蒙特卡洛方法计算圆周率的三种实现-MPI openmp pthread
蒙特卡洛方法实现计算圆周率的方法比较简单,其思想是假设我们向一个正方形的标靶上随机投掷飞镖,靶心在正中央,标靶的长和宽都是2 英尺。同时假设有一个圆与标靶内切。圆的半径是1英尺,面积是π平方英尺。如果击中点在标靶上是均匀分布的(我们总会击中正方形),那么飞镖击中圆的数量近似满足等式
飞镖落在圆内的次数/飞镖落在标靶内的总次数=π/4
因为环包含的面积与正方形面积的比值是π/4。
因为环所包含的面积与正方形面积的比值是π/4。
我们可以用这个公式和随机数产生器来估计π的值。
伪代码如下:
number_in_circle=;
for(toss=;toss<number_of_tosses;toss++){
x=random double between - and ;
y=random double between - and ;
distance_squared=x*x+y*y;
if(distance_squared<=) number_in_cycle++;
}
pi_estimate=*number_in_cycle/((double)number_in_tosses);
这种采用了随机(随机投掷)的方法称为蒙特卡洛(Monte Carlo)方法。
编写了一个采用蒙特卡洛方法的MPI,Pthread,OpenMP程序估计π的值。
使用MPI编写时,进程0读取总的投掷次数,并把它们广播给各个进程。使用MPI_Reduce求出局部变量number_in_cycle的全局总和,并让进程0打印它。
使用Pthread编写时,有主线程读入总的投掷数,然后输出估算值。
使用OpenMP编写时,在开启任何线程前读取总的投掷次数。使用reduction子句计算飞镖集中环内的次数。在合并所有的线程后,打印结果。
这三个程序中,投掷次数可能都非常大,可能总的投掷次数和击中环内的次数都得用long int型来表示。
下面是MPI程序代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<mpi.h>
void read_num(long long int *num_point,int my_rank,MPI_Comm comm);
void compute_pi(long long int num_point,long long int* num_in_cycle,long long int* local_num_point,int comm_sz,long long int *total_num_in_cycle,MPI_Comm comm,int my_rank);
int main(int argc,char** argv){
long long int num_in_cycle,num_point,total_num_in_cycle,local_num_point;
int my_rank,comm_sz;
MPI_Comm comm;
MPI_Init(NULL,NULL);//初始化
comm=MPI_COMM_WORLD;
MPI_Comm_size(comm,&comm_sz);//得到进程总数
MPI_Comm_rank(comm,&my_rank);//得到进程编号
read_num(&num_point,my_rank,comm);//读取输入数据
compute_pi(num_point,&num_in_cycle,&local_num_point,comm_sz,&total_num_in_cycle,comm,my_rank);
MPI_Finalize();
return ;
}
void read_num(long long int* num_point,int my_rank,MPI_Comm comm){
if(my_rank==){
printf("please input num in sqaure \n");
scanf("%lld",num_point);
}
/*
广播函数
int MPI_Bcast(
void* data_p //in/out
int count //in
MPI_Datatype datatype //in
int source_proc //in
MPI_Comm comm //in
)
*/
MPI_Bcast(num_point,,MPI_LONG_LONG,,comm); }
void compute_pi(long long int num_point,long long int* num_in_cycle,long long int* local_num_point,int comm_sz,long long int *total_num_in_cycle,MPI_Comm comm,int my_rank){
*num_in_cycle=;
*local_num_point=num_point/comm_sz;
double x,y,distance_squared;
srand(time(NULL));
for(long long int i=;i< *local_num_point;i++){
x=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
x=x*-;
y=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
y=y*-;
distance_squared=x*x+y*y;
if(distance_squared<=)
*num_in_cycle=*num_in_cycle+;
}
/*
全局函数
MPI_Reduce(
void* input_data_p //in
void* output_data_p //out
int count //in
MPI_Datatype datatype //in
MPI_Op oprtator //in
int dest_process //in
MPI_Comm comm //in
)
*/
MPI_Reduce(num_in_cycle,total_num_in_cycle,,MPI_LONG_LONG,MPI_SUM,,comm);
if(my_rank==){
double pi=(double)*total_num_in_cycle/(double)num_point*;
printf("the estimate value of pi is %lf\n",pi);
}
}
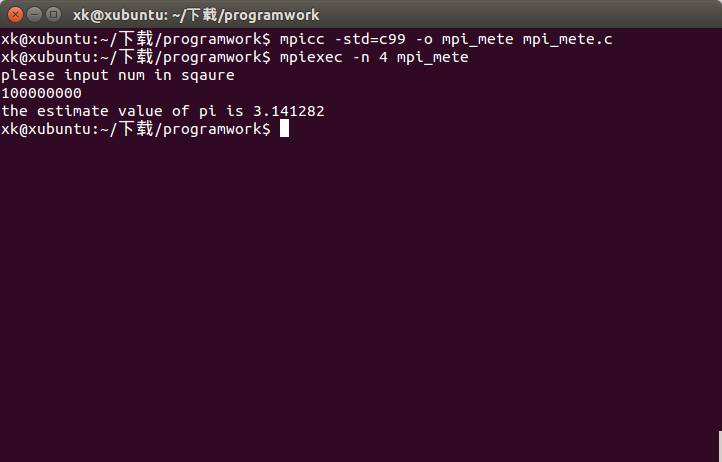
进行编译 mpicc -std=c99 -o mpi_mete mpi_mete.c
执行 mpiexec -n mpi_mete
输入数据
下面是Pthread程序代码
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<pthread.h>
int thread_count;
long long int num_in_circle,n;
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* compute_pi(void* rank);
int main(int argc,char* argv[]){
long thread;
pthread_t* thread_handles;
thread_count=strtol(argv[],NULL,);
printf("please input the number of point\n");
scanf("%lld",&n);
thread_handles=(pthread_t*)malloc(thread_count*sizeof(pthread_t));
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
for(thread=;thread<thread_count;thread++){
//创建线程
/*
int pthread_create(
pthread_t* thread_p //out
const pthread_attr_t* attr_p
void* (*start_routine)(void*) //in
void* arg_p //in
)
第一个参数是一个指针,指向对应的pthread_t对象。注意,pthread_t对象不是pthread_create函数分配的,必须在调用pthread_create函数前就为pthread_t
对象分配内存空间。第二个参数不用,所以只是函数调用时把NULL传递参数。第三个参数表示该线程将要运行的函数;最后一个参数也是一个指针,指向传给函数start_routine的参数
*/
pthread_create(&thread_handles[thread],NULL,compute_pi,(void*)thread);
}
//停止线程
/*
int pthread_join(
pthread_t thread /in
void** ret_val_p /out
)
第二个参数可以接收任意由pthread_t对象所关联的那个线程产生的返回值。
*/
for(thread=;thread<thread_count;thread++){
pthread_join(thread_handles[thread],NULL);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
double pi=*(double)num_in_circle/(double)n;
printf("the esitimate value of pi is %lf\n",pi);
}
void* compute_pi(void* rank){
long long int local_n;
local_n=n/thread_count;
double x,y,distance_squared;
for(long long int i=;i<local_n;i++){
x=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
y=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
distance_squared=x*x+y*y;
if(distance_squared<=){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
num_in_circle++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
return NULL;
}
进行编译 gcc -std=c99 -o pth_mete pth_mete.c
运行 ./pth_mete
输入数据结果如下

下面是OpenMP代码
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<omp.h>
int main(int argc,char** argv){
long long int num_in_cycle=;
long long int num_point;
int thread_count;
thread_count=strtol(argv[],NULL,);
printf("please input the number of point\n");
scanf("%lld",&num_point);
srand(time(NULL));
double x,y,distance_point;
long long int i;
#pragma omp parallel for num_threads(thread_count) default(none) \
reduction(+:num_in_cycle) shared(num_point) private(i,x,y,distance_point)
for( i=;i<num_point;i++){
x=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
y=(double)rand()/(double)RAND_MAX;
distance_point=x*x+y*y;
if(distance_point<=){
num_in_cycle++;
}
}
double estimate_pi=(double)num_in_cycle/num_point*;
printf("the estimate value of pi is %lf\n",estimate_pi);
return ;
}
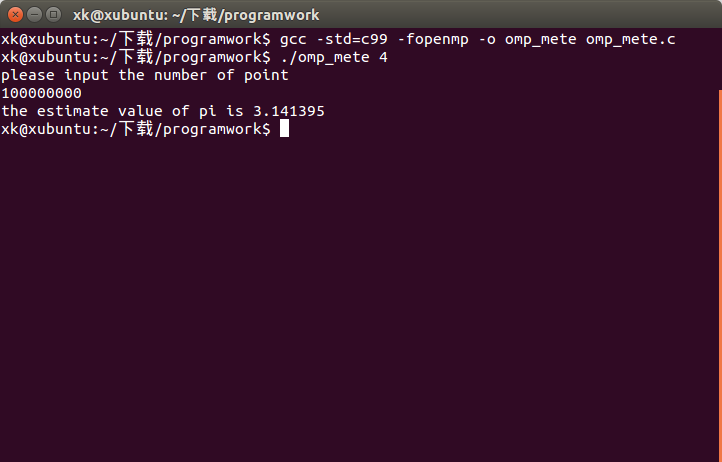
编译代码 gcc -std=c99 -fopenmp -o omp_mete omp_mete.c
执行 ./omp_mete
结果如下
蒙特卡洛方法计算圆周率的三种实现-MPI openmp pthread的更多相关文章
- root的方法大体上有以下三种
root的方法大体上有以下三种一.手机软件安卓版直接root.这种方法不需要电脑的支持,也很安全.安卓版软件有:kingroot,360一键root,一键root大师,Towelroot,支持云roo ...
- Struts2中Action接收参数的方法主要有以下三种:
Struts2中Action接收参数的方法主要有以下三种: 1.使用Action的属性接收参数(最原始的方式): a.定义:在Action类中定义属性,创建get和set方法: b.接 ...
- 用蒙特卡洛方法计算派-python和R语言
用蒙特卡洛方法算pi-基于python和R语言 最近follow了MOOC上一门python课,开始学Python.同时,买来了概率论与数理统计,准备自学一下统计.(因为被鄙视过不是统计专业却想搞数据 ...
- C++中实现回调机制的几种方式(一共三种方法,另加三种)
(1)Callback方式Callback的本质是设置一个函数指针进去,然后在需要需要触发某个事件时调用该方法, 比如Windows的窗口消息处理函数就是这种类型. 比如下面的示例代码,我们在Down ...
- HTML5结合CSS的三种方法+结合JS的三种方法
HTML5+CSS: HTML中应用CSS的三种方法 一.内联 内联样式通过style属性直接套进HTML中去. 示例代码 <pstylepstyle="color:red" ...
- mybatis之接口方法多参数的三种实现方式
关键代码举例: DaoMapper.xml <!-- 传入多个参数时,自动转换为map形式 --> <insert id="insertByColumns" us ...
- 算法之美--1.蒙特卡洛方法计算pi
基本思想: 利用圆与其外接正方形面积之比为pi/4的关系,通过产生大量均匀分布的二维点,计算落在单位圆和单位正方形的数量之比再乘以4便得到pi的近似值.样本点越多,计算出的数据将会越接近真识的pi(前 ...
- C#中Math类的计算整数的三种方法
1.Math.Round:四舍六入五取偶 引用内容 Math.Round( Math.Round( Math.Round( Math.Round( Math.Round( Math.Round( Ma ...
- jar包生制作几种方法,jar包导出三种方法:eclipse导出、jar命令、FatJar插件
Eclipse将引用了第三方jar包的Java项目打包成jar文件的两种方法 方案一:用Eclipse自带的Export功能 步骤1:准备主清单文件 “MANIFEST.MF”, 由于是打包引用了第三 ...
随机推荐
- JDK内置性能监测工具使用
Java自带的性能监测工具用法简介——jstack.jconsole.jinfo.jmap.jdb.jsta.jvisualvmJDK内置工具使用 一.javah命令(C Header and Stu ...
- Android入门之文件系统操作
Android入门之文件系统操作(二)文件操作相关指令 (转) (一)获取总根 File[] fileList=File.listRoots(); //返回fileList.length为1 // ...
- Spring的AOP浅尝
项目中使用到了Spring,写了一个简单的例子,跟大家分享一下,由于自己写东西,所以在技术选择上充分自由,虽然对于Spring的利弊众说纷纭,我也不能评判,反正我是尝试用了,记得在上学时候老师讲Spr ...
- Winform打砖块游戏制作step by step第7节---碰撞检测
一 引子 为了让更多的编程初学者,轻松愉快地掌握面向对象的思考方法,对象继承和多态的妙用,故推出此系列随笔,还望大家多多支持. 预备知识,无GDI画图基础的童鞋请先阅读一篇文章让你彻底弄懂WinFor ...
- Android 版 Facebook 登录
Android 版 Facebook SDK 让用户可以通过 Facebook 登录注册您的应用.通过 Facebook 登录您的应用时,用户可以向应用授予权限,以便您可以检索信息或以用户的身份在 F ...
- Android开发中多进程共享数据
# 背景 最近在工作中遇到一个需求,需要在接收到推送的时候将推送获得的数据存起来,以供app启动时使用.我们会认为这不是So easy吗?只要把数据存到SharedPreferences中,然后让ap ...
- 资源相互引用时 需添加 PerformSubstitution=True
获取或设置一个布尔值,该值确定在对由 WebResourceAttribute 类引用的嵌入式资源的处理过程中是否分析其他 Web 资源 URL,并用到该资源的完整路径替换. 如:一个CSS文件引用其 ...
- Java:集合类的区别详解
Java中集合类的区别 Array是数组,不在集合框架范畴之内,一旦选定了,它的容量大小就不能改变了,所以通常在编程中不选用数组来存放. 集合 : 集合对象:用于管理其他若干对象的对象 数组:长度不可 ...
- gzip解压和压缩
我发现网上很少有这样完整例子,加上英文有不好,走了好多弯路.我现在把从网上找到例子帖出来,可以解压HTTP gzip的 #include <stdlib.h> #include <s ...
- js获取上传图片的尺寸大小
当上传图片时,有时候需要控制下上传图片的尺寸大小,需要给个提示 //获取图片的尺寸,控制尺寸大小 var reader = new FileReader(), img = new Image(); / ...
