shared_ptr的线程安全性
一:
All member functions (including copy constructor and copy assignment) can be called by multiple threads on different instances of shared_ptr without additional synchronization even if these instances are copies and share ownership of the same object. If multiple threads of execution access the same shared_ptr without synchronization and any of those accesses uses a non-const member function of shared_ptr then a data race will occur; the shared_ptr overloads of atomic functions can be used to prevent the data race.
多线程环境下,调用不同shared_ptr实例的成员函数是不需要额外的同步手段的,即使这些shared_ptr拥有的是同样的对象。但是如果多线程访问(有写操作)同一个shared_ptr,则需要同步,否则就会有race condition 发生。也可以使用 shared_ptr overloads of atomic functions 来防止race condition的发生。
To satisfy thread safety requirements, the reference counters are typically incremented using an equivalent of std::atomic::fetch_add with std::memory_order_relaxed (decrementing requires stronger ordering to safely destroy the control block).
shared_ptr的引用计数本身是安全且无锁的。
http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/memory/shared_ptr
二:
It is only the control block itself which is thread-safe.
I put that on its own line for emphasis. The contents of the shared_ptr are not thread-safe, nor is writing to the same shared_ptr instance. Here's something to demonstrate what I mean:
// In main()
shared_ptr<myClass> global_instance = make_shared<myClass>();
// (launch all other threads AFTER global_instance is fully constructed)
//In thread 1
shared_ptr<myClass> local_instance = global_instance;
This is fine, in fact you can do this in all threads as much as you want. And then when local_instance is destructed (by going out of scope), it is also thread-safe. Somebody can be accessing global_instance and it won't make a difference. The snippet you pulled from msdn basically means "access to the control block is thread-safe" so other shared_ptr<> instances can be created and destroyed on different threads as much as necessary.
//In thread 1
local_instance = make_shared<myClass>();
This is fine. It will affect the global_instance object, but only indirectly. The control block it points to will be decremented, but done in a thread-safe way. local_instance will no longer point to the same object (or control block) as global_instance does.
//In thread 2
global_instance = make_shared<myClass>();
This is almost certainly not fine if global_instance is accessed from any other threads (which you say you're doing). It needs a lock if you're doing this because you're writing to wherever global_instance lives, not just reading from it. So writing to an object from multiple threads is bad unless it's you have guarded it through a lock. So you can read from global_instance the object by assigning new shared_ptr<> objects from it but you can't write to it.
结论:多个线程同时读同一个shared_ptr对象是线程安全的,但是如果是多个线程对同一个shared_ptr对象进行读和写,则需要加锁。
// In thread 3
*global_instance = 3;
int a = *global_instance;
// In thread 4
*global_instance = 7;
The value of a is undefined. It might be 7, or it might be 3, or it might be anything else as well. The thread-safety of the shared_ptr<> instances only applies to managing shared_ptr<> instances which were initialized from each other, not what they're pointing to.
多线程读写shared_ptr所指向的同一个对象,不管是相同的shared_ptr对象,还是不同的shared_ptr对象,也需要加锁保护。例子如下:
shared_ptr<long> global_instance = make_shared<long>(0);
std::mutex g_i_mutex; void thread_fcn()
{
//std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(g_i_mutex); //shared_ptr<long> local = global_instance; for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
{
*global_instance = *global_instance + 1;
//*local = *local + 1;
}
} int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
thread thread1(thread_fcn);
thread thread2(thread_fcn); thread1.join();
thread2.join(); cout << "*global_instance is " << *global_instance << endl; return 0;
}
在线程函数thread_fcn的for循环中,2个线程同时对*global_instance进行加1的操作。这就是典型的非线程安全的场景,最后的结果是未定的,运行结果如下:
*global_instance is 197240539
如果使用的是每个线程的局部shared_ptr对象local,因为这些local指向相同的对象,因此结果也是未定的,运行结果如下:
*global_instance is 160285803
因此,这种情况下必须加锁,将thread_fcn中的第一行代码的注释去掉之后,不管是使用global_instance,还是使用local,得到的结果都是:
*global_instance is 200000000
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14482830/stdshared-ptr-thread-safety
三:为什么多线程读写 shared_ptr 要加锁?
以下内容,摘自陈硕的 http://blog.csdn.net/solstice/article/details/8547547
shared_ptr的引用计数本身是安全且无锁的,但对象的读写则不是,因为 shared_ptr 有两个数据成员(指向被管理对象的指针,和指向控制块的指针),读写操作不能原子化。根据文档(http://www.boost.org/doc/libs/release/libs/smart_ptr/shared_ptr.htm#ThreadSafety), shared_ptr 的线程安全级别和内建类型、标准库容器、std::string 一样,即:
• 一个 shared_ptr 对象实体可被多个线程同时读取(文档例1);
• 两个 shared_ptr 对象实体可以被两个线程同时写入(例2),“析构”算写操作;
• 如果要从多个线程读写同一个 shared_ptr 对象,那么需要加锁(例3~5)。
请注意,以上是 shared_ptr 对象本身的线程安全级别,不是它管理的对象的线程安全级别。
本文具体分析一下为什么“因为 shared_ptr 有两个数据成员,读写操作不能原子化”使得多线程读写同一个 shared_ptr 对象需要加锁。这个在我看来显而易见的结论似乎也有人抱有疑问,那将导致灾难性的后果,值得我写这篇文章。本文以 boost::shared_ptr 为例,与 std::shared_ptr 可能略有区别。
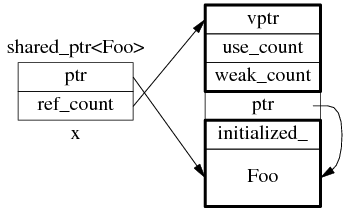
1:shared_ptr 的数据结构
shared_ptr 是引用计数型(reference counting)智能指针,几乎所有的实现都采用在堆(heap)上放个计数值(count)的办法(除此之外理论上还有用循环链表的办法,不过没有实例)。具体来说,shared_ptr<Foo> 包含两个成员,一个是指向 Foo 的指针 ptr,另一个是 ref_count 指针(其类型不一定是原始指针,有可能是 class 类型,但不影响这里的讨论),指向堆上的 ref_count 对象。ref_count 对象有多个成员,具体的数据结构如图 1 所示,其中 deleter 和 allocator 是可选的。
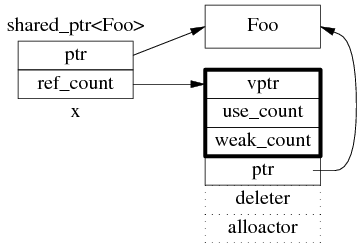
图 1:shared_ptr 的数据结构。
为了简化并突出重点,后文只画出 use_count 的值:
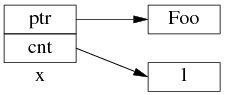
以上是 shared_ptr<Foo> x(new Foo); 对应的内存数据结构。
如果再执行 shared_ptr<Foo> y = x; 那么对应的数据结构如下。
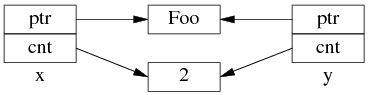
但是 y=x 涉及两个成员的复制,这两步拷贝不会同时(原子)发生。中间步骤 1,复制 ptr 指针:
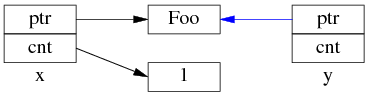
中间步骤 2,复制 ref_count 指针,导致引用计数加 1:
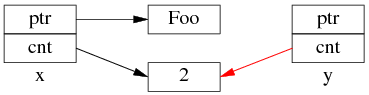
步骤1和步骤2的先后顺序跟实现相关(因此步骤 2 里没有画出 y.ptr 的指向),我见过的都是先1后2。
既然 y=x 有两个步骤,如果没有 mutex 保护,那么在多线程里就有 race condition。
2:多线程无保护读写 shared_ptr 可能出现的 race condition
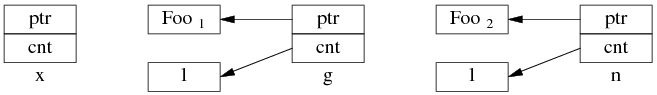
考虑一个简单的场景,有 3 个 shared_ptr<Foo> 对象 x、g、n:
shared_ptr<Foo> g(new Foo); // 线程之间共享的 shared_ptr
shared_ptr<Foo> x; // 线程 A 的局部变量
shared_ptr<Foo> n(new Foo); // 线程 B 的局部变量
一开始,各安其事:
线程 A 执行 x = g; (即 read g),以下完成了步骤 1,还没来及执行步骤 2。这时切换到了 B 线程。
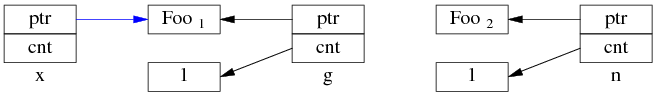
同时编程 B 执行 g = n; (即 write g),两个步骤一起完成了。先是步骤 1:
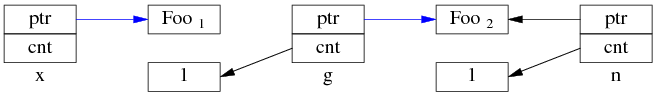
再是步骤 2:

这时 Foo1 对象已经销毁,x.ptr 成了空悬指针!
最后回到线程 A,完成步骤 2:
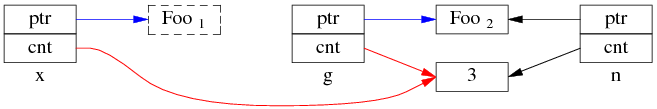
多线程无保护地读写 g,造成了“x 是空悬指针”的后果。这正是多线程读写同一个 shared_ptr 必须加锁的原因。
当然,race condition 远不止这一种,其他线程交织(interweaving)有可能会造成其他错误。
杂项
shared_ptr 作为 unordered_map 的 key
如果把 boost::shared_ptr 放到 unordered_set 中,或者用于 unordered_map 的 key,那么要小心 hash table 退化为链表。
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6404765/c-shared-ptr-as-unordered-sets-key/12122314#12122314
直到 Boost 1.47.0 发布之前,unordered_set<std::shared_ptr<T> > 虽然可以编译通过,但是其 hash_value 是 shared_ptr 隐式转换为 bool 的结果。也就是说,如果不自定义hash函数,那么 unordered_{set/map} 会退化为链表。https://svn.boost.org/trac/boost/ticket/5216
Boost 1.51 在 boost/functional/hash/extensions.hpp 中增加了有关重载,现在只要包含这个头文件就能安全高效地使用 unordered_set<std::shared_ptr> 了。
这也是 muduo 的 examples/idleconnection 示例要自己定义 hash_value(const boost::shared_ptr<T>& x) 函数的原因(书第 7.10.2 节,p.255)。因为 Debian 6 Squeeze、Ubuntu 10.04 LTS 里的 boost 版本都有这个 bug。
为什么要尽量使用 make_shared()?
为了节省一次内存分配,原来 shared_ptr<Foo> x(new Foo); 需要为 Foo 和 ref_count 各分配一次内存,现在用 make_shared() 的话,可以一次分配一块足够大的内存,供 Foo 和 ref_count 对象容身。数据结构是:
不过 Foo 的构造函数参数要传给 make_shared(),后者再传给 Foo::Foo(),这只有在 C++11 里通过 perfect forwarding 才能完美解决。
(.完.)
shared_ptr的线程安全性的更多相关文章
- shared_ptr的线程安全
1.9 再论shared_ptr 的线程安全 虽然我们借shared_ptr 来实现线程安全的对象释放,但是shared_ptr 本身不是100% 线程安全的.它的引用计数本身是安全且无锁的,但对象的 ...
- 关于java中final关键字与线程安全性
在Java5中,final关键字是非常重要而事实上却经常被忽视其作为同步的作用.本质上讲,final能够做出如下保证:当你创建一个对象时,使用final关键字能够使得另一个线程不会访问到处于" ...
- Java并发编程学习笔记(一)——线程安全性
主要概念:线程安全性.原子性.原子变量.原子操作.竟态条件.复合操作.加锁机制.重入.活跃性与性能. 1.当多个线程访问某个状态变量并且其中有一个线程执行写入操作时,必须采用同步机制来协同这些线程对变 ...
- Spring并发访问的线程安全性问题
Spring并发访问的线程安全性问题 http://windows9834.blog.163.com/blog/static/27345004201391045539953/ 由于Spring MVC ...
- pthread的线程安全性
pthread不一定能够保证线程安全性,特别是在开启编译器优化的情况下,某些编译器优化很可能破坏pthread的线程安全性. 由于不同的编译器可能有不同的优化技术,所以pthread的实现与编译器有很 ...
- SimpleDateFormat 的性能和线程安全性
系统正常运行一段时间后,QA报给我一个异常: java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: GC overhead limit exceeded at java.text.DecimalFo ...
- 《Java并发编程实战》第二章 线程安全性 读书笔记
一.什么是线程安全性 编写线程安全的代码 核心在于要对状态訪问操作进行管理. 共享,可变的状态的訪问 - 前者表示多个线程訪问, 后者声明周期内发生改变. 线程安全性 核心概念是正确性.某个类的行为与 ...
- JAVA并发编程实战---第二章:线程安全性
对象的状态是指存储在状态变量中的数据.对象的状态可能包括其他依赖对象的域.例如HashMap的状态不仅存储在HashMap本身,还存储在许多Map.Entry对象中.对象的状态中包含了任何可能影响其外 ...
- Java线程安全性中的对象发布和逸出
发布(Publish)和逸出(Escape)这两个概念倒是第一次听说,不过它在实际当中却十分常见,这和Java并发编程的线程安全性就很大的关系. 什么是发布?简单来说就是提供一个对象的引用给作用域之外 ...
随机推荐
- std::map插入失败会返回什么
总所周知,map不能存在2个相同的key,那么如果是后插入的key,对应的value不会添加上去,也不会覆盖原来的,此时会返回一个std::pair<iterator,bool>,可以根据 ...
- Luogu P1530 分数化小数 Fractions to Decimals(模拟)
P1530 分数化小数 Fractions to Decimals 题意 题目描述 写一个程序,输入一个形如\(N/D\)的分数(\(N\)是分子,\(D\)是分母),输出它的小数形式.如果小数有循环 ...
- 2018-2019年中国CDN市场发展报告:阿里云成为中国CDN市场的领军者
近日,权威ICT市场咨询机构计世资讯(CCW Research)发布<2018-2019年中国CDN市场发展报告>,报告显示,当前,随着新型信息技术在中国不断应用,以及互联网化新业务的快速 ...
- Django项目:CRM(客户关系管理系统)--34--26PerfectCRM实现King_admin自定义排序
ordering = ['-qq'] #自定义排序,默认'-id' #base_admin.py # ————————24PerfectCRM实现King_admin自定义操作数据———————— f ...
- 【noip】跟着洛谷刷noip题
传送门 1.铺地毯 d1t1 模拟 //Twenty #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<iostream> # ...
- 移动端页面输入法挡住input输入框的解决方法
1,宽高用了百分比或者vw/vh布局的,input输入框的最外层父容器的可用JS动态设置为当前窗口的宽高(防止输入法的弹出令页面变形) 2,最外层父容器用了fixed定位的,不要用top:0;要用bo ...
- uni-app开发微信小程序引入UI组件库(Vant-weapp)步骤
uni-app开发微信小程序引入UI组件库(Vant-weapp)步骤 这里以vant-weapp为例 uni-app官方文档介绍引入组件的方法 1. 新建相关目录 根目录下创建 wxcomponen ...
- angular4 自定义表单验证Validator
表单的验证条件有时候满足不了需求就可以自定义验证 唯一要求返回是ValidatorFn export interface ValidatorFn{ (c:AbstractControl):Valida ...
- 实时查看linux网卡流量 的base脚本
#!/bin/bash " ] do eth=$ RXpre=$(cat /proc/net/dev | grep $eth | tr : " " | awk '{pri ...
- WebSocket前后端实现
websocket.jsp <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" ...
