Android自绘制控件
开发过程中,我们免不了需要用到一些自定义的 View,自定义 View 一般可分为三类:
① 继承类 View —— 一般继承系统以后的基本 View,新增/重置一些自定义属性 ,例如两端对齐的TextView;
② 组合类 View —— 将系统某几个基本View组合在一起形成一个新的View,例如末尾带 ”ד(清空) 的EditText,就是将EditText和ImageView组合在一起来实现;
③ 自绘制 View —— 某些特殊的设计控件,无法通过上两种方式实现时,我们就需要考虑通过自绘制来进行处理,本篇我们将着重介绍此类 View 的实现过程。
下面我们通过自定义一个圆形的Button(DCircleButton)来进行说明:
自定义View的步骤:
① 自定义 View 的属性;
② 在自定义 View 的构造方法中获取 View 的属性值;
③ 重写测量尺寸的方法 onMeasure(int, int); (是否需要重写根据具体根据需求);
④ 重写绘制方法 onDraw(Canvas c);
⑤ 在布局XML文件中,使用自定义 View 的属性。
1. 自定义 View 的属性:
在目录 res/values 下新建 attrs.xml 属性文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<!--name 是自定义控件的类名-->
<declare-styleable name="DCircleButton" parent="android.widget.Button">
<attr name="txtSize" format="dimension"/>
<attr name="text" format="string"/>
<attr name="txtColor" format="color"/>
<attr name="txtBackgroundColor" format="color"/>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
② 定义属性名称及类型。
dimension(字体大小)string(字符串)color(颜色)boolean(布尔类型)float(浮点型)integer(整型)enmu(枚举)fraction(百分比)等。
2. 在构造方法中获取属性值,并绘制
第一步:继承View,实现(AS会提示)以下四种,
public DCircleButton(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public DCircleButton(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public DCircleButton(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public DCircleButton(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
第二步,改写这四种构造,让其逐级递进:
public DCircleButton(Context context) {
super(context, null);
}
public DCircleButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs, 0);
}
public DCircleButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public DCircleButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
第三步,我们在最后一个方法获取属性值:
private void initAttrs(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray tArr = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.DCircleButton);
if (null != tArr) {
txtColor = tArr.getColor(R.styleable.DCircleButton_txtColor, Color.BLACK); // 获取文字颜色
txtSize = tArr.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.DCircleButton_txtSize, 18); // 获取文字大小
txt = tArr.getString(R.styleable.DCircleButton_text); // 获取文字内容
backgroundColor = tArr.getColor(R.styleable.DCircleButton_txtBackgroundColor, Color.GRAY); // 获取文字背景颜色
tArr.recycle();
}
}
第四步,绘制
/** 字体颜色 **/
private int txtColor;
/** 字体背景颜色 **/
private int backgroundColor;
/** 字体大小 **/
private int txtSize;
/** 按钮文字内容 **/
private String txt;
/** 圆半径 **/
private float mDrawableRadius; /** 字体背景画笔 **/
private Paint mBackgroundPaint;
/** 字体画笔 **/
private Paint mTxtPaint; public DCircleButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
initAttrs(context, attrs);
init();
}
/** 初始化 **/
private void init() {
mBackgroundPaint = new Paint();
mBackgroundPaint.setColor(backgroundColor); mTxtPaint = new Paint();
mTxtPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER);
mTxtPaint.setColor(txtColor);
mTxtPaint.setTextSize(txtSize);
} @Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
mDrawableRadius = Math.min(getWidth() >> 1, getHeight() >> 1);
canvas.drawCircle(getWidth() >> 1, getHeight() >> 1, mDrawableRadius, mBackgroundPaint);
if (null != txt)
canvas.drawText(txt, getWidth() >> 1, getHeight() >> 1, mTxtPaint);
}
3. 布局中应用
<dinn.circle.button.DCircleButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:text="我是按钮"
app:txtBackgroundColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark"
app:txtColor="@android:color/white"
app:txtSize="20sp" />
4. 运行结果
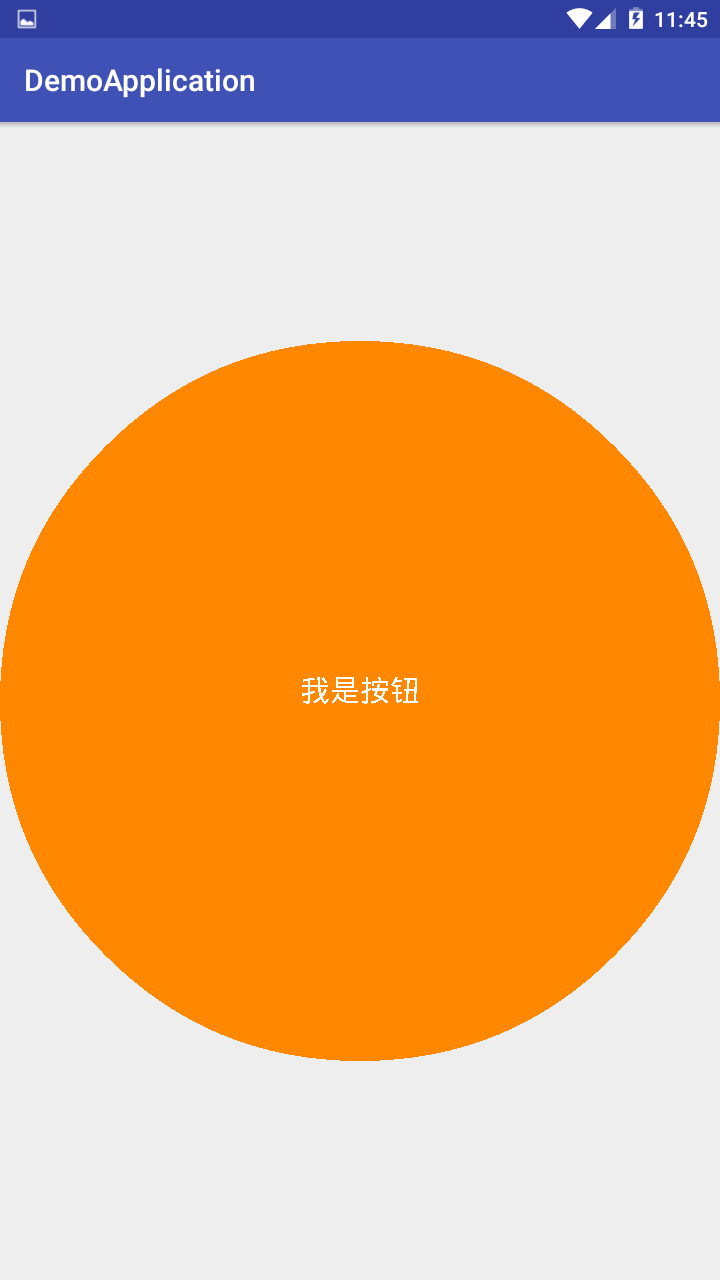
这个时候回发现按钮是充满屏幕的,但是布局中我们设置的尺寸属性为“wrap_content”。其实是由于我们在自定义View的流程中还有一个onMeasure方法没有重写。
5. 重写onMeasure控制View的大小
当你没有重写onMeasure方法时候,系统调用默认的onMeasure方法。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
这个方法的作用是:测量控件的大小。其实Android系统在加载布局的时候是由系统测量各子View的大小来告诉父View我需要占多大空间,然后父View会根据自己的大小来决定分配多大空间给子View。
那么从上面的效果来看,当你在布局中设置View的大小为”wrap_content”时,其实系统测量出来的大小是“match_parent”。为什么会是这样子呢?
那得从MeasureSpec的specMode模式说起了。一共有三种模式:
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:父视图希望子视图的大小是specSize中指定的大小;一般是设置了明确的值或者是MATCH_PARENT。
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:子视图的大小最多是specSize中的大小;表示子布局限制在一个最大值内,一般为WARP_CONTENT。
MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:父视图不对子视图施加任何限制,子视图可以得到任意想要的大小;表示子布局想要多大就多大,很少使用。
我们看看系统源码 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 是如何实现的:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
从上面的代码 getDefaultSize() 方法中看出,原来 MeasureSpec.AT_MOST 和 MeasureSpec.EXACTLY 走的是同一个分支,也就是父视图希望子视图的大小是specSize中指定的大小。
得出来的默认值就是填充整个父布局。因此,不管你布局大小是 ”wrap_content” 还是 “match_parent” 效果都是充满整个父布局。那我想要 ”wrap_content” 的效果怎么办?那么只有重写onMeasure方法了。
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 测量模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
// 父布局希望子布局的大小,如果布局里面设置的是固定值,这里取布局里面的固定值和父布局大小值中的最小值.
// 如果设置的是match_parent,则取父布局的大小
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int width;
int height;
Rect mBounds = new Rect();
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = widthSize;
} else {
mTxtPaint.setTextSize(txtSize);
mTxtPaint.getTextBounds(txt, 0, txt.length(), mBounds);
float textWidth = mBounds.width();
int desired = (int) (getPaddingLeft() + textWidth + getPaddingRight());
width = desired;
} if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = heightSize;
} else {
height = width;
}
// 最后调用父类方法,把View的大小告诉父布局。
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
这样实现的最终效果如下:

Android自绘制控件的更多相关文章
- Android 中常见控件的介绍和使用
1 TextView文本框 1.1 TextView类的结构 TextView 是用于显示字符串的组件,对于用户来说就是屏幕中一块用于显示文本的区域.TextView类的层次关系如下: java.la ...
- 【风马一族_Android】第4章Android常用基本控件
第4章Android常用基本控件 控件是Android用户界面中的一个个组成元素,在介绍它们之前,读者必须了解所有控件的父类View(视图),它好比一个盛放控件的容器. 4.1View类概述 对于一个 ...
- Android自己定义控件系列五:自己定义绚丽水波纹效果
尊重原创!转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/cyp331203/article/details/41114551 今天我们来利用Android自己定义控件实现一个比較有趣的效果 ...
- 带着问题写React Native原生控件--Android视频直播控件
最近在做的采用React Native项目有一个需求,视频直播与直播流播放同一个布局中,带着问题去思考如何实现,能更容易找到问题关键点,下面分析这个控件解决方法: 现在条件:视频播放控件(开源的ijk ...
- Android自己定义控件:进度条的四种实现方式
前三种实现方式代码出自: http://stormzhang.com/openandroid/2013/11/15/android-custom-loading/ (源代码下载)http://down ...
- Android自定义view控件
转载自: http://blog.163.com/ppy2790@126/blog/static/103242241201382210910473/ 开发自定义控件的步骤: 1.了解View的工作原理 ...
- android 自己定义控件
Android自己定义View实现非常easy 继承View,重写构造函数.onDraw.(onMeasure)等函数. 假设自己定义的View须要有自己定义的属性.须要在values下建立attrs ...
- Android笔记---常用控件以及用法
这篇文章主要记录下Android的常用控件以及使用的方法,Android 给我们提供了大量的UI控件,合理地使用这些控件就可以非常轻松地编写出相当不错的界面,这些是Android学习的基础,没有什么业 ...
- Android中ListView控件的使用
Android中ListView控件的使用 ListView展示数据的原理 在Android中,其实ListView就相当于web中的jsp,Adapter是适配器,它就相当于web中的Servlet ...
随机推荐
- Aircoinst 三层架构ASP.NET开源
<注意! 本源码为我本人所写,可能有点烂.仅供学习使用,请勿进行商业用途~!> <本源码永久归于MineLSG 及 Aircoinst_慈 所拥有> 使用方法:直接拷贝 一.结 ...
- Android | 教你如何用代码开发一个拍照翻译小程序
引子 想必有很多小伙伴喜欢外出旅游,能去海外玩一圈那是更好不过了,旅游前大家一定会对吃.穿.住.行.游玩路线做各种攻略,然后满怀期待的出发- 想象中的旅游 出发前,想象中的旅游目的地可能有漂亮 ...
- ASP.NET Core中的Controller
ASP.NET CORE出现之前我们实现的Controller,MVC都继承自Controller基类,WebApi的话继承自ApiController.现在ASP.NET CORE把MVC跟WebA ...
- flask-url参数
flask-url参数 无约束(string)传参 from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/<id>') de ...
- 汇编刷题 已知整数变量A和B,试编写完成下列操作的程序
1.若两个数中有一个是奇数,一个是偶数,则将它们互换储存地址 2.若两个数都是奇数,则分别加一 3.若两个数都是偶数,则不变 DATA SEGMENT A DB 12H B DB 25H DATA E ...
- javascript入门 之 ztree (十 checkbox选中事件)
<!DOCTYPE html> <HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE> ZTREE DEMO - beforeCheck / onCheck< ...
- python-从酷狗下载爬取自己想要的音乐-可以直接拿来体验哟
因为最近发现咪咕音乐版权好多,当时我就在想是不是可以爬取下来,然后花了一些时间,发现有加密,虽然找到了接口,但是只能手动下载VIP歌曲,对于我们学IT的人来说,这是不能忍的,于是就懒得去解密抓取了,但 ...
- Java编程最差实践常见问题详细说明(1)转
Java编程最差实践常见问题详细说明(1)转 原文地址:http://www.odi.ch/prog/design/newbies.php 每天在写Java程序, 其实里面有一些细节大家可能没 ...
- 如何教零基础的人认识Python
前言 文的文字及图片来源于网络,仅供学习.交流使用,不具有任何商业用途,版权归原作者所有,如有问题请及时联系我们以作处理. 作者: 编程派 PS:如有需要Python学习资料的小伙伴可以加点击下方链接 ...
- stand up meeting 1/14/2016
part 组员 工作 工作耗时/h 明日计划 工作耗时/h UI 冯晓云 主要对生词本卡片的整体设计做修改:协助主程序完成popup部分 ...
