Persistent Bookcase
2 seconds
512 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are data structures that always preserves the previous version of itself and access to it when it is modified.
After reaching home Alina decided to invent her own persistent data structure. Inventing didn't take long: there is a bookcase right behind her bed. Alina thinks that the bookcase is a good choice for a persistent data structure. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf.
The bookcase consists of n shelves, and each shelf has exactly m positions for books at it. Alina enumerates shelves by integers from 1to n and positions at shelves — from 1 to m. Initially the bookcase is empty, thus there is no book at any position at any shelf in it.
Alina wrote down q operations, which will be consecutively applied to the bookcase. Each of the operations has one of four types:
- 1 i j — Place a book at position j at shelf i if there is no book at it.
- 2 i j — Remove the book from position j at shelf i if there is a book at it.
- 3 i — Invert book placing at shelf i. This means that from every position at shelf i which has a book at it, the book should be removed, and at every position at shelf i which has not book at it, a book should be placed.
- 4 k — Return the books in the bookcase in a state they were after applying k-th operation. In particular, k = 0 means that the bookcase should be in initial state, thus every book in the bookcase should be removed from its position.
After applying each of operation Alina is interested in the number of books in the bookcase. Alina got 'A' in the school and had no problem finding this values. Will you do so?
The first line of the input contains three integers n, m and q (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 103, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the bookcase dimensions and the number of operations respectively.
The next q lines describes operations in chronological order — i-th of them describes i-th operation in one of the four formats described in the statement.
It is guaranteed that shelf indices and position indices are correct, and in each of fourth-type operation the number k corresponds to some operation before it or equals to 0.
For each operation, print the number of books in the bookcase after applying it in a separate line. The answers should be printed in chronological order.
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2
4 0
1
4
0
4 2 6
3 2
2 2 2
3 3
3 2
2 2 2
3 2
2
1
3
3
2
4
2 2 2
3 2
2 2 1
2
1
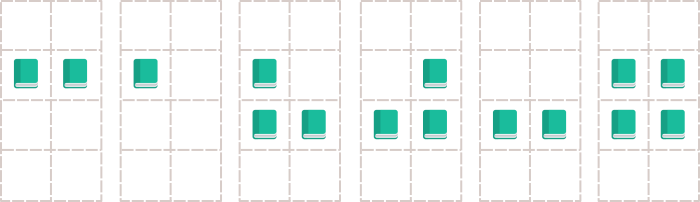
This image illustrates the second sample case.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <climits>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#define rep(i,m,n) for(i=m;i<=n;i++)
#define rsp(it,s) for(set<int>::iterator it=s.begin();it!=s.end();it++)
#define mod 1000000007
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define vi vector<int>
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define ll long long
#define pi acos(-1.0)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define Lson L, mid, rt<<1
#define Rson mid+1, R, rt<<1|1
const int maxn=1e5+;
const int dis[][]={{,},{-,},{,-},{,}};
using namespace std;
ll gcd(ll p,ll q){return q==?p:gcd(q,p%q);}
ll qpow(ll p,ll q){ll f=;while(q){if(q&)f=f*p;p=p*p;q>>=;}return f;}
int n,m,k,t,s[maxn][],ans[maxn],sum[],q[],p[][];
vi a[maxn];
void dfs(int now)
{
for(int x:a[now])
{
if(s[x][]==)
{
ans[x]=ans[now];
dfs(x);
}
else if(s[x][]==)
{
if((q[s[x][]]^p[s[x][]][s[x][]])==)
{
p[s[x][]][s[x][]]^=;
sum[s[x][]]++;
ans[x]=ans[now]+;
dfs(x);
p[s[x][]][s[x][]]^=;
sum[s[x][]]--;
}
else ans[x]=ans[now],dfs(x);
}
else if(s[x][]==)
{
if((q[s[x][]]^p[s[x][]][s[x][]])==)
{
p[s[x][]][s[x][]]^=;
sum[s[x][]]--;
ans[x]=ans[now]-;
dfs(x);
p[s[x][]][s[x][]]^=;
sum[s[x][]]++;
}
else ans[x]=ans[now],dfs(x);
}
else
{
q[s[x][]]^=;
ans[x]=ans[now]-*sum[s[x][]]+m;
sum[s[x][]]=m-sum[s[x][]];
dfs(x);
q[s[x][]]^=;
sum[s[x][]]=m-sum[s[x][]];
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&t);
rep(i,,t)
{
scanf("%d",&s[i][]);
if(s[i][]==||s[i][]==)
{
scanf("%d%d",&s[i][],&s[i][]);
a[i-].pb(i);
}
else if(s[i][]==)
{
scanf("%d",&s[i][]);
a[i-].pb(i);
}
else
{
scanf("%d",&s[i][]);
a[s[i][]].pb(i);
}
}
dfs();
rep(i,,t)printf("%d\n",ans[i]);
//system("Pause");
return ;
}
Persistent Bookcase的更多相关文章
- CodeForces #368 div2 D Persistent Bookcase DFS
题目链接:D Persistent Bookcase 题意:有一个n*m的书架,开始是空的,现在有k种操作: 1 x y 这个位置如果没书,放书. 2 x y 这个位置如果有书,拿走. 3 x 反转这 ...
- 【Codeforces-707D】Persistent Bookcase DFS + 线段树
D. Persistent Bookcase Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase
Persistent Bookcase Problem Description: Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persisten ...
- Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2) D. Persistent Bookcase 离线 暴力
D. Persistent Bookcase 题目连接: http://www.codeforces.com/contest/707/problem/D Description Recently in ...
- codeforces 707D D. Persistent Bookcase(dfs)
题目链接: D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input ...
- CF707D Persistent Bookcase
CF707D Persistent Bookcase 洛谷评测传送门 题目描述 Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent ...
- Persistent Bookcase CodeForces - 707D (dfs 离线处理有根树模型的问题&&Bitset)
Persistent Bookcase CodeForces - 707D time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megaby ...
- D. Persistent Bookcase(Codeforces Round #368 (Div. 2))
D. Persistent Bookcase time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 512 megabytes input stand ...
- codeforces 707D:Persistent Bookcase
Description Recently in school Alina has learned what are the persistent data structures: they are d ...
随机推荐
- Adobe Flash CC 2014 下载及破解
来源 :http://prodesigntools.com/adobe-cc-2014-direct-download-links.html 地址:http://trials3.adobe.com/A ...
- ios控件 UILabel
UILabel 的作用是显示文本 UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 100, 100, 40)]; lab ...
- Linux教程之配置权限受限制的SFTP
SFTP 在Linux下是一个很方便很安全的文件传输工具,我常常用它在Linux服务器上替代传统的ftp来传输文件.众所周知SFTP账号是基于SSH账号的,默认情况下访问服务器的权限很大,下面的教程就 ...
- QML Flipable、Flickable和状态与动画 下篇
本文介绍的是Flickable和状态与动画,我们以前接触过QML相关的内容,那么本文介绍的内容就很明了了.先来看内容. AD: Flickable和状态与动画 下篇是本节要介绍的内容,Flickabl ...
- 7z 的命令行
用于压缩和解压缩 来源:http://blog.csdn.net/shuckstark/article/details/7598443 挺有用的东西,写脚本时用处多多, 7z.exe和7za.exe ...
- C#获取本机局域网ip和公网ip
1.获取局域网ip IPAddress ipAddr = Dns.Resolve(Dns.GetHostName()).AddressList[0];//获得当前IP地址 string ip=ipAd ...
- NSNumber(把数字存进数组字典等的问题)
官方文档地址https://developer.apple.com/library/ios/documentation/Cocoa/Reference/Foundation/Classes/NSNum ...
- 【最短路】 poj 2387
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <limits.h> #include <string.h& ...
- CSS中如何把Span标签设置为固定宽度
一.形如<span>ABC</span>独立行设置SPAN为固定宽度方法如下: span {width:60px; text-align:center; display:blo ...
- Ubuntu配置eclipse
1.安装jdk 去官网下载最新版jdk,目前是 jdk-8u45-linux-x64.tar.gz 创建Java的目标路径文件夹,这里我们放在/usr/lib/jvm下面.在终端下操作: sudo m ...
