python内置函数与匿名函数
内置函数
| Built-in Functions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| abs() | dict() | help() | min() | setattr() |
| all() | dir() | hex() | next() | slice() |
| any() | divmod() | id() | object() | sorted() |
| ascii() | enumerate() | input() | oct() | staticmethod() |
| bin() | eval() | int() | open() | str() |
| bool() | exec() | isinstance() | pow() | super() |
| bytes() | float() | iter() | print() | tuple() |
| callable() | format() | len() | property() | type() |
| chr() | frozenset() | list() | range() | vars() |
| classmethod() | getattr() | locals() | repr() | zip() |
| compile() | globals() | map() | reversed() | __import__() |
| complex() | hasattr() | max() | round() | |
| bytearray() | filter() | issubclass() | pow() | super() |
| delattr() | hash() | memoryview() | set | |
截止到python版本3.6.2,现在python一共为我们提供了68个内置函数。它们就是python提供给你直接可以拿来使用的所有函数。
内置函数分类
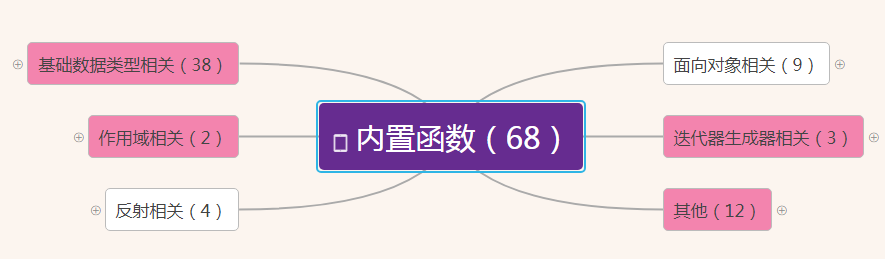
作用域相关
基于字典的形式获取局部变量和全局变量
globals()——获取全局变量的字典
locals()——获取执行本方法所在命名空间内的局部变量的字典
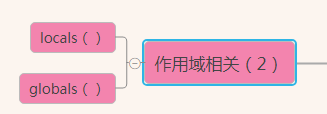
其他
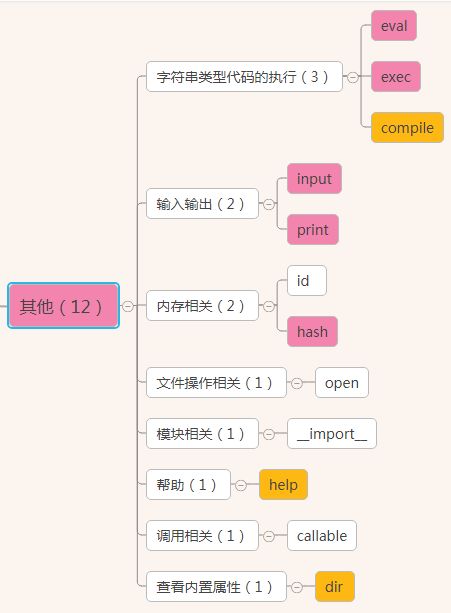
输入输出相关
input()输入
s = input("请输入内容 : ") #输入的内容赋值给s变量
print(s) #输入什么打印什么。数据类型是str
input用法
print输出
def print(self, *args, sep=' ', end='\n', file=None): # known special case of print
"""
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
file: 默认是输出到屏幕,如果设置为文件句柄,输出到文件
sep: 打印多个值之间的分隔符,默认为空格
end: 每一次打印的结尾,默认为换行符
flush: 立即把内容输出到流文件,不作缓存
"""
print源码剖析
f = open('tmp_file','w')
print(,,sep=',',file = f,flush=True)
file关键字说明
from time import sleep
for i in range(,,):
sleep(0.1)
str="*"*(i//2)
print('\r%s%%:%s'%(i,str),end="",flush=True)
打印进度条
数据类型相关
type(s)返回s的数据类型
s="abc"
print(type(s))#<class 'str'>
type说明
内存相关
id(s) s是参数,返回一个变量的内存地址
hash(s) s是参数,返回一个可hash变量的哈希值,不可hash的变量被hash之后会报错。
l1=[,,]
l2=(,,)
print(hash(l2))#
print(hash(l1))#TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
hash举例
hash函数会根据一个内部的算法对当前可hash变量进行处理,返回一个int数字。
*每一次执行程序,内容相同的变量hash值在这一次执行过程中不会发生改变。
文件操作相关
open() 打开一个文件,返回一个文件操作符(文件句柄)
操作文件的模式有r,w,a,r+,w+,a+ 共6种,每一种方式都可以用二进制的形式操作(rb,wb,ab,rb+,wb+,ab+)
可以用encoding指定编码.
模块操作相关
__import__导入一个模块
os = __import__('os')
print(os.path.abspath('.'))
__import__
帮助方法
help(s) s为函数名
help(str) #输出
class str(object)
| str(object='') -> str
| str(bytes_or_buffer[, encoding[, errors]]) -> str
|
| Create a new string object from the given object. If encoding or
| errors is specified, then the object must expose a data buffer
| that will be decoded using the given encoding and error handler.
| Otherwise, returns the result of object.__str__() (if defined)
| or repr(object).
| encoding defaults to sys.getdefaultencoding().
| errors defaults to 'strict'.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, value, /)
| Return self+value.
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| Return key in self.
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __format__(...)
| S.__format__(format_spec) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(self, key, /)
| Return self[key].
|
| __getnewargs__(...)
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __hash__(self, /)
| Return hash(self).
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __le__(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| __len__(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| __lt__(self, value, /)
| Return self<value.
|
| __mod__(self, value, /)
| Return self%value.
|
| __mul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.n
|
| __ne__(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| __repr__(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| __rmod__(self, value, /)
| Return value%self.
|
| __rmul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.
|
| __sizeof__(...)
| S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes
|
| __str__(self, /)
| Return str(self).
|
| capitalize(...)
| S.capitalize() -> str
|
| Return a capitalized version of S, i.e. make the first character
| have upper case and the rest lower case.
|
| casefold(...)
| S.casefold() -> str
|
| Return a version of S suitable for caseless comparisons.
|
| center(...)
| S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
|
| count(...)
| S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
| string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are
| interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| encode(...)
| S.encode(encoding='utf-8', errors='strict') -> bytes
|
| Encode S using the codec registered for encoding. Default encoding
| is 'utf-8'. errors may be given to set a different error
| handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
| a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
| 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
| codecs.register_error that can handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
|
| endswith(...)
| S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
|
| Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
| With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
| With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
| suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
|
| expandtabs(...)
| S.expandtabs(tabsize=) -> str
|
| Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
| If tabsize is not given, a tab size of characters is assumed.
|
| find(...)
| S.find(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Return - on failure.
|
| format(...)
| S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
| The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
|
| format_map(...)
| S.format_map(mapping) -> str
|
| Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from mapping.
| The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
|
| index(...)
| S.index(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
|
| isalnum(...)
| S.isalnum() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isalpha(...)
| S.isalpha() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isdecimal(...)
| S.isdecimal() -> bool
|
| Return True if there are only decimal characters in S,
| False otherwise.
|
| isdigit(...)
| S.isdigit() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are digits
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isidentifier(...)
| S.isidentifier() -> bool
|
| Return True if S is a valid identifier according
| to the language definition.
|
| Use keyword.iskeyword() to test for reserved identifiers
| such as "def" and "class".
|
| islower(...)
| S.islower() -> bool
|
| Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
| at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
|
| isnumeric(...)
| S.isnumeric() -> bool
|
| Return True if there are only numeric characters in S,
| False otherwise.
|
| isprintable(...)
| S.isprintable() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are considered
| printable in repr() or S is empty, False otherwise.
|
| isspace(...)
| S.isspace() -> bool
|
| Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
| and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
|
| istitle(...)
| S.istitle() -> bool
|
| Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
| character in S, i.e. upper- and titlecase characters may only
| follow uncased characters and lowercase characters only cased ones.
| Return False otherwise.
|
| isupper(...)
| S.isupper() -> bool
|
| Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
| at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
|
| join(...)
| S.join(iterable) -> str
|
| Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
| iterable. The separator between elements is S.
|
| ljust(...)
| S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S left-justified in a Unicode string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
|
| lower(...)
| S.lower() -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
|
| lstrip(...)
| S.lstrip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| partition(...)
| S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
|
| Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
| the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
| found, return S and two empty strings.
|
| replace(...)
| S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of S with all occurrences of substring
| old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
| given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
|
| rfind(...)
| S.rfind(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Return - on failure.
|
| rindex(...)
| S.rindex(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
|
| Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
| such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
| arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
|
| Raises ValueError when the substring is not found.
|
| rjust(...)
| S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> str
|
| Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
| done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
|
| rpartition(...)
| S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
|
| Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
| the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
| separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
|
| rsplit(...)
| S.rsplit(sep=None, maxsplit=-) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
| delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and
| working to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
| splits are done. If sep is not specified, any whitespace string
| is a separator.
|
| rstrip(...)
| S.rstrip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| split(...)
| S.split(sep=None, maxsplit=-) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the words in S, using sep as the
| delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
| splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
| whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are
| removed from the result.
|
| splitlines(...)
| S.splitlines([keepends]) -> list of strings
|
| Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
| Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
| is given and true.
|
| startswith(...)
| S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
|
| Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
| With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
| With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
| prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
|
| strip(...)
| S.strip([chars]) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
| whitespace removed.
| If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
|
| swapcase(...)
| S.swapcase() -> str
|
| Return a copy of S with uppercase characters converted to lowercase
| and vice versa.
|
| title(...)
| S.title() -> str
|
| Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with title case
| characters, all remaining cased characters have lower case.
|
| translate(...)
| S.translate(table) -> str
|
| Return a copy of the string S in which each character has been mapped
| through the given translation table. The table must implement
| lookup/indexing via __getitem__, for instance a dictionary or list,
| mapping Unicode ordinals to Unicode ordinals, strings, or None. If
| this operation raises LookupError, the character is left untouched.
| Characters mapped to None are deleted.
|
| upper(...)
| S.upper() -> str
|
| Return a copy of S converted to uppercase.
|
| zfill(...)
| S.zfill(width) -> str
|
| Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
| of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| maketrans(x, y=None, z=None, /)
| Return a translation table usable for str.translate().
|
| If there is only one argument, it must be a dictionary mapping Unicode
| ordinals (integers) or characters to Unicode ordinals, strings or None.
| Character keys will be then converted to ordinals.
| If there are two arguments, they must be strings of equal length, and
| in the resulting dictionary, each character in x will be mapped to the
| character at the same position in y. If there is a third argument, it
| must be a string, whose characters will be mapped to None in the result.
help用法
在控制台执行help()进入帮助模式。可以随意输入变量或者变量的类型。输入q退出
或者直接执行help(o),o是参数,查看和变量o有关的操作。。。
和调用相关
callable(s),s是参数,看这个变量是不是可调用。
如果s是一个函数名,就会返回True
def func():pass
print(callable(func))#True
print(callable())#Flase
callable实例
查看参数所属类型的所有内置方法
dir() 默认查看全局空间内的属性,也接受一个参数,查看这个参数内的方法或变量
dir(list) ['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
dir实例
和数字相关
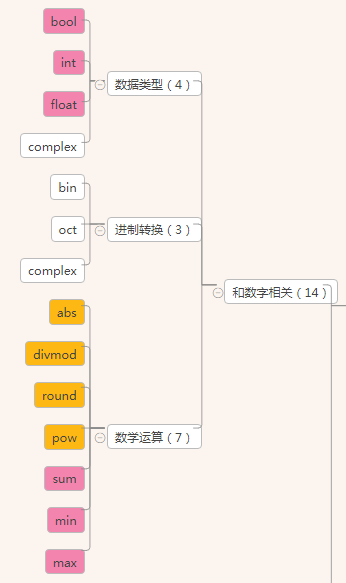
数字——数据类型相关:bool,int,float,complex
数字——进制转换相关:bin,oct,hex
数字——数学运算:abs,divmod,min,max,sum,round,pow
和数据结构相关
序列——列表和元组相关的:list和tuple
序列——字符串相关的:str,format,bytes,bytearry,memoryview,ord,chr,ascii,repr
ret=bytearray('xiaozhangmen',encoding='utf-8')
print(ret)#bytearray(b'xiaozhangmen')
bytearray
ret = memoryview(bytes('你好',encoding='utf-8'))
print(len(ret))
print(bytes(ret[:]).decode('utf-8'))
print(bytes(ret[:]).decode('utf-8'))
memoryview
序列:reversed,slice
l=[,,,,,]
l.reverse()
print(l)#[, , , , , ]
reverse
l=[1,2,3,4,5,6]
sli=slice(1,4,2)#slice看起来返回的是一个规则,拿到这个规则后再对列表进行操作
print(l[sli])#[2, 4]
slice
数据集合——字典和集合:dict,set,frozenset
数据集合:len,sorted,enumerate,all,any,zip,filter,map
filter:使用指定方法过滤可迭代对象的元素
def is_odd(x):
return x % 2 == 1
print(filter(is_odd,[1,2,3,4,5,6]))#<filter object at 0x00000000022EC240>
print(list(filter(is_odd,[1,2,3,4,5,6])))#[1, 3, 5]
filter
map:python中的map函数应用于每一个可迭代的项,返回的是一个结果list。如果有其他的可迭代参数传进来,map函数则会把每一个参数都以相应的处理函数进行迭代处理。map()函数接收两个参数,一个是函数,一个是序列,map将传入的函数依次作用到序列的每个元素,并把结果作为新的list返回。
def pow(x):
return x**2
print(map(pow,[0,1,2,3]))#<map object at 0x000000000291C1D0>
print(list(map(pow,[0,1,2,3])))#[0, 1, 4, 9]
map
匿名函数
匿名函数:为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数
匿名函数格式:
函数名 = lambda 参数 :返回值 #参数可以有多个,用逗号隔开
#匿名函数不管逻辑多复杂,只能写一行,且逻辑执行结束后的内容就是返回值
#返回值和正常的函数一样可以是任意数据类型
匿名函数实例
#如把下面函数改为匿名函数
def add(x,y):
return x+y add1=lambda x,y:x+y print(add(1,2))
print(add1(1,2))
面试题笔记:
现有两个元组(('a'),('b')),(('c'),('d')),请使用python中匿名函数生成列表[{'a':'c'},{'b':'d'}]
#答案一
test = lambda t1,t2 :[{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)]
print(test(t1,t2))
#答案二
print(list(map(lambda t:{t[0]:t[1]},zip(t1,t2))))
#还可以这样写
print([{i:j} for i,j in zip(t1,t2)])
Code
1.下面程序的输出结果是:
d = lambda p:p*2
t = lambda p:p*3
x = 2
x = d(x)
x = t(x)
x = d(x)
print x 2.现有两元组(('a'),('b')),(('c'),('d')),请使用python中匿名函数生成列表[{'a':'c'},{'b':'d'}] 3.以下代码的输出是什么?请给出答案并解释。
def multipliers():
return [lambda x:i*x for i in range(4)]
print([m(2) for m in multipliers()])
请修改multipliers的定义来产生期望的结果。
习题
python内置函数与匿名函数的更多相关文章
- Python内置的字符串处理函数整理
Python内置的字符串处理函数整理 作者: 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 时间:2013-01-29我要评论 Python内置的字符串处理函数整理,收集常用的Python 内置的各种字符串处理 ...
- python内置常用高阶函数(列出了5个常用的)
原文使用的是python2,现修改为python3,全部都实际输出过,可以运行. 引用自:http://www.cnblogs.com/duyaya/p/8562898.html https://bl ...
- Python 内置的一些高效率函数用法
1. filter(function,sequence) 将sequence中的每个元素,依次传进function函数(可以自定义,返回的结果是True或者False)筛选,返回符合条件的元素,重组 ...
- 学习Pytbon第十天 函数2 内置方法和匿名函数
print( all([1,-5,3]) )#如果可迭代对象里所有元素都为真则返回真.0不为真print( any([1,2]) )#如果数据里面任意一个数据为真返回则为真a= ascii([1,2, ...
- Python内置进制转换函数(实现16进制和ASCII转换)
在进行wireshark抓包时你会发现底端窗口报文内容左边是十六进制数字,右边是每两个十六进制转换的ASCII字符,这里使用Python代码实现一个十六进制和ASCII的转换方法. hex() 转换一 ...
- Python内置的字符串处理函数
生成字符串变量 str='python String function' 字符串长度获取:len(str) 例:print '%s length=%d' % (str,len(str)) 连接字符 ...
- Py修行路 python基础 (十三)匿名函数 与 内置函数
一.匿名函数 1.定义: 匿名函数顾名思义就是指:是指一类无需定义标识符(函数名)的函数或子程序. 2.语法格式:lambda 参数:表达式 lambda语句中,开头先写关键字lambda,冒号前是 ...
- Python内置函数系列
Python内置(built-in)函数随着python解释器的运行而创建.在Python的程序中,你可以随时调用这些函数,不需要定义. 作用域相关(2) locals() :以字典类型返回当前位置 ...
- Python内置高阶函数map()
map()函数map()是 Python 内置的高阶函数,它接收一个函数 f 和一个 list,并通过把函数 f 依次作用在 list 的每个元素上,得到一个新的 list 并返回. 例如,对于lis ...
- Python中的高阶函数与匿名函数
Python中的高阶函数与匿名函数 高阶函数 高阶函数就是把函数当做参数传递的一种函数.其与C#中的委托有点相似,个人认为. def add(x,y,f): return f( x)+ f( y) p ...
随机推荐
- 关于PHP新手学习的一些指导与建议,新手快到我碗里来!
新手小白想要系统性学好PHP开发,首先需要了解需要学些什么,然后给自己定下来一个学习路线,然后就朝着这个路线奋斗吧! 关于学习路线:(1) 熟悉HTML/CSS/JS等网页基本元素,完成阶段可自行制作 ...
- 怎么配置Jupyter Notebook默认启动目录?
前言 系统环境:win10 x64:跟环境也没啥关系,在LInux下也一样... 前段时间重换了系统后,发现Jupyter Notebook的默认启动目录不太对呀,所以,就翻到了以前的笔记,还是记在这 ...
- Python学习之--socket
1.Socket概述 网络上的两个程序通过一个双向的通信连接实现数据的交换,这个连接的一端称为一个socket.socket通常也称作"套接字",用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个 ...
- Haproxy配置日志显示
安装完haproxy后,日志默认是记录在系统日志下的.为了便于排错以及查看日志,我们需要将haproxy日志剥离出来. 在配置前,我们先来了解下日志的level: local0-local7 16-2 ...
- bzoj4974 字符串大师
4974: 字符串大师 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 310 Solved: 155[Submit][Status][Discuss] ...
- 关于C#中函数的认识
对于C#语言中的函数,大概分之为函数的声明及其调用. 函数的声明: 1.函数的声明是指给一段代码取名称. 2.函数的声明位置必须在类中. 3.函数声明的语法: 函数声明的语法:static void ...
- ElasticSearch 学习记录之集群分片内部原理
分片内部原理 分片是如何工作的 为什么ES搜索是近实时性的 为什么CRUD 操作也是实时性 ES 是怎么保证更新被持久化时断电也不丢失数据 为什么删除文档不会立即释放空间 refresh, flush ...
- 》》stroll--各种特效下拉菜单
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8&quo ...
- It appears that the Web Project,“”,has no Web Root directory setup
1 错误描写叙述 2 错误原因 因为项目是用eclipse新建的,web的根文件夹文件夹是WebContent.而MyEclipse新建的项目的Web根文件夹是WebRoot.直接将eclipse项目 ...
- vue的组件和生命周期
Vue里组件的通信 通信:传参.控制.数据共享(A操控B做一个事件) 模式:父子组件间.非父子组件 父组件可以将一条数据传递给子组件,这条数据可以是动态的,父组件的数据更改的时候,子组件接收的也会变化 ...
