Spring AOP中级——应用场景
在《Spring AOP初级——入门及简单应用》中对AOP作了简要的介绍,以及一些专业术语的解释,同时写了一个简单的Spring AOPdemo。本文将继续探讨Spring AOP在实际场景中的应用。
对用户操作日志的记录是很常见的一个应用场景,本文选取“用户管理”作为本文Spring AOP的示例。当然,该示例只是对真实场景的模拟,实际的环境一定比该示例更复杂。
该示例的完整代码路径在https://github.com/yu-linfeng/BlogRepositories/tree/master/repositories/Spring%20AOP%E4%B8%AD%E7%BA%A7%E2%80%94%E2%80%94%E5%BA%94%E7%94%A8%E5%9C%BA%E6%99%AF。本文仅对Spring AOP相关的代码进行讲解。
在这个示例中首次采用RESTful架构风格,对于以下RESTful API的设计可能并不完美,如果有熟悉、精通RESTful架构风格的朋友希望能够指出我的错误。

使用RESTful的前后端分离架构风格后,我感受到了前所未有的畅快,所以此次示例并没有前端页面的展示,完全使用JUnit进行单元测试包括对HTTP请求的Mock模拟,这部分代码不会进行详细讲解,之后会继续深入JUnit单元测试的一些学习研究。
数据库只有一张表:
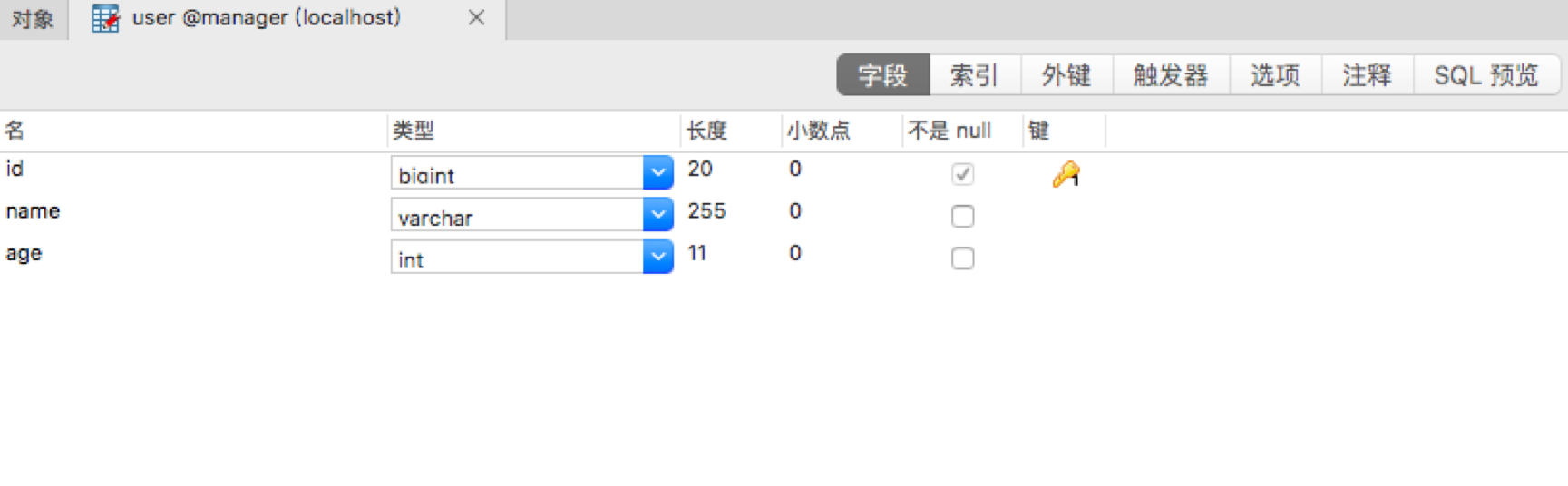
回到正题,我们回顾下切面由哪两个部分组成: 通知 切点 首先明确我们需要在何时记录日志:
通知
切点
首先明确我们需要在何时记录日志:
1. 查询所有用户时,并没有参数(此示例没有作分页),只有在返回时才会有数据的返回,所以对查询所有用户的方法采用返回通知(AfterReturning)。
2. 新增用户时,会带有新增的参数,此时可采用前置通知(Before)。
3. 修改用户时,也会带有新增的参数,此时同样采用前置通知(Before)。
4. 删除用户时,通常会带有唯一标识符ID,此时采用前置通知(Before)记录待删除的用户ID。
在明确了通知类型后,此时我们需要明确切点,也就是在哪个地方记录日志。当然上面实际已经明确了日志记录的位置,但主要是切面表达式的书写。 在有了《Spring AOP初级——入门及简单应用》的基础,相信对日志切面类已经比较熟悉了:
- package com.manager.aspect;
- import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
- import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
- import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
- import java.util.Arrays;
- /**
- * 日志切面
- * Created by Kevin on 2017/10/29.
- */
- @Aspect
- @Component
- public class LogAspect {
- /**
- * 操作日志文件名
- */
- private static final String OPERATION_LOG_NAME = "operationLog";
- private static final String LOG_FORMATTER = "%s.%s - %s";
- Logger log = Logger.getLogger(OPERATION_LOG_NAME);
- /**
- * 对查询方法记录日志的切点
- */
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.query*(..))")
- public void query(){}
- /**
- * 对新增方法记录日志的切点
- */
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.add*(..))")
- public void add(){}
- /**
- * 对修改方法记录日志的切点
- */
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.update*(..))")
- public void update(){}
- /**
- * 对删除方法记录日志的切点
- */
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.manager..*.*Controller.delete*(..))")
- public void delete(){}
- @AfterReturning(value = "query()", returning = "rvt")
- public void queryLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object rvt) {
- String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
- String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
- String returnResult = rvt.toString();
- log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, returnResult));
- }
- @Before("add()")
- public void addLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
- String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
- Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs();
- log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params)));
- }
- @Before("update()")
- public void updateLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
- String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
- Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs();
- log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params)));
- }
- @Before("delete()")
- public void deleteLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
- String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
- String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
- Object[] params = joinPoint.getArgs();
- log.info(String.format(LOG_FORMATTER, className, methodName, Arrays.toString(params)));
- }
- }
上面的日志切面类中出现了JointPoint类作为参数的情况,这个参数能够传递被通知方法的相信,例如被通知方法所处的类以及方法名等。在第47行中的Object rvt参数就是获取被通知方法的返回值。 上面的切面并没有关注被通知方法的参数,如果要使得切面和被通知方法参数参数关联可以使用以下的方式:
- @Pointcut("execution(* com.xxx.demo.Demo.method(int)) && args(arg)")
- public void aspectMethod(int arg){}
- @Before(“aspectMedhot(arg)”)
- public void method(int arg) {
- //此时arg参数就是被通知方法的参数
- }
本例中最主要的切面部分就完成了。注意在结合Spring时需要在applicationContext.xml中加入以下语句:
- <!--启用AspectJ自动代理,其中proxy-target-class为true表示使用CGLib的代理方式,false表示JDK的代理方式,默认false-->
- <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
示例中关于log4j、pom.xml依赖、JUnit如何结合Spring进行单元测试等等均可可以参考完整代码。特别是JUnit是很值得学习研究的一部分,这部分在将来慢慢我也会不断学习推出新的博客,在这里就只贴出JUnit的代码,感兴趣的可以浏览一下:
- package com.manager.user.controller;
- import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
- import com.manager.user.pojo.User;
- import org.junit.Before;
- import org.junit.Test;
- import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
- import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
- import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
- import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
- import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
- import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
- import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
- import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
- import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
- import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
- /**
- * UserController单元测试
- * Created by Kevin on 2017/10/26.
- */
- @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
- @ContextConfiguration({"classpath*:applicationContext.xml", "classpath*:spring-servlet.xml"})
- @WebAppConfiguration
- public class UserControllerTest {
- @Autowired
- private WebApplicationContext wac;
- private MockMvc mvc;
- @Before
- public void initMockHttp() {
- this.mvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(wac).build();
- }
- @Test
- public void testQueryUsers() throws Exception {
- mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/users"))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
- }
- @Test
- public void testAddUser() throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setName("kevin");
- user.setAge(23);
- mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/users")
- .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
- .content(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user)))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.name").value("kevin"))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.age").value(23));
- }
- @Test
- public void testQueryUserById() throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setId(8);
- mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/users/" + user.getId()))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.name").value("kevin"))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.age").value(23));
- }
- @Test
- public void testUpdateUserById() throws Exception {
- User user = new User();
- user.setId(9);
- user.setName("tony");
- user.setAge(99);
- mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.put("/users/" + user.getId())
- .contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
- .content(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user)))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
- }
- @Test
- public void testDeleteUserById() throws Exception {
- long id = 10;
- mvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/users/" + id))
- .andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
- }
- }
有了初级和中级,接下来必然就是Spring AOP高级——源码实现。
这是一个能给程序员加buff的公众号

Spring AOP中级——应用场景的更多相关文章
- [转]彻底征服 Spring AOP 之 实战篇
Spring AOP 实战 看了上面这么多的理论知识, 不知道大家有没有觉得枯燥哈. 不过不要急, 俗话说理论是实践的基础, 对 Spring AOP 有了基本的理论认识后, 我们来看一下下面几个具体 ...
- 161110、彻底征服 Spring AOP 之 实战篇
Spring AOP 实战 看了上面这么多的理论知识, 不知道大家有没有觉得枯燥哈. 不过不要急, 俗话说理论是实践的基础, 对 Spring AOP 有了基本的理论认识后, 我们来看一下下面几个具体 ...
- Spring技术内幕:Spring AOP的实现原理(二)
**二.AOP的设计与实现 1.JVM的动态代理特性** 在Spring AOP实现中, 使用的核心技术时动态代理.而这样的动态代理实际上是JDK的一个特性.通过JDK的动态代理特性,能够为随意Jav ...
- Spring Aop 应用实例与设计浅析
0.代码概述 代码说明:第一章中的代码为了突出模块化拆分的必要性,所以db采用了真实操作.下面代码中dao层使用了打印日志模拟插入db的方法,方便所有人运行demo. 1.项目代码地址:https:/ ...
- 彻底征服 Spring AOP 之 实战篇
Spring AOP 实战 看了上面这么多的理论知识, 不知道大家有没有觉得枯燥哈. 不过不要急, 俗话说理论是实践的基础, 对 Spring AOP 有了基本的理论认识后, 我们来看一下下面几个 ...
- 关于 Spring AOP (AspectJ) 该知晓的一切
关联文章: 关于Spring IOC (DI-依赖注入)你需要知道的一切 关于 Spring AOP (AspectJ) 你该知晓的一切 本篇是年后第一篇博文,由于博主用了不少时间在构思这篇博文,加上 ...
- 关于 Spring AOP (AspectJ) 你该知晓的一切
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「zejian_」的原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明.原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/javazej ...
- Spring AOP 实战运用
Spring AOP 实战 看了上面这么多的理论知识, 不知道大家有没有觉得枯燥哈. 不过不要急, 俗话说理论是实践的基础, 对 Spring AOP 有了基本的理论认识后, 我们来看一下下面几个具体 ...
- Spring AOP应用场景你还不知道?这篇一定要看!
回顾一下Spring AOP的知识 为什么会有面向切面编程(AOP)? 我们知道Java是一个面向对象(OOP)的语言,但它有一些弊端,比如当我们需要为多个不具有继承关系的对象引入一个公共行为,例如日 ...
随机推荐
- Struts2第十篇【数据校验、代码方式、XML配置方式、错误信息返回样式】
回顾以前的数据校验 使用一个FormBean对象来封装着web端来过来的数据 维护一个Map集合保存着错误信息-对各个字段进行逻辑判断 //表单提交过来的数据全都是String类型的,birthday ...
- 如何手动获取Spring容器中的bean(ApplicationContextAware 接口)
ApplicationContextAware 接口的作用 先来看下Spring API 中对于 ApplicationContextAware 这个接口的描述: 即是说,当一个类实现了这个接口之 ...
- 百度编辑器不能插入html标签解决方法
找到此方法: me.addInputRule(function (root) { var allowDivTransToP = this.options.allowDivTransToP; var v ...
- MapReduce执行过程
Mapper任务的执行过程: 第一阶段是把输入文件按照一定的标准分片(InputSplit),每个输入片的大小是固定的.默认情况下,输入片(InputSplit)的大小与数据块(Block)的大小是相 ...
- BZOJ2748_音量调节_KEY
[HAOI2012]音量调节 Time Limit: 3 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Description 一个吉他手准备参加一场演出.他不喜欢在演出时始终使用同一个音量,所以 ...
- CentOS更新源
1.首先备份/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS ...
- BCB中AnsiString类方法小结
AnsiString类是BCB中最常见类之一,了解它对以后深入学习BCB大有帮助. 介绍AnsiString类之前,先要介绍一些背景知识.VCL(Visual Component Library 可视 ...
- 【重点突破】——Canvas技术绘制随机改变的验证码
一.引言 本文主要是我在学习Canvas技术绘图时的一个小练习,绘制随机改变的验证码图片,虽然真正的项目里不这么做,但这个练习是一个掌握Canvas技术很好的综合练习.(真正的项目中验证码图片使用服务 ...
- 【POJ】2115 C Looooops(扩欧)
Description A Compiler Mystery: We are given a C-language style for loop of type for (variable = A; ...
- vue2组件之select2调用
目前,项目中使用了纯前端的静态项目+RESTFul接口的模式.为了更好的对数据进行操作,前端使用了vue2的mvvm功能,但是由于不是单页面应用,所以,并没有涉及到其它的如vue-route等功能,也 ...
