.Neter所应该彻底了解的委托
本文将通过引出几个问题来,并且通过例子来剖析C#中的委托以及用法,做抛砖引玉的作用
对于委托我发现大部分人都有以下问题,或者可能在面试中遇过这样的:
- 委托是不是相当于C/C++的函数指针?
- 委托究竟是什么?
- 委托究竟是用来干嘛的?
- 委托跟匿名函数的区别?
- 委托与事件的关系?
我们先来声明和使用C++的函数指针:
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; typedef int (*Foohandle)(int a,int b); int fooMenthod(int a, int (*foohandle1)(int a,int b)) //回调函数
{
return a + (*foohandle1)(,);//也可以写成foohandle1(2,3)
} int add(int a,int b) {
return a + b;
} int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
} int main()
{
Foohandle foohandle = add;
int (*foohandle1)(int a, int b) = &add;
cout << foohandle(,)<<endl;
cout << foohandle1(,) << endl;
cout << typeid(Foohandle).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(foohandle).name()<<endl;
cout << typeid(foohandle1).name() << endl;
cout << fooMenthod(, add)<<endl;
cout << fooMenthod(, multiply);
}
输出结果如下:
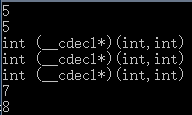
在代码中,我声明定义了两个函数add和multiply,然后用typedef方式声明了函数指针,接着我分别将add赋值给Foohandle这种函数指针类型的foohandle变量,然后用&add这种解地址的方式赋值给一个返回值为int,且带有两个参数的函数指针foohandle1,其中(*foohandle1)是函数名,最后我输出发现它们类型和输出都是一致的,再后面,我们定义了一个fooMenthod函数,返回值是int,且其中一个参数是函数指针,那么我再最后调用两次,分别将add和multiply函数,赋值给它,这时候add和multiply就是fooMenthod函数的回调函数,且此时输出结果会被两个函数内部不同实现所影响
那么我们可以做个总结:
- 首先函数指针就是一个内存地址,指向函数的入口内存地址
- 当函数指针做一个函数的参数时,确实会起到一定解耦作用
- 函数指针很明显是类型不安全的
我们再来声明和使用委托:
public delegate int Foohandle(int a, int b);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Foohandle foohandle = new Foohandle(add);
Console.WriteLine(foohandle(, ));
Console.WriteLine(foohandle.GetType().Name);
Console.WriteLine(fooMenthod(, add));
Console.WriteLine(fooMenthod(, multiply));
Console.WriteLine($"foohandle所调用函数函数名:{foohandle.Method.Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"foohandle所调用函数的返回值类型{foohandle.Method.ReturnType.ToString()}");
Console.WriteLine("foohandle所调用函数参数类型以及参数名分别为:");
Console.WriteLine($"Type:{foohandle.Method.GetParameters()[0].ParameterType},Name:{foohandle.Method.GetParameters()[0].Name}");
Console.WriteLine($"Type:{foohandle.Method.GetParameters()[1].ParameterType},Name:{foohandle.Method.GetParameters()[1].Name}");
Console.Read();
} static int fooMenthod(int a, Foohandle foohandle) //传给参数函数的就是回调函数
{
return a + foohandle(, );
} static int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
} static int multiply(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
}
输出结果:
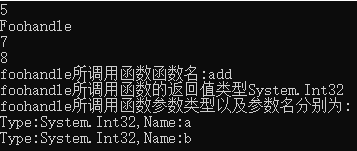
很明显,不管是声明和使用方式,都和c++那边一样,就连输出结果也差不多,但是很有意思的是,foohandle的类型是Foohandle,且我居然能从foohandle输出所调函数的一切信息,包括函数名,返回值,参数类型和参数名,而且和c++那边不同的是,我们没有直接操作内存地址,好像看起来是安全的?那么Foohandle类型又是什么?
委托是啥?
先来个例子:
namespace DelegateSample
{ public delegate void FooHandle(int value);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FooHandle fooHandle = new FooHandle(multiply);
fooHandle();
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle.Target:{fooHandle.Target},fooHandle.Method:{fooHandle.Method},fooHandle.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
FooHandle fooHandle1 = new FooHandle(new Foo().Add);
fooHandle1.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle1.Target:{fooHandle1.Target},fooHandle1.Method:{fooHandle1.Method},fooHandle1.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle1.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
Console.Read();
} static void multiply(int a)
{
Console.WriteLine(a*);
}
} public class Foo
{
public void Add(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine(value + );
}
}
}
我们看看输出的结果:
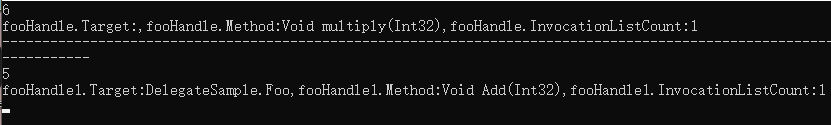
很明显,这里是一个最简单的委托声明,实例化初始化一个委托对象,然后调用的最简单的场景
我们不关注输出的第一行,很明显,对象实例化后,可以访问其中的三个公开public的函数成员,
分别是Target(object类型),Method(MethodInfo类型),而GetInvocationList函数是一个返回值为一个Delegate[]的无参函数
在上面代码,其实我还特地将委托FooHandle声明在Program类外面,其实在这里我们已经知道委托是什么了,实例化对象,且能够声明在类外面,其实它本质就是一个类,我们通过反编译来验证:
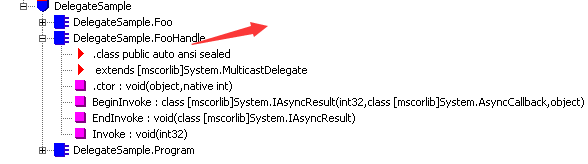
大概是这样,伪代码如下:
public class FooHandle: MulticastDelegate
{
public FooHandle(object @object,IntPtr menthod);//构造方法 void Invoke(int value)//调用委托,编译后公共语言运行时给delegate提供的特殊方法 void EndInvoke(System.IAsyncResult asyncResult)// 编译后公共语言运行时给MulticastDelegate提供的特殊方法 // 编译后公共语言运行时给MulticastDelegate提供的特殊方法
void BeginInvoke(int value,System.AsyncCallback callback, object obj)
}
我们可以看编译后FooHandle就是一个类,且继承MulticastDelegate,且继承链关系在msdn是这样的:

且我们发现上面公开的三个函数成员都来自于Delegate类,且编译后生成了几个公共运行时提供的特殊方法,Invoke方法我们很清楚,是来调用委托的,我们先来看看委托初始化后的情况,通过查看Delegate的源码,我们发现Delegate有两个构造函数:
1.委托对象初始化构造函数是实例函数:
[SecuritySafeCritical]
protected Delegate(object target, string method)
{
if (target == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("target");
}
if (method == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("method");
}
if (!BindToMethodName(target, (RuntimeType)target.GetType(), method, (DelegateBindingFlags)))
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Arg_DlgtTargMeth"));
}
}
2.委托对象初始化构造函数是静态函数:
[SecuritySafeCritical]
protected Delegate(Type target, string method)
{
if (target == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("target");
}
if (target.IsGenericType && target.ContainsGenericParameters)
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Arg_UnboundGenParam"), "target");
}
if (method == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("method");
}
RuntimeType runtimeType = target as RuntimeType;
if (runtimeType == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_MustBeRuntimeType"), "target");
}
BindToMethodName(null, runtimeType, method, (DelegateBindingFlags));
}
最后共同调用的方法:
//调用CLR的内部代码
[MethodImpl(MethodImplOptions.InternalCall)]
[SecurityCritical]
private extern bool BindToMethodName(object target, RuntimeType methodType, string method, DelegateBindingFlags flags);
虽然我们看不到BindToMethodName方法的实现,已经很明显了,委托对象初始化构造函数是静态函数传参进去BindToMethodName的第一个object的target参数为null,那我们大概把之前的伪代码的构造函数这么实现了:
伪代码部分:
internal object _target//目标对象;
internal IntPtr _methodPtr//目标方法;
internal IntPtr _methodPtrAux//用来判断Target是否为空; //foolHandle的构造方法实现:
public FooHandle(object @object,IntPtr menthod)
{
_methodPtr=menthod;//multiply
_methodPtrAux=;//只要不等于nul } //foolHandle1的构造方法实现:
public FooHandle(object @object,IntPtr menthod)
{
_methodPtr=menthod//Add
_methodPtrAux=//为null
_target=foo; }
Delegate Target属性源代码部分:
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public object Target
{
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
get
{
return GetTarget();
}
} [SecuritySafeCritical]
internal virtual object GetTarget()
{
if (!_methodPtrAux.IsNull())
{
return null;
}
return _target;
}
而获取Method的方法就不展开了,就是通过反射来获取,那我们已经知道Target和Method属性究竟是怎么回事了,我们还发现没讲到GetInvocationList方法是怎么回事?我们知道委托是支持多播委托的,也就是大概这样,修改上述代码为:
namespace DelegateSample
{
public delegate void FooHandle(int value);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FooHandle fooHandle = new FooHandle(multiply);
fooHandle();
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle.Target:{fooHandle.Target},fooHandle.Method:{fooHandle.Method},fooHandle.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
FooHandle fooHandle1 = new FooHandle(new Foo().Add);
fooHandle1.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle1.Target:{fooHandle1.Target},fooHandle1.Method:{fooHandle1.Method},fooHandle1.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle1.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------------新增代码------------------------------------------------------");
FooHandle fooHandle2 = new FooHandle(new Program().Minus);
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle2.Target:{fooHandle2.Target},fooHandle1.Method:{fooHandle2.Method},fooHandle1.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle2.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
fooHandle2(2);
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
FooHandle fooHandle3 = null;
fooHandle3 += fooHandle;
fooHandle3 =(FooHandle)Delegate.Combine(fooHandle3,fooHandle1);//相当于fooHandle3+=fooHandle1;
fooHandle3 += new Program().Minus;
Console.WriteLine($"fooHandle3.Target:{fooHandle3.Target},fooHandle3.Method:{fooHandle3.Method},fooHandle3.InvocationListCount:{fooHandle3.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
fooHandle3(2);
foreach (var result in fooHandle3.GetInvocationList())
{
Console.WriteLine($"result.Target:{result.Target},result.Method:{result.Method},result.InvocationListCount:{result.GetInvocationList().Count()}");
}
Console.Read();
} private void Minus(int a)
{
Console.WriteLine(a-1);
} static void multiply(int a)
{
Console.WriteLine(a * );
}
} public class Foo
{
public void Add(int value)
{
Console.WriteLine(value + );
}
}
}
输出结果是:

上面新增的代码,我声明了一个新的委托变量fooHandle3初始化为null,接着分别用三种不同的方式将委托或者函数加给fooHandle,之后输出后相当于分别按序调用输出了三个方法,而我们遍历其中的fooHandle3.GetInvocationList()委托数组,输出的也确实三个方法,但是注意到了没,我在fooHandle3 += new Program().Minus这段确实没有声明一个委托变量,我们可以注意到其中的(FooHandle)Delegate.Combine(fooHandle3,fooHandle1)这句,Combine很明显是需要两个委托变量的,查看编译后的代码我们可以得知到底发生了啥?
Il关键代码如下:
//fooHandle3 += fooHandle
IL_00f7: call class [mscorlib]System.Delegate [mscorlib]System.Delegate::Combine(class [mscorlib]System.Delegate,
class [mscorlib]System.Delegate)
IL_00fc: castclass DelegateSample.FooHandle
IL_0101: stloc.
IL_0102: ldloc.
IL_0103: ldloc.
//fooHandle3 =(FooHandle)Delegate.Combine(fooHandle3,fooHandle1)
IL_0104: call class [mscorlib]System.Delegate [mscorlib]System.Delegate::Combine(class [mscorlib]System.Delegate,
class [mscorlib]System.Delegate)
IL_0109: castclass DelegateSample.FooHandle
IL_010e: stloc.
IL_010f: ldloc.
//new Program()
IL_0110: newobj instance void DelegateSample.Program::.ctor()
IL_0115: ldftn instance void DelegateSample.Program::Minus(int32)
//new FooHandle()新增了一个FooHandle委托变量
IL_011b: newobj instance void DelegateSample.FooHandle::.ctor(object,
native int)
//fooHandle3 += new Program().Minus
IL_0120: call class [mscorlib]System.Delegate [mscorlib]System.Delegate::Combine(class [mscorlib]System.Delegate,
class [mscorlib]System.Delegate)
也就是三种不同方式都会被翻译为Combine方法,如果是直接+=函数这种情况,后台也会new一个委托变量,将方法赋值给该变量再加到fooHandle3,那么我们可以知道,最关键的核心代码就应该是Delegate.combine这个静态方法了,我们来看看源码是怎么回事:
Delegate类的:
[__DynamicallyInvokable]
public static Delegate Combine(Delegate a, Delegate b)
{
if ((object)a == null)
{
return b;
}
return a.CombineImpl(b);
} protected virtual Delegate CombineImpl(Delegate d)
{
throw new MulticastNotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Multicast_Combine"));
}
MulticastDelegate类的:
[SecurityCritical]
private object _invocationList;//委托链表 [SecurityCritical]
private IntPtr _invocationCount; [SecuritySafeCritical]
protected sealed override Delegate CombineImpl(Delegate follow)
{
if ((object)follow == null)
{
return this;
}
if (!Delegate.InternalEqualTypes(this, follow))
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Arg_DlgtTypeMis"));
}
MulticastDelegate multicastDelegate = (MulticastDelegate)follow;
int num = ;
object[] array = multicastDelegate._invocationList as object[];
if (array != null)
{
num = (int)multicastDelegate._invocationCount;
}
object[] array2 = _invocationList as object[];
int num2;
object[] array3;
if (array2 == null)
{
num2 = + num;
array3 = new object[num2];
array3[] = this;
if (array == null)
{
array3[] = multicastDelegate;
}
else
{
for (int i = ; i < num; i++)
{
array3[ + i] = array[i];
}
}
return NewMulticastDelegate(array3, num2);
}
int num3 = (int)_invocationCount;
num2 = num3 + num;
array3 = null;
if (num2 <= array2.Length)
{
array3 = array2;
if (array == null)
{
if (!TrySetSlot(array3, num3, multicastDelegate))
{
array3 = null;
}
}
else
{
for (int j = ; j < num; j++)
{
if (!TrySetSlot(array3, num3 + j, array[j]))
{
array3 = null;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (array3 == null)
{
int num4;
for (num4 = array2.Length; num4 < num2; num4 *= )
{
}
array3 = new object[num4];
for (int k = ; k < num3; k++)
{
array3[k] = array2[k];
}
if (array == null)
{
array3[num3] = multicastDelegate;
}
else
{
for (int l = ; l < num; l++)
{
array3[num3 + l] = array[l];
}
}
}
return NewMulticastDelegate(array3, num2, thisIsMultiCastAlready: true);
}
GetInvocationList方法的实现:
//Delgate类的
public virtual Delegate[] GetInvocationList()
{
return new Delegate[]
{
this
};
} //MulticastDelegate类的
public sealed override Delegate[] GetInvocationList()
{
object[] array = _invocationList as object[];
Delegate[] array2;
if (array == null)
{
array2 = new Delegate[]
{
this
};
}
else
{
int num = (int)_invocationCount;
array2 = new Delegate[num];
for (int i = ; i < num; i++)
{
array2[i] = (Delegate)array[i];
}
}
return array2;
}
其实我们看到这里,就可以知道其中的一个最主要就是_invocationList变量,也就是当调用Combine的时候,会判断左边委托变量是否为空,如果为空,会返回右边的委托变量,不为空就会调用CombineImpl方法,以上面那个例子来说fooHandle3的_invocationList存储着所有附加到委托变量,包含对象本身,也就是为啥遍历fooHandle3.GetInvocationList,输出了三个附加到fooHandle3变量的委托变量,这里例子fooHandle3初始化为null,还有意思的是fooHandle3的Targt和Menthod属性是最后附加的那个委托变量的Target和Menthod,而当委托由返回值,也同理返回最后一个函数的返回值,那么fooHandle3大概的结构如下图:
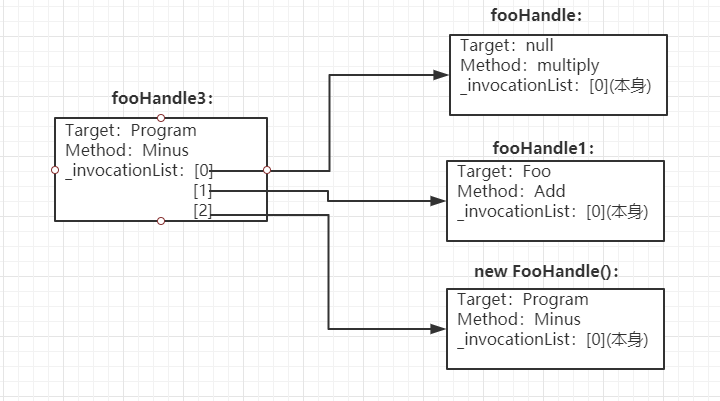
我们到现在只用到+=,其实-=就是调用其Delegate.Remove方法,跟Combine方法作用相反,具体就不多概述
看到这里我们终于可以回答一开头抛出的几个问题?
委托是不是相当于C/C++的函数指针?
很明显,不是的,从数据结构来说,c++函数指针表示一块指向函数的内存地址,它其实和直接写函数名没啥区别,因为我们调用函数时的函数名,也是函数入口地址,而委托却是个类,是一块托管内存,使用Invoke后它就会被clr释放了,它的函数成员能够存储所调函数的所有信息,这是函数指针没做到的,但是在某些特殊情况下,C++的函数指针就和委托一样,有兴趣的朋友可以去看下p/invoke方面知识
委托是什么?
委托本质是类,且支持多播委托的本质是维护一个私有的_invocationList委托链对象,+=和-=都是调用其静态方法Combine和Remove
委托是用来做啥的?
委托和c++函数指针一样,都可以作为函数中转器,在调用者和被调用者中起解耦作用,可作为函数的参数,当回调函数
委托跟匿名函数的区别?
我们先来声明和使用匿名函数:
public delegate int Foohandle(int a, int b);
Foohandle foohandle = delegate (int a, int b) { return a + b; };//匿名方法方式
Foohandle foohandle1= (a, b)=> a + b;//Lambda 表达式方式
foohandle.Invoke(,);//输出4
foohandle1.Invoke(,);//输出4
我们来看下msdn是怎么定义匿名函数的:

很明显,匿名函数只是个表达式,可以用来初始化委托的,而委托是个类,其实通过查看IL,后台都会实例化一个新的委托对象,并把该表达式作为函数赋给它
委托与事件的关系?
同样的我们来声明和使用事件:
public class Foo
{
public delegate void Foohandel(int a, int b); public event Foohandel foohandle; public Foo()
{
foohandle = new Foohandel(add);
foohandle(,);//在Foo里面可以直接调用事件
Console.WriteLine($"{foohandle.Target},{foohandle.Method}");
} public void excute(int a,int b)//公开给外部类调用事件的函数
{
foohandle?.Invoke(a,b);
} private void add(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a + b);
}
} class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Foo foo = new Foo();
//foo.foohandle = new Foo.Foohandel(multiply);编译不过,提示foo.foohandle只能出现再+=和-=左边
foo.foohandle +=new Foo.Foohandel(multiply);
foo.excute(, );
Console.Read();
} static void multiply(int a,int b)
{
Console.WriteLine(a * b);
}
}
输出结果:
EventSample.Foo,Void add(Int32, Int32)
我们发现,在Foo类里面,事件foohandle就是相当于委托,但是在外部,我们再program的main函数访问它时候,我们发现foohandle只能做+=或者-=,也不能访问其函数成员Target和Menthod,而我们只能通过调用excute函数去调用,这时候我们可以知道,Event其实是基于委托的,在内部类相当于委托,在外部就只能有委托的多播功能,其余都不能访问,其实我们想到,属性是不是这样。。。有兴趣的朋友可以去了解事件的原理,也是很有趣
最后的最后,我们还要谈下委托的一个功能:
委托的参数逆变和返回值的协变
由于委托也支持泛型委托,因此我们可以看看微软定义好的
public delegate void Action<in T>(T obj);//其中in表示逆变
public delegate TResult Func<out TResult>();//其中out表示协变 class Program
{
static Action<object> action;
static Func<string> func;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
action = (object a) => { Console.WriteLine(a.ToString()); };
Action<string> action1 = action;//参数逆变
action("Hello!"); func = () => { return "I am Func"; };
Func<object> func1 = func;//返回值协变
Console.WriteLine(func1());
Console.ReadLine();
} }
输出结果:
Hello!
I am Func
想要了解更深的朋友可以去了解泛型的协变和逆变,在这里就不深入探讨了
.Neter所应该彻底了解的委托的更多相关文章
- C#中的委托解析
谈及到C#的基本特性,“委托”是不得不去了解和深入分析的一个特性.对于大多数刚入门的程序员谈到“委托”时,都会想到“将方法作为方法的参数进行传递”,很多时候都只是知道简单的定义,主要是因为“委托”在理 ...
- 个人随想:对于一个.Neter来说,如果一直想走技术路线,该怎么走下去
前言 首先我不是一个合格的.Neter,也许在这里我的技术算是很菜的,不过我也是有想法的人,下面罗列出我的想法和将要实现的技术路线图. 1.学习一门底层语言 比如学习C语言,学习C语言的最终目的我觉得 ...
- C#的委托
之前本人一直在写一些相对比较基础的C#代码,现在做了一段时间项目了,遇到更麻烦的问题,比如今天要讨论的委托和事件,这个算是C#进阶篇的内容吧.现在自己就把这些天所学习的和自己所理解的和大家分享.有错请 ...
- 深刻理解:C#中的委托、事件
C#中的事件还真是有点绕啊,以前用JavaScript的我,理解起来还真是废了好大劲!刚开始还真有点想不明白为什么这么绕,想想和JS的区别,最后终于恍然大悟! C#中事件绕的根本原因: C#的方法,它 ...
- c# 三种常见的委托
参考 <编写高质量代码:改善C#程序的157个建议> , 尽量使用FCL中的委托声明. FCL: FrameWork Class Library 三种常用:Action.Func.Pre ...
- C# 中的委托和事件
觉得这篇文章写的非常好,大神之作,由简入繁,对我这种初学者来说帮忙很大,特此留存下. 摘自:http://tracefact.net/CSharp-Programming/Delegates-and- ...
- C#中的委托与事件并存的理由
更多资源:http://denghejun.github.io 问题 有了委托为什么还要有事件? 理论上,事件能完成的事情委托完全可以胜任,但是我们思考的这一方面是功能性,我们必须从他们各自的特点分析 ...
- Objective-C中的委托(代理)模式
我个人更喜欢把委托(Delegate)模式称为代理(Proxy)模式.还是那句话,第一次接触代理模式是在Java中接触的,在Java中实现代理模式和接口是少不了的.当时学习Spring的时候用到了接口 ...
- C# 中的委托和事件(转)
引言 委托 和 事件在 .Net Framework中的应用非常广泛,然而,较好地理解委托和事件对很多接触C#时间不长的人来说并不容易.它们就像是一道槛儿,过了这个槛的人,觉得真是太容易了,而没有过去 ...
随机推荐
- Flex 和 Bison 使用方法
背景知识 在学编译原理的时候,同时在做南京大学的编译原理课程实验,这里是链接,整个实验的效果是实现一个完整的 C-- 语法的编译器.C-- 语法是他们老师指定的一种类 C 语言. Flex 和 Bis ...
- Pyinstaller打包scrapy
环境 Windows7 Python3.65 scrapy1.74 PyInstaller3.5 创建打包脚本 在与scrapy.cfg同路径创建start.py # -*- coding: utf- ...
- [BZOJ4310] 跳蚤 SAM || SA
没有代码的. 传送门 先二分出第 \(mid\) 大的字串 \(s\),然后从后往前切割,每次大于 \(s\) 了就不行. 涉及到的操作:求第 \(mid\) 大子串:比较两个字串(求 \(lcp\) ...
- 常用的webpack优化方法
1. 前言 关于webpack,相信现在的前端开发人员一定不会陌生,因为它已经成为前端开发人员必不可少的一项技能,它的官方介绍如下: webpack 是一个模块打包器.webpack的主要目标是将 J ...
- mariadb数据类型
MariaDB 数据类型: MariaDB数据类型可以分为 数字,日期和时间以及字符串值. 使用数据类型的原则:够用就行,尽量使用范围小的,而不用大的 常用的数据类型: a. 整数:int, bit ...
- ThinkPHP v5.1.x POP 链分析
环境:MacOS 10.13 MAMAP Prophp 7.0.33 + xdebugVisual Studio Code前言我所理解的 POP Chain:利用魔术方法并巧妙构造特殊属性调用一系列函 ...
- php的精度计算问题(bcadd和bcsub)
一.前言 我们在进行php开发的时候经常会遇到浮点型的问题,特别是涉及金额的部分,常常需要进行加减运算.当小数点的位数比较多的时候,往往容易犯一些很低级的错误.这里记录一下php的精度计算和封装的小d ...
- NetCore基于EasyNetQ的高级API使用RabbitMq
一.消息队列 消息队列作为分布式系统中的重要组件,常用的有MSMQ,RabbitMq,Kafa,ActiveMQ,RocketMQ.至于各种消息队列的优缺点比较,在这里就不做扩展了,网上资源很多. 更 ...
- 移动端viewport模版
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta cont ...
- beta week 2/2 Scrum立会报告+燃尽图 01
此作业要求参见https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/nenu/2019fall/homework/9954 一.小组情况 队名:扛把子 组长:孙晓宇 组员:宋晓丽 梁梦瑶 韩昊 ...
