Baozi Leetcode solution 1036: Escape a Large Maze
Problem Statement
In a 1 million by 1 million grid, the coordinates of each grid square are (x, y) with 0 <= x, y < 10^6.
We start at the source square and want to reach the target square. Each move, we can walk to a 4-directionally adjacent square in the grid that isn't in the given list of blocked squares.
Return true if and only if it is possible to reach the target square through a sequence of moves.
Example 1:
Input: blocked = [[0,1],[1,0]], source = [0,0], target = [0,2]
Output: false
Explanation:
The target square is inaccessible starting from the source square, because we can't walk outside the grid.
Example 2:
Input: blocked = [], source = [0,0], target = [999999,999999]
Output: true
Explanation:
Because there are no blocked cells, it's possible to reach the target square.
Note:
0 <= blocked.length <= 200blocked[i].length == 20 <= blocked[i][j] < 10^6source.length == target.length == 20 <= source[i][j], target[i][j] < 10^6source != target
Hints
- If we become stuck, there's either a loop around the source or around the target.
- If there is a loop around say, the source, what is the maximum number of squares it can have?
Problem link
Video Tutorial
You can find the detailed Youtube video tutorial here
国内:B站的视频戳这里
Thought Process
At first, I am puzzled why this problem would be a hard one. It seems simply applying a BFS would get the answer. So here we go.
Brute force, simple BFS
Of course it will hit memory limit because I am allocating a 2-dimensional visited array. Assume boolean is 8 bit -> 1B, 1 Million * 1 Million = 1TB, OMG, immediately using a set instead.
P.S. fun fact, you can use this method to test how much memory leetcode allocate to this problem, you can use binary search and memory is around 300MB
However, this would start hitting Time Limit Exception. Now I begin to notice a few constrains, e.g., the block size is only 200 while the grid is 1M*1M. Simply going from source to target worst case would cause a timeout.
Next thought would be does it help if we sort the block array? While we are doing the BFS, if the block is already larger/smaller than the max/min of the block, we can early stop. However, this won't help if we simply place a block near the target. Also, this would be a nightmare to implement.
Check block loops on source and target
Following the two hints, it would be natural to come up with this idea. Given such huge contrast between the block size (0,200) and the grid size (1M, 1M), all we need to do is to check if there is any loops built by block on source and target b/c if there is a loop, we cannot explore outside of the loop. However, notice if target and source are in the same loop, then we are fine.
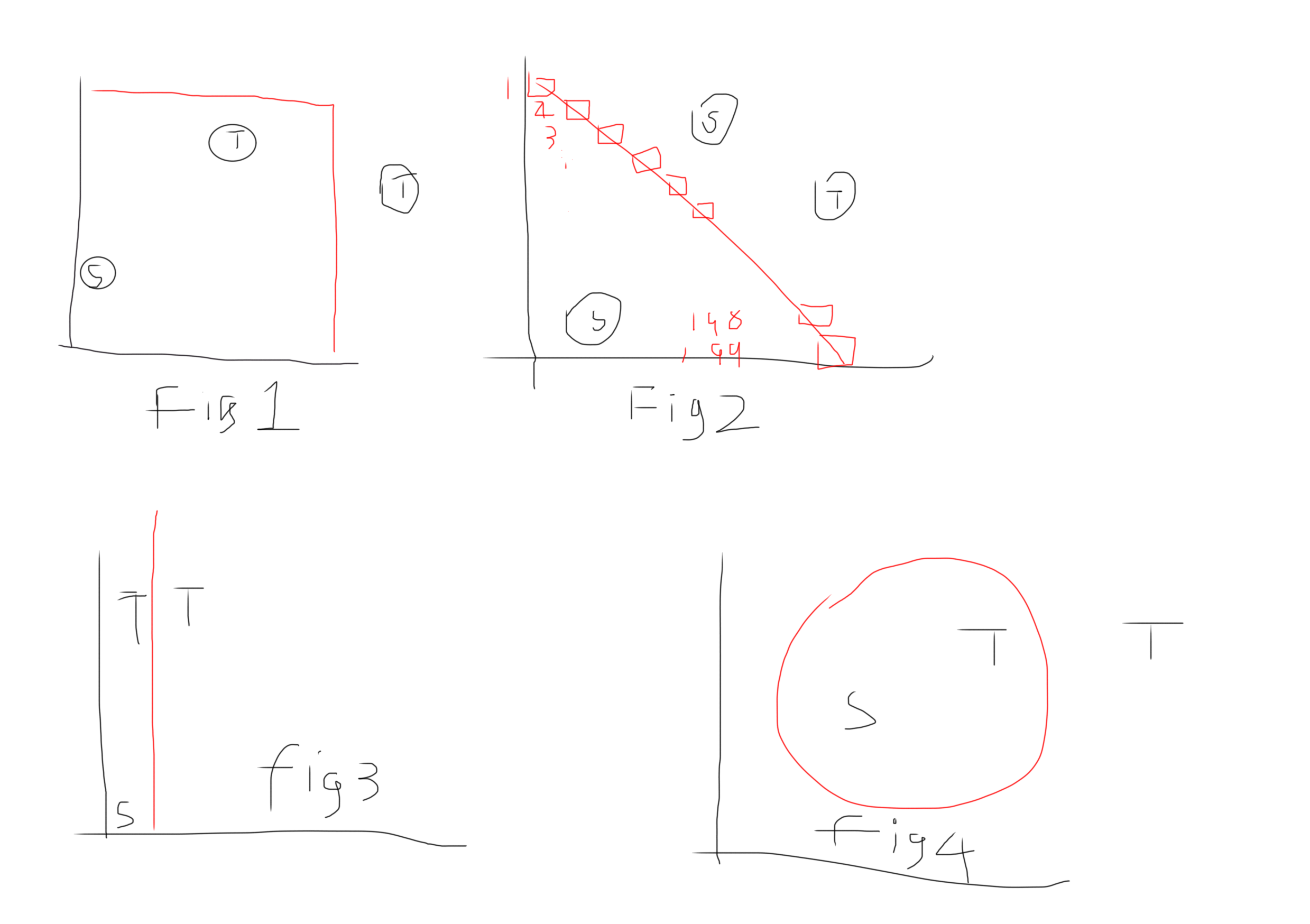
There are two ways to early stop this loop checking. One way is to count the BFS steps, the other way is to follow the hints, given 200 blocks, what's the max area it can cover. Given the length 200, Fig 2 in the below graph can result in the largest area. Therefore, we can early terminate the BFS search once we covered more than 19900 blocks. (We can relax this a bit to 20000, doesn't matter)
- Fig 1 area = 100 * 100 = 10000
- Fig 2 area = 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + 199 = (1+199)*199/2 = 19900
- Fig 3 area = 1 * 200 = 200
- Fig 4 area = 790 (2*Pi*R = 100, thus R = 15.92, Pi * R^2 = 790 )
Solutions
Brute force, simple BFS
private final int[] xDirection = {1, 0, -1, 0};
private final int[] yDirection = {0, -1, 0, 1};
private final int ONE_MILLION = 1000000;
public boolean isEscapePossible(int[][] blocked, int[] source, int[] target) {
if (blocked == null || source == null || target == null) {
return false;
}
Set<String> blockLookup = this.indexBlockedMatrixToSet(blocked);
int m = ONE_MILLION;
int n = ONE_MILLION;
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String sourceString = source[0] + "," + source[1];
queue.offer(sourceString);
visited.add(sourceString);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String[] curBlock = queue.poll().split(",");
int curX = Integer.parseInt(curBlock[0]);
int curY = Integer.parseInt(curBlock[1]);
if (curX == target[0] && curY == target[1]) {
return true;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextX = curX + xDirection[i];
int nextY = curY + yDirection[i];
if (this.shouldExplore(nextX, nextY, ONE_MILLION, ONE_MILLION, blockLookup, visited)) {
String nextKey = nextX + "," + nextY;
visited.add(nextKey);
queue.offer(nextKey);
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean shouldExplore(
int x,
int y,
int row,
int col,
Set<String> blockLookup,
Set<String> visited) {
if (!(x >= 0 && x < row && y >=0 && y < col)) {
return false;
}
String index = x + "," + y;
if (visited.contains(index)) {
return false;
}
if (blockLookup.contains(index)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private Set<String> indexBlockedMatrixToSet(int[][] blocked) {
Set<String> lookup = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < blocked.length; i++) {
int x = blocked[i][0];
int y = blocked[i][1];
String index = x + "," + y;
lookup.add(index);
}
return lookup;
}
Time Complexity: O(N), N = 1M * 1M, essentially need to cover the entire huge grid
Space Complexity: O(N), N = 1M*1M, essentially all the nodes need to be put to visited set
Check block loops on source and target
private final int[] xDirection = {1, 0, -1, 0};
private final int[] yDirection = {0, -1, 0, 1};
private final int ONE_MILLION = 1000000;
private final int MAX_COUNT_THRESHOLD = 20000;
public boolean isEscapePossible(int[][] blocked, int[] source, int[] target) {
if (blocked == null || source == null || target == null) {
return false;
}
Set<String> blockLookup = this.indexBlockedMatrixToSet(blocked);
boolean isSourceLoop = this.isLoopAroundPoint(source, target, blockLookup);
if (isSourceLoop) {
return false;
}
boolean isTargetLoop = this.isLoopAroundPoint(target, source, blockLookup);
if (isTargetLoop) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private boolean isLoopAroundPoint(int[] source, int[] target, Set<String> blockLookup) {
int count = 0;
Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>();
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
String index = source[0] + "," + source[1];
queue.offer(index);
visited.add(index);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String[] curBlock = queue.poll().split(",");
int curX = Integer.parseInt(curBlock[0]);
int curY = Integer.parseInt(curBlock[1]);
// here think about
if (count >= MAX_COUNT_THRESHOLD) {
return false;
}
if (curX == target[0] && curY == target[1]) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextX = curX + xDirection[i];
int nextY = curY + yDirection[i];
if (this.shouldExplore(nextX, nextY, ONE_MILLION, ONE_MILLION, blockLookup, visited)) {
String nextKey = nextX + "," + nextY;
count++;
visited.add(nextKey);
queue.offer(nextKey);
}
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean shouldExplore(
int x,
int y,
int row,
int col,
Set<String> blockLookup,
Set<String> visited) {
if (!(x >= 0 && x < row && y >=0 && y < col)) {
return false;
}
String index = x + "," + y;
if (visited.contains(index)) {
return false;
}
if (blockLookup.contains(index)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
private Set<String> indexBlockedMatrixToSet(int[][] blocked) {
Set<String> lookup = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < blocked.length; i++) {
int x = blocked[i][0];
int y = blocked[i][1];
String index = x + "," + y;
lookup.add(index);
}
return lookup;
}
Time Complexity: O(N), N in terms of block size
Space Complexity: O(N), N in terms of block size
References
Baozi Leetcode solution 1036: Escape a Large Maze的更多相关文章
- [Swift]LeetCode1036.逃离大迷宫 | Escape a Large Maze
In a 1 million by 1 million grid, the coordinates of each grid square are (x, y) with 0 <= x, y & ...
- Baozi Leetcode Solution 205: Isomorphic Strings
Problem Statement Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic. Two strings are isomo ...
- Baozi Leetcode Solution 290: Word Pattern
Problem Statement Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern. Here follo ...
- leetcode solution cracked tutorial
leetcode solution cracked tutorial problemset https://leetcode.com/problemset/all/ Top Interview Que ...
- 【LeetCode】789. Escape The Ghosts 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode.c ...
- 【LeetCode】830. Positions of Large Groups 解题报告(Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 日期 题目地址:https://leetcode.c ...
- 73th LeetCode Weekly Contest Escape The Ghosts
You are playing a simplified Pacman game. You start at the point (0, 0), and your destination is(tar ...
- Leetcode solution 291: Word Pattern II
Problem Statement Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern. Here follo ...
- Leetcode solution 227: Basic Calculator II
Problem Statement Implement a basic calculator to evaluate a simple expression string. The expressio ...
随机推荐
- 关于git远程分支操作
对于用户来说,git给人提交到本地的机会.我们可以在自己的机器上创建不同的branch,来测试和存放不同的代码. 对于代码管理员而言,git有许多优良的特性.管理着不同的分支,同一套源代码可以出不一样 ...
- SSL Converter & Formats
https://www.sslshopper.com/ssl-converter.html PEM Format The PEM format is the most common format th ...
- request的跳转
使用request.getRequestDispather(url).forword(request,response)方法跳转页面 地址栏的路径不会发生改变,在后续的ajax调用 使用window. ...
- vue的checkbox或多选的select的代码例子
另外一种实现checkbox的vue绑定方法代码: 给v-model绑定一个相同的数组类型的属性: <div id="app"> <label>jack&l ...
- Mybatis_two
SqlMapConfig.xml配置文件 SqlMapConfig.xml中配置的内容和顺序如下: properties(属性) settings(全局配置参数) typeAliases(类型别名) ...
- 关于exe4j打包问题
一.eclipse导出jar Export-->Runnable JAR file 这里有两种情况: 选择 Package required libraries into generated j ...
- 【Flink】深入理解Flink-On-Yarn模式
1. 前言 Flink提供了两种在yarn上运行的模式,分别为Session-Cluster和Per-Job-Cluster模式,本文分析两种模式及启动流程. 下图展示了Flink-On-Yarn模式 ...
- Programming In Lua 第三章
1, 2, 3, 4, 5,lua中,只有false和nil为假,0和空字符串为真. 6, 7,
- python基本数据类型之数字类型和其相关运算
数字(number) Python3 支持 int.float.bool.complex(复数). 在Python 3里,只有一种整数类型 int,表示为长整型,没有 python2 中的 Long. ...
- 用python的matplotlib和numpy库绘制股票K线均线和成交量的整合效果(含量化验证交易策略代码)
在用python的matplotlib和numpy库绘制股票K线均线的整合效果(含从网络接口爬取数据和验证交易策略代码)一文里,我讲述了通过爬虫接口得到股票数据并绘制出K线均线图形的方式,在本文里,将 ...
