入门大数据---Hbase_Java_API
一、简述
截至到目前 (2019.04),HBase 有两个主要的版本,分别是 1.x 和 2.x ,两个版本的 Java API 有所不同,1.x 中某些方法在 2.x 中被标识为 @deprecated 过时。所以下面关于 API 的样例,我会分别给出 1.x 和 2.x 两个版本。完整的代码见本仓库:
同时你使用的客户端的版本必须与服务端版本保持一致,如果用 2.x 版本的客户端代码去连接 1.x 版本的服务端,会抛出 NoSuchColumnFamilyException 等异常。
二、Java API 1.x 基本使用
2.1 新建Maven工程,导入项目依赖
要使用 Java API 操作 HBase,需要引入 hbase-client。这里选取的 HBase Client 的版本为 1.2.0。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0</version>
</dependency>
2.2 API 基本使用
public class HBaseUtils {
private static Connection connection;
static {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", "2181");
// 如果是集群 则主机名用逗号分隔
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop001");
try {
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 创建 HBase 表
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param columnFamilies 列族的数组
*/
public static boolean createTable(String tableName, List<String> columnFamilies) {
try {
HBaseAdmin admin = (HBaseAdmin) connection.getAdmin();
if (admin.tableExists(tableName)) {
return false;
}
HTableDescriptor tableDescriptor = new HTableDescriptor(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
columnFamilies.forEach(columnFamily -> {
HColumnDescriptor columnDescriptor = new HColumnDescriptor(columnFamily);
columnDescriptor.setMaxVersions(1);
tableDescriptor.addFamily(columnDescriptor);
});
admin.createTable(tableDescriptor);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除 hBase 表
*
* @param tableName 表名
*/
public static boolean deleteTable(String tableName) {
try {
HBaseAdmin admin = (HBaseAdmin) connection.getAdmin();
// 删除表前需要先禁用表
admin.disableTable(tableName);
admin.deleteTable(tableName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 插入数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamilyName 列族名
* @param qualifier 列标识
* @param value 数据
*/
public static boolean putRow(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamilyName, String qualifier,
String value) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamilyName), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier), Bytes.toBytes(value));
table.put(put);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 插入数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamilyName 列族名
* @param pairList 列标识和值的集合
*/
public static boolean putRow(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamilyName, List<Pair<String, String>> pairList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
pairList.forEach(pair -> put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamilyName), Bytes.toBytes(pair.getKey()), Bytes.toBytes(pair.getValue())));
table.put(put);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 根据 rowKey 获取指定行的数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
*/
public static Result getRow(String tableName, String rowKey) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
return table.get(get);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取指定行指定列 (cell) 的最新版本的数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamily 列族
* @param qualifier 列标识
*/
public static String getCell(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String qualifier) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
if (!get.isCheckExistenceOnly()) {
get.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
Result result = table.get(get);
byte[] resultValue = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
return Bytes.toString(resultValue);
} else {
return null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索全表
*
* @param tableName 表名
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索表中指定数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param filterList 过滤器
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName, FilterList filterList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setFilter(filterList);
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索表中指定数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param startRowKey 起始 RowKey
* @param endRowKey 终止 RowKey
* @param filterList 过滤器
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName, String startRowKey, String endRowKey,
FilterList filterList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setStartRow(Bytes.toBytes(startRowKey));
scan.setStopRow(Bytes.toBytes(endRowKey));
scan.setFilter(filterList);
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 删除指定行记录
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
*/
public static boolean deleteRow(String tableName, String rowKey) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
table.delete(delete);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除指定行的指定列
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param familyName 列族
* @param qualifier 列标识
*/
public static boolean deleteColumn(String tableName, String rowKey, String familyName,
String qualifier) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
delete.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(familyName), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
}
2.3 单元测试
以单元测试的方式对上面封装的 API 进行测试。
public class HBaseUtilsTest {
private static final String TABLE_NAME = "class";
private static final String TEACHER = "teacher";
private static final String STUDENT = "student";
@Test
public void createTable() {
// 新建表
List<String> columnFamilies = Arrays.asList(TEACHER, STUDENT);
boolean table = HBaseUtils.createTable(TABLE_NAME, columnFamilies);
System.out.println("表创建结果:" + table);
}
@Test
public void insertData() {
List<Pair<String, String>> pairs1 = Arrays.asList(new Pair<>("name", "Tom"),
new Pair<>("age", "22"),
new Pair<>("gender", "1"));
HBaseUtils.putRow(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey1", STUDENT, pairs1);
List<Pair<String, String>> pairs2 = Arrays.asList(new Pair<>("name", "Jack"),
new Pair<>("age", "33"),
new Pair<>("gender", "2"));
HBaseUtils.putRow(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey2", STUDENT, pairs2);
List<Pair<String, String>> pairs3 = Arrays.asList(new Pair<>("name", "Mike"),
new Pair<>("age", "44"),
new Pair<>("gender", "1"));
HBaseUtils.putRow(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey3", STUDENT, pairs3);
}
@Test
public void getRow() {
Result result = HBaseUtils.getRow(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey1");
if (result != null) {
System.out.println(Bytes
.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(STUDENT), Bytes.toBytes("name"))));
}
}
@Test
public void getCell() {
String cell = HBaseUtils.getCell(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey2", STUDENT, "age");
System.out.println("cell age :" + cell);
}
@Test
public void getScanner() {
ResultScanner scanner = HBaseUtils.getScanner(TABLE_NAME);
if (scanner != null) {
scanner.forEach(result -> System.out.println(Bytes.toString(result.getRow()) + "->" + Bytes
.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(STUDENT), Bytes.toBytes("name")))));
scanner.close();
}
}
@Test
public void getScannerWithFilter() {
FilterList filterList = new FilterList(FilterList.Operator.MUST_PASS_ALL);
SingleColumnValueFilter nameFilter = new SingleColumnValueFilter(Bytes.toBytes(STUDENT),
Bytes.toBytes("name"), CompareOperator.EQUAL, Bytes.toBytes("Jack"));
filterList.addFilter(nameFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = HBaseUtils.getScanner(TABLE_NAME, filterList);
if (scanner != null) {
scanner.forEach(result -> System.out.println(Bytes.toString(result.getRow()) + "->" + Bytes
.toString(result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(STUDENT), Bytes.toBytes("name")))));
scanner.close();
}
}
@Test
public void deleteColumn() {
boolean b = HBaseUtils.deleteColumn(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey2", STUDENT, "age");
System.out.println("删除结果: " + b);
}
@Test
public void deleteRow() {
boolean b = HBaseUtils.deleteRow(TABLE_NAME, "rowKey2");
System.out.println("删除结果: " + b);
}
@Test
public void deleteTable() {
boolean b = HBaseUtils.deleteTable(TABLE_NAME);
System.out.println("删除结果: " + b);
}
}
三、Java API 2.x 基本使用
3.1 新建Maven工程,导入项目依赖
这里选取的 HBase Client 的版本为最新的 2.1.4。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
3.2 API 的基本使用
2.x 版本相比于 1.x 废弃了一部分方法,关于废弃的方法在源码中都会指明新的替代方法,比如,在 2.x 中创建表时:HTableDescriptor 和 HColumnDescriptor 等类都标识为废弃,取而代之的是使用 TableDescriptorBuilder 和 ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder 来定义表和列族。
以下为 HBase 2.x 版本 Java API 的使用示例:
public class HBaseUtils {
private static Connection connection;
static {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.property.clientPort", "2181");
// 如果是集群 则主机名用逗号分隔
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop001");
try {
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 创建 HBase 表
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param columnFamilies 列族的数组
*/
public static boolean createTable(String tableName, List<String> columnFamilies) {
try {
HBaseAdmin admin = (HBaseAdmin) connection.getAdmin();
if (admin.tableExists(TableName.valueOf(tableName))) {
return false;
}
TableDescriptorBuilder tableDescriptor = TableDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
columnFamilies.forEach(columnFamily -> {
ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder cfDescriptorBuilder = ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily));
cfDescriptorBuilder.setMaxVersions(1);
ColumnFamilyDescriptor familyDescriptor = cfDescriptorBuilder.build();
tableDescriptor.setColumnFamily(familyDescriptor);
});
admin.createTable(tableDescriptor.build());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除 hBase 表
*
* @param tableName 表名
*/
public static boolean deleteTable(String tableName) {
try {
HBaseAdmin admin = (HBaseAdmin) connection.getAdmin();
// 删除表前需要先禁用表
admin.disableTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
admin.deleteTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 插入数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamilyName 列族名
* @param qualifier 列标识
* @param value 数据
*/
public static boolean putRow(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamilyName, String qualifier,
String value) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamilyName), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier), Bytes.toBytes(value));
table.put(put);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 插入数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamilyName 列族名
* @param pairList 列标识和值的集合
*/
public static boolean putRow(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamilyName, List<Pair<String, String>> pairList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
pairList.forEach(pair -> put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamilyName), Bytes.toBytes(pair.getKey()), Bytes.toBytes(pair.getValue())));
table.put(put);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 根据 rowKey 获取指定行的数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
*/
public static Result getRow(String tableName, String rowKey) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
return table.get(get);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取指定行指定列 (cell) 的最新版本的数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param columnFamily 列族
* @param qualifier 列标识
*/
public static String getCell(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String qualifier) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
if (!get.isCheckExistenceOnly()) {
get.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
Result result = table.get(get);
byte[] resultValue = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
return Bytes.toString(resultValue);
} else {
return null;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索全表
*
* @param tableName 表名
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索表中指定数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param filterList 过滤器
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName, FilterList filterList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setFilter(filterList);
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 检索表中指定数据
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param startRowKey 起始 RowKey
* @param endRowKey 终止 RowKey
* @param filterList 过滤器
*/
public static ResultScanner getScanner(String tableName, String startRowKey, String endRowKey,
FilterList filterList) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.withStartRow(Bytes.toBytes(startRowKey));
scan.withStopRow(Bytes.toBytes(endRowKey));
scan.setFilter(filterList);
return table.getScanner(scan);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 删除指定行记录
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
*/
public static boolean deleteRow(String tableName, String rowKey) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
table.delete(delete);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 删除指定行指定列
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param rowKey 唯一标识
* @param familyName 列族
* @param qualifier 列标识
*/
public static boolean deleteColumn(String tableName, String rowKey, String familyName,
String qualifier) {
try {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
delete.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(familyName), Bytes.toBytes(qualifier));
table.delete(delete);
table.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
}
四、正确连接Hbase
在上面的代码中,在类加载时就初始化了 Connection 连接,并且之后的方法都是复用这个 Connection,这时我们可能会考虑是否可以使用自定义连接池来获取更好的性能表现?实际上这是没有必要的。
首先官方对于 Connection 的使用说明如下:
Connection Pooling For applications which require high-end multithreaded
access (e.g., web-servers or application servers that may serve many
application threads in a single JVM), you can pre-create a Connection,
as shown in the following example:
对于高并发多线程访问的应用程序(例如,在单个 JVM 中存在的为多个线程服务的 Web 服务器或应用程序服务器),
您只需要预先创建一个 Connection。例子如下:
// Create a connection to the cluster.
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
try (Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tablename))) {
// use table as needed, the table returned is lightweight
}
之所以能这样使用,这是因为 Connection 并不是一个简单的 socket 连接,接口文档 中对 Connection 的表述是:
A cluster connection encapsulating lower level individual connections to actual servers and a
connection to zookeeper. Connections are instantiated through the ConnectionFactory class.
The lifecycle of the connection is managed by the caller, who has to close() the connection
to release the resources.
Connection 是一个集群连接,封装了与多台服务器(Matser/Region Server)的底层连接以及与 zookeeper 的连接。
连接通过 ConnectionFactory 类实例化。连接的生命周期由调用者管理,调用者必须使用 close() 关闭连接以释放资源。
之所以封装这些连接,是因为 HBase 客户端需要连接三个不同的服务角色:
- Zookeeper :主要用于获取
meta表的位置信息,Master 的信息; - HBase Master :主要用于执行 HBaseAdmin 接口的一些操作,例如建表等;
- HBase RegionServer :用于读、写数据。
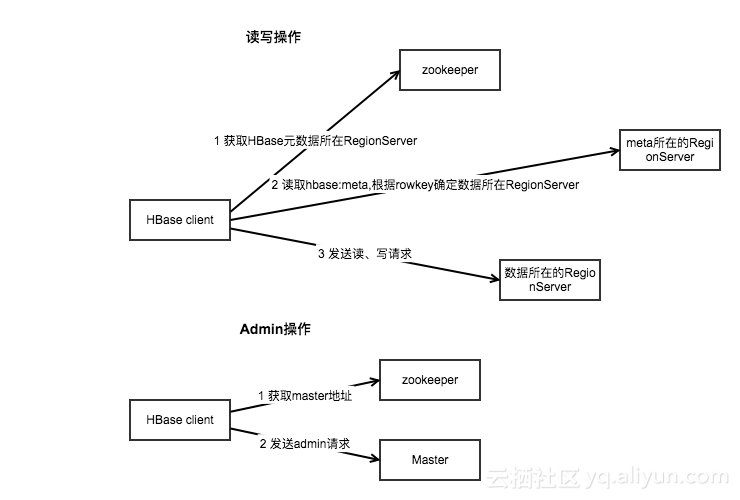
Connection 对象和实际的 Socket 连接之间的对应关系如下图:
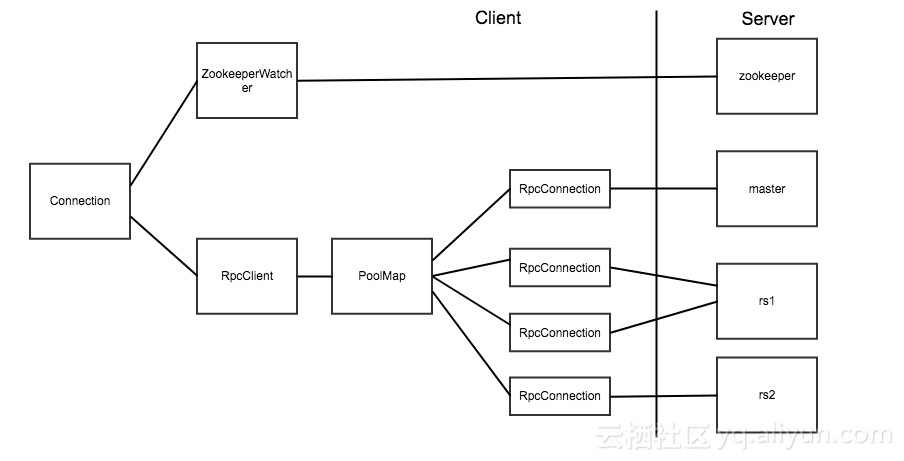
上面两张图片引用自博客:连接 HBase 的正确姿势
在 HBase 客户端代码中,真正对应 Socket 连接的是 RpcConnection 对象。HBase 使用 PoolMap 这种数据结构来存储客户端到 HBase 服务器之间的连接。PoolMap 的内部有一个 ConcurrentHashMap 实例,其 key 是 ConnectionId(封装了服务器地址和用户 ticket),value 是一个 RpcConnection 对象的资源池。当 HBase 需要连接一个服务器时,首先会根据 ConnectionId 找到对应的连接池,然后从连接池中取出一个连接对象。
@InterfaceAudience.Private
public class PoolMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private PoolType poolType;
private int poolMaxSize;
private Map<K, Pool<V>> pools = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public PoolMap(PoolType poolType) {
this.poolType = poolType;
}
.....
HBase 中提供了三种资源池的实现,分别是 Reusable,RoundRobin 和 ThreadLocal。具体实现可以通 hbase.client.ipc.pool.type 配置项指定,默认为 Reusable。连接池的大小也可以通过 hbase.client.ipc.pool.size 配置项指定,默认为 1,即每个 Server 1 个连接。也可以通过修改配置实现:
config.set("hbase.client.ipc.pool.type",...);
config.set("hbase.client.ipc.pool.size",...);
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
由此可以看出 HBase 中 Connection 类已经实现了对连接的管理功能,所以我们不必在 Connection 上在做额外的管理。
另外,Connection 是线程安全的,但 Table 和 Admin 却不是线程安全的,因此正确的做法是一个进程共用一个 Connection 对象,而在不同的线程中使用单独的 Table 和 Admin 对象。Table 和 Admin 的获取操作 getTable() 和 getAdmin() 都是轻量级,所以不必担心性能的消耗,同时建议在使用完成后显示的调用 close() 方法来关闭它们。
参考资料
入门大数据---Hbase_Java_API的更多相关文章
- 入门大数据---Flink学习总括
第一节 初识 Flink 在数据激增的时代,催生出了一批计算框架.最早期比较流行的有MapReduce,然后有Spark,直到现在越来越多的公司采用Flink处理.Flink相对前两个框架真正做到了高 ...
- 入门大数据---Spark_Streaming整合Flume
一.简介 Apache Flume 是一个分布式,高可用的数据收集系统,可以从不同的数据源收集数据,经过聚合后发送到分布式计算框架或者存储系统中.Spark Straming 提供了以下两种方式用于 ...
- 入门大数据---SparkSQL外部数据源
一.简介 1.1 多数据源支持 Spark 支持以下六个核心数据源,同时 Spark 社区还提供了多达上百种数据源的读取方式,能够满足绝大部分使用场景. CSV JSON Parquet ORC JD ...
- 入门大数据---Hadoop是什么?
简单概括:Hadoop是由Apache组织使用Java语言开发的一款应对大数据存储和计算的分布式开源框架. Hadoop的起源 2003-2004年,Google公布了部分GFS和MapReduce思 ...
- 入门大数据---MapReduce-API操作
一.环境 Hadoop部署环境: Centos3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 Hadoop2.6.5 Java1.8.0_221 代码运行环境: Windows 10 Hadoop 2.6 ...
- 入门大数据---Flume整合Kafka
一.背景 先说一下,为什么要使用 Flume + Kafka? 以实时流处理项目为例,由于采集的数据量可能存在峰值和峰谷,假设是一个电商项目,那么峰值通常出现在秒杀时,这时如果直接将 Flume 聚合 ...
- 入门大数据---安装ClouderaManager,CDH和Impala,Hue,oozie等服务
1.要求和支持的版本 (PS:我使用的环境,都用加粗标识了.) 1.1 支持的操作系统版本 操作系统 版本 RHEL/CentOS/OL with RHCK kernel 7.6, 7.5, 7.4, ...
- 入门大数据---Kylin是什么?
一.Kylin是什么? Apache Kylin是一个开源的.分布式的分析型数据仓库,提供Hadoop/Spark 上的SQL查询接口及多维度分析(OLAP)能力以支持超大规模的数据,最初由eBay开 ...
- 大数据学习系列之Hadoop、Spark学习线路(想入门大数据的童鞋,强烈推荐!)
申明:本文出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/zlslch/p/5448857.html(该博客干货较多) 1 Java基础: 视频方面: 推荐<毕向东JAVA ...
随机推荐
- CSS3新增伪类有那些?
p:first-of-type 选择属于其父元素的首个元素 p:last-of-type 选择属于其父元素的最后元素 p:only-of-type 选择属于其父元素唯一的元素 p:only-child ...
- 细说Java多线程之内存可见性笔记
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有) 说明:多线程的内存可见性涉及到多线程间的数据争用,也涉及到了多线程间的数据可见性 一.共享变量在线程间的 ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 834 树中距离之和(DFS+分析)
834. 树中距离之和 给定一个无向.连通的树.树中有 N 个标记为 0-N-1 的节点以及 N-1 条边 . 第 i 条边连接节点 edges[i][0] 和 edges[i][1] . 返回一个表 ...
- github下载速度太慢,这里有已经下载完的nacos-server.zip组件
nacos: 分布式系统微服务的注册中心和配置中心 .. 在微服务系统中,起到很重要的作用.小伙伴老是给我抱怨,说这个github下面很慢慢,半天下载不下来,所有这样呢,我就把已经下载好的 nacos ...
- 洛谷P1255 数楼梯
题目描述 楼梯有N阶,上楼可以一步上一阶,也可以一步上二阶. 编一个程序,计算共有多少种不同的走法. 分析与代码 走n阶楼梯,无论是走一次走1阶还是2阶,总得迈出一步, 所以求n阶楼梯 ...
- 数据结构与算法-python描述-单向循环链表
# coding:utf-8 # 单向循环链表的相关操作: # is_empty() 判断链表是否为空 # length() 返回链表的长度 # travel() 遍历 # add(item) 在头部 ...
- jQuery实现瀑布流布局
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- HashMap(二)之面试题系列
定义类考题 什么是Hash?什么是HashMap? HashMap 的工作原理是什么 HashMap HashTable的区别 为什么要用HashMap 源码类考题 什么是hash碰撞,怎么减少碰撞, ...
- 数值格式化 NumberFormat、 DecimalFormat、 RoundingMode
NumberFormat [简介] java.text.NumberFormat extends java.text.Format extends java.lang.Object 实现的接口:Ser ...
- Web应用中解决问题的方案步骤?
我们学一个东西,通常两个目的: - 为了解决现有的问题 - 为了解决将来可能会有的问题 所以,在学这些东西之前,先必须了解,它们是用来解决什么问题的. 在Web应用中,我们需要解决的问题可以归纳为三类 ...
