【分布式锁】01-使用Redisson实现可重入分布式锁原理
前言
主流的分布式锁一般有三种实现方式:
- 数据库乐观锁
- 基于Redis的分布式锁
- 基于ZooKeeper的分布式锁
之前我在博客上写过关于mysql和redis实现分布式锁的具体方案:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wang-meng/p/10226618.html
里面主要是从实现原理出发。
这次【分布式锁】系列文章主要是深入redis客户端reddision源码和zk 这两种分布式锁的实现原理。
可靠性
首先,为了确保分布式锁可用,我们至少要确保锁的实现同时满足以下四个条件:
- 互斥性。在任意时刻,只有一个客户端能持有锁。
- 不会发生死锁。即使有一个客户端在持有锁的期间崩溃而没有主动解锁,也能保证后续其他客户端能加锁。
- 具有容错性。只要大部分的Redis节点正常运行,客户端就可以加锁和解锁。
- 解铃还须系铃人。加锁和解锁必须是同一个客户端,客户端自己不能把别人加的锁给解了。
Redisson加锁原理
redisson是一个非常强大的开源的redis客户端框架, 官方地址:
https://redisson.org/
使用起来很简单,配置好maven和连接信息,这里直接看代码实现:
- RLock lock = redisson.getLock("anyLock");
- lock.lock();
- lock.unlock();
redisson具体的执行加锁逻辑都是通过lua脚本来完成的,lua脚本能够保证原子性。
先看下RLock初始化的代码:
- public class Redisson implements RedissonClient {
- @Override
- public RLock getLock(String name) {
- return new RedissonLock(connectionManager.getCommandExecutor(), name);
- }
- }
- public class RedissonLock extends RedissonExpirable implements RLock {
- public RedissonLock(CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
- super(commandExecutor, name);
- this.commandExecutor = commandExecutor;
- this.id = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getId();
- this.internalLockLeaseTime = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout();
- this.entryName = id + ":" + name;
- }
首先看下RedissonLock 的id返回的是一个UUID对象,每个机器都对应一个自己的id属性,id 值就类似于:"8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586"
接着往后看lock()的代码实现:
- public class RedissonLock extends RedissonExpirable implements RLock {
- @Override
- public void lock() {
- try {
- lockInterruptibly();
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
- }
- }
- @Override
- public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
- lockInterruptibly(-1, null);
- }
- @Override
- public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
- // 获取当前线程id
- long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
- Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
- // lock acquired
- if (ttl == null) {
- return;
- }
- RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
- commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
- try {
- while (true) {
- ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
- // lock acquired
- if (ttl == null) {
- break;
- }
- // waiting for message
- if (ttl >= 0) {
- getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- } else {
- getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
- }
- }
- } finally {
- unsubscribe(future, threadId);
- }
- }
- <T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) {
- internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
- return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
- "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
- "redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return nil; " +
- "end; " +
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
- "redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return nil; " +
- "end; " +
- "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
- Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()), internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
- }
- }
这里省略了一些中间代码,这里主要看tryAcquire() 方法,这里传递的过期时间为-1,然后就是当前的线程id,接着就是核心的lua脚本执行流程,我们来一步步看看是如何执行的:
- "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
- "redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return nil; " +
- "end; " +
KEYS[1] 参数是:“anyLock”ARGV[2] 是:“id + ":" + threadId”
首先用的exists 判断redis中是否存在当前key,如果不存在就等于0,然后执行hset指令,将“anyLock id:threadId 1”存储到redis中,最终redis存储的数据类似于:
- {
- "8743c9c0-0795-4907-87fd-6c719a6b4586:1":1
- }
偷偷说一句,最后面的一个1 是为了后面可重入做的计数统计,后面会有讲解到。
接着往下看,然后使用pexpire设置过期时间,默认使用internalLockLeaseTime为30s。最后返回为null,即时加锁成功。
Redisson 可重入原理
我们看下锁key存在的情况下,同一个机器同一个线程如何加锁的?
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
- "redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return nil; " +
- "end; " +
- "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
ARGV[2] 是:“id + ":" + threadId”
如果同一个机器同一个线程再次来请求,这里就会是1,然后执行hincrby, hset设置的value+1 变成了2,然后继续设置过期时间。
同理,一个线程重入后,解锁时value - 1
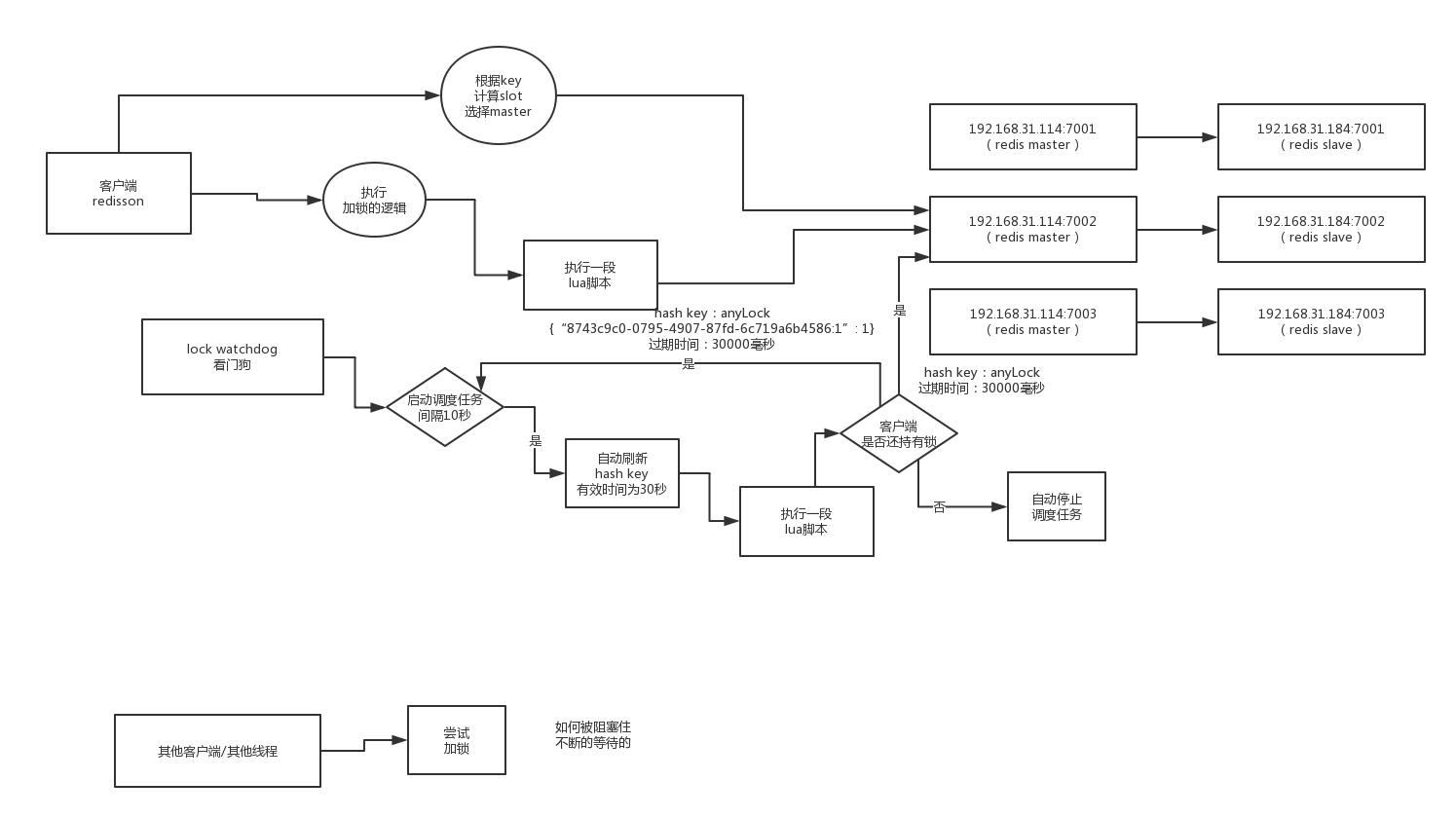
Redisson watchDog原理
如果一个场景:现在有A,B在执行业务,A加了分布式锁,但是生产环境是各种变化的,如果万一A锁超时了,但是A的业务还在跑。而这时由于A锁超时释放,B拿到锁,B执行业务逻辑。这样分布式锁就失去了意义?
所以Redisson 引入了watch dog的概念,当A获取到锁执行后,如果锁没过期,有个后台线程会自动延长锁的过期时间,防止因为业务没有执行完而锁过期的情况。
我们接着来看看具体实现:
- private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, final long threadId) {
- if (leaseTime != -1) {
- return tryLockInnerAsync(leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
- }
- RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().getCfg().getLockWatchdogTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
- ttlRemainingFuture.addListener(new FutureListener<Long>() {
- @Override
- public void operationComplete(Future<Long> future) throws Exception {
- if (!future.isSuccess()) {
- return;
- }
- Long ttlRemaining = future.getNow();
- // lock acquired
- if (ttlRemaining == null) {
- scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);
- }
- }
- });
- return ttlRemainingFuture;
- }
当我们tryLockInnerAsync执行完之后,会添加一个监听器,看看监听器中的具体实现:
- protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
- return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return 1; " +
- "end; " +
- "return 0;",
- Collections.<Object>singletonList(getName()),
- internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
- }
这里面调度任务每隔10s钟执行一次,lua脚本中是续约过期时间,使得当前线程持有的锁不会因为过期时间到了而失效
 01_redisson watchdog_.png
01_redisson watchdog_.png
Redisson 互斥性原理
还是看上面执行加锁的lua脚本,最后会执行到:
- "return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);",
返回锁还有多久时间过期,我们继续接着看代码:
- @Override
- public void lockInterruptibly(long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
- long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
- Long ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
- // 返回ttl说明加锁成功,不为空则是加锁失败
- if (ttl == null) {
- return;
- }
- RFuture<RedissonLockEntry> future = subscribe(threadId);
- commandExecutor.syncSubscription(future);
- try {
- // 死循环去尝试获取锁
- while (true) {
- // 再次尝试加锁
- ttl = tryAcquire(leaseTime, unit, threadId);
- // 如果ttl=null说明抢占锁成功
- if (ttl == null) {
- break;
- }
- // ttl 大于0,抢占锁失败,这个里面涉及到Semaphore,后续会讲解
- if (ttl >= 0) {
- getEntry(threadId).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
- } else {
- getEntry(threadId).getLatch().acquire();
- }
- }
- } finally {
- unsubscribe(future, threadId);
- }
- }
Redisson锁释放原理
直接看lua代码:
- protected RFuture<Boolean> unlockInnerAsync(long threadId) {
- return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
- // 判断锁key值是否存在
- "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then " +
- "redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return 1; " +
- "end;" +
- // 判断当前机器、当前线程id对应的key是否存在
- "if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[3]) == 0) then " +
- "return nil;" +
- "end; " +
- // 计数器数量-1 可重入锁
- "local counter = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[3], -1); " +
- // 如果计数器大于0,说明还在持有锁
- "if (counter > 0) then " +
- "redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]); " +
- "return 0; " +
- "else " +
- // 使用del指令删除key
- "redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); " +
- "redis.call('publish', KEYS[2], ARGV[1]); " +
- "return 1; "+
- "end; " +
- "return nil;",
- Arrays.<Object>asList(getName(), getChannelName()), LockPubSub.unlockMessage, internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
- }
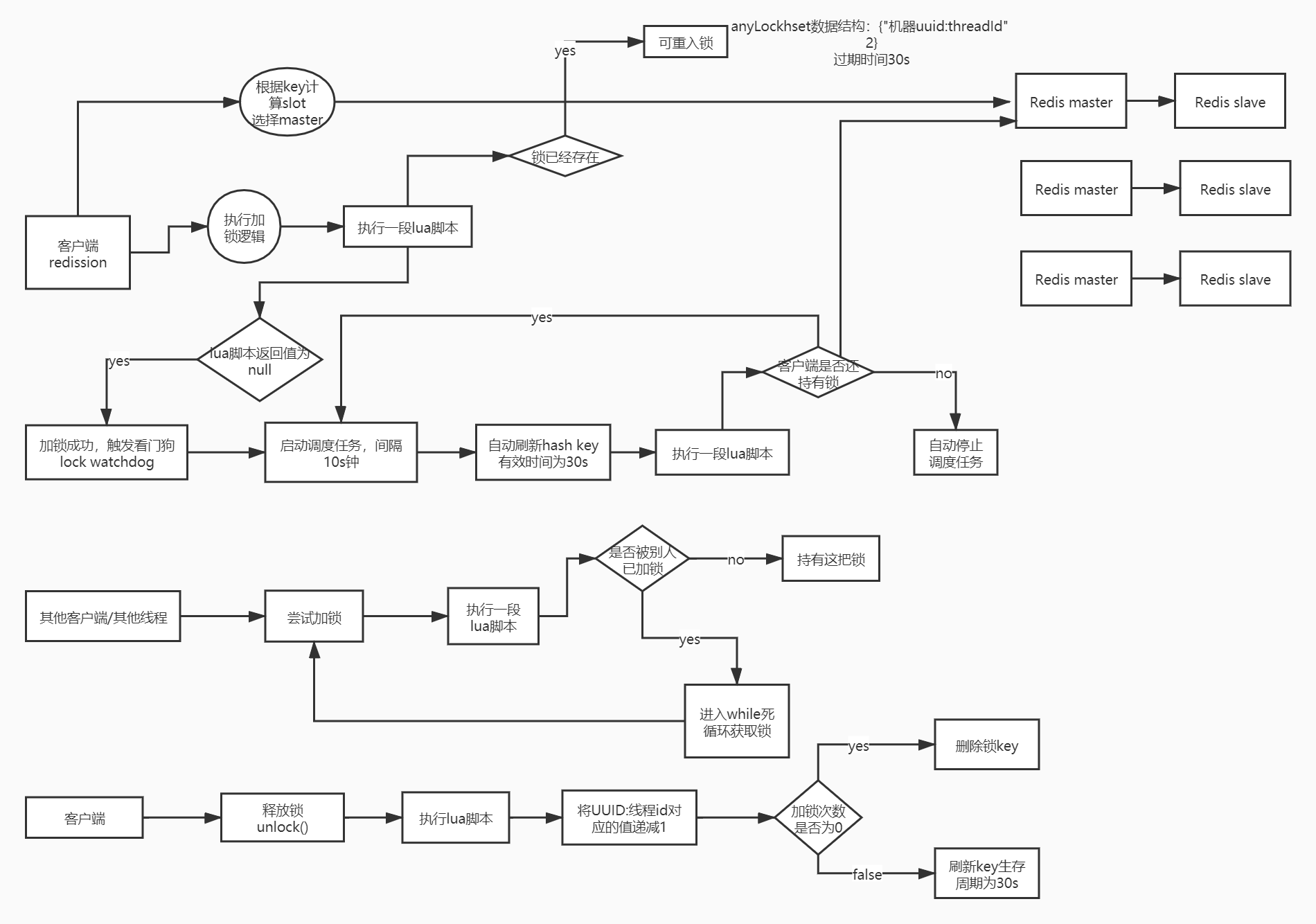
总结
一图总结:
 01_redission 可重入锁实现原理.jpg
01_redission 可重入锁实现原理.jpg
【分布式锁】01-使用Redisson实现可重入分布式锁原理的更多相关文章
- Redis分布式锁—Redisson+RLock可重入锁实现篇
前言 平时的工作中,由于生产环境中的项目是需要部署在多台服务器中的,所以经常会面临解决分布式场景下数据一致性的问题,那么就需要引入分布式锁来解决这一问题. 针对分布式锁的实现,目前比较常用的就如下几种 ...
- 四、curator recipes之共享重入互斥锁
简介 curator的recipes实现了可重入互斥锁,允许你在分布式场景下多个进程之间实现锁的互斥以协调多进程执行. 相关类:InterProcessMutex 官方文档:http://curato ...
- 线程执行synchronized同步代码块时再次重入该锁过程中抛异常,是否会释放锁
一个线程执行synchronized同步代码时,再次重入该锁过程中,如果抛出异常,会释放锁吗? 如果锁的计数器为1,抛出异常,会直接释放锁: 那如果锁的计数器为2,抛出异常,会直接释放锁吗? 来简单测 ...
- 可重入排他锁ReentrantLock源码浅析
1.引子 "ReentrantLock"单词中的“Reentrant”就是“重入”的意思,正如其名,ReentrantLock是一个支持重入的排他锁,即同一个线程中可以多次获得同步 ...
- redis 不可重入分布式锁(setNx()和getset()方法实现)
通常如果在单机环境,使用synchronized或juc ReentrantLock 实现锁机制,但如果是分布式系统,则需要借助第三方工具实现,比如redis.zookeeper等.redis为单进程 ...
- redis实现分布式锁需要考虑的因素以及可重入锁实现
死锁 错误例子 解决方式 防止死锁 通过设置超时时间 不要使用setnx key expire 20 不能保证原子性 如果setnx程序就挂了 没有执行expire就死锁了 reidis2 ...
- Java并发编程原理与实战十一:锁重入&自旋锁&死锁
一.锁重入 package com.roocon.thread.t6; public class Demo { /* 当第一个线程A拿到当前实例锁后,进入a方法,那么,线程A还能拿到被当前实例所加锁的 ...
- ReentrantReadWriteLock可重入,锁升级,锁降级
public class ReentrantReadWriteLockTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedE ...
- Java并发包源码学习系列:ReentrantLock可重入独占锁详解
目录 基本用法介绍 继承体系 构造方法 state状态表示 获取锁 void lock()方法 NonfairSync FairSync 公平与非公平策略的差异 void lockInterrupti ...
随机推荐
- JAVA递归、非递归遍历二叉树
前序遍历:1.访问根节点 2.前序遍历左子树 3.前序遍历右子树 中序遍历:1.中序遍历左子树 2.访问根节点 3.中序遍历右子树 后序遍历:1.后序遍历左子树 2.后序遍历右子树 3.访问根节点-- ...
- JSF技术web.xml配置解析
对Java tutorial-examples中jsf hell1的web.xml配置文件的解析 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF ...
- 我们一起学React Native(一):环境配置
最近想在项目中实现跨平台,对比一下主流的实现方式,选用了React Native.参考网上的教程,对于一直都是原生移动端开发,对前端的知识不是很了解的,感觉入门不是特别简单.于是打算把学习React ...
- Python Mock 的入门
Mock是什么 Mock这个词在英语中有模拟的这个意思,因此我们可以猜测出这个库的主要功能是模拟一些东西.准确的说,Mock是Python中一个用于支持单元测试的库,它的主要功能是使用mock对象替代 ...
- hihoCoder 1128 二分查找
Description Input and Output Codes 描述#1128 : 二分·二分查找 Description Nettle最近在玩<艦これ>,因此Nettle收集了很多 ...
- IDEA系列(九)Intellij IDEA界面介绍 - 哲也的博客
原文出处:https://github.com/judasn/IntelliJ-IDEA-Tutorial 首次打开 重点说明: IntelliJ IDEA 是没有类似 Eclipse 的工作空间的概 ...
- 【转载】Java DecimalFormat 用法
转载只供个人学习参考,以下查看请前往原出处:http://blog.csdn.net/wangchangshuai0010/article/details/8577982 我们经常要将数字进行格式化, ...
- 微软发布Microsoft Concept Graph和Microsoft Concept Tagging模型
Concept Graph和Microsoft Concept Tagging模型"> 当我们在讨论人工智能时,请注意,我们通常在讨论弱人工智能. 虽然我们现有的资源与之前可谓不同 ...
- python爬虫之selenium+打码平台识别验证码
1.常用的打码平台:超级鹰.打码兔等 2.打码平台在识别图形验证码和点触验证码上比较好用 (1)12306点触验证码 from selenium import webdriver from selen ...
- python settings 中通过字符串导入模块
1. 项目文件结构 set_test ├─ main.py # 入口函数 │ ├─notify # 自定义的模块 │ ├─ email.py # 自定义模块 │ ├─ msg.py # 自定义模块 │ ...
