Deep Learning Tutorial - Classifying MNIST digits using Logistic Regression
Deep Learning Tutorial 由 Montreal大学的LISA实验室所作,基于Theano的深度学习材料.Theano是一个python库,使得写深度模型更容易些,也可以在GPU上训练深度模型。所以首先得了解python和numpy。其次,阅读Theano basic tutorial。
Deep Learning Tutorial 包括:
监督学习算法:
Logistic Regression - using Theano for something simple
Multilayer perceptron - introduction to layers
Deep Convolutional Network - a simplified version of LeNet5
无监督和半监督学习算法:
Auto Encoders, Denoising Autoencoders - description of autoencoders
Stacked Denoising Auto-Encoders - easy steps into unsupervised pre-training for deep nets
Restricted Boltzmann Machines - single layer generative RBM model
Deep Belief Networks - unsupervised generative pre-training of stacked RBMs followed by supervised fine-tuning
建立mcRBM模型:
HMC Sampling
其他:
Contractive auto-encoders:
Semantic Parsing of Speech using Recurrent Net
LSTM network
Modeling and generating sequences of polyphonic music
1.Getting started:
存储数据时用shared variables(共享变量),用小批量索引来操作数据。共享变量与利用GPU有关,如果数据时共享变量,Theano可以复制整个数据在GPU上通过一个简单的命令,不需要从CPU存储上复制任何信息。当在GPU上存储数据时需要的类型是floats,因此代码type为floatX。由于y为标签,所以要将y cast为int。
2.损失函数:
0-1损失: 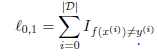
对数似然损失: ,因为0-1损失函数不可微,我们一般用最大化对数似然损失,即最小化负的对 数似然损失。
,因为0-1损失函数不可微,我们一般用最大化对数似然损失,即最小化负的对 数似然损失。
3.梯度下降
批梯度、随机梯度、小批量梯度
4.正则化
L1,L2正则化(权重衰减)
5.提前停止(Early-Stopping)
之前没注意这个算法,后面的logistic回归分类手写数字识别时用到了它。思想大致是:在验证数据集上如果连续多次迭代过程中损失函数不再显著降低,那么应该提前结束训练,同时也可防止过拟合。
6.Theano tips
若要存储在程序运行过程后所优化得到的权重参数,利用pickle或深拷贝,如果参数为共享变量w,v,u,可这样操作:
>>> import cPickle
>>> save_file = open(’path’, ’wb’) # this will overwrite current contents
>>> cPickle.dump(w.get_value(borrow=True), save_file, -1) # the -1 is for HIGHEST_PROTOCOL
>>> cPickle.dump(v.get_value(borrow=True), save_file, -1) # .. and it triggers much more efficient
>>> cPickle.dump(u.get_value(borrow=True), save_file, -1) # .. storage than numpy’s default
>>> save_file.close()
若要用这些w,v,u来预测或评价,可以再load一下:
>>> save_file = open(’path’)
>>> w.set_value(cPickle.load(save_file), borrow=True)
>>> v.set_value(cPickle.load(save_file), borrow=True)
>>> u.set_value(cPickle.load(save_file), borrow=True)
建议不要pickle训练或测试函数为长期储存,Theano函数与python深拷贝和pickle机制兼容,如果你更新了Theano文件使其内部改变,那么可能将无法在un-pickle你的模型。
CLASSIFYING MNIST DIGITS USING LOGISTIC REGRESSION
logistic regression模型(打分or评价函数):
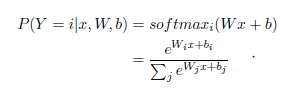
logistic regression模型(损失函数):
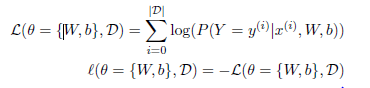
整体代码:
#coding=UTF-8
import cPickle
import gzip
import os
import sys
import timeit
import numpy
import theano
import theano.tensor as T class LogisticRegression(object): #此类有三个函数
def __init__(self, input, n_in, n_out):
self.W = theano.shared(value=numpy.zeros((n_in, n_out), dtype=theano.config.floatX),name='W',borrow=True) #初始化参数
self.b = theano.shared(value=numpy.zeros((n_out,), dtype=theano.config.floatX), name='b', borrow=True)
self.p_y_given_x = T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(input, self.W) + self.b) #计算打分、评价结果
self.y_pred = T.argmax(self.p_y_given_x, axis=1) #挑出可能性最大的类别标签
self.params = [self.W, self.b]
self.input = input def negative_log_likelihood(self, y):
return -T.mean(T.log(self.p_y_given_x)[T.arange(y.shape[0]), y]) #计算损失函数 def errors(self, y): #计算错误率
if y.ndim != self.y_pred.ndim:
raise TypeError('y should have the same shape as self.y_pred', ('y', y.type, 'y_pred', self.y_pred.type))
if y.dtype.startswith('int'):
return T.mean(T.neq(self.y_pred, y))
else:
raise NotImplementedError() def load_data(dataset):
f = gzip.open(dataset,'rb')
train_set, valid_set, test_set = cPickle.load(f)
f.close() #下载数据 def shared_dataset(data_xy, borrow=True): #将数据类型改为共享数据类型
data_x, data_y = data_xy
shared_x = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_x, dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=borrow)
shared_y = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(data_y, dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=borrow)
return shared_x, T.cast(shared_y, 'int32') test_set_x, test_set_y = shared_dataset(test_set)
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = shared_dataset(valid_set)
train_set_x, train_set_y = shared_dataset(train_set)
rval = [(train_set_x, train_set_y), (valid_set_x, valid_set_y), (test_set_x, test_set_y)] #改好的三种共享数据类型
return rval def sgd_optimization_mnist(learning_rate=0.13, n_epochs=1000, dataset='data/mnist.pkl.gz', batch_size=600): #随机梯度下降
datasets = load_data(dataset) #学习速率0.13,迭代次数1000,批梯度大小600
train_set_x, train_set_y = datasets[0]
valid_set_x, valid_set_y = datasets[1]
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
n_train_batches = train_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_valid_batches = valid_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size
n_test_batches = test_set_x.get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] / batch_size #计算三种数据的批量数目,若train_set有6000个样本,批梯度大小为600,
print '...building the model' #则n_train_batches为10.
index = T.lscalar()
x = T.matrix('x')
y = T.ivector('y')
classifier = LogisticRegression(input=x, n_in=28 * 28, n_out=10) #Classifer为这个分类器
cost = classifier.negative_log_likelihood(y)
test_model = theano.function( #测试模型
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y),
givens={
x: test_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: test_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
validate_model = theano.function( #验证模型
inputs=[index],
outputs=classifier.errors(y), #输出为错误率
givens={
x: valid_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: valid_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
g_W = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.W)
g_b = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=classifier.b)
updates = [(classifier.W, classifier.W - learning_rate * g_W), (classifier.b, classifier.b - learning_rate * g_b)]
train_model = theano.function( #训练模型
inputs=[index],
outputs=cost,
updates=updates,
givens={
x: train_set_x[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[index * batch_size: (index + 1) * batch_size]
}
)
print '...training the model' #以下运用了early-stop算法,并非普通的迭代n次后停止
patience = 5000
patience_increase = 2
improvement_threshold = 0.995
validation_frequency = min(n_train_batches, patience / 2)
best_validation_loss = numpy.inf
test_score = 0.
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
done_looping = False
epoch = 0
while (epoch < n_epochs) and (not done_looping): #设置最大迭代次数n_epochs
epoch = epoch + 1
for minibatch_index in xrange(n_train_batches): #小批量梯度,实际中n_train)batches=83
minibatch_avg_cost = train_model(minibatch_index)
iter = (epoch - 1) * n_train_batches + minibatch_index #minibatch_index最大只能取到82
if (iter + 1) % validation_frequency == 0: #满足这个条件说明完整的迭代了一个epoch,即将所有训练样本迭代了一次
validation_losses = [validate_model(i) for i in xrange(n_valid_batches)]
this_validation_loss = numpy.mean(validation_losses) #计算验证集错误率
print('epoch %i, minibatch %i / %i, validation error %f %%' %(epoch, minibatch_index + 1, n_train_batches, this_validation_loss * 100.))
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss: #如果找到了优者
if this_validation_loss < best_validation_loss * improvement_threshold: #如果找到了优者*0.995(即很吊的优者)
patience = max(patience, iter * patience_increase) #遇到了更吊的优者就更新参数
best_validation_loss = this_validation_loss #不论屌不屌,只要找到优者就存起来
test_losses = [test_model(i) for i in xrange(n_test_batches)]
test_score = numpy.mean(test_losses) #计算测试集的错误率
print(('epoch %i, minibatch %i / %i, test error of'' best model %f %%') %(epoch,minibatch_index + 1,n_train_batches,test_score * 100.))
with open('best_model.pkl', 'w') as f:cPickle.dump(classifier, f) #存储已跑完的训练模型结果!
if patience <= iter: #当满足这个条件跳出迭代!
done_looping = True
break
end_time = timeit.default_timer()
print(('Optimization complete with best validation score of %f %%,''with test performance %f %%') %(best_validation_loss*100.,test_score*100.))
print 'The code run for %d epochs,with %f epochs/esc' % (epoch, 1.*epoch/(end_time-start_time)) def predict():
classifier = cPickle.load(open('best_model.pkl')) #调出已存好了的训练模型!
predict_model = theano.function(inputs=[classifier.input], outputs=classifier.y_pr ed) #预测模型
dataset = 'data/mnist.pkl.gz'
datasets = load_data(dataset)
test_set_x, test_set_y = datasets[2]
test_set_x = test_set_x.get_value() #取出其值
#test_set_y = test_set_y
predicted_values = predict_model(test_set_x[:10]) #取出前10个预测下
print("predicted values for the first 10 examples in test set:")
print predicted_values
Deep Learning Tutorial - Classifying MNIST digits using Logistic Regression的更多相关文章
- Deep Learning Tutorial - Convolutional Neural Networks(LENET)
CNN很多概述和要点在CS231n.Neural Networks and Deep Learning中有详细阐述,这里补充Deep Learning Tutorial中的内容.本节前提是前两节的内容 ...
- 深度学习材料:从感知机到深度网络A Deep Learning Tutorial: From Perceptrons to Deep Networks
In recent years, there’s been a resurgence in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It’s spread beyo ...
- 深度学习 Deep LearningUFLDL 最新Tutorial 学习笔记 2:Logistic Regression
1 Logistic Regression 简述 Linear Regression 研究连续量的变化情况,而Logistic Regression则研究离散量的情况.简单地说就是对于推断一个训练样本 ...
- 读《Deep Learning Tutorial》(台湾大学 李宏毅 深度学习教学ppt)后杂记
原ppt下载:pan.baidu.com/s/1nv54p9R,密码:3mty 需深入实践并理解的重要概念: Deep Learning: SoftMax Fuction(输出层归一化函数,与sigm ...
- (原创)Stanford Machine Learning (by Andrew NG) --- (week 3) Logistic Regression & Regularization
coursera上面Andrew NG的Machine learning课程地址为:https://www.coursera.org/course/ml 我曾经使用Logistic Regressio ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial
http://www.slideshare.net/tw_dsconf/ss-62245351?qid=c0f0f97a-6ca8-4df0-97e2-984452215ee7&v=& ...
- 读李宏毅《一天看懂深度学习》——Deep Learning Tutorial
大牛推荐的入门用深度学习导论,刚拿到有点懵,第一次接触PPT类型的学习资料,但是耐心看下来收获还是很大的,适合我这种小白入门哈哈. 原PPT链接:http://www.slideshare.net/t ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅(一)深度学习介绍
大纲 深度学习介绍 深度学习训练的技巧 神经网络的变体 展望 深度学习介绍 深度学习介绍 深度学习属于机器学习的一种.介绍深度学习之前,我们先大致了解一下机器学习. 机器学习,拿监督学习为例,其本质上 ...
- Deep Learning Tutorial - Multilayer perceptron
Multilayer perceptron:多层感知器 本节实现两层网络(一个隐层)作为分类器实现手写数字分类.引入的内容:激活函数(双曲正切.L1和L2正则化).Theano的共享变量.grad.f ...
随机推荐
- Linux最常用的基础命令
Linux最常用的基础命令个人总结 计算机基础知识: 32bit和64bit系统的区别.系统运行机制 32bit=内存的最大寻址空间是2**32,也就是说最大只能使用4GB的内存64bit=内存的最大 ...
- 运维监控-使用Zabbix Server 创建 Actions
运维监控-使用Zabbix Server 创建 Actions 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. zabbix的action默认是关闭的,因此我们想使用它就得先启用哟. ...
- 利用curl 实现URL监控
#curl 命令介绍 curl命令在运维中经常使用,但运维中常用的参数也并不多,因此也是列表如下 -I/--head 显示响应头信息 -m/--max-time <seconds> 访 ...
- CentOS7 图形化方式安装 Oracle 18c 单实例
下载 Oracle 数据库,zip 包 https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/enterprise-edition/downloads/index.h ...
- 快速傅里叶变换(Fast Fourier Transform, FFT)和短时傅里叶变换(short-time Fourier transform,STFT )【资料整理】【自用】
1. 官方形象展示FFT:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av19141078/?spm_id_from=333.788.b_636f6d6d656e74.6 2. 讲解 ...
- Jsp的四大作用域与九大对象
内置对象特点: 1. 由JSP规范提供,不用编写者实例化. 2. 通过Web容器实现和管理 3. 所有JSP页面均可使用 4. 只有在脚本元素的表达式或代码段中才可使用(<%=使用内置对象%&g ...
- 047、管理Docker Machine(2019-03012 周二)
参考https://www.cnblogs.com/CloudMan6/p/7248188.html 用docker-machine创建machine的过程很简洁,非常适合多主机环境.除此之外 ...
- 数据结构Java实现01----线性表与顺序表
一.线性结构: 如果一个数据元素序列满足: (1)除第一个和最后一个数据元素外,每个数据元素只有一个前驱数据元素和一个后继数据元素: (2)第一个数据元素没有前驱数据元素: (3)最后一个数据元素没有 ...
- electron入门
Electron是由Github开发,用HTML,CSS和JavaScript来构建跨平台桌面应用程序的一个开源库. Electron通过将Chromium和Node.js合并到同一个运行时环境中,并 ...
- JS创建对象之动态原型模式
动态原型模式把所有信息都封装在了构造函数中,而通过在构造函数中初始化原型(仅在必要的情况下),又保持了 同时使用构造函数和原型的优点:换句话说,可以通过检查某个应该存在的方法是否有效,来决定是否需要初 ...
