Codeforces Round #632 (Div. 2) 题解
空山新雨后,天气晚来秋。
明月松间照,清泉石上流。
竹喧归浣女,莲动下渔舟。
随意春芳歇,王孙自可留。——王维
A. Little Artem
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1333/problem/A
Young boy Artem tries to paint a picture, and he asks his mother Medina to help him. Medina is very busy, that's why she asked for your help.
Artem wants to paint an n×m board. Each cell of the board should be colored in white or black.
Lets B be the number of black cells that have at least one white neighbor adjacent by the side. Let W be the number of white cells that have at least one black neighbor adjacent by the side. A coloring is called good if B=W+1.
The first coloring shown below has B=5 and W=4 (all cells have at least one neighbor with the opposite color). However, the second coloring is not good as it has B=4, W=4 (only the bottom right cell doesn't have a neighbor with the opposite color).
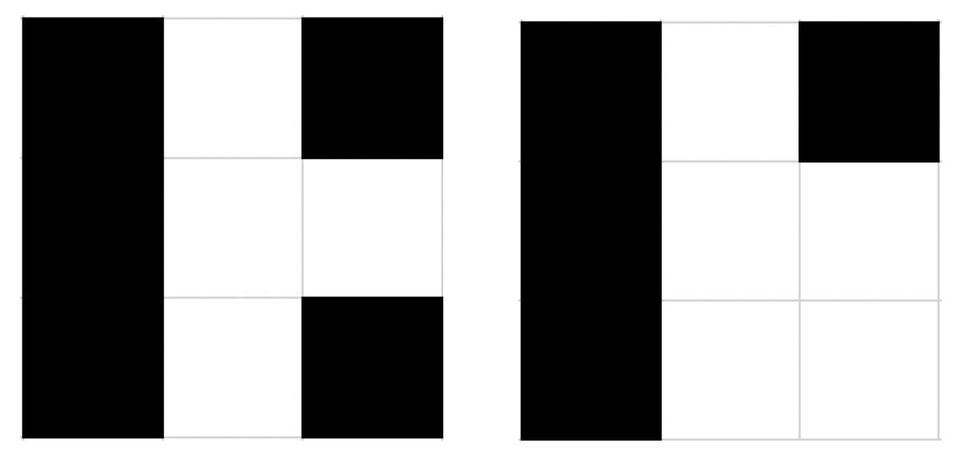
Please, help Medina to find any good coloring. It's guaranteed that under given constraints the solution always exists. If there are several solutions, output any of them.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases.
The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤20). Each of the next t lines contains two integers n,m (2≤n,m≤100) — the number of rows and the number of columns in the grid.
Output
For each test case print n lines, each of length m, where i-th line is the i-th row of your colored matrix (cell labeled with 'B' means that the cell is black, and 'W' means white). Do not use quotes.
It's guaranteed that under given constraints the solution always exists.
Example
input
2
3 2
3 3
output
BW
WB
BB
BWB
BWW
BWB
Note
In the first testcase, B=3, W=2.
In the second testcase, B=5, W=4. You can see the coloring in the statement.
此题考验直觉(算法真功夫),最简单地,直接将图形左上角涂成W,其余都为B即可。
可惜,我的功夫不够,讨论了半天,当时代码:
https://codeforces.com/contest/1333/submission/76088370
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
putchar('W');
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++ i)
{
putchar('B');
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++ i)
{
puts("");
for(int j = 0; j < m; ++ j)
putchar('B');
}
}
return 0;
}
B. Kind Anton
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1333/problem/B
Once again, Boris needs the help of Anton in creating a task. This time Anton needs to solve the following problem:
There are two arrays of integers a and b of length n. It turned out that array a contains only elements from the set {−1,0,1}.
Anton can perform the following sequence of operations any number of times:
Choose any pair of indexes (i,j) such that 1≤i<j≤n. It is possible to choose the same pair (i,j) more than once.
Add ai to aj. In other words, j-th element of the array becomes equal to ai+aj.
For example, if you are given array [1,−1,0], you can transform it only to [1,−1,−1], [1,0,0] and [1,−1,1] by one operation.
Anton wants to predict if it is possible to apply some number (zero or more) of these operations to the array a so that it becomes equal to array b. Can you help him?
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases.
The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤10000). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1≤n≤105) — the length of arrays.
The second line of each test case contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (−1≤ai≤1) — elements of array a. There can be duplicates among elements.
The third line of each test case contains n integers b1,b2,…,bn (−109≤bi≤109) — elements of array b. There can be duplicates among elements.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 105.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing "YES" if it's possible to make arrays a and b equal by performing the described operations, or "NO" if it's impossible.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
Example
input
5
3
1 -1 0
1 1 -2
3
0 1 1
0 2 2
2
1 0
1 41
2
-1 0
-1 -41
5
0 1 -1 1 -1
1 1 -1 1 -1
output
YES
NO
YES
YES
NO
Note
In the first test-case we can choose (i,j)=(2,3) twice and after that choose (i,j)=(1,2) twice too. These operations will transform [1,−1,0]→[1,−1,−2]→[1,1,−2]
In the second test case we can't make equal numbers on the second position.
In the third test case we can choose (i,j)=(1,2) 41 times. The same about the fourth test case.
In the last lest case, it is impossible to make array a equal to the array b.
题意概述:
给你由0、1、-1构成的序列a,要求每次操作可以选择两个数(i,j),使得a[j] += a[i],问你是否可以将序列a转化为b。
考虑:a[i] < b[i]则意味着当i之前存在着某个数>0,换句话说:a[i] > b[j]意味着i之前存在某个数<0,否则无法完成转化操作。
不解释。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#define maxn 200000 + 6
using namespace std;
int n, a[maxn], b[maxn], s_plus[maxn] = {}, s_minus[maxn] = {};
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if(a[i] == -1)
{
s_minus[i] = s_minus[i - 1] + 1;
s_plus[i] = s_plus[i - 1];
}
else if(a[i] == 1)
{
s_minus[i] = s_minus[i - 1];
s_plus[i] = s_plus[i - 1] + 1;
} else s_plus[i] = s_plus[i - 1], s_minus[i] = s_minus[i - 1];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) scanf("%d", &b[i]);
if(a[1] != b[1])
{
puts("NO");
memset(s_plus, 0, sizeof(s_plus));
memset(s_minus, 0, sizeof(s_minus));
continue;
}
bool valid = true;
for(int i = n; i >= 2; -- i)
{
if(a[i] == b[i]) continue;
if(a[i] < b[i])
{
if(s_plus[i - 1]) continue;
else
{
puts("NO");
valid = false;
break;
}
}
else
{
if(s_minus[i - 1]) continue;
else
{
puts("NO");
valid = false;
break;
}
}
}
memset(s_plus, 0, sizeof(s_plus));
memset(s_minus, 0, sizeof(s_minus));
if(valid) puts("YES");
}
return 0;
}
C. Eugene and an array
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1333/problem/C
Eugene likes working with arrays. And today he needs your help in solving one challenging task.
An array c is a subarray of an array b if c can be obtained from b by deletion of several (possibly, zero or all) elements from the beginning and several (possibly, zero or all) elements from the end.
Let's call a nonempty array good if for every nonempty subarray of this array, sum of the elements of this subarray is nonzero. For example, array [−1,2,−3] is good, as all arrays [−1], [−1,2], [−1,2,−3], [2], [2,−3], [−3] have nonzero sums of elements. However, array [−1,2,−1,−3] isn't good, as his subarray [−1,2,−1] has sum of elements equal to 0.
Help Eugene to calculate the number of nonempty good subarrays of a given array a.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1≤n≤2×105) — the length of array a.
The second line of the input contains n integers a1,a2,…,an (−109≤ai≤109) — the elements of a.
Output
Output a single integer — the number of good subarrays of a.
Examples
input
3
1 2 -3
output
5
input
3
41 -41 41
output
3
Note
In the first sample, the following subarrays are good: [1], [1,2], [2], [2,−3], [−3]. However, the subarray [1,2,−3] isn't good, as its subarray [1,2,−3] has sum of elements equal to 0.
In the second sample, three subarrays of size 1 are the only good subarrays. At the same time, the subarray [41,−41,41] isn't good, as its subarray [41,−41] has sum of elements equal to 0.
这道题很不错,足以迷惑我。还是基础不扎实。
预处理前缀和。如果[L,R]和为0,那么有:
s[R] = s[L - 1];
接着就变成了刘汝佳的“滑动窗口”;
- 每次枚举“g好”序列的左端点,向右扩展直到有重复的停止扩展;
- 将该序列长度累和;
- 重复上述过程;
- 具体讲解见刘汝佳《算法竞赛 入门经典》chapter 8;
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 200000 + 5;
set <long long> cur;
int n, a[maxn];
long long s[maxn];
int main()
{
cur.clear();
memset(s, 0, sizeof(s));
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
}
int head = 0, tail = 0;
long long sum = 0;
while(head <= n)
{
while(!cur.count(s[tail]) && tail <= n)
{
cur.insert(s[tail]);
++ tail;
}
sum += tail - head - 1;
cur.erase(s[head]);
++ head;
}
printf("%lld\n", sum);
return 0;
}
D. Challenges in school №41
网址:https://codeforces.com/contest/1333/problem/D?csrf_token=752bb72c3fd70a04956d182748915494
There are n children, who study at the school №41. It is well-known that they are good mathematicians. Once at a break, they arranged a challenge for themselves. All children arranged in a row and turned heads either to the left or to the right.
Children can do the following: in one second several pairs of neighboring children who are looking at each other can simultaneously turn the head in the opposite direction. For instance, the one who was looking at the right neighbor turns left and vice versa for the second child. Moreover, every second at least one pair of neighboring children performs such action. They are going to finish when there is no pair of neighboring children who are looking at each other.
You are given the number n, the initial arrangement of children and the number k. You have to find a way for the children to act if they want to finish the process in exactly k seconds. More formally, for each of the k moves, you need to output the numbers of the children who turn left during this move.
For instance, for the configuration shown below and k=2 children can do the following steps:
At the beginning, two pairs make move: (1,2) and (3,4). After that, we receive the following configuration:
At the second move pair (2,3) makes the move. The final configuration is reached. Good job.
It is guaranteed that if the solution exists, it takes not more than n2 "headturns".
Input
The first line of input contains two integers n and k (2≤n≤3000, 1≤k≤3000000) — the number of children and required number of moves.
The next line contains a string of length n and consists only of characters L and R, where L means that the child looks to the left and R means that the child looks to the right.
Output
If there is no solution, print a single line with number −1.
Otherwise, output k lines. Each line has to start with a number ni (1≤ni≤n2) — the number of pairs of children, who turn at this move. After that print ni distinct integers — the numbers of the children who will turn left during this move.
After performing all "headturns", there can't be a pair of two neighboring children looking at each other.
If there are many solutions, print any of them.
Examples
input
2 1
RL
output
1 1
input
2 1
LR
output
-1
input
4 2
RLRL
output
2 1 3
1 2
Note
The first sample contains a pair of children who look at each other. After one move, they can finish the process.
In the second sample, children can't make any move. As a result, they can't end in k>0 moves.
The third configuration is described in the statement.
这道题把朝向右看作0,朝向左看成1,操作相当于冒泡排序(但仍有区别);
具体地,在一步操作中,可以将(0,1)->(1,0),但如果存在相邻两数均为1的情况时,就不可以连续进行操作,需要特殊进行处理;
接着,记录两个参量:mink,maxk,前者代表最少可以操作的次数(每一次都把可以操作的全部操作),后者不难意识到,即为操作的总次数。
若k在[mink, maxk],则说明问题有解;否则,输出-1;
那么怎么分配就随意了,我的做法是将操作记录在mink中,每一次的总操作数量和实际操作数比较,若大于,则将该mink操作全部拆为k + 1次操作;否则,能拆多少就拆多少;
若剩余的mink操作数等于当前实际剩余操作数,就按照预处理的顺次输出答案。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#define maxn 3000 + 5
using namespace std;
vector <int> book[maxn];
int n, k, a[maxn], mink, maxk;
int main()
{
char ch[maxn];
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
scanf("%s", ch);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
if(ch[i] == 'L') a[i] = 1;
else a[i] = 0;
}
maxk = mink = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++ i)
{
int cnt = 0;
book[i].clear();
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++ j)
{
if(a[j] > a[j - 1])
{
swap(a[j], a[j - 1]);
book[i].push_back(j);
++ j;
++ cnt;
}
}
if(cnt == 0) break;
++ mink;
maxk += cnt;
}
if(k < mink || k > maxk) puts("-1");
else
{
int i, j, delta, num = k;
for(i = 0; i < mink; ++ i)
{
delta = num - (mink - i);
if(delta == 0)
{
printf("%d ", book[i].size());
for(j = 0; j < book[i].size(); ++ j)
printf("%d ", book[i][j]);
puts("");
-- num;
}
else
{
int tmp = (book[i].size() - 1) - delta;
if(tmp <= 0)
{
for(j = 0; j < book[i].size(); ++ j) printf("1 %d\n", book[i][j]);
num -= book[i].size();
}
else
{
num -= delta + 1;
for(j = 0; j < delta; ++ j) printf("1 %d\n", book[i][j]);
printf("%d ", book[i].size() - delta);
for(j = delta; j < book[i].size(); ++ j) printf("%d ", book[i][j]);
puts("");
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #632 (Div. 2) 题解的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #632 (Div. 2)
Codeforces Round #632 (Div. 2) 这一场打的好差呀,这几次艰难上的分全部掉回去了,感觉就像一夜回到了解放前. 说实话,就是被B卡到了,没看到只能从小的放到大的... Lit ...
- Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #182 (Div. 1)题解 A题:Yaroslav and Sequence1 题意: 给你\(2*n+1\)个元素,你每次可以进行无数种操作,每次操作必须选择其 ...
- Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解
目录 Codeforces Round #608 (Div. 2) 题解 前言 A. Suits 题意 做法 程序 B. Blocks 题意 做法 程序 C. Shawarma Tent 题意 做法 ...
- Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #525 (Div. 2)题解 题解 CF1088A [Ehab and another construction problem] 依据题意枚举即可 # inclu ...
- Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解
Codeforces Round #528 (Div. 2)题解 A. Right-Left Cipher 很明显这道题按题意逆序解码即可 Code: # include <bits/stdc+ ...
- Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解940A 940B 940C 940D 940E 940F
Codeforces Round #466 (Div. 2) 题解 A.Points on the line 题目大意: 给你一个数列,定义数列的权值为最大值减去最小值,问最少删除几个数,使得数列的权 ...
- Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解
Codeforces Round #677 (Div. 3) 题解 A. Boring Apartments 题目 题解 简单签到题,直接数,小于这个数的\(+10\). 代码 #include &l ...
- Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解
Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题解 写得有点晚了,估计都官方题解看完切掉了,没人看我的了qaq. 目录 Codeforces Round #665 (Div. 2) 题 ...
- Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) 题解【ABCD】
Codeforces Round #160 (Div. 1) A - Maxim and Discounts 题意 给你n个折扣,m个物品,每个折扣都可以使用无限次,每次你使用第i个折扣的时候,你必须 ...
随机推荐
- 对oracle里面clob字段里面xml的增删改查学习
这段时间,我使用系统表里面有clob字段里面存放的xml信息,我们如何对xml进行增删改查操作呢,自己参考了很多也学到很多,给大家分享一下 首先我们先建测试表 CREATE TABLE EFGP_23 ...
- Codeforces 631 (Div. 2) D. Dreamoon Likes Sequences 位运算^ 组合数 递推
https://codeforces.com/contest/1330/problem/D 给出d,m, 找到一个a数组,满足以下要求: a数组的长度为n,n≥1; 1≤a1<a2<⋯&l ...
- linux神器 strace解析
除了人格以外,人最大的损失,莫过于失掉自信心了. 前言 strace可以说是神器一般的存在了,对于研究代码调用,内核级调用.系统级调用有非常重要的作用.打算了一周了,只有原文,一直没有梳理,拖延症犯了 ...
- django-rest-framework权限验证
django-rest-framework权限验证 在项目根目录下新建utils的文件 新建permissions.py from rest_framework.permissions import ...
- 搭建环境-git常见使用总结
Descripton:git 一.Git安装和本地用户全局配置 官网下载并且安装 查看是否安装成功win + R输入git,出现git命令指南,则安装成功 全局配置本地用户,在git Bash中进行下 ...
- 28.2 api-- System (gc、arraycopy、exit)
/* * System:包含一些有用的类字段和方法.它不能被实例化 * static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int d ...
- 22 Extends 继承(子类、父类)
本章主要介绍继承的 概念.方法重写(@Override注解的使用).使用场景.方法的执行顺序 /*1.继承的 概念 * 继承:多个类有共同的成员变量和成员方法,抽取到另外一个类中(父类),在让多个类去 ...
- C# 基础知识系列- 9 字符串的更多用法(二)
0. 前言 上一篇文章介绍了字符串自身的一些方法,就是对象方法.在字符串体系中,还有一些是string类提供的静态方法.这两部分构成了字符串体系,当然还有一些三方库为字符串提供了扩展方法. 这里简单的 ...
- coding++:Spring 中的 AOP 原理
为什么使用 AOP 如下场景: 现在有一个情景: 我们要把大象放进冰箱,步骤为:打开冰箱->放入大象->关闭冰箱 如果再把大象拿出来,步骤为:打开冰箱->拿出大象->关闭冰箱 ...
- JuiceSSH:安卓平台免费好用的 SSH 客户端
为了解决上下班路上或者没带电脑时,查看 Linux 服务器日志或者紧急运维的需求,最终找到了 JuiceSSH 这款软件,强烈推荐给大家. 简介 JuiceSSH 是一个为 Android 打造的全功 ...
