Linux下RIAD的实现及mdadm命令的基本用法
一、RAID简述
磁盘阵列(Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks,RAID),是把多个物理磁盘组成一个阵列,当作一个逻辑磁盘使用,它将数据以分段或条带的方式储存在不同的磁盘中,这样可以通过在多个磁盘上同时存储和读取数据来大幅提高存储系统的数据吞吐量
二、RAID分类
1、外接式磁盘阵列:常被使用在大型服务器上,专业的硬件磁盘阵列盘柜,价格昂贵,主要厂商:IBM、HP、EMC等
2、内接式磁盘阵列:需要技术人员来使用操作,同时需要配备硬件RAID卡或者阵列卡
3、软件仿真式磁盘阵列:通过操作系统自身提供的磁盘管理功能(软件功能实现)将多个硬盘配置成逻辑盘,价格相对较便宜
三、RAID级别
1、RAID 0
最早出现的RAID模式,属于条带模式,至少需要两块磁盘,成本低,可以提高整个磁盘的性能和吞吐量;但是没有容错机制,磁盘损坏易丢失数据
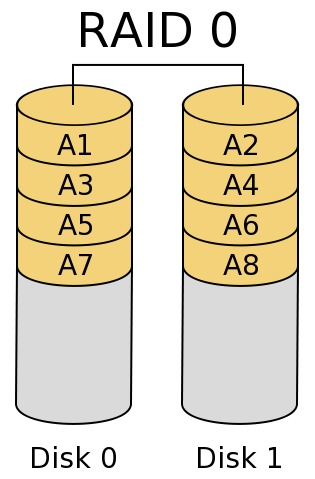
2、RAID 1
磁盘镜像模式,数据在写入一块磁盘的同时,会在另一块闲置的磁盘上生成镜像文件,通过二次读写实现磁盘镜像,磁盘控制器的负载也相当大,所以多磁盘控制器使用可以缓解读写负载

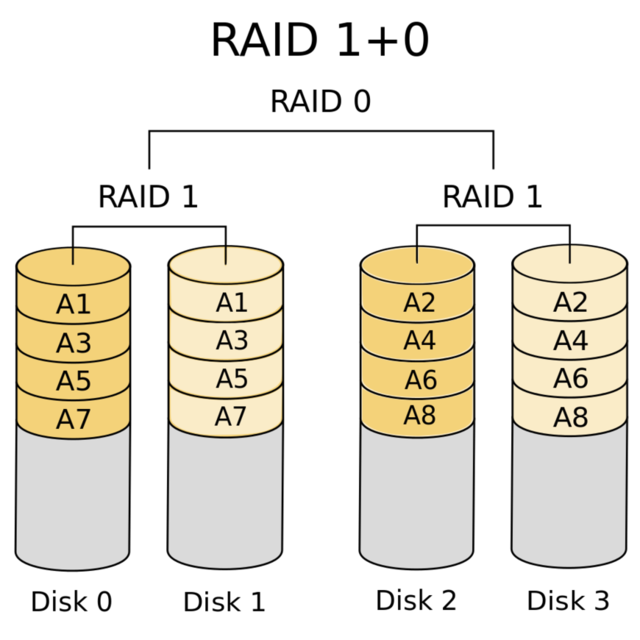
3、RAID 1 + 0
高可靠性与高效磁盘结构,下层是两个RAID 1,两个RAID 1之上是RAID 0,至少四块硬盘
4、RAID 0 + 1
高效率与高性能磁盘结构, 下层是两个RAID 0,两个RAID 1之上是RAID 1,至少四块硬盘

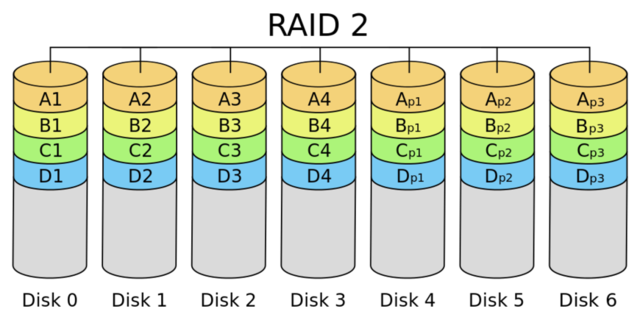
5、RAID 2
带海明码校验,这种编码技术需要多个磁盘存放检查及恢复信息,使得RAID 2技术实施更复杂,商业中用的比较少
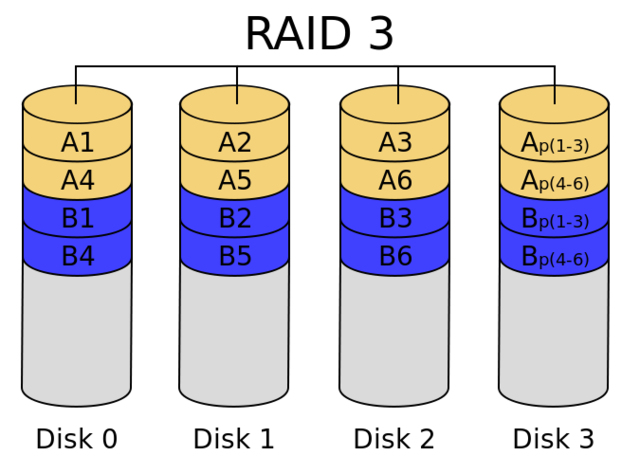
6、RAID 3
带奇偶校验码的并行传送,只能查错不能纠错
7、RAID 4
它对数据的访问是按数据块进行的,也就是按磁盘进行的,每次是一个盘。在图上可以这么看,RAID3是一次一横条,而RAID4一次一竖条
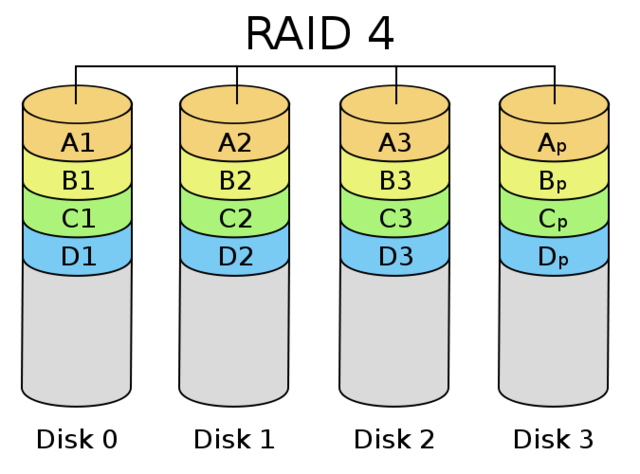
8、RAID 5
分布式奇偶校验的独立磁盘结构,可靠性强,只损坏一块硬盘时,系统会根据存储的奇偶校验位重建数据,如果同时损坏两块硬盘时数据将完全损坏
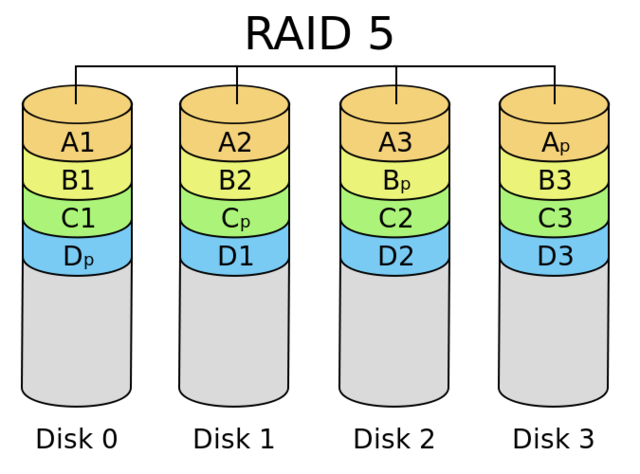
9、RAID 6
带有两种分布存储的奇偶校验码的独立磁盘结构,多一种校验主要是用于要求数据绝对不能出错的场合
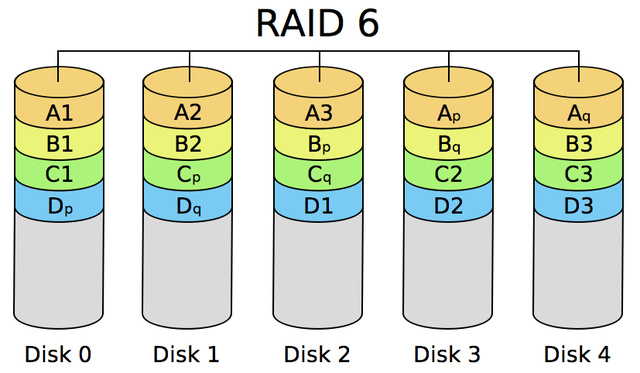
10、RAID 7
所有的I/O传送均是同步进行的,可以分别控制,这样提高了系统的并行性,提高系统访问数据的速度,带有高速缓冲存储器,由于采用并行结构和高速缓冲存储器,因此数据访问效率大大提高
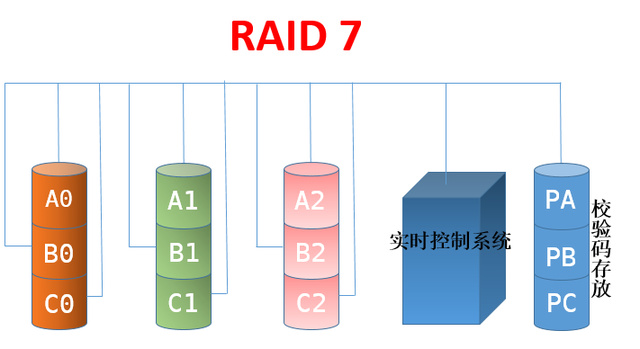
四、常见RAID级别总结
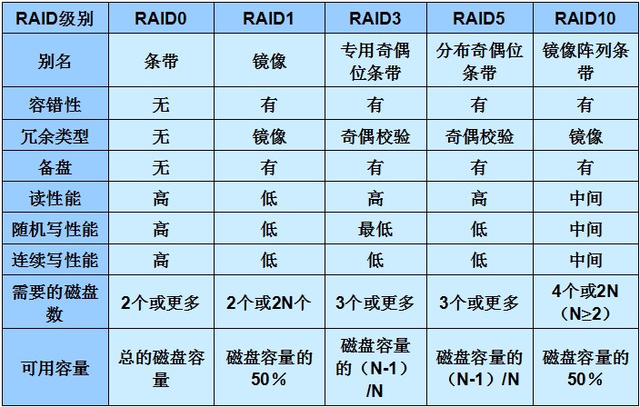
以上内容来源于网络
了解了raid的级别和各个级别下的优缺点后,我们在Linux下怎么实现raid呢
接下来我们介绍一款软件mdadm (multiple devices admin的简称),它是Linux下的一款标准的软件 RAID 管理工具,作者是Neil Brown,它能够诊断、监控和收集详细的阵列信息 ,在linux系统中目前以MD(Multiple Devices)虚拟块设备的方式实现软件RAID,利用多个底层的块设备虚拟出一个新的虚拟设备,并且利用条带化(stripping)技术将数据块均匀分布到多个磁盘上来提高虚拟设备的读写性能,利用不同的数据冗祭算法来保护用户数据不会因为某个块设备的故障而完全丢失,而且还能在设备被替换后将丢失的数据恢复到新的设备上.
目前MD支持linear,multipath,raid0(stripping),raid1(mirror),raid4,raid5,raid6,raid10等不同的冗余级别和级成方式,当然也能支持多个RAID陈列的层叠组成raid1 0,raid5 1等类型的陈列。
五、在Linux上创建一个raid5的一个磁盘阵列,并有一块盘作为热备份盘(也就是说当我阵列里有一块盘坏了,这块盘马上就替上去,把坏了的盘替换下来)。
首先我们要创建一个raid5的磁盘阵列,我们至少需要3块盘,这里我们创建4块盘,有一块作为热备盘。接下来我们使用fdisk 来对/dev/sdb 进行分区(这里的分区来模拟磁盘)
[root@test ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb WARNING: DOS-compatible mode is deprecated. It's strongly recommended to
switch off the mode (command 'c') and change display units to
sectors (command 'u'). Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only) Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xaebe4f2c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 1306 10490413+ 5 Extended Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (1-1306, default 1):
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-1306, default 1306): +2G Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (263-1306, default 263):
Using default value 263
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (263-1306, default 1306): +2G Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (525-1306, default 525):
Using default value 525
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (525-1306, default 1306): +2G Command (m for help): n
Command action
l logical (5 or over)
p primary partition (1-4)
l
First cylinder (787-1306, default 787):
Using default value 787
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (787-1306, default 1306): +2G Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xaebe4f2c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 1306 10490413+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1 262 2104452 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 263 524 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb7 525 786 2104483+ 83 Linux
/dev/sdb8 787 1048 2104483+ 83 Linux
提示:我们在/dev/sdb上面分了4块2G大小的分区,接下来我们要对其分区的类型更改为Linux raid auto
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-8): 5
Hex code (type L to list codes): L 0 Empty 24 NEC DOS 81 Minix / old Lin bf Solaris
1 FAT12 39 Plan 9 82 Linux swap / So c1 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
2 XENIX root 3c PartitionMagic 83 Linux c4 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
3 XENIX usr 40 Venix 80286 84 OS/2 hidden C: c6 DRDOS/sec (FAT-
4 FAT16 <32M 41 PPC PReP Boot 85 Linux extended c7 Syrinx
5 Extended 42 SFS 86 NTFS volume set da Non-FS data
6 FAT16 4d QNX4.x 87 NTFS volume set db CP/M / CTOS / .
7 HPFS/NTFS 4e QNX4.x 2nd part 88 Linux plaintext de Dell Utility
8 AIX 4f QNX4.x 3rd part 8e Linux LVM df BootIt
9 AIX bootable 50 OnTrack DM 93 Amoeba e1 DOS access
a OS/2 Boot Manag 51 OnTrack DM6 Aux 94 Amoeba BBT e3 DOS R/O
b W95 FAT32 52 CP/M 9f BSD/OS e4 SpeedStor
c W95 FAT32 (LBA) 53 OnTrack DM6 Aux a0 IBM Thinkpad hi eb BeOS fs
e W95 FAT16 (LBA) 54 OnTrackDM6 a5 FreeBSD ee GPT
f W95 Ext'd (LBA) 55 EZ-Drive a6 OpenBSD ef EFI (FAT-12/16/
10 OPUS 56 Golden Bow a7 NeXTSTEP f0 Linux/PA-RISC b
11 Hidden FAT12 5c Priam Edisk a8 Darwin UFS f1 SpeedStor
12 Compaq diagnost 61 SpeedStor a9 NetBSD f4 SpeedStor
14 Hidden FAT16 <3 63 GNU HURD or Sys ab Darwin boot f2 DOS secondary
16 Hidden FAT16 64 Novell Netware af HFS / HFS+ fb VMware VMFS
17 Hidden HPFS/NTF 65 Novell Netware b7 BSDI fs fc VMware VMKCORE
18 AST SmartSleep 70 DiskSecure Mult b8 BSDI swap fd Linux raid auto
1b Hidden W95 FAT3 75 PC/IX bb Boot Wizard hid fe LANstep
1c Hidden W95 FAT3 80 Old Minix be Solaris boot ff BBT
1e Hidden W95 FAT1
Hex code (type L to list codes): fd
Changed system type of partition 5 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-8): 6
Hex code (type L to list codes): fd
Changed system type of partition 6 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-8): 7
Hex code (type L to list codes): fd
Changed system type of partition 7 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): t
Partition number (1-8): 8
Hex code (type L to list codes): fd
Changed system type of partition 8 to fd (Linux raid autodetect) Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xaebe4f2c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 1306 10490413+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1 262 2104452 fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb6 263 524 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb7 525 786 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb8 787 1048 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
查看分区情况,并通知内核
[root@test ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00058c8c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 52 409600 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 52 4457 35388416 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 4457 5222 6144000 82 Linux swap / Solaris Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xaebe4f2c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 1306 10490413+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1 262 2104452 fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb6 263 524 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb7 525 786 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb8 787 1048 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect Disk /dev/md0: 2152 MB, 2152857600 bytes
2 heads, 4 sectors/track, 525600 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 8 * 512 = 4096 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
[root@test ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb5 /dev/sdb
[root@test ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb6 /dev/sdb
[root@test ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb7 /dev/sdb
[root@test ~]# partx -a /dev/sdb8 /dev/sdb
创建好分区和分区类型后,我们就开始在Linux上创建raid5
[root@test ~]# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 3 -x 1 /dev/sdb{5,6,7,8}
mdadm: /dev/sdb5 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid1 devices=2 ctime=Thu Nov 1 18:08:48 2018
mdadm: /dev/sdb6 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid1 devices=2 ctime=Thu Nov 1 18:08:48 2018
mdadm: /dev/sdb7 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid1 devices=2 ctime=Thu Nov 1 18:08:48 2018
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md0 started.
查看创建好的raid信息
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb7[4] sdb8[3](S) sdb6[1] sdb5[0]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/2] [UU_]
[>....................] recovery = 3.9% (83552/2102272) finish=0.8min speed=41776K/sec unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:23 2018
State : clean, degraded, recovering
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 2 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Rebuild Status : 43% complete Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : f1c7f735:ac34fde5:8ee6bb5b:55189221
Events : 7 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
1 8 22 1 active sync /dev/sdb6
4 8 23 2 spare rebuilding /dev/sdb7 3 8 24 - spare /dev/sdb8
提示:可以看出3块盘用于阵列,还有一块盘空闲状态。
到此我们在Linux上创建raid5 就创建完成了,接下来我们要想使用其磁盘阵列,就得先格式化文件系统(就是指定其磁盘的文件系统类型),然后在挂着至根文件系统我们就可以正常使用了
格式化磁盘阵列,需要注意的是创建好的磁盘真列,在Linux里就是以/dev/md0 命名的,当然我们格式化指定也是/dev/md0,当然我们这里是使用的md0 也可以使用其他的,比如md1 md2都可以,这个要看你创建raid是使用的那个了,一般我们都是顺序来,方便记忆。
[root@test ~]# mke2fs -t ext3 /dev/md0
mke2fs 1.41.12 (17-May-2010)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=128 blocks, Stripe width=256 blocks
262944 inodes, 1051136 blocks
52556 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1077936128
33 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
7968 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736 Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done This filesystem will be automatically checked every 34 mounts or
180 days, whichever comes first. Use tune2fs -c or -i to override.
挂载和查看其挂着情况
[root@test ~]# mkdir test/raid5 -p
[root@test ~]# mount /dev/md0 test/raid5
[root@test ~]# ll test/raid5/
total 16
drwx------ 2 root root 16384 Nov 1 19:35 lost+found
[root@test ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 34G 1.6G 30G 6% /
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 380M 41M 320M 12% /boot
/dev/md0 4.0G 137M 3.7G 4% /root/test/raid5
提示:可以看出我们创建的raid5 就挂载至根文件系统了,当然这里要提示下,我们现在挂载的,系统重新启动后就会消失,要想其永久生效,我们可以把挂载信息写入/etc/fstab 里面。这样重新启动系统会默认去读/etc/fstab文件里的内容。这里说下/etc/fstab 这个配置文件的格式,第一个字段是要挂载的设备,第二个字段是挂载点,第三个字段是挂载的文件系统类型,第四个是挂载的选项,默认是defaults如果要开启acl或其他选项需要用逗号隔开,第五个字段是转储频率(每多少天做一次完全备份),第6个字段是文件系统检测次序(只有根可以为1),了解了其配置文件的格式后我们就可以把我们刚才的raid5 写入配置文件
/dev/md0 /root/test/raid5 ext3 defaults 0 0
提示:要挂载的设备也可以使用uuid
接下来我们来模拟其raid5 坏了一块盘的情况,看看我们准备的热备盘是否能够顶替其坏了的磁盘。
[root@test ~]# mdadm /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb6
mdadm: set /dev/sdb6 faulty in /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 19:55:51 2018
State : clean, degraded, recovering
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 3
Failed Devices : 1
Spare Devices : 1 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Rebuild Status : 5% complete Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : f1c7f735:ac34fde5:8ee6bb5b:55189221
Events : 20 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
3 8 24 1 spare rebuilding /dev/sdb8
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7 1 8 22 - faulty /dev/sdb6
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb7[4] sdb8[3] sdb6[1](F) sdb5[0]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/2] [U_U]
[====>................] recovery = 21.4% (450048/2102272) finish=0.4min speed=56256K/sec unused devices: <none>
提示:可以看出我们给的热备盘在其阵列中有坏的磁盘后,会自动顶替其坏的磁盘。顶替上去后,磁盘自动会恢复其阵列里的数据,以保证其阵列能够正常使用。
移除坏的盘
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 19:56:20 2018
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 3
Failed Devices : 1
Spare Devices : 0 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : f1c7f735:ac34fde5:8ee6bb5b:55189221
Events : 37 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
3 8 24 1 active sync /dev/sdb8
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7 1 8 22 - faulty /dev/sdb6
[root@test ~]# mdadm /dev/md0 --remove /dev/sdb6
mdadm: hot removed /dev/sdb6 from /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 3
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 19:59:54 2018
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 3
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 0 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : f1c7f735:ac34fde5:8ee6bb5b:55189221
Events : 38 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
3 8 24 1 active sync /dev/sdb8
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7
接下来我们在添加一块盘至raid里(这里不再演示怎么去重新分区,我们这里就用/dev/sdb6就可以)
[root@test ~]# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb6
mdadm: added /dev/sdb6
[root@test ~]# mdadm --detail /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 20:03:12 2018
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 1 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : f1c7f735:ac34fde5:8ee6bb5b:55189221
Events : 39 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
3 8 24 1 active sync /dev/sdb8
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7 5 8 22 - spare /dev/sdb6
停止raid
[root@test ~]# mdadm -S /dev/md0
mdadm: Cannot get exclusive access to /dev/md0:Perhaps a running process, mounted filesystem or active volume group?
[root@test ~]# umount /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda2 34G 1.6G 30G 6% /
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 380M 41M 320M 12% /boot
[root@test ~]# mdadm -S /dev/md0
mdadm: stopped /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
mdadm: cannot open /dev/md0: No such file or directory
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]#
提示:要想停止其阵列,首先要卸载其文件系统,然后在停止,通过上面的例子我们可以看出,当我们停止掉md0后,其/dev/md0文件也不存在。也就是说我们停止掉其磁盘阵列,也就把其磁盘阵列的组合关系给解散了,所以对其的文件也会相应消失。这样一来我们如果要想再使用其阵列怎么办呢?只有重新创建磁盘阵列或装配,在创建好后,我们要做一件事 ,就是把其raid信息保存至配置文件,这样我们以后就算停止掉其raid磁盘阵列,也可以快速进行装配。
[root@test ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 5221 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x00058c8c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 1 52 409600 83 Linux
Partition 1 does not end on cylinder boundary.
/dev/sda2 52 4457 35388416 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 4457 5222 6144000 82 Linux swap / Solaris Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 2610 cylinders
Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xaebe4f2c Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 1 1306 10490413+ 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1 262 2104452 fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb6 263 524 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb7 525 786 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
/dev/sdb8 787 1048 2104483+ fd Linux raid autodetect
[root@test ~]# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l 5 -n 3 -x 1 /dev/sdb{5,6,7,8}
mdadm: /dev/sdb5 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices=3 ctime=Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
mdadm: /dev/sdb6 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices=3 ctime=Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
mdadm: /dev/sdb7 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices=3 ctime=Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
mdadm: /dev/sdb8 appears to be part of a raid array:
level=raid5 devices=3 ctime=Thu Nov 1 19:27:13 2018
Continue creating array? y
mdadm: Defaulting to version 1.2 metadata
mdadm: array /dev/md0 started.
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 20:20:44 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 20:21:03 2018
State : clean, degraded, recovering
Active Devices : 2
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 2 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Rebuild Status : 68% complete Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : 6074e103:c5bae142:7c9fa17c:8cc5495d
Events : 11 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
1 8 22 1 active sync /dev/sdb6
4 8 23 2 spare rebuilding /dev/sdb7 3 8 24 - spare /dev/sdb8
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb7[4] sdb8[3](S) sdb6[1] sdb5[0]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/3] [UUU] unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D --scan > /etc/mdadm.conf
[root@test ~]# cat /etc/mdadm.conf
ARRAY /dev/md0 metadata=1.2 spares=1 name=test:0 UUID=6074e103:c5bae142:7c9fa17c:8cc5495d
提示:以上是重新创建md0,在我们使用mdadm这个工具时,它有个模式可以方便我们重新装载-A
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb7[4] sdb8[3](S) sdb6[1] sdb5[0]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/3] [UUU] unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -S /dev/md0
mdadm: stopped /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -A /dev/md0 /dev/sdb{5,6,7,8}
mdadm: /dev/md0 has been started with 3 drives and 1 spare.
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb5[0] sdb8[3](S) sdb7[4] sdb6[1]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/3] [UUU] unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]#
提示:当我们保存的有配置文件信息我们也可直接进行装配,不需要指定其磁盘信息。
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 20:20:44 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 20:21:13 2018
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 1 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : 6074e103:c5bae142:7c9fa17c:8cc5495d
Events : 18 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
1 8 22 1 active sync /dev/sdb6
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7 3 8 24 - spare /dev/sdb8
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb5[0] sdb8[3](S) sdb7[4] sdb6[1]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/3] [UUU] unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -S /dev/md0
mdadm: stopped /dev/md0
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
mdadm: cannot open /dev/md0: No such file or directory
[root@test ~]# mdadm -A /dev/md0
mdadm: /dev/md0 has been started with 3 drives and 1 spare.
[root@test ~]# cat /proc/mdstat
Personalities : [raid1] [raid6] [raid5] [raid4]
md0 : active raid5 sdb5[0] sdb8[3](S) sdb7[4] sdb6[1]
4204544 blocks super 1.2 level 5, 512k chunk, algorithm 2 [3/3] [UUU] unused devices: <none>
[root@test ~]# mdadm -D /dev/md0
/dev/md0:
Version : 1.2
Creation Time : Thu Nov 1 20:20:44 2018
Raid Level : raid5
Array Size : 4204544 (4.01 GiB 4.31 GB)
Used Dev Size : 2102272 (2.00 GiB 2.15 GB)
Raid Devices : 3
Total Devices : 4
Persistence : Superblock is persistent Update Time : Thu Nov 1 20:21:13 2018
State : clean
Active Devices : 3
Working Devices : 4
Failed Devices : 0
Spare Devices : 1 Layout : left-symmetric
Chunk Size : 512K Name : test:0 (local to host test)
UUID : 6074e103:c5bae142:7c9fa17c:8cc5495d
Events : 18 Number Major Minor RaidDevice State
0 8 21 0 active sync /dev/sdb5
1 8 22 1 active sync /dev/sdb6
4 8 23 2 active sync /dev/sdb7 3 8 24 - spare /dev/sdb8
[root@test ~]#
提示:当我们有保存的有装载的配置信息,我们就直接重新装载,不用指定其磁盘,以上就是最最基本的管理raid以及创建raid,当然我们也可以创建多个不同级别的raid,其方法同上。
以上是我个人的一些总结和看法,如有错误,欢迎大家指出,谢谢大家。
Linux下RIAD的实现及mdadm命令的基本用法的更多相关文章
- 构建LINUX下的入侵检测系统——LIDS 系统管理命令--vlock
构建LINUX下的入侵检测系统——LIDS 系统管理命令--vlock http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-306663-id-2440200.html LIDS官方网站: ...
- Linux下如何保持gnome-terminal窗口执行命令后停留而不立刻关闭(gnome-terminal -x)
Linux下如何保持gnome-terminal窗口执行命令后停留而不立刻关闭(gnome-terminal -x) 转自:http://jakfruit.blog.163.com/blog/stat ...
- Linux下df与du两个命令的差别?
Linux下df与du两个命令的差别? 一.df显示文件系统的使用情况,与du比較,就是更全盘化. 最经常使用的就是 df -T,显示文件系统的使用情况并显示文件系统的类型. 举比例如以下: [roo ...
- linux 下文件重命名/移动/复制命令(转)
linux 下文件重命名/移动/复制命令(转) linux下重命名文件:使用mv命令就可以了, 例:要把名为:abc 重命名为:123 可以这样操作: 重命名:MV命令 1.进入你的文件目录,运行 ...
- linux下使用script和scriptreplay对命令行操作进行录像
转自:linux下用script和scriptreplay对命令行操作录像 在Linux中可以使用script命令来记录命令行的操作过程,并使用scriptreplay命令对命令操作进行回放,操作步骤 ...
- linux下查看动态链接库依赖关系的命令 x86: ldd *.so arm: arm-linux-readelf -d *.so 实际例子: 以项目中用到的库librtsp.so分析: lijun@ubuntu:~/workspace$ arm-hisiv100nptl-linux-ld -d librtsp.so arm-hisiv100nptl-linux-ld:
linux下查看动态链接库依赖关系的命令 x86:ldd *.so arm:arm-linux-readelf -d *.so 实际例子:以项目中用到的库librtsp.so分析:l ...
- Linux下mysql使用systemctl restart mysqld命令失败
Linux下mysql使用systemctl restart mysqld命令失败: 解决方法:将mysql赋予root的权限 vim /etc/passwd 找到mysql开头的一行文件mysql: ...
- Linux下的压缩zip,解压缩unzip命令详解及实例
实例:压缩服务器上当前目录的内容为xxx.zip文件 zip -r xxx.zip ./* 解压zip文件到当前目录 unzip filename.zip ====================== ...
- Linux下更好用的帮助命令—cheat
导读 Linux系统中,我们经常会用man命令来帮助查看这个命令的具体用法,man是很强大的,但是英语不好的同学用man用起来可能不那么顺手,自然而然的就出现了cheat命令,cheat命令就是通过简 ...
随机推荐
- WPF写圆形头像,带消息提醒图标
<DockPanel VerticalAlignment="Top" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch" Margin=" ...
- SVN部署(基于Linux)
第一步:通过yum命令安装svnserve,命令如下: yum -y install subversion 此命令会全自动安装svn服务器相关服务和依赖,安装完成会自动停止命令运行 若需查看svn安装 ...
- OpenCV支持Qt用户界面
在运行opencv程序的时候报下面的错误: ... The library is compiled without QT support in function ... 原因是在使用cmake安装op ...
- 01 【PMP】组织结构类型
[PMP]组织结构类型 1.简单型 描述:人员并肩工作,所有者/经营者直接做出主要决定并监督执行. PM角色:兼职(协调员) PM权限:极少(无) 项目管理人员:极少(无) 资源可用性:极少(无) ...
- luogu P3878 [TJOI2010]分金币
[返回模拟退火略解] 题目描述 今有 nnn 个数 {ai}\{a_i\}{ai},把它们分成两堆{X},{Y}\{X\},\{Y\}{X},{Y},求一种分配使得∣∑i∈Xai−∑i∈Yai∣|\ ...
- 一张图看懂Rxjava的原理
前言 Rxjava是NetFlix出品的Java框架, 官方描述为 a library for composing asynchronous and event-based programs usin ...
- vue —— Toast 内 加变量
toast正常使用: 在页面内引入: import { Toast } from 'mint-ui' 使用的时候,简单到飞起: Toast('领取成功'); 而如果想在toast中加入变量,也很简单: ...
- 2.单核CPU是如何实现多进程的?
单核cpu之所以能够实现多进程,主要是依靠于操作系统的进程的调度算法 如时间片轮转算法,在早期,举例说明:有5个正在运行的程序(即5个进程) : QQ 微信 有道词典 网易云 ...
- 定制的print()输出格式
#定制print时的显示内容 #烤地瓜案例:主要显示格式digua("cd1","cd2","cd3""),而不是就直接在一个列表 ...
- Apache POI使用指南(HSSFWorkbook生成excel)
说 明: 官网:http://poi.apache.org/ 由于poi的功能多样,可以生成ppt.word.excel.......,本文就以生成excel为例进行说明,相信聪明的你一定能举一反三 ...
