Spring_AOP基于AspectJ的注解开发&JDBC的模板使用&事务管理(学习笔记3)
一:AOP基于AspectJ的注解开发
1,简单的实例:
1)引入相应的jar包

2)在配置文件里引入相关约束
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
</beans>3)编写目标类和切面类并配置到IoC容器中,在配置文件中开启注解的AOP开发
<!-- 开启注解的AOP开发 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- 引入目标类 -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao"></bean>
<!-- 引入切面类 -->
<bean id="myAspectAnno" class="com.test.spring.demo1.MyAspectAnno"></bean>4)在编写切面类时即可加入相关的注解
@Aspect//表明该类为切面类
public class MyAspectAnno {
//前置通知
@Before(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.delete(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("前置通知代码========");
}
}2,注解通知的分类
- @Before(前置通知)
- @AfterReturning(后置通知)
- @Around(环绕通知)
- @AfterThrowing(异常通知)
- @After(最终通知)
@Aspect//表明该类为切面类
public class MyAspectAnno {
//前置通知
@Before("execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.save(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("前置通知代码========");
}
//后置通知
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.delete(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturning(Object result){
System.out.println("后置通知代码"+result);
}
//环绕通知
@Around(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.update(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前代码====");
Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕后代码===");
return obj;
}
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.find(..))",throwing="ex")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable ex){
System.out.println("异常通知代码===="+ex.getMessage());
}
//最终通知
@After(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.find(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知代码=======");
}
}- @Pointcut (注解切入点)
//异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value="MyAspectAnno.pointcut1()",throwing="ex")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable ex){
System.out.println("异常通知代码===="+ex.getMessage());
}
//最终通知
@After(value="MyAspectAnno.pointcut1()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知代码=======");
}
//切入点的注解
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.find(..))")
private void pointcut1(){};
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.test.spring.demo1.UserDao.update(..))")
private void pointcut2(){};二:Spring JDBC模板使用
1,简单实例
1)引入相关jar包
2)将Spring内置连接池和JDBC模板配置到配置文件中
<!-- 配置内置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<!-- 注入属性 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///Spring_day003_jdbc" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class=" org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>3)编写测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcDemo2 {
@Resource(name="jdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate JdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void demo01(){
JdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(null,?,?)","零",1000d);
}
}
2,配置第三方连接池
1)配置dbcp连接池
首先引入dbcp的相干jar包

在配置文件中配置dbcp连接池
<!--配置dbcp连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class=" org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<!-- 注入属性 -->
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///Spring_day003_jdbc" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class=" org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>2)配置c3p0连接池(常用)
引入相关jar包

在配置文件中配置c3p0连接池
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!-- 属性注入 -->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql:///Spring_day003_jdbc" />
<property name="user" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class=" org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>3)将连接池配置信息放入外部文件中,并引入到配置文件中
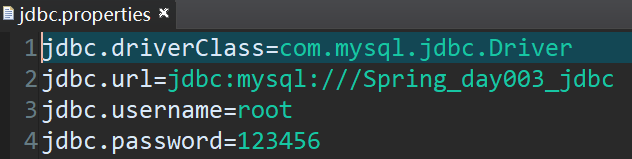
<!-- 引入外部属性文件 -->
<!-- 1,通过配置bean标签,较少使用 -->
<!-- <bean class=" org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
</bean> -->
<!-- 2,通过配置context标签,常用 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 配置c3p0连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!-- 属性注入 -->
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 配置JDBC模板 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class=" org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!-- 注入连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>3,使用JDBC模板进行简单CRUD操作
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class JdbcDemo2 {
@Resource(name="jdbcTemplate")
private JdbcTemplate JdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void demo01(){
JdbcTemplate.update("insert into account values(null,?,?)","44",1000d);
}
@Test
//删除
public void delete(){
JdbcTemplate.update("delete from account where id=?",1);
}
@Test
//更改
public void update(){
JdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=? where id=?","23333",2);
}
@Test
//查询单个字段值
public void query01(){
String obj = JdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select name from account where id=?", String.class,3);
System.out.println(obj);
}
@Test
//查询并封装到一个对象中
public void query02(){
Account account = JdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select * from account where id=?", new myRowMapper(),2);
System.out.println(account);
}
@Test
//查询并封装到list集合里
public void query03(){
List<Account> accountList = JdbcTemplate.query("select * from account",new myRowMapper());
for (Account account : accountList) {
System.out.println(account);
}
}
}
//将查询到的数据封装到实体对象中
class myRowMapper implements RowMapper<Account>{
@Override
public Account mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Account account =new Account();
account.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
account.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
account.setMoney(resultSet.getDouble("money"));
return account;
}
}三:Spring的事务管理
1,事务简介
事务:逻辑上的一组操作,组成这组操作的各个单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败
事务的特性:
- 原子性(事务不可分割)
- 一致性(事务前后数据保持一致)
- 隔离性(各个事务之间不受干扰)
- 持久性(事务过后,数据应持久保留在数据库中)
事务失去隔离性后引发的问题:
- 脏读:一个事务读取到其他事务未提交的数据
- 不可重复度:一个事务读取到其他事务已提交的update数据
- 幻读:一个事务读取到其他事务已提交的insert数据
- 会引起写入操作的丢失
事务的隔离级别(isolate):
- read uncommitted(未提交读,什么都不能解决)
- read committed(提交读,只解决脏读,oracle默认)
- repeatable read(重复读,只能解决脏读和不可重复读,幻读可能发生,mysql默认)
- serializable(串行化,不允许事务的并行,什么都可以解决,但效率低)
2,Spring事务管理的API
1)PlatformTransactionManager(平台事务管理)
这是一个接口,其中有两个实现类:
- DataSourceTransactionManger:底层通过JDBC管理事务
- HibernateTransactionManger:底层通过Hibernate来管理事务
2)TransactionDefinition(事务定义)
定义事务的隔离级别,超时信息,传播行为,是否只读
3)TransactionStatus(事务状态)
事务是否提交等状态信息
4)事务API之间的联系:
事务管理平台通过事务定义的信息来管理,过程中事务的状态存在TransactionStatus中
3,Spring事务的传播行为(解决Service层方法互相调用的问题,例A方法被B方法调用,但A方法中可能存在事务)
1)保证多个操作在同一个事务中
PROPAGATION REQUIRED(默认) ,如果A中有事务,使用A中的事务,如果A中没有事务,创建一个新的事务将操作包含进来
2)保证多个操作不在同一个事务中
PROPAGATION REQUIRES NEW ,如果A中有事务,则将A事务挂起(暂停),创建一个新事务,只包含自身操作,如果A中没有事务,则创建一个新事务,包含自身操作
3) 嵌套式事务
PROPAGATION NESTED 如果A中有事务,按照A的事务执行,执行完后,设置一个保存点后,执行B的操作,如果没有异常,执行通过,如果有异常,可以回滚到执行A操作前,也可以回滚到执行A操作后(保存点)
4,第一类:编程式事务管理
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理模板,能够简化事务管理 -->
<bean id="transactionTemplate"
class="org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate">
<property name="transactionManager" ref="transactionManager" />
</bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.test.spring.tx.AccountServiceImp">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao" />
<!-- 在业务层注入事务模板 -->
<property name="transactionTemplate" ref="transactionTemplate" />
</bean>public class AccountServiceImp implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate;
public void setTransactionTemplate(TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate) {
this.transactionTemplate = transactionTemplate;
}
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfor(final String from,final String to,final Double money) {
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
@Override
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus arg0) {
accountDao.from(from, money);
//int i=1/0;
accountDao.to(to, money);
}
});
}
}
5,声明式事务管理(底层采用AOP)
注意:引入相关的AOP开发的jar包
1)xml方式(在配置文件中配置)
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务的增强 -->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 事务的管理规则 -->
<tx:method name="update*"/>
<tx:method name="save*"/>
<tx:method name="delete*"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="transfor"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- AOP的配置 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切入点 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.test.spring.tx2.AccountServiceImp.*(..))" id="pointcut1"/>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut1"/>
</aop:config>2)注解方式
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 开启事务注解 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>配置好后在业务层应用注解:
@Transactional(isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT,propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public class AccountServiceImp implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void transfor(String from,String to,Double money) {
accountDao.from(from, money);
int i=1/0;
accountDao.to(to, money);
}
}
Spring_AOP基于AspectJ的注解开发&JDBC的模板使用&事务管理(学习笔记3)的更多相关文章
- 十四 Spring的AOP的基于AspectJ的注解开发
Spring的AOP的基于AspectJ的注解开发 创建项目,引入jar包 编写目标类.切面类 配置目标类.切面类 在注解文件里开启AOP的开发 <?xml version="1.0& ...
- 基于AspectJ的注解方式进行AOP开发
-------------------siwuxie095 基于 AspectJ 的注解方式进行 AOP 开发 ...
- Spring_day03--课程安排_基于aspectj的注解aop_Spring的jdbcTemplate操作
Spring_day03 上节内容回顾 今天内容介绍 基于aspectj的注解aop Spring的jdbcTemplate操作 增加 修改 删除 查询 Spring配置c3p0连接池和dao使用jd ...
- Spring框架学习09——基于AspectJ的AOP开发
1.基于注解开发AspectJ (1)AspectJ注解 基于注解开发AspectJ要比基于XML配置开发AspectJ便捷许多,所以在实际开发中推荐使用注解方式.关于注解的相关内容如下: @Aspe ...
- Spring 基于 AspectJ 的 AOP 开发
Spring 基于 AspectJ 的 AOP 开发 在 Spring 的 aop 代理方式中, AspectJ 才是主流. 1. AspectJ 简介 AspectJ 是一个基于 java 语言的 ...
- day39-Spring 08-Spring的AOP:基于AspectJ的注解
基于AspectJ的注解的开发要重点掌握. 这些表达式肯定要应用在我们的某些个增强上. 学习AspectJ也是两种形式:一种是XML,一种是注解.AspectJ的增强,就是那些通知的类型.Aspect ...
- Java开发学习(十一)----基于注解开发bean作用范围与生命周期管理
一.注解开发bean作用范围与生命周期管理 前面使用注解已经完成了bean的管理,接下来将通过配置实现的内容都换成对应的注解实现,包含两部分内容:bean作用范围和bean生命周期. 1.1 环境准备 ...
- 分享六个基于Bootstrap的实用开发教程和模板演示
关于Bootstrap,相信大家一定不陌生,它已经成为现在主流产业的一个重要工具,Bootstrap提供了优雅的HTML和CSS规范,它基于jQuery框架开发的,它在jQuery框架的基础上进行了更 ...
- Java数据库连接--JDBC调用存储过程,事务管理和高级应用
相关链接:Jdbc调用存储过程 一.JDBC常用的API深入详解及存储过程的调用 1.存储过程的介绍 我们常用的操作数据库语言SQL语句在执行的时候要先进行编译,然后执行,而存储过程是在大型数据库系统 ...
随机推荐
- Delphi检测用户是否具有administrator权限(OpenThreadToken,OpenProcessToken,GetTokenInformation,AllocateAndInitializeSid和EqualSid)
检测用户是否具有administrator权限const SECURITY_NT_AUTHORITY: TSIDIdentifierAuthority = (Value: (0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ...
- CentOS7 firewall与iptables防火墙的使用与开放端口
如何关闭firewall并开启iptables防火墙 如何使用firewall防火墙 如何关闭firewall并开启iptables防火墙 1.停止firewall systemctl stop fi ...
- 在mac上尝试docker-swarm
声明:本博客欢迎转发,但请保留原作者信息!新浪微博:@Lingxian_kong;博客地址:孔令贤的博客;内容系本人学习.研究和总结,如有雷同,实属荣幸! 安装docker-machine 我的安装环 ...
- qt获取网络ip地址的类
最近在学习qt网络编程,基于tcp和udp协议. 看了一些别人的程序和qt4自带的例子,困扰我最大的问题就是获取ip的类,总结起来还挺多的. 主要介绍常用的QtNetwork Module中的QHos ...
- sql小计汇总 rollup用法实例分析
这里介绍sql server2005里面的一个使用实例: ),city ),score int) GO 1. 只有一个汇总 select province as 省,sum(score) as 分数 ...
- request的跳转
使用request.getRequestDispather(url).forword(request,response)方法跳转页面 地址栏的路径不会发生改变,在后续的ajax调用 使用window. ...
- linux上java和golang环境变量的设置
JAVA环境变量 (1).打开~/.bashrc完成环境配置( 作用类似于/etc/bashrc, 只是针对用户自己而言,不对其他用户生效.) 文件追加 expo ...
- hgoi#20190517
T1-Mike and gcd problem Mike给定一个n个元素的整数序列,A=[a1,a2,...,an],每次操作可以选择一个i(1≤i<n),将a[i],a[i+1]变成a[i]- ...
- 03 Javascript的数据类型
数据类型包括:基本数据类型和引用数据类型 基本数据类型指的是简单的数据段,引用数据类型指的是有多个值构成的对象. 当我们把变量赋值给一个变量时,解析器首先要确认的就是这个值是基本类型值还是引用类型值 ...
- 【LEETCODE】32、LeetCode的第35题,查找插入的位置
凉凉,看来想做好一个题还不容易啊... 有点难受... 1.看看题目吧 Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the ...
