Redis之quicklist源码分析
一、quicklist简介
Redis列表是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。你可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)。
一个列表最多可以包含 232 - 1 个元素 (4294967295, 每个列表超过40亿个元素)。
其底层实现所依赖的内部数据结构就是quicklist,主要特点有:
1. list是一个双向链表。
2. 在list的两端追加和删除数据极为方便,时间复杂度为O(1)。
3. list也支持在任意中间位置的存取操作,时间复杂度为O(N)。
在看源码之前(版本3.2.2),我们先看一下quicklist中的几个主要数据结构:
一个quicklist由多个quicklistNode组成,每个quicklistNode指向一个ziplist,一个ziplist包含多个entry元素,每个entry元素就是一个list的元素,示意图如下:
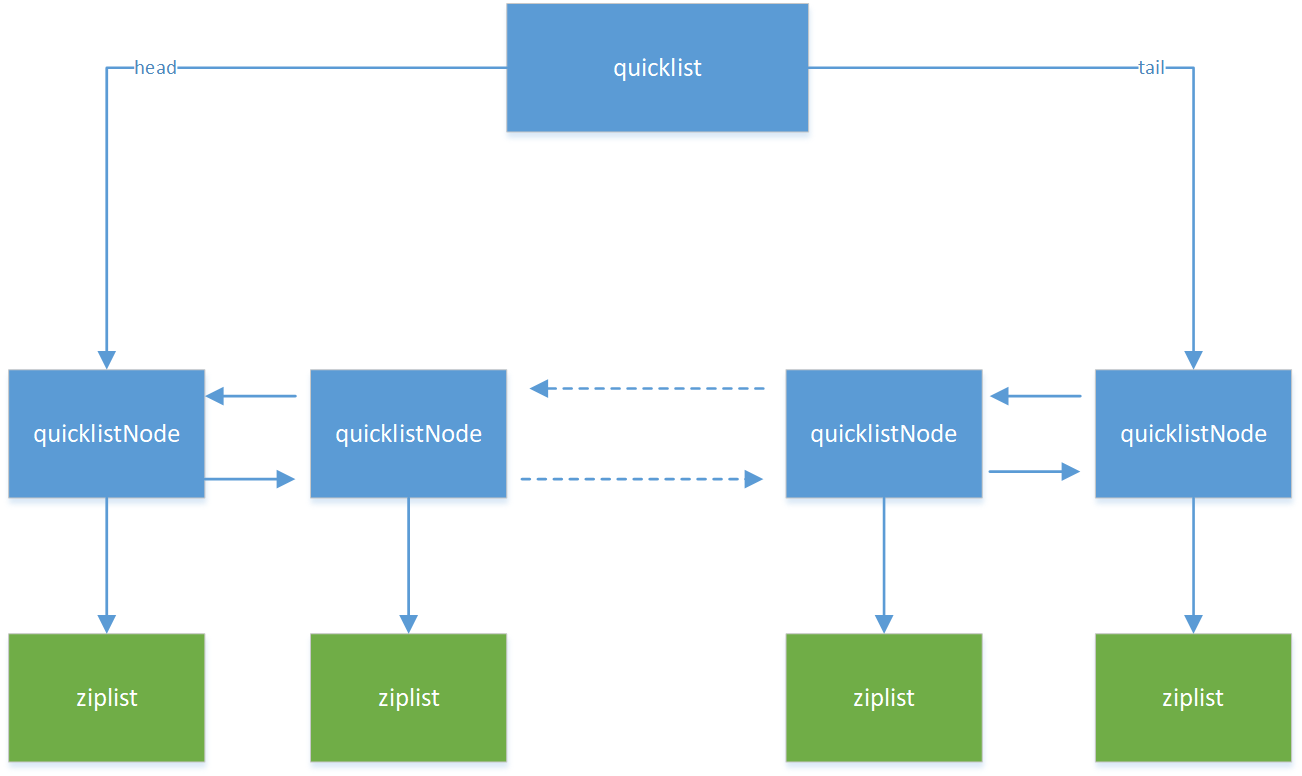
图1:quicklist
二、quicklist数据结构源码
下面分别看下quicklist、quicklistNode的源码(代码文件是Quicklist.h,ziplist后面文章再分析):
quicklist:
/*
quicklist结构占用32个字节(64位系统),其中字段:
head:指向第一个quicklistNode。
tail:指向最后一个quicklistNode。
count:在所有ziplist中entry的个数总和。
len:quicklistNode的个数。
fill:ziplist大小限定,由server.list_max_ziplist_size给定。
compress:节点压缩深度设置,由server.list-compress-depth给定,0表示关闭压缩。
*/
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists */
unsigned int len; /* number of quicklistNodes */
int fill : ; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : ; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
} quicklist;
quicklistNode:
/*
prev: 指向前一个quicklistNode。
next: 指向下一个quicklistNode。
zl: 指向当前节点的ziplist。
sz:ziplist占用空间的字节数。
count: ziplist中元素个数。
encoding:编码类型,RAW==1 or LZF==2。
container:容器类型,NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2
recompress:bool类型,true表示该节点数据临时被解压了。
attempted_compress: bool类型,用于测试阶段。
extra: 填充字典,将来可能会用到。
*/
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */
unsigned int count : ; /* count of items in ziplist */
unsigned int encoding : ; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : ; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */
unsigned int recompress : ; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : ; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int extra : ; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
三、quicklist的增删改查
1. 创建quicklist
在执行push命令时(例如lpush),发现无此key时,会创建并初始化quicklist,如下:
void pushGenericCommand(client *c, int where) {
int j, waiting = , pushed = ;
robj *lobj = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[]);
if (lobj && lobj->type != OBJ_LIST) {
addReply(c,shared.wrongtypeerr);
return;
}
for (j = ; j < c->argc; j++) {
c->argv[j] = tryObjectEncoding(c->argv[j]);
if (!lobj) { // key不存在,则首先创建key对象并加入db中
lobj = createQuicklistObject(); // 初始化quicklist对象
quicklistSetOptions(lobj->ptr, server.list_max_ziplist_size,
server.list_compress_depth); // 使用redis server的配置项做初始化
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[],lobj); // 把quicklist添加到redis db中
}
// 把新元素加入list中
listTypePush(lobj,c->argv[j],where);
pushed++;
}
addReplyLongLong(c, waiting + (lobj ? listTypeLength(lobj) : ));
if (pushed) {
char *event = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? "lpush" : "rpush";
signalModifiedKey(c->db,c->argv[]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_LIST,event,c->argv[],c->db->id);
}
server.dirty += pushed;
}
再看下createQuicklistObject:
/* Create a new quicklist.
* Free with quicklistRelease(). */
quicklist *quicklistCreate(void) {
struct quicklist *quicklist; quicklist = zmalloc(sizeof(*quicklist));
quicklist->head = quicklist->tail = NULL;
quicklist->len = ;
quicklist->count = ;
quicklist->compress = ;
quicklist->fill = -;
return quicklist;
}
2. 添加元素
继续看上面源码中的listTypePush方法:
void listTypePush(robj *subject, robj *value, int where) {
if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST) {
int pos = (where == LIST_HEAD) ? QUICKLIST_HEAD : QUICKLIST_TAIL;
value = getDecodedObject(value);
size_t len = sdslen(value->ptr);// 计算新元素长度
quicklistPush(subject->ptr, value->ptr, len, pos); // 加入到quicklist
decrRefCount(value);
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown list encoding");
}
}
继续看quicklistPush:
/* Wrapper to allow argument-based switching between HEAD/TAIL pop */
void quicklistPush(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, const size_t sz,
int where) {
if (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD) { // 添加到list头部
quicklistPushHead(quicklist, value, sz);
} else if (where == QUICKLIST_TAIL) { // 添加到list尾部
quicklistPushTail(quicklist, value, sz);
}
} /* Add new entry to head node of quicklist.
*
* Returns 0 if used existing head.
* Returns 1 if new head created.
在quicklist的头部节点添加新元素:
如果新元素添加在head中,返回0,否则返回1.
*/
int quicklistPushHead(quicklist *quicklist, void *value, size_t sz) {
quicklistNode *orig_head = quicklist->head;
// 如果head不为空,且空间大小满足新元素的存储要求,则新元素添加到head中,否则新加一个quicklistNode
if (likely(
_quicklistNodeAllowInsert(quicklist->head, quicklist->fill, sz))) {
quicklist->head->zl =
ziplistPush(quicklist->head->zl, value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(quicklist->head);
} else {
// 创建新的quicklistNode
quicklistNode *node = quicklistCreateNode();
// 把新元素添加到新建的ziplist中
node->zl = ziplistPush(ziplistNew(), value, sz, ZIPLIST_HEAD);
// 更新ziplist的长度到quicklistNode的sz字段,再把新node添加到quicklist中,即添加到原head前面
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
_quicklistInsertNodeBefore(quicklist, quicklist->head, node);
}
quicklist->count++;
quicklist->head->count++;
return (orig_head != quicklist->head);
}
ziplistpush会把新元素添加到ziplist中,这部分代码后面文章再分析。
3. 获取元素
获取元素方法是quicklistPop方法(quicklist.c),如下:
/* Default pop function
*
* Returns malloc'd value from quicklist */
int quicklistPop(quicklist *quicklist, int where, unsigned char **data,
unsigned int *sz, long long *slong) {
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
if (quicklist->count == )
return ;
// pop一个元素
int ret = quicklistPopCustom(quicklist, where, &vstr, &vlen, &vlong,
_quicklistSaver);
if (data)
*data = vstr;
if (slong)
*slong = vlong;
if (sz)
*sz = vlen;
return ret;
}
具体实现在quicklistPopCustom:
/* pop from quicklist and return result in 'data' ptr. Value of 'data'
* is the return value of 'saver' function pointer if the data is NOT a number.
*
* If the quicklist element is a long long, then the return value is returned in
* 'sval'.
*
* Return value of 0 means no elements available.
* Return value of 1 means check 'data' and 'sval' for values.
* If 'data' is set, use 'data' and 'sz'. Otherwise, use 'sval'.
如果quicklist中无元素,返回0,否则返回1.
当返回1时,需要检查data和sval两个字段:
1. 如果是string类型,则把结果地址保存在data指针中,长度保存在sz。
2. 如果是long long类型,则把值保存在sval字段中。
*/
int quicklistPopCustom(quicklist *quicklist, int where, unsigned char **data,
unsigned int *sz, long long *sval,
void *(*saver)(unsigned char *data, unsigned int sz)) {
unsigned char *p;
unsigned char *vstr;
unsigned int vlen;
long long vlong;
int pos = (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD) ? : -; if (quicklist->count == )
return ; if (data)
*data = NULL;
if (sz)
*sz = ;
if (sval)
*sval = -; quicklistNode *node;
if (where == QUICKLIST_HEAD && quicklist->head) {
node = quicklist->head;
} else if (where == QUICKLIST_TAIL && quicklist->tail) {
node = quicklist->tail;
} else {
return ;
}
// p: 0 取ziplist的第一个元素; -1 取ziplist的最后一个元素;
p = ziplistIndex(node->zl, pos);
if (ziplistGet(p, &vstr, &vlen, &vlong)) {
if (vstr) {
if (data)
*data = saver(vstr, vlen);
if (sz)
*sz = vlen;
} else {
if (data)
*data = NULL;
if (sval)
*sval = vlong;
}
// 从quicklist中删除该元素
quicklistDelIndex(quicklist, node, &p);
return ;
}
return ;
}
再看下quicklistDelIndex:
/* Delete one entry from list given the node for the entry and a pointer
* to the entry in the node.
*
* Note: quicklistDelIndex() *requires* uncompressed nodes because you
* already had to get *p from an uncompressed node somewhere.
*
* Returns 1 if the entire node was deleted, 0 if node still exists.
* Also updates in/out param 'p' with the next offset in the ziplist.
从quicklistNode中删除一个entry:
1. 从ziplist中删除entry。
2. quicklistNode中的entry个数减1:
如果quicklistNode中entry个数为0,则从quicklist中删除当前的quicklistNode。
否则,更新quicklistNode中的sz字段。
*/
REDIS_STATIC int quicklistDelIndex(quicklist *quicklist, quicklistNode *node,
unsigned char **p) {
int gone = ; node->zl = ziplistDelete(node->zl, p);
node->count--;
if (node->count == ) {
gone = ;
__quicklistDelNode(quicklist, node);
} else {
quicklistNodeUpdateSz(node);
}
quicklist->count--;
/* If we deleted the node, the original node is no longer valid */
return gone ? : ;
}
至此,quicklist的主体结构代码,和主要的两个方法push和pop的代码就分析结束了,下一篇分析quicklist底层存储ziplist的源代码。
本篇内容参考了钱文品的《Redis深度历险:核心原理与应用实践》,特此感谢!
Redis之quicklist源码分析的更多相关文章
- Redis 内存管理 源码分析
要想了解redis底层的内存管理是如何进行的,直接看源码绝对是一个很好的选择 下面是我添加了详细注释的源码,需要注意的是,为了便于源码分析,我把redis为了弥补平台差异的那部分代码删了,只需要知道有 ...
- Redis网络模型的源码分析
Redis的网络模型是基于I/O多路复用程序来实现的.源码中包含四种多路复用函数库epoll.select.evport.kqueue.在程序编译时会根据系统自动选择这四种库其中之一.下面以epoll ...
- Redis之ziplist源码分析
一.ziplist简介 从上一篇分析我们知道quicklist的底层存储使用了ziplist(压缩列表),由于压缩列表本身也有不少内容,所以重新开了一篇,在正式源码之前,还是先看下ziplist的特点 ...
- Redis 数据结构-字符串源码分析
相关文章 Redis 初探-安装与使用 Redis常用指令 本文将从以下几个部分进行介绍 1.前言 2.常用命令 3.字符串结构 4.字符串实现 5.命令是如果操作字符串的 前言 平时在使用 Redi ...
- Redis网络库源码分析(1)之介绍篇
一.前言 Redis网络库是一个单线程EPOLL模型的网络库,和Memcached使用的libevent相比,它没有那么庞大,代码一共2000多行,因此比较容易分析.其实网上已经有非常多有关这个网络库 ...
- 第10课:[实战] Redis 网络通信模块源码分析(3)
redis-server 接收到客户端的第一条命令 redis-cli 给 redis-server 发送的第一条数据是 *1\r\n\$7\r\nCOMMAND\r\n .我们来看下对于这条数据如何 ...
- 第09课:【实战】Redis网络通信模块源码分析(2)
侦听 fd 与客户端 fd 是如何挂载到 EPFD 上去的 同样的方式,要把一个 fd 挂载到 EPFD 上去,需要调用系统 API epoll_ctl ,搜索一下这个函数名.在文件 ae_epoll ...
- 第08课:【实战】Redis网络通信模块源码分析(1)
我们这里先研究redis-server端的网络通信模块.除去Redis本身的业务功能以外,Redis的网络通信模块实现思路和细节非常有代表性.由于网络通信模块的设计也是Linux C++后台开发一个很 ...
- Redis网络库源码分析(3)之ae.c
一.aeCreateEventLoop & aeCreateFileEvent 上一篇文章中,我们已经将服务器启动,只是其中有些细节我们跳过了,比如aeCreateEventLoop函数到底做 ...
随机推荐
- Vulnhub靶场DC-1 WP
前言 之前提到过最近在做vlunhub的靶场复现工作,今天开始更新writeup吧.(对着walkthrough一顿乱抄嘻嘻嘻) 关于DC-1(官网翻译来的) 描述 DC-1是一个专门构建的易受攻击的 ...
- python基础知识8——常见内置模块
Python之路-python(常用模块学习) 模块介绍 time &datetime模块 random os sys shutil shelve xml处理 yaml处理 configpar ...
- pd库dataframe基本操作
一.查看数据(查看对象的方法对于Series来说同样适用) 1.查看DataFrame前xx行或后xx行 a=DataFrame(data); a.head(6)表示显示前6行数据,若head()中不 ...
- 更新statsmodels出现的一系列问题
在statsmodels的开发12版本文档上正好看到使用三因子模型进行rolling regression,但是代码来自最新版本,而我的是老版本,运行下列代码会出现这个问题: No module na ...
- 【问题解决】-《java.lang.NoClassDefFoundException》
此问题相比与ClassNotFoundException,不容易找到,当然这两者都属于jvm加载类时的错误.导致 NoClassDefFoundException的原因:编译时不报错,运行时在内存中找 ...
- VSCode 快速生成 .vue 模版
VSCode 快速生成 .vue 模版 安装vscode 官网:https://code.visualstudio.com/ 安装 Vetur 插件,识别 vue 文件 插件库中搜索Vetur,点击安 ...
- 宝塔phpmyadmin可能问题及解决方法
1. 端口问题检查宝塔phpmyadmin的默认端口888是否放行,和在服务器的安全组规则有没有添加888端口 2.phpmyadmin的php版本问题 在phpmyadmin的设置里的版本选择php ...
- 【nodejs 爬虫】使用 puppeteer 爬取链家房价信息
使用 puppeteer 爬取链家房价信息 目录 使用 puppeteer 爬取链家房价信息 页面结构 爬虫库 pupeteer 库 实现 打开待爬页面 遍历区级页面 方法一 方法二 遍历街道页面 遍 ...
- 微信小程序生成带参数的二维码(小程序码)独家asp.net的服务端c#完整代码
一)我先用的小程序端的wx.request去调用API,发现竟然是一个坑! wx.request({ url: 'https://api.weixin.qq.com/wxa/getwxacodeunl ...
- 汇编学习二-VB(常见函数分析)
VB代码如下所示 push ebp 00401FF1 . 8BEC mov ebp,esp 00401FF3 . 83EC 0C sub esp,0xC push <jmp.&MSVBV ...
