算法导论:Trie字典树
1、 概述
Trie树,又称字典树,单词查找树或者前缀树,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构,如英文字母的字典树是一个26叉树,数字的字典树是一个10叉树。
Trie一词来自retrieve,发音为/tri:/ “tree”,也有人读为/traɪ/ “try”。
Trie树可以利用字符串的公共前缀来节约存储空间。如下图所示,该trie树用10个节点保存了6个字符串pool、prize、preview、prepare、produce、progress
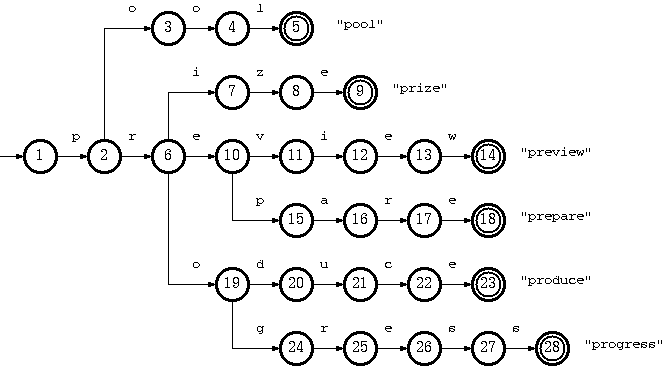
在该trie树中,字符串preview,prepare公共前缀是“pre”,因此可以只存储一份“pre”以节省空间。当然,如果系统中存在大量字符串且这些字符串基本没有公共前缀,则相应的trie树将非常消耗内存,这也是trie树的一个缺点。
Trie树的基本性质可以归纳为:
(1)根结点不包含字符,除根节点意外每个结点只包含一个字符。
(2)从根结点到某一个结点,路径上经过的字符连接起来,为该结点对应的字符串。
(3)每个结点的所有子结点包含的字符串不相同。
注意:每个结点可以有没有或者一个或者多个字结点,叶子结点没有子结点
2、数据结构表示
/**
* 定义字典树的数据结构
* c 当前节点值
* isLeaf 是否是叶子结点
* children 孩子,key是孩子结点值,value是孩子结点的下一个字典树
*
*/
class TrieNode {
char c;
boolean isLeaf;
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = new HashMap<Character,TrieNode>();
public TrieNode(char c){
this.c = c;
}
public TrieNode() {}
}
3、Trie字典树查找
利用children HashMap,key是结点值,value是子结点
/**
* 查找 返回最后的字符
* @param word
* @return
*/
public TrieNode searchNode(String word){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = root.children;
TrieNode t = null;// 临时结点
// 遍历字符串word的每个字符
for(int i = 0;i<word.length();i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if(!children.containsKey(c)){
return null;
}else{
t = children.get(c);
children = t.children;
}
}
// 返回最后一个结点,若空word不存在,若非空,并且是叶子结点则存在
return t;
}
对返回的t进行判断, 返回最后一个结点,若空word不存在,若非空,并且是叶子结点则存在
/**
* 查找是否存在 word字符
* @param word
* @return
*/
public boolean search(String word){
TrieNode t= searchNode(word);
// t.c 是字符串word最后一个结点值
return t!=null && t.isLeaf;
}
查找前缀字符
/**
* 查找前缀字符
* @param prefix
* @return
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchNode(prefix) != null;
}
4、Trie字典树的插入
/**
* 插入
* @param word
*/
public void insert(String word){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> childern = root.children;
for(int i=0;i< word.length();i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
TrieNode t = null;
// 孩子结点中包括了 c 字符
if(childern.containsKey(c)){
t = childern.get(c);// c字符所在结点的 子字典树,进入下一个字典树
}else{
t = new TrieNode(c);// 不存在的时候新建结点
childern.put(c,t);// key value
}
childern = t.children;// 字典树的 孩子结点
if(i == word.length() - 1){ // 插入是叶子结点的时候
t.isLeaf = true;
}
}
}
再说明下children
root
root.val 是结点值
root.children 的Key 是 root结点的孩子结点
root.children 的value 和 root.children中的Key一一对应,表示value的孩子结点
5、Trie字典树的删除
这个时间复杂度比较多
判断是否可以删除
定义parent child两个结点
当parent的孩子数量 > 1个 并且child的孩子有且只有一个的时候,将parent对于的这个孩子child删除
这里利用上面的searchNode,从下向上对word的子串进行判断
但是这里有个问题,举个例子好说:我们需要删除“pool”,但是“poo”在字典树也是合法的字符,我这样的程序也将“poo”进行了删除,如果定义一个计数器,比较好,当计数器为0的时候进行删除
/**
* 删除
* 删除的是word这个字符串,首先要找到word和其他字符串的公共前缀,从最后一个公共前缀开始删除,结点
* 值为 null
* @param word
*/
public void delete(String word){
boolean flag = search(word);
if(flag==false){
System.out.println("不存在该字符串:"+word);
return;
}
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> childern = root.children;
TrieNode child = null;// 定义子结点
for(int i=word.length();i>=1 ;i--){
String subWord = word.substring(0,i);
TrieNode parent = searchNode(subWord);
if(child!=null &&
parent.children.size() !=1 &&
child.children.size()==1){
// 删除孩子结点
parent.children.remove(child.c);
System.out.println("删除成功:"+word);
return;
}else{
child = parent;
}
}
}
6、字典树的层次输出
利用二叉树层次遍历的思想
定义ArrayList或者队列,每次讲该层结点放到队列中,并删除父结点
public void printTrie(){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = null;
int size = 0;
ArrayList<TrieNode> tree = new ArrayList<TrieNode>();
tree.add(root);
while(tree.size()!=0){
size = tree.size();
for(int i =0;i<size;i++){
children = tree.get(0).children;
tree.remove(0);
// 把children中 value的值都放入到 tree中
if(children == null)
break;
for(TrieNode tN:children.values()){
tree.add(tN);
System.out.print(tN.c +"\t");
}
System.out.print("\\");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
上面程序对该层的元素进行了输出,
以“\” 为分割部分的字符表示其父结点在:左上最近的结点
但是当某层出现单个字符的时候不能够很好的表示
同时,输出的时候发现每一层的最后一个结点是空,表示不理解
上面例子输出结果:
p \
r o \
e o i \o \
v p \g d \z \l \
i \a \r \u \e \\
e \r \e \c \\
w \e \s \e \
\\s \\
\
最后s字符判断父结点出错,因为结点左侧过多的空的时候,只输出一个“\”,但是为什么输出一个“\”,我不理解,不知道哪里处理错误
全部程序
package twotree; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* 定义字典树的数据结构
* c 当前节点值
* isLeaf 是否是叶子结点
* children 孩子,key是孩子结点值,value是孩子结点的下一个字典树
*
*/
class TrieNode {
char c;
boolean isLeaf;
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = new HashMap<Character,TrieNode>();
public TrieNode(char c){
this.c = c;
}
public TrieNode() {}
}
class Trie{
private TrieNode root = null;
public Trie(){
root = new TrieNode();
}
/**
* 删除
* 删除的是word这个字符串,首先要找到word和其他字符串的公共前缀,从最后一个公共前缀开始删除,结点
* 值为 null
* @param word
*/
public void delete(String word){
boolean flag = search(word);
if(flag==false){
System.out.println("不存在该字符串:"+word);
return;
}
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> childern = root.children;
TrieNode child = null;// 定义子结点
for(int i=word.length();i>=1 ;i--){
String subWord = word.substring(0,i);
TrieNode parent = searchNode(subWord);
if(child!=null &&
parent.children.size() !=1 &&
child.children.size()==1){
// 删除孩子结点
parent.children.remove(child.c);
System.out.println("删除成功:"+word);
return;
}else{
child = parent;
}
}
}
/**
* 插入
* @param word
*/
public void insert(String word){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> childern = root.children;
for(int i=0;i< word.length();i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
TrieNode t = null;
// 孩子结点中包括了 c 字符
if(childern.containsKey(c)){
t = childern.get(c);// c字符所在结点的 子字典树
}else{
t = new TrieNode(c);// 不存在的时候新建结点
childern.put(c,t);// key value
}
childern = t.children;// 字典树的 孩子结点
if(i == word.length() - 1){ // 插入是叶子结点的时候
t.isLeaf = true;
}
}
}
/**
* 查找 返回最后的字符
* @param word
* @return
*/
public TrieNode searchNode(String word){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = root.children;
TrieNode t = null;// 临时结点
// 遍历字符串word的每个字符
for(int i = 0;i<word.length();i++){
char c = word.charAt(i);
if(!children.containsKey(c)){
return null;
}else{
t = children.get(c);
children = t.children;
}
}
// 返回最后一个结点,若空word不存在,若非空,并且是叶子结点则存在
return t;
}
/**
* 查找是否存在 word字符
* @param word
* @return
*/
public boolean search(String word){
TrieNode t= searchNode(word);
// t.c 是字符串word最后一个结点值
return t!=null && t.isLeaf;
}
/**
* 查找前缀字符
* @param prefix
* @return
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchNode(prefix) != null;
}
public void printTrie(){
HashMap<Character,TrieNode> children = null;
int size = 0;
ArrayList<TrieNode> tree = new ArrayList<TrieNode>();
tree.add(root);
while(tree.size()!=0){
size = tree.size(); for(int i =0;i<size;i++){
children = tree.get(0).children; tree.remove(0);
// 把children中 value的值都放入到 tree中
if(children == null)
break;
for(TrieNode tN:children.values()){
tree.add(tN);
System.out.print(tN.c +"\t");
}
System.out.print("\\");
}
System.out.println(); } } }
public class TrieTest { public static void main(String[] args){
Trie trie = new Trie();
// pool、prize、preview、prepare、produce、progress
System.out.println("\t insert");
trie.insert("pool");
trie.insert("prize");
trie.insert("preview");
trie.insert("prepare");
trie.insert("produce");
//trie.insert("produces");
trie.insert("progress");
System.out.println("\t printTrie");
trie.printTrie();
System.out.println("\t search");
System.out.println(trie.search("pool")); System.out.println(trie.search("produce")); System.out.println(trie.search("pop"));
System.out.println("\t searchNode");
System.out.println(trie.searchNode("pop") == null);
System.out.println(trie.searchNode("pop")); System.out.println(trie.searchNode("produce") == null);
System.out.println(trie.searchNode("produce").c); System.out.println("\t startsWith");
System.out.println(trie.startsWith("pre"));
System.out.println(trie.startsWith("hello"));
System.out.println(trie.startsWith("pop")); System.out.println("\t delete");
trie.delete("pool"); System.out.println("\t printTrie");
trie.printTrie(); trie.delete("produce"); System.out.println("\t printTrie");
trie.printTrie();
}
}
输出结果
insert
printTrie
p \
r o \
e o i \o \
v p \g d \z \l \
i \a \r \u \e \\
e \r \e \c \\
w \e \s \e \
\\s \\
\
search
true
true
false
searchNode
true
null
false
e
startsWith
true
false
false
delete
删除成功:pool
printTrie
p \
r \
e o i \
v p \g d \z \
i \a \r \u \e \
e \r \e \c \\
w \e \s \e \
\\s \\
\
删除成功:produce
printTrie
p \
r \
e o i \
v p \g \z \
i \a \r \e \
e \r \e \\
w \e \s \
\\s \
\
7、 Trie树的应用
Trie是一种非常简单高效的数据结构,但有大量的应用实例。
(1) 字符串检索
事先将已知的一些字符串(字典)的有关信息保存到trie树里,查找另外一些未知字符串是否出现过或者出现频率。
举例:
@ 给出N 个单词组成的熟词表,以及一篇全用小写英文书写的文章,请你按最早出现的顺序写出所有不在熟词表中的生词。
@ 给出一个词典,其中的单词为不良单词。单词均为小写字母。再给出一段文本,文本的每一行也由小写字母构成。判断文本中是否含有任何不良单词。例如,若rob是不良单词,那么文本problem含有不良单词。
(2)字符串最长公共前缀
Trie树利用多个字符串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,反之,当我们把大量字符串存储到一棵trie树上时,我们可以快速得到某些字符串的公共前缀。
举例:
@ 给出N 个小写英文字母串,以及Q 个询问,即询问某两个串的最长公共前缀的长度是多少?
解决方案:首先对所有的串建立其对应的字母树。此时发现,对于两个串的最长公共前缀的长度即它们所在结点的公共祖先个数,于是,问题就转化为了离线(Offline)的最近公共祖先(Least Common Ancestor,简称LCA)问题。
而最近公共祖先问题同样是一个经典问题,可以用下面几种方法:
1. 利用并查集(Disjoint Set),可以采用采用经典的Tarjan 算法;
2. 求出字母树的欧拉序列(Euler Sequence )后,就可以转为经典的最小值查询(Range Minimum Query,简称RMQ)问题了;
(3)排序
Trie树是一棵多叉树,只要先序遍历整棵树,输出相应的字符串便是按字典序排序的结果。
举例:
@ 给你N 个互不相同的仅由一个单词构成的英文名,让你将它们按字典序从小到大排序输出。
(4) 作为其他数据结构和算法的辅助结构
如后缀树,AC自动机等
8、 Trie树复杂度分析
(1) 插入、查找的时间复杂度均为O(N),其中N为字符串长度。
(2) 空间复杂度是26^n级别的,非常庞大(可采用双数组实现改善)。
9、 总结
Trie树是一种非常重要的数据结构,它在信息检索,字符串匹配等领域有广泛的应用,同时,它也是很多算法和复杂数据结构的基础,如后缀树,AC自动机等。
参考1:http://dongxicheng.org/structure/trietree/
参考2:http://linux.thai.net/~thep/datrie/datrie.html#Ref_Fredkin1960
算法导论:Trie字典树的更多相关文章
- 萌新笔记——用KMP算法与Trie字典树实现屏蔽敏感词(UTF-8编码)
前几天写好了字典,又刚好重温了KMP算法,恰逢遇到朋友吐槽最近被和谐的词越来越多了,于是突发奇想,想要自己实现一下敏感词屏蔽. 基本敏感词的屏蔽说起来很简单,只要把字符串中的敏感词替换成"* ...
- 用KMP算法与Trie字典树实现屏蔽敏感词(UTF-8编码)
前几天写好了字典,又刚好重温了KMP算法,恰逢遇到朋友吐槽最近被和谐的词越来越多了,于是突发奇想,想要自己实现一下敏感词屏蔽. 基本敏感词的屏蔽说起来很简单,只要把字符串中的敏感词替换成“***”就可 ...
- 萌新笔记——C++里创建 Trie字典树(中文词典)(一)(插入、遍历)
萌新做词典第一篇,做得不好,还请指正,谢谢大佬! 写了一个词典,用到了Trie字典树. 写这个词典的目的,一个是为了压缩一些数据,另一个是为了尝试搜索提示,就像在谷歌搜索的时候,打出某个关键字,会提示 ...
- Trie字典树 动态内存
Trie字典树 #include "stdio.h" #include "iostream" #include "malloc.h" #in ...
- 标准Trie字典树学习二:Java实现方式之一
特别声明: 博文主要是学习过程中的知识整理,以便之后的查阅回顾.部分内容来源于网络(如有摘录未标注请指出).内容如有差错,也欢迎指正! 系列文章: 1. 标准Trie字典树学习一:原理解析 2.标准T ...
- 817E. Choosing The Commander trie字典树
LINK 题意:现有3种操作 加入一个值,删除一个值,询问pi^x<k的个数 思路:很像以前lightoj上写过的01异或的字典树,用字典树维护数求异或值即可 /** @Date : 2017- ...
- C++里创建 Trie字典树(中文词典)(一)(插入、遍历)
萌新做词典第一篇,做得不好,还请指正,谢谢大佬! 写了一个词典,用到了Trie字典树. 写这个词典的目的,一个是为了压缩一些数据,另一个是为了尝试搜索提示,就像在谷歌搜索的时候,打出某个关键字,会提示 ...
- 数据结构 -- Trie字典树
简介 字典树:又称单词查找树,Trie树,是一种树形结构,是一种哈希树的变种. 优点:利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少无谓的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高. 性质: 1. 根节 ...
- 踹树(Trie 字典树)
Trie 字典树 ~~ 比 KMP 简单多了,无脑子选手学不会KMP,不会结论题~~ 自己懒得造图了OI WIKI 真棒 字典树大概长这么个亚子 呕吼真棒 就是将读进去的字符串根据当前的字符是什么和所 ...
随机推荐
- licens 问题 Error (292028): Specified license is not valid for this machine
集成网卡调试的时候坏了,造成了quartus 不可以用,MAC地址不对应了... 应该怎么解决呢??.
- [SSH服务]——一些安全性配置和补充实验
SSH 安全性和配置 转载于 http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/aix/library/au-sshsecurity/ 对于一些之前列举的代码示例,许多系统管理 ...
- NSNumber、NSValue、NSDate、NSObject
注:OC中数组和字典只能存储OC对象不能存放基本数据类型. NSNumber NSNumber可以用来把一个基本数据类型包装成一个NSNumber类型的对象. NSNumber *number = [ ...
- Asp.Net 操作word 第二篇[推荐]
引言:前段时间有项目要用c#生成Word格式的计算报告,通过网络查找到很多内容,但是都很凌乱,于是自己决定将具体的步骤总结整理出来,以便于更好的交流和以后相似问题可以迅速的解决! 现通过具体的示例演示 ...
- Why Every Professional Should Consider Blogging
转自http://www.pixelstech.net/article/1327829407-Why-Every-Professional-Should-Consider-Blogging ften ...
- 【Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal】cpp
题目: Given a binary tree, return the zigzag level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from lef ...
- IT小小鸟读后感
我是一只小小鸟(读后感) 当我成为闽江学院的一名学子时,我选择了我自己的专业(软件工程).成为大一新生的我对着未来充满着希望憧憬.但现实并不是美好的我得替今后的我想想以后大学毕业了到底我到了社会上要用 ...
- NYOJ-235 zb的生日 AC 分类: NYOJ 2013-12-30 23:10 183人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
DFS算法: #include<stdio.h> #include<math.h> void find(int k,int w); int num[23]={0}; int m ...
- File not found images\Thumbs.db.
启动eclipse正常,部署项目的时候发生这个错误. 解决办法: 1. 从tomcat中删除这个项目,并清空work目录下的缓存 2. 在eclipse中执行project>Clean>C ...
- 研究AFIncrementalStore
一.增量存贮(AFIncrementalStore:NSIncrementalStore)在CoreData中所处位置
