path);
LineReader reader=new LineReader(infs,conf);
Text line=new Text();
while(reader.readLine(line)>0){
ArrayList<Double> center=TextToArray(line);
result.add(center);
}
reader.close();
return result;
} public static void deleteDir(String deletepath) throws IOException{
Configuration conf=new Configuration();
Path path=new Path(deletepath);
FileSystem fs=path.getFileSystem(conf);
fs.delete(path,true);
} public static boolean CompareCenters(String oldPath,String newPath) throws IOException{
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> oldcenters=Utils.GetCenterFromHDFS(oldPath,false);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> newcenters=Utils.GetCenterFromHDFS(newPath,true);
//
// System.out.println(" ");
//
// System.out.println("oldcenters's size is "+oldcenters.size());
// System.out.println("newcenters's size is "+newcenters.size());
//
// System.out.println(" ");
int row=oldcenters.size();
int col=oldcenters.get(0).size();
double distance=0.0;
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=1;j<col;j++){
double oldpoint=Math.abs(oldcenters.get(i).get(j));
double newpoint=Math.abs(newcenters.get(i).get(j));
distance+=Math.pow((oldpoint-newpoint)/(oldpoint+newpoint),2);
}
}
if(distance==0.0){
Utils.deleteDir(newPath);
return true;
}else{
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Path outPath = new Path(oldPath);
FileSystem fs=outPath.getFileSystem(conf);
FSDataOutputStream overWrite=fs.create(outPath,true);
overWrite.writeChars("");
overWrite.close(); Path inPath=new Path(newPath);
FileStatus[] listFiles=fs.listStatus(inPath);
for(int i=0;i<listFiles.length;i++){
FSDataOutputStream out=fs.create(outPath);
FSDataInputStream in=fs.open(listFiles[i].getPath());
IOUtils.copyBytes(in,out,4096,true);
}
Utils.deleteDir(newPath);
}
return false;
} public static double getDistance(ArrayList<Double> point1,ArrayList<Double> point2){
double distance=0.0;
if(point1.size()!=point2.size()){
System.err.println("point size not match!!");
System.exit(1);
}else{
for(int i=0;i<point1.size();i++){
double t1=Math.abs(point1.get(i));
double t2=Math.abs(point2.get(i));
distance+=Math.pow((t1-t1)/(t1+t2),2);
}
}
return distance;
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String oldpath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/Kmeans_input/center_input/centers.txt";
String newpath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/Kmeans_input/test";
if(Utils.CompareCenters(oldpath,newpath)){
System.out.println("equals");
}else{
System.out.println("not equals");
}
/*
ArrayList<ArrayList<Double>> centers=Utils.GetCenterFromHDFS(path,true);
for(ArrayList<Double> center:centers){
System.out.println(" ");
for(double point:center){
System.out.println(point);
}
}
*/
//String deletepath="hdfs://10.107.8.110:9000/output/";
//Utils.deleteDir(deletepath);
} }
Kmeans在MapReduce中的实现的更多相关文章
- Hadoop学习笔记—11.MapReduce中的排序和分组
一.写在之前的 1.1 回顾Map阶段四大步骤 首先,我们回顾一下在MapReduce中,排序和分组在哪里被执行: 从上图中可以清楚地看出,在Step1.4也就是第四步中,需要对不同分区中的数据进行排 ...
- Hadoop学习笔记—12.MapReduce中的常见算法
一.MapReduce中有哪些常见算法 (1)经典之王:单词计数 这个是MapReduce的经典案例,经典的不能再经典了! (2)数据去重 "数据去重"主要是为了掌握和利用并行化思 ...
- MapReduce中作业调度机制
MapReduce中作业调度机制主要有3种: 1.先入先出FIFO Hadoop 中默认的调度器,它先按照作业的优先级高低,再按照到达时间的先后选择被执行的作业. 2.公平调度器(相当于时间 ...
- Mapreduce中的字符串编码
Mapreduce中的字符串编码 $$$ Shuffle的执行过程,需要经过多次比较排序.如果对每一个数据的比较都需要先反序列化,对性能影响极大. RawComparator的作用就不言而喻,能够直接 ...
- MapReduce中一次reduce方法的调用中key的值不断变化分析及源码解析
摘要:mapreduce中执行reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context),调用一次reduce方法,迭代val ...
- Hadoop学习之路(二十三)MapReduce中的shuffle详解
概述 1.MapReduce 中,mapper 阶段处理的数据如何传递给 reducer 阶段,是 MapReduce 框架中 最关键的一个流程,这个流程就叫 Shuffle 2.Shuffle: 数 ...
- [MapReduce_5] MapReduce 中的 Combiner 组件应用
0. 说明 Combiner 介绍 && 在 MapReduce 中的应用 1. 介绍 Combiner: Map 端的 Reduce,有自己的使用场景 在相同 Key 过多的情况下 ...
- Hadoop案例(七)MapReduce中多表合并
MapReduce中多表合并案例 一.案例需求 订单数据表t_order: id pid amount 1001 01 1 1002 02 2 1003 03 3 订单数据order.txt 商品信息 ...
- MapReduce中的分布式缓存使用
MapReduce中的分布式缓存使用 @(Hadoop) 简介 DistributedCache是Hadoop为MapReduce框架提供的一种分布式缓存机制,它会将需要缓存的文件分发到各个执行任务的 ...
随机推荐
- VS2013使用技巧汇总
1. Peek View 在不新建TAB的情况下快速查看.编辑一个函数的代码. 以前要看一个函数的实现,需要在使用的地方点击F12跳转到该函数,实际上这是很浪费时间的.VS2013Peek View便 ...
- jsp ${param.id}用法
它的取值范围Page,Request,Session,Application. ${param.id} 与输入有关,相对于 request.getParameter("id").意 ...
- 【转】Java 内部类种类及使用解析
Java 内部类种类及使用解析 内部类Inner Class 将相关的类组织在一起,从而降低了命名空间的混乱. 一个内部类可以定义在另一个类里,可以定义在函数里,甚至可以作为一个表达式的一部分. Ja ...
- OpenCV4Android释疑: 透析Android以JNI调OpenCV的三种方式(让OpenCVManager永不困扰)
OpenCV4Android释疑: 透析Android以JNI调OpenCV的三种方式(让OpenCVManager永不困扰) 前文曾详细探讨了关于OpenCV的使用,原本以为天下已太平.但不断有人反 ...
- android执行外部命令、检测文件是否存在、自动检测U盘路径
private final String UDiskFileName = "/2969_logo/bootfile.image"; private final String Loc ...
- [转]MD5加密算法的java实现
import java.security.MessageDigest; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; /* * MD5 算法 */ pu ...
- GoF 设计模式:浅浅印象
23种设计模式,常常多个模式结合使用,主要是为了解决中大型软件项目"类和对象"膨胀的问题,进而有效组织类的结构而提出的.可划分为3类:创建型(关于类的创建),结构型(多个类的组织) ...
- 二叉树,平衡树,红黑树,B~/B+树汇总
二叉查找树(BST),平衡二叉查找树(AVL),红黑树(RBT),B~/B+树(B-tree).这四种树都具备下面几个优势: (1) 都是动态结构.在删除,插入操作的时候,都不需要彻底重建原始的索引树 ...
- 别说你不知道java中的包装类,wrapper type,以及容易在自动拆箱中出现的问题
很多时候,会有人问你,你知道什么是包装类吗? 或者高端一点问你你知道,wrapper type,是什么吗? 然后你就懵逼了,学了java很多时候都不知道这是啥. 其实问你的人,可能只是想问你,java ...
- jQuery两种扩展插件的方式
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content ...
