后缀自动机 && 题目
因为明天要讲解后缀自动机了,所以只能抱抱佛脚,临时做做题目。其实很久以前看过,但是不太懂,看的是clj的原文,不太懂。现在只能临时看看是怎么弄的,应付下。
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1、自动机A为后缀自动机,A(sub) = true当且仅当sub是str的后缀。
2、一个较差的和后缀自动机有相同功能的东西是trie,把所有后缀都insert进去trie里面,但是空间&&时间复杂度O(N^2),不行。
3、有一个空间和时间复杂度都是O(N)的,就是:以ACADD为例子
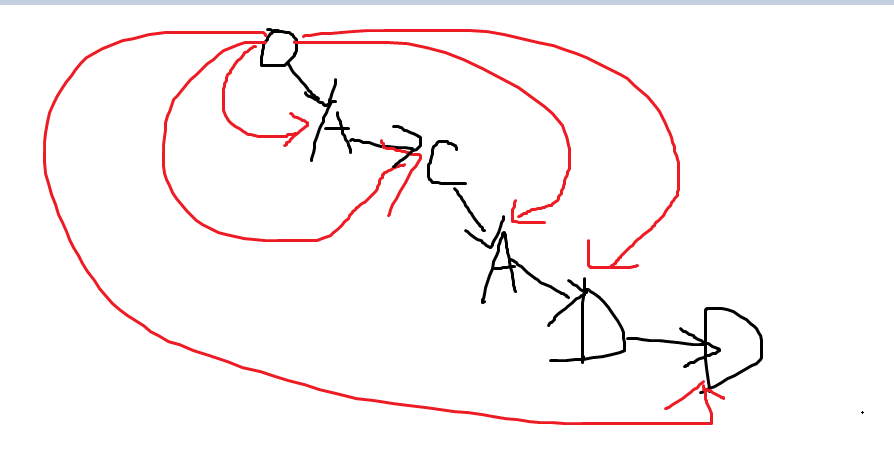
也就是向每个字符都添加一条边,然后顺着这条边遍历,就能找到所有后缀。也能保存所有子串。
但是查找复杂度O(N^2)
注意到连接去字符'A'的边是有两条的,也就是这个图只能用邻接表来存,不能像trie这样用pNext[26]这样存,所以查找是O(N^2)
SAM就是为了解决了这样的问题而诞生的,也就是每一种字母边,只能存在一条。
后缀自动机是一个基于trie的字符串有向图,时间和空间复杂度均为O(N)
构造过程:
假设现在已经建立好前t个字符的后缀自动机,现在要增加一个字符x,使得其变成tx的后缀自动机。
每个节点保存的信息如下:
int cnt; // cnt表示后缀自动机中从root走到它最多需要多少步
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
上面保存的信息都比较易懂,关键看看pNext[N]和fa,pNext[N]其实就是和字典树的26枚指针一样,只是为了O(1)判断是否存在这种字母的边。fa,指向的是一个能接受后缀的节点。什么叫能接受后缀的节点?比如我现在要建立"sazaa"的sam,一开始建立了's'的,如下图
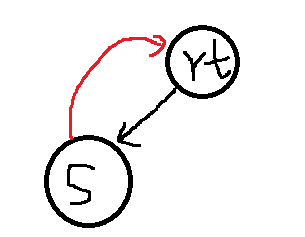
红色的是fa边,然后现在新来一个字符'a',要使得其变成"sa"的sam,sam有什么特征呢,就是对于每一个"sa"的后缀,他都要能够识别。
那么,现在的末尾节点s,是肯定能够接受后缀的,然后爬fa边,去到root,root也和'a'连一条边,因为我也需要识别'a'这个后缀。
所以总的来说,fa边是为了寻找可以添加后缀节点的节点,使得其能识别当前建立的前缀串的所有后缀的。
在建立的时候,会遇到一种情况就是重边,我们用下标来判断是否能识别这个字符,那么很明显不能连接两条边。
但是建立的过程中,我们确实需要两条边。
比如建立到第四个"a"的时候,由于root-->a(2)已经有边,所以就不能连接root--->a(4)
那么怎么办呢,看cnt。
分两种情况,p和q的定义看代码
1、p->cnt + 1 = q->cnt
2、p->cnt + 1 != q->cnt
第一种情况,p->cnt + 1 = q->cnt说明p和q中间不包含任何其他字符,所以直接把q当作np接受新的后缀即可。
第二种情况可以通过虚拟一个节点,使得变成第一种情况
struct Node {
int cnt; // cnt表示后缀自动机中从root走到它最多需要多少步
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int cnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (cnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].cnt = cnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->cnt + , NULL);
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->cnt == p->cnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->cnt = p->cnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
例子"sazaa"
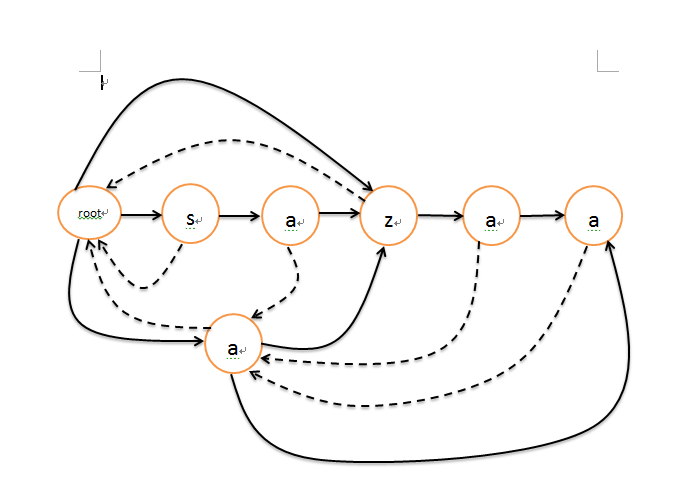
ask && question
①、识别了一个子串后,若想得到它在原串中的开始位置,假设子串长度是lensub,识别到最后一个字符在原串中是第pos个位置,那么开始位置 beginPos = = pos – lensub + 1
②、后缀自动机也能识别所有的子串,按序dfs后,当前拾得的所以字符串都是主串的一个子串,不重不漏。
例如上面的"sazaa",dfs后
有:
s
sa
saz
saza
sazaa
a
az
aza
azaa
aa
z
za
zaa
不重不漏。
③、你说sam仅能识别后缀,那么现在为什么又能识别任何一个子串?
是这样的,sam为了不浪费空间,一个节点可能有多重身份,比如sazaa里面,最后面那个a(5),是被虚拟出来的那个节点(最下面那个a代替的),使得最下面那个a有三个身份,一是代替a(5)和a(4)接受后缀字符,三是自己作为一个后缀'a',其实可以在trie中很简单地用一个DFN标志当前这个节点是否能成为现在sam的后缀节点。是成为现在sam的后缀节点,因为sam的建立是在线的,是sam1的后缀节点,不一定是sam2的后缀节点。
④、一个很好的SAM教程。
http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1441
#1441 : 后缀自动机一·基本概念
描述
小Hi:今天我们来学习一个强大的字符串处理工具:后缀自动机(Suffix Automaton,简称SAM)。对于一个字符串S,它对应的后缀自动机是一个最小的确定有限状态自动机(DFA),接受且只接受S的后缀。
小Hi:比如对于字符串S="aabbabd",它的后缀自动机是:
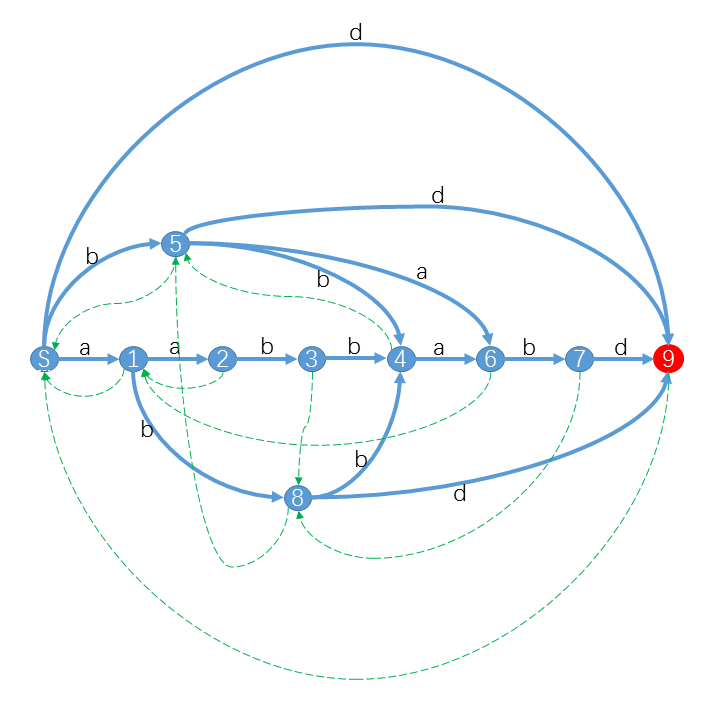
其中红色状态是终结状态。你可以发现对于S的后缀,我们都可以从S出发沿着字符标示的路径(蓝色实线)转移,最终到达终结状态。例如"bd"对应的路径是S59,"abd"对应的路径是S189,"abbabd"对应的路径是S184679。而对于不是S后缀的字符串,你会发现从S出发,最后会到达非终结状态或者“无路可走”。特别的,对于S的子串,最终会到达一个合法状态。例如"abba"路径是S1846,"bbab"路径是S5467。而对于其他不是S子串的字符串,最终会“无路可走”。 例如"aba"对应S18X,"aaba"对应S123X。(X表示没有转移匹配该字符)
小Ho:好像很厉害的样子!对于任意字符串都能构造出一个SAM吗?另外图中那些绿色虚线是什么?
小Hi:是的,任意字符串都能构造出一个SAM。我们知道SAM本质上是一个DFA,DFA可以用一个五元组 <字符集,状态集,转移函数、起始状态、终结状态集>来表示。下面我们将依次介绍对于一个给定的字符串S如何确定它对应的 状态集 和 转移函数 。至于那些绿色虚线虽然不是DFA的一部分,却是SAM的重要部分,有了这些链接SAM是如虎添翼,我们后面再细讲。
SAM的States
小Hi:这一节我们将介绍给定一个字符串S,如何确定S对应的SAM有哪些状态。首先我们先介绍一个概念 子串的结束位置集合 endpos。对于S的一个子串s,endpos(s) = s在S中所有出现的结束位置集合。还是以S="aabbabd"为例,endpos("ab") = {3, 6},因为"ab"一共出现了2次,结束位置分别是3和6。同理endpos("a") = {1, 2, 5}, endpos("abba") = {5}。
小Hi:我们把S的所有子串的endpos都求出来。如果两个子串的endpos相等,就把这两个子串归为一类。最终这些endpos的等价类就构成的SAM的状态集合。例如对于S="aabbabd":
| 状态 | 子串 | endpos |
|---|---|---|
| S | 空串 | {0,1,2,3,4,5,6} |
| 1 | a | {1,2,5} |
| 2 | aa | {2} |
| 3 | aab | {3} |
| 4 | aabb,abb,bb | {4} |
| 5 | b | {3,4,6} |
| 6 | aabba,abba,bba,ba | {5} |
| 7 | aabbab,abbab,bbab,bab | {6} |
| 8 | ab | {3,6} |
| 9 | aabbabd,abbabd,bbabd,babd,abd,bd,d | {7} |
小Ho:这些状态恰好就是上面SAM图中的状态。
小Hi:没错。此外,这些状态还有一些美妙的性质,且等我一一道来。首先对于S的两个子串s1和s2,不妨设length(s1) <= length(s2),那么 s1是s2的后缀当且仅当endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2),s1不是s2的后缀当且仅当endpos(s1) ∩ endpos(s2) = ∅。
小Ho:我验证一下啊... 比如"ab"是"aabbab"的后缀,而endpos("ab")={3,6},endpos("aabbab")={6},是成立的。"b"是"ab"的后缀,endpos("b")={3,4,6}, endpos("ab")={3,6}也是成立的。"ab"不是"abb"的后缀,endpos("ab")={3,6},endpos("abb")={4},两者没有交集也是成立的。怎么证明呢?
小Hi:证明还是比较直观的。首先证明s1是s2的后缀=>endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2):既然s1是s2后缀,所以每次s2出现时s1以必然伴随出现,所以有endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2)。再证明endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2)=>s1是s2的后缀:我们知道对于S的子串s2,endpos(s2)不会是空集,所以endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2)=>存在结束位置x使得s1结束于x,并且s2也结束于x,又length(s1) <= length(s2),所以s1是s2的后缀。综上我们可知s1是s2的后缀当且仅当endpos(s1) ⊇ endpos(s2)。s1不是s2的后缀当且仅当endpos(s1) ∩ endpos(s2) = ∅是一个简单的推论,不再赘述。
小Ho:我好像对SAM的状态有一些认识了!我刚才看上面的表格就觉得SAM的一个状态里包含的子串好像有规律。考虑到SAM中的一个状态包含的子串都具有相同的endpos,那它们应该都互为后缀?
小Hi:你观察力还挺敏锐的。下面我们就来讲讲一个状态包含的子串究竟有什么关系。上文提到我们把S的所有子串按endpos分类,每一类就代表一个状态,所以我们可以认为一个状态包含了若干个子串。我们用substrings(st)表示状态st中包含的所有子串的集合,longest(st)表示st包含的最长的子串,shortest(st)表示st包含的最短的子串。例如对于状态7,substring(7)={aabbab,abbab,bbab,bab},longest(7)=aabbab,shortest(7)=bab。
小Hi:对于一个状态st,以及任意s∈substrings(st),都有s是longest(st)的后缀。证明比较容易,因为endpos(s)=endpos(longest(st)),所以endpos(s) ⊇ endpos(longest(st)),根据我们刚才证明的结论有s是longest(st)的后缀。
小Hi:此外,对于一个状态st,以及任意的longest(st)的后缀s,如果s的长度满足:length(shortest(st)) <= length(s) <= length(longsest(st)),那么s∈substrings(st)。 证明也是比较容易,因为:length(shortest(st)) <= length(s) <= length(longsest(st)),所以endpos(shortest(st)) ⊇ endpos(s) ⊇ endpos(longest(st)), 又endpos(shortest(st)) = endpos(longest(st)),所以endpos(shortest(st)) = endpos(s) = endpos(longest(st)),所以s∈substrings(st)。
小Ho:这么说来,substrings(st)包含的是longest(st)的一系列连续后缀?
小Hi:没错。比如你看状态7中包含的就是aabbab的长度分别是6,5,4,3的后缀;状态6包含的是aabba的长度分别是5,4,3,2的后缀。
SAM的Suffix Links
小Hi:前面我们讲到substrings(st)包含的是longest(st)的一系列连续后缀。这连续的后缀在某个地方会“断掉”。比如状态7,包含的子串依次是aabbab,abbab,bbab,bab。按照连续的规律下一个子串应该是"ab",但是"ab"没在状态7里,你能想到这是为什么么?
小Ho:aabbab,abbab,bbab,bab的endpos都是{6},下一个"ab"当然也在结束位置6出现过,但是"ab"还在结束位置3出现过,所以"ab"比aabbab,abbab,bbab,bab出现次数更多,于是就被分配到一个新的状态中了。
小Hi:没错,当longest(st)的某个后缀s在新的位置出现时,就会“断掉”,s会属于新的状态。比如上例中"ab"就属于状态8,endpos("ab"}={3,6}。当我们进一步考虑"ab"的下一个后缀"b"时,也会遇到相同的情况:"b"还在新的位置4出现过,所以endpos("b")={3,4,6},b属于状态5。在接下去处理"b"的后缀我们会遇到空串,endpos("")={0,1,2,3,4,5,6},状态是起始状态S。
小Hi:于是我们可以发现一条状态序列:7->8->5->S。这个序列的意义是longest(7)即aabbab的后缀依次在状态7、8、5、S中。我们用Suffix Link这一串状态链接起来,这条link就是上图中的绿色虚线。
小Ho:原来如此。
小Hi:Suffix Links后面会有妙用,我们暂且按下不表。
SAM的Transition Function
小Hi:最后我们来介绍SAM的转移函数。对于一个状态st,我们首先找到从它开始下一个遇到的字符可能是哪些。我们将st遇到的下一个字符集合记作next(st),有next(st) = {S[i+1] | i ∈ endpos(st)}。例如next(S)={S[1], S[2], S[3], S[4], S[5], S[6], S[7]}={a, b, d},next(8)={S[4], S[7]}={b, d}。
小Hi:对于一个状态st来说和一个next(st)中的字符c,你会发现substrings(st)中的所有子串后面接上一个字符c之后,新的子串仍然都属于同一个状态。比如对于状态4,next(4)={a},aabb,abb,bb后面接上字符a得到aabba,abba,bba,这些子串都属于状态6。
小Hi:所以我们对于一个状态st和一个字符c∈next(st),可以定义转移函数trans(st, c) = x | longest(st) + c ∈ substrings(x) 。换句话说,我们在longest(st)(随便哪个子串都会得到相同的结果)后面接上一个字符c得到一个新的子串s,找到包含s的状态x,那么trans(st, c)就等于x。
小Ho:吼~ 终于把SAM中各个部分搞明白了。
小Hi:SAM的构造有时空复杂度均为O(length(S))的算法,我们将在后面介绍。这一期你可以先用暴力算法依照定义构造SAM,先对SAM有个直观认识再说。
小Ho:没问题,暴力算法我最拿手了。我先写程序去了。
习题:
字符串的最小表示法
https://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem&problem=660
因为sam能识别所有的子串,那么把整个串复制一遍去后面,那么所有情况将会都考虑到。
贪心从root出发,找放在第一个地方的字母,有'a'就选'a',没'a'就选b等等等等。
选够lenstr个,就会知道那个最小表示法的那个串是什么。然后去原串找那个位置出现了这个串即可。
我用了hash来找。给个数据:sazaa
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 4e5 + ;
const int N = ;
struct Node {
int cnt, id, pos; // cnt表示在后缀自动机中从root走到它最多需要多少步
//id表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,需要id判断
//pos表示它在原串中的位置。
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaon[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; // 用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int cnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (cnt != -) {
suffixAutomaon[t].cnt = cnt, suffixAutomaon[t].fa = NULL;
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaon[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaon[t] = *node; //保留了node节点指向的信息
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
}
return &suffixAutomaon[t++];
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->cnt + , NULL);
np->pos = pos, last = np; //最后一个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->cnt == p->cnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
return;
}
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->cnt = p->cnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn];
void dfs(int id, string s) {
cout << s << endl;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]) {
char fuck = i + 'a';
dfs(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->id, s + fuck);
}
}
}
int lenstr;
vector<int> pos;
bool tofind(int id) {
if (pos.size() == lenstr) return true;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i] == NULL) continue;
pos.push_back(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->pos);
if (tofind(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->id)) return true;
pos.pop_back();
}
return false;
}
LL f[maxn];
LL poseed[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
strncpy(str + lenstr + , str + , lenstr);
str[ * lenstr + ] = '\0';
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
for (int i = ; i <= * lenstr; ++i) {
f[i] = f[i - ] * + str[i];
}
build(str, * lenstr);
pos.clear();
tofind();
LL now = ;
for (int i = ; i < pos.size(); ++i) {
// printf("%c", str[pos[i]]);
now = now * + str[pos[i]];
}
// printf("\n");
// printf("%d\n", pos[0]);
for (int i = lenstr; i <= * lenstr; ++i) {
LL t = f[i] - poseed[lenstr] * f[i - lenstr];
if (t == now) {
printf("%d\n", i - lenstr + );
return;
}
}
assert(false);
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
poseed[] = ;
for (int i = ; i <= maxn - ; ++i) poseed[i] = poseed[i - ] * ;
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) work();
return ;
}
上面这题其实不用hash
怎么找pos?
选够了lenstr个后,肯定知道最后一个在原串中是什么位置,然后那个位置 - lenstr +1就是答案。
(因为字符串长度是lenstr嘛)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 4e5 + ;
const int N = ;
struct Node {
int cnt, id, pos; // cnt表示在后缀自动机中从root走到它最多需要多少步
//id表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,需要id判断
//pos表示它在原串中的位置。
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaon[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; // 用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int cnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (cnt != -) {
suffixAutomaon[t].cnt = cnt, suffixAutomaon[t].fa = NULL;
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaon[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaon[t] = *node; //保留了node节点指向的信息
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
}
return &suffixAutomaon[t++];
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->cnt + , NULL);
np->pos = pos, last = np; //最后一个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->cnt == p->cnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
return;
}
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->cnt = p->cnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn];
void dfs(int id, string s) {
cout << s << endl;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]) {
char fuck = i + 'a';
dfs(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->id, s + fuck);
}
}
}
int lenstr;
vector<int> pos;
bool tofind(int id) {
if (pos.size() == lenstr) return true;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i] == NULL) continue;
pos.push_back(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->pos);
if (tofind(suffixAutomaon[id].pNext[i]->id)) return true;
pos.pop_back();
}
return false;
}
LL f[maxn];
LL poseed[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
strncpy(str + lenstr + , str + , lenstr);
str[ * lenstr + ] = '\0';
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
for (int i = ; i <= * lenstr; ++i) {
f[i] = f[i - ] * + str[i];
}
build(str, * lenstr);
pos.clear();
tofind();
cout << (pos.back() - lenstr + ) << endl;
// LL now = 0;
// for (int i = 0; i < pos.size(); ++i) {
//// printf("%c", str[pos[i]]);
// now = now * 131 + str[pos[i]];
// }
//// printf("\n");
//// printf("%d\n", pos[0]);
// for (int i = lenstr; i <= 2 * lenstr; ++i) {
// LL t = f[i] - poseed[lenstr] * f[i - lenstr];
// if (t == now) {
// printf("%d\n", i - lenstr + 1);
// return;
// }
// }
// assert(false);
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
poseed[] = ;
for (int i = ; i <= maxn - ; ++i) poseed[i] = poseed[i - ] * ;
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) work();
return ;
}
两个串的最长公共子串。
Longest Common Substring SPOJ - LCS
http://www.spoj.com/problems/LCS/en/
其实是后缀数组裸体,直接后缀数组然后枚举每一个height合法的情况的min(sa[i - 1], sa[i]) <= lenstr && max(sa[i - 1], sa[i]) >= lenstr + 1
然后更新答案即可。(后缀数组那个mx应该是128而不是lenstr,用到了更大的再用更大的)
复杂度(nlogn)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = * + ;
int sa[maxn], x[maxn], y[maxn], book[maxn]; //book[]大小起码是lenstr,book[rank[]]
bool cmp(int r[], int a, int b, int len) { //这个必须是int r[],
return r[a] == r[b] && r[a + len] == r[b + len];
}
void da(char str[], int sa[], int lenstr, int mx) {
int *fir = x, *sec = y, *ToChange;
for (int i = ; i <= mx; ++i) book[i] = ; //清0
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) {
fir[i] = str[i]; //开始的rank数组,只保留相对大小即可,开始就是str[]
book[str[i]]++; //统计不同字母的个数
}
for (int i = ; i <= mx; ++i) book[i] += book[i - ]; //统计 <= 这个字母的有多少个元素
for (int i = lenstr; i >= ; --i) sa[book[fir[i]]--] = i;
// <=str[i]这个字母的有x个,那么,排第x的就应该是这个i的位置了。
//倒过来排序,是为了确保相同字符的时候,前面的就先在前面出现。
//p是第二个关键字0的个数
for (int j = , p = ; p <= lenstr; j <<= , mx = p) { //字符串长度为j的比较
//现在求第二个关键字,然后合并(合并的时候按第一关键字优先合并)
p = ;
for (int i = lenstr - j + ; i <= lenstr; ++i) sec[++p] = i;
//这些位置,再跳j格就是越界了的,所以第二关键字是0,排在前面
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i)
if (sa[i] > j) //如果排名第i的起始位置在长度j之后
sec[++p] = sa[i] - j;
//减去这个长度j,表明第sa[i] - j这个位置的第二个是从sa[i]处拿的,排名靠前也//正常,因为sa[i]排名是递增的
//sec[]保存的是下标,现在对第一个关键字排序
for (int i = ; i <= mx; ++i) book[i] = ; //清0
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) book[fir[sec[i]]]++;
for (int i = ; i <= mx; ++i) book[i] += book[i - ];
for (int i = lenstr; i >= ; --i) sa[book[fir[sec[i]]]--] = sec[i];
//因为sec[i]才是对应str[]的下标
//现在要把第二关键字的结果,合并到第一关键字那里。同时我需要用到第一关键//字保存的记录,所以用指针交换的方式达到快速交换数组中的值
ToChange = fir, fir = sec, sec = ToChange;
fir[sa[]] = ; //固定的是0 因为sa[1]固定是lenstr那个0
p = ;
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) //fir是当前的rank值,sec是前一次的rank值
fir[sa[i]] = cmp(sec, sa[i - ], sa[i], j) ? p - : p++;
}
return ;
}
int height[maxn], RANK[maxn];
void calcHight(char str[], int sa[], int lenstr) {
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) RANK[sa[i]] = i; //O(n)处理出rank[]
int k = ;
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr - ; ++i) {
//最后一位不用算,最后一位排名一定是1,然后sa[0]就尴尬了
k -= k > ;
int j = sa[RANK[i] - ]; //排名在i前一位的那个串,相似度最高
while (str[j + k] == str[i + k]) ++k;
height[RANK[i]] = k;
}
return ;
}
char str[maxn], sub[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s%s", str + , sub + );
int lenstr = strlen(str + ), lensub = strlen(sub + );
str[lenstr + ] = '';
strcpy(str + lenstr + , sub + );
str[lenstr + lensub + ] = '';
str[lenstr + lensub + ] = '\0';
int tot = lenstr + lensub + ;
da(str, sa, tot + , );
calcHight(str, sa, tot + );
int ans = ;
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
for (int i = ; i <= tot + ; ++i) {
// printf("%d ", height[i]);
// printf("%d ", sa[i]);
int mi = min(sa[i - ], sa[i]);
int mx = max(sa[i - ], sa[i]);
if (mi <= lenstr && mx >= lenstr + ) {
ans = max(ans, height[i]);
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
用sam的话,首先建立第一个串的sam,然后用第二个串在sam中爬,怎么爬?
因为知道sam是能识别所有子串的。那么直接从第二个串开头位置开始枚举,从sam的root出发。
如果当前走到的sam节点能识别现在枚举的字符x,那么走过去,同时匹配数量++
如果不能,则需要走p->fa使得去到某一个能识别x字符的节点,
那么这个时候匹配了多少个?
ans = 走到这个sam节点所需的最大步数 +1个,
+1是因为匹配了x字符,
注意到sam中每个节点的fa要么是和它相同的字符,要么就是root
而且它的p->fa->cnt肯定不会比p->cnt大,意思就是本来匹配过的字符,现在同样能匹配。
复杂度O(n)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = * + ;
const int N = ;
struct Node {
int cnt, id, pos; // cnt表示在后缀自动机中从root走到它最多需要多少步
//id表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,需要id判断
//pos表示它在原串中的位置。
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaon[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; // 用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int cnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (cnt != -) {
suffixAutomaon[t].cnt = cnt, suffixAutomaon[t].fa = NULL;
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaon[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaon[t] = *node; //保留了node节点指向的信息
suffixAutomaon[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
}
return &suffixAutomaon[t++];
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->cnt + , NULL);
np->pos = pos, last = np; //最后一个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->cnt == p->cnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
return;
}
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->cnt = p->cnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn], sub[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s%s", str + , sub + );
int lenstr = strlen(str + ), lensub = strlen(sub + );
build(str, lenstr);
int ans = ;
int len = ;
struct Node *p = root;
for (int i = ; i <= lensub; ++i) {
int x = sub[i] - 'a';
if (p->pNext[x]) {
p = p->pNext[x];
len++;
} else {
while (p && !p->pNext[x]) p = p->fa;
if (p == NULL) {
len = ;
p = root;
} else {
len = p->cnt + ;
p = p->pNext[x];
}
}
ans = max(ans, len);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
还有一题是应用了SAM的在线功能
http://www.cnblogs.com/liuweimingcprogram/p/7296402.html
SAM求不同子串个数。
http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1445?sid=1147665
我们知道对于SAM的每一个状态,都能识别若干个子串,
记这些子串的最大长度是longest(st),最小长度是small(st),那么一共出现了mx - mi + 1个子串,所以只需要build的时候
找到mxcnt和micnt即可。注意每个状态能识别的子串都是不一样的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // 7-->8的那些"ab",自己是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn];
int lenstr;
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
build(str, lenstr);
LL ans = ;
for (int i = ; i <= t - ; ++i) {
ans += suffixAutomaton[i].mxCnt - suffixAutomaton[i].miCnt + ;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
Substrings SPOJ - NSUBSTR
这题就
http://www.spoj.com/problems/NSUBSTR/en/
http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1449?sid=1149820
上面有详解
主要思路,如果知道每一个节点的endpos大小,那么是很好做的。
endpos意思就是当前这个节点所能识别的子串,在原串中的结束位置是什么。
如果"ab"在原串中结束位置是3, 6,那么子串"ab"出现次数就是2次。(这里隐含着长度是1的至少出现了2次)
而每个节点所能识别的子串长度是从 miCnt --- mxCnt的,所以ans[miCnt --- mxCnt] = max(endpos)
关键是怎么求endpos。
通过拓扑 + suffixLink求。
主要就是如果fa由x和y组成,那么|fa| >= |x| + |y|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false;
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->flag = true;
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是7-->8的那些"ab",np是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn * ];
int lenstr;
int in[maxn * ];
int dp[maxn * ];
queue<int> que;
int ans[maxn * ];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
build(str, lenstr);
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) dp[i] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que.push(i);
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!cur) break;
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] += dp[cur];
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que.push(suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id);
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
ans[suffixAutomaton[i].mxCnt] = max(ans[suffixAutomaton[i].mxCnt], dp[suffixAutomaton[i].id]);
}
for (int i = lenstr - ; i >= ; --i) {
ans[i] = max(ans[i], ans[i + ]);
}
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) {
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
}
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
2017年9月4日 00:29:36
自己给自己出了一道题
给定一个文本串str,一个模式串sub
求解sub的每一个前缀,在文本串str中的出现次数,允许重叠。
首先对str建立sam,然后用sub在sam中爬,如果不能识别了,也就不能识别后面的了。此时候ans应该是0
如果能,那么出现次数就是endpos的大小。这个使用dp预处理出来即可。
str: aabaabbaab
sub: aabba
ans : 6 3 3 1 1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false;
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->flag = true;
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是7-->8的那些"ab",np是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
}
char str[maxn * ];
int lenstr;
int in[maxn * ];
int dp[maxn * ];
queue<int> que;
int ans[maxn * ];
char sub[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
build(str, lenstr);
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) dp[i] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que.push(i);
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!cur) break;
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] += dp[cur];
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que.push(suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id);
}
scanf("%s", sub + );
int lensub = strlen(sub + );
int now = ;
for (int i = ; i <= lensub; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[sub[i] - 'a']) {
now = suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[sub[i] - 'a']->id;
ans[i] = dp[now];
} else break;
}
for (int i = ; i <= lensub; ++i) {
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
}
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
这题嘛,可以
用了sam做了但是MLE了
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6153
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 1e6 + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false;
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->flag = true;
last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是7-->8的那些"ab",np是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) {
if (str[i] >= 'a' && str[i] <= 'z')
addChar(str[i] - 'a', i);
else addChar(str[i] - 'A' + , i);
}
}
char str[maxn];
int lenstr;
int in[maxn];
int dp[maxn];
int que[maxn];
int ans[maxn];
char sub[maxn];
const int MOD = 1e9 + ;
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
reverse(str + , str + + lenstr);
build(str, lenstr);
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) dp[i] = ;
}
int head = , tail = ;
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que[tail++] = i;
}
while (head < tail) {
int cur = que[head++];
if (!cur) break;
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] += dp[cur];
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que[tail++] = suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id;
}
scanf("%s", sub + );
int lensub = strlen(sub + );
reverse(sub + , sub + + lensub);
int now = ;
int en = lensub + ;
for (int i = ; i <= lensub; ++i) {
int id;
if (sub[i] >= 'a' && sub[i] <= 'z') id = sub[i] - 'a';
else id = sub[i] - 'A' + ;
if (suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[id]) {
now = suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[id]->id;
ans[i] = dp[now];
} else {
en = i;
break;
}
}
LL haha = ;
for (int i = ; i < en; ++i) {
haha += 1LL * i * ans[i];
if (haha >= MOD) haha %= MOD;
}
printf("%I64d\n", haha);
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
work();
return ;
}
确实可以我做了。这题
http://codeforces.com/contest/432/problem/D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 1e5 + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false;
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->flag = true;
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是7-->8的那些"ab",np是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'A', i);
}
char str[maxn * ];
int lenstr;
int in[maxn * ];
int dp[maxn * ];
queue<int> que;
int ans[maxn * ];
char sub[maxn];
int tonext[maxn];
void get_next(char str[], int lenstr) {
int i = , j = ;
tonext[] = ;
while (i <= lenstr) {
if (j == || str[i] == str[j]) {
tonext[++i] = ++j;
} else j = tonext[j];
}
return;
}
struct node {
int len;
LL val;
bool operator < (const struct node & rhs) const {
return len < rhs.len;
}
} out[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
build(str, lenstr);
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) dp[i] = ;
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que.push(i);
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!cur) break;
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] += dp[cur];
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que.push(suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id);
}
strcpy(sub + , str + );
int lensub = lenstr;
int now = ;
for (int i = ; i <= lensub; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[sub[i] - 'A']) {
now = suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[sub[i] - 'A']->id;
ans[i] = dp[now];
} else break;
}
get_next(str, lenstr);
int len = ;
out[len].len = lenstr, out[len].val = ;
int t = tonext[lenstr + ];
while (t > ) {
++len;
out[len].len = t - , out[len].val = ans[t - ];
t = tonext[t];
}
printf("%d\n", len);
for (int i = len; i >= ; --i) {
printf("%d %I64d\n", out[i].len, out[i].val);
}
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
和这题:http://acm.gdufe.edu.cn/Problem/read/id/1338
但是卡STL得queue。不是不是不是,是卡了%I64d的输出,%lld和%d都ac
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 1e6 + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn * ], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false;
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
void addChar(int x, int pos) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last, *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
np->flag = true;
np->pos = pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是7-->8的那些"ab",np是"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
// p: 当前往上爬到的可以接受后缀的节点
// np:当前插入字符x的新节点
// q: q = p->pNext[x],q就是p中指向的x字符的节点
// nq:因为q->cnt != p->cnt + 1而新建出来的模拟q的节点
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
void build(char str[], int lenstr) {
init();
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) addChar(str[i] - 'A', i);
}
char str[maxn * ];
int lenstr;
int in[maxn * ];
int dp[maxn * ];
int que[maxn * ];
int ans[maxn * ];
char sub[maxn];
int tonext[maxn];
void get_next(char str[], int lenstr) {
int i = , j = ;
tonext[] = ;
while (i <= lenstr) {
if (j == || str[i] == str[j]) {
tonext[++i] = ++j;
} else j = tonext[j];
}
return;
}
struct node {
int len;
int val;
} out[maxn];
void work() {
scanf("%s", str + );
lenstr = strlen(str + );
build(str, lenstr);
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) dp[i] = ;
}
int head = , tail = ;
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que[tail++] = i;
}
while (head < tail) {
int cur = que[head++];
if (!cur) break;
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] += dp[cur];
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que[tail++] = suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id;
}
int now = ;
for (int i = ; i <= lenstr; ++i) {
if (suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[str[i] - 'A']) {
now = suffixAutomaton[now].pNext[str[i] - 'A']->id;
ans[i] = dp[now];
} else break;
}
get_next(str, lenstr);
int len = ;
out[len].len = lenstr, out[len].val = ;
int t = tonext[lenstr + ];
while (t > ) {
++len;
out[len].len = t - , out[len].val = ans[t - ];
t = tonext[t];
}
printf("%d\n", len);
for (int i = len; i >= ; --i) {
printf("%d %d\n", out[i].len, out[i].val);
}
}
int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
求两个串的最短公共子串,并且出现次数只能是1次
http://www.cnblogs.com/liuweimingcprogram/p/7483425.html
Longest Common Substring II
https://vjudge.net/problem/SPOJ-LCS2
求N个串的LCS
这题卡时间卡的好死,1e6的广义后缀自动机被卡了,应该带点常数,被卡了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int MOD = 1e9 + ;
const int maxn = 2e6 + , N = ;
struct Node {
int mxCnt; //mxCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最大长度
int miCnt; //miCnt表示后缀自动机中当前节点识别子串的最小长度
int id; //表示它是第几个后缀自动机节点,指向了它,但是不知道是第几个,用id判断
int pos; //pos表示它在原串中的位置。
bool flag; //表示当前节点是否能识别前缀
bool R[]; // 广义后缀自动机识别此状态是否在第R[i]个主串中出现过
struct Node *pNext[N], *fa;
}suffixAutomaton[maxn], *root, *last; //大小需要开2倍,因为有一些虚拟节点
int t; //用到第几个节点
struct Node *create(int mxCnt = -, struct Node *node = NULL) { //新的节点
if (mxCnt != -) {
suffixAutomaton[t].mxCnt = mxCnt, suffixAutomaton[t].fa = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) suffixAutomaton[t].pNext[i] = NULL;
} else {
suffixAutomaton[t] = *node; //保留了node节点所有的指向信息。★全部等于node
//可能需要注意下pos,在原串中的位置。现在pos等于原来node的pos
}
suffixAutomaton[t].id = t; //必须要有的,不然id错误
suffixAutomaton[t].flag = false; //默认不是前缀节点
return &suffixAutomaton[t++];
}
namespace IO
{
const int MT = 7e7;
char buf[MT];
int c, sz;
void begin()
{
c = ;
sz = fread(buf, , MT,stdin);
}
inline bool read(int &t)
{
while (c < sz && buf[c] != '-' &&(buf[c] < '' || buf[c] > '')) c++;
if (c >= sz) return ;
bool flag = ;
if (buf[c] == '-') flag = , c++;
for (t = ; c < sz && '' <= buf[c] && buf[c] <= '' ; c++) t = t * + buf[c] - '';
if (flag) t = -t;
return ;
}
inline int read(char s[]) {
while (c < sz && (buf[c] == ' ' || buf[c] == '\n')) c++;
if (c >= sz) return false;
int len = ;
while (c < sz && buf[c] != ' ' && buf[c] != '\n') s[len++] = buf[c], c++;
s[len] = ;
return len;
}
}
using namespace IO;
void addChar(int x, int pos, int id) { //pos表示在原串的位置
struct Node *p = last;
if (p->pNext[x] != NULL) { // 有了,就不需要np,广义后缀自动机
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (p->mxCnt + == q->mxCnt) {
last = q; //用来接收后缀字符
q->flag = true;
q->R[id] = true;
q->pos |= << pos;
return;
}
//现在的q没办法成为接受后缀的点
//那么就开一个节点模拟它,所以这个节点是id的前缀节点
struct Node * nq = create(-, q);
nq->pos |= << pos;
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) nq->R[i] = false;
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ;
nq->R[id] = true;
nq->flag = true; //这个点是属于id的。是id的前缀节点,因为q不能接受后缀
q->fa = nq; //这里是没有np的
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = nq;
last = nq; //成为接受后缀的节点。
return;
}
struct Node *np = create(p->mxCnt + , NULL);
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) np->R[i] = false; //每次都要清空
np->R[id] = true;
np->flag = true; //前缀节点
np->pos = << pos, last = np; //last是最尾那个可接收后缀字符的点。
for (; p != NULL && p->pNext[x] == NULL; p = p->fa) p->pNext[x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
np->fa = root;
np->miCnt = ; // 从根节点引一条边过来
return;
}
struct Node *q = p->pNext[x];
if (q->mxCnt == p->mxCnt + ) { //中间没有任何字符,可以用来代替接受后缀、
np->fa = q;
np->miCnt = q->mxCnt + ; // q是状态8的"ab",np是状态7的"bab"长度是2+1
return;
}
struct Node *nq = create(-, q); // 新的q节点,用来代替q,帮助np接收后缀字符
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) nq->R[i] = false;
nq->mxCnt = p->mxCnt + ; //就是需要这样,这样中间不包含任何字符
q->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + , np->miCnt = nq->mxCnt + ;
q->fa = nq, np->fa = nq; //现在nq是包含了本来q的所有指向信息
for (; p && p->pNext[x] == q; p = p->fa) {
p->pNext[x] = nq;
}
}
void init() {
t = ;
root = last = create(, NULL);
}
char str[maxn];
LL dp[maxn][];
queue<int> que;
int in[maxn];
int is[maxn];
void work() {
begin();
init();
int all = ;
while (read(str + )) {
last = root;
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) {
addChar(str[i] - 'a', all, all);
}
++all;
// printf("%s\n", str + 1);
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
in[suffixAutomaton[i].fa->id]++;
if (suffixAutomaton[i].flag) {
for (int j = ; j < all; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = suffixAutomaton[i].R[j];
}
}
is[i] = suffixAutomaton[i].pos;
}
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) {
que.push(i);
}
}
while (!que.empty()) {
int cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!cur) break;
for (int i = ; i < all; ++i) {
dp[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id][i] += dp[cur][i];
is[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] |= is[cur];
}
in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id]--;
if (in[suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id] == ) que.push(suffixAutomaton[cur].fa->id);
}
int ans = ;
for (int i = ; i < t; ++i) {
if (is[i] == ( << all) - ) {
ans = max(ans, suffixAutomaton[i].mxCnt);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
} int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
自己想着先用一个串建立sam,然后其他串去爬,求得每个串的每个前缀与第一个串的LCS,然后发现这样不行,每个串的前缀都不同
然后看了下题解,这题是对状态进行搞事,和我上面的思路差不多,但是是记录在sam的每一个状态上,很好。
具体就是,对剩下的串都去sam中求LCS,记录在sam每个节点的信息中,然后N个串的LCS肯定是每个状态的LCS的min值
然后对所有状态进行max即可。
细节:首先假设求LCS大家都懂了。
可以知道的是,加如状态s的LCS值是len,那么fa[s]的LCS值肯定是mxCnt[fa[s]]
mxCnt就是状态能识别子串的最大长度。
因为fa[s]都是s的后缀嘛,所以是必然的。
然后就可以咯,沿着fa更新上去就好,注意如果这个节点有值了的话就可以不需要继续往上爬了,道理很简单,不然TLE
wa点:同一个串,是可以走到同一个状态多次的,因为有可能匹配不成功,然后返回了root那里。
所以走到同一个状态的时候要取max值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 1e6 + , N = ;
struct SAM {
int mxCnt[maxn << ], son[maxn << ][N], fa[maxn << ], pos[maxn << ];
// int flag[maxn << 1][3]; //是否前缀节点
int flag[maxn << ][];
int root, last, DFN, t;
int cmp[maxn << ][];
int create() {
++t;
for (int i = ; i < ; ++i) cmp[t][i] = ;
mxCnt[t] = pos[t] = fa[t] = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) son[t][i] = NULL;
return t;
}
void init() {
++DFN;
t = , root = ;
last = create();
}
void addChar(int x, int _pos, int id) { // _pos表示在原串中的位置
int p = last;
int np = create();
last = np;
mxCnt[np] = mxCnt[p] + , pos[np] = << _pos; //前缀节点
flag[np][id] = DFN;
for (; p && son[p][x] == NULL; p = fa[p]) son[p][x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
fa[np] = root;
return;
}
int q = son[p][x];
if (mxCnt[q] == mxCnt[p] + ) {
fa[np] = q;
return;
}
int nq = create(); //用来代替q的,默认不是前缀节点
pos[nq] = pos[q]; //pos要和q相同
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) son[nq][i] = son[q][i];
fa[nq] = fa[q], mxCnt[nq] = mxCnt[p] + ;
fa[q] = nq, fa[np] = nq;
for (; p && son[p][x] == q; p = fa[p]) son[p][x] = nq;
}
int dp[maxn << ][], in[maxn << ], que[maxn << ];
void topo() {
for (int i = ; i <= t; ++i) {
in[fa[i]]++;
for (int j = ; j < ; ++j) {
dp[i][j] = flag[i][j] == DFN;
}
}
int head = , tail = ;
for (int i = ; i <= t; ++i) {
if (in[i] == ) que[tail++] = i;
}
while (head < tail) {
int cur = que[head++];
if (cur == root) break;
pos[fa[cur]] |= pos[cur];
for (int j = ; j < ; ++j) {
dp[fa[cur]][j] += dp[cur][j];
}
in[fa[cur]]--;
if (in[fa[cur]] == ) que[tail++] = fa[cur];
}
}
} sam;
char str[maxn];
void work() {
int iii = ;
while (scanf("%s", str + ) > ) {
int len = ;
int now = sam.root;
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) {
int id = str[i] - 'a';
if (sam.son[now][id]) {
now = sam.son[now][id];
len++;
} else {
while (now && !sam.son[now][id]) {
now = sam.fa[now];
}
if (now == ) {
len = , now = sam.root;
} else {
len = sam.mxCnt[now] + ;
now = sam.son[now][id];
}
}
sam.cmp[now][iii] = max(len, sam.cmp[now][iii]); //wa点
int res = now, ttt = now;
while (res) {
ttt = res;
res = sam.fa[res];
if (sam.cmp[res][iii]) break;
if (sam.cmp[ttt][iii]) {
sam.cmp[res][iii] = sam.mxCnt[res];
}
}
}
iii++;
}
int ans = ;
for (int i = ; i <= sam.t; ++i) {
int t = inf;
for (int j = ; j < iii; ++j) {
t = min(t, sam.cmp[i][j]);
}
ans = max(ans, t);
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
} int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
scanf("%s", str + );
sam.init();
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) sam.addChar(str[i] - 'a', , );
work();
return ;
}
hdu 4416
和上面LCS的那题一样,sam后求出每个状态的最大匹配数量即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL;
const int maxn = 1e5 + , N = ;
struct SAM {
int mxCnt[maxn << ], son[maxn << ][N], fa[maxn << ], pos[maxn << ];
// int flag[maxn << 1][3]; //是否前缀节点
int root, last, DFN, t;
int cmp[maxn << ];
int create() {
++t;
mxCnt[t] = pos[t] = fa[t] = NULL;
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) son[t][i] = NULL;
return t;
}
void init() {
++DFN;
t = , root = ;
last = create();
}
void addChar(int x, int _pos, int id) { // _pos表示在原串中的位置
int p = last;
int np = create();
last = np;
mxCnt[np] = mxCnt[p] + , pos[np] = << _pos; //前缀节点
for (; p && son[p][x] == NULL; p = fa[p]) son[p][x] = np;
if (p == NULL) {
fa[np] = root;
return;
}
int q = son[p][x];
if (mxCnt[q] == mxCnt[p] + ) {
fa[np] = q;
return;
}
int nq = create(); //用来代替q的,默认不是前缀节点
pos[nq] = pos[q]; //pos要和q相同
for (int i = ; i < N; ++i) son[nq][i] = son[q][i];
fa[nq] = fa[q], mxCnt[nq] = mxCnt[p] + ;
fa[q] = nq, fa[np] = nq;
for (; p && son[p][x] == q; p = fa[p]) son[p][x] = nq;
}
} sam;
char str[maxn];
void work() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%s", str + );
sam.init();
for (int i = ; str[i]; ++i) sam.addChar(str[i] - 'a', , );
for (int i = ; i <= sam.t; ++i) {
sam.cmp[i] = sam.mxCnt[sam.fa[i]];
}
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%s", str + );
int len = , now = sam.root;
for (int j = ; str[j]; ++j) {
int id = str[j] - 'a';
if (sam.son[now][id]) {
now = sam.son[now][id];
len++;
} else {
while (now && !sam.son[now][id]) now = sam.fa[now];
if (now == ) {
now = sam.root;
len = ;
} else {
len = sam.mxCnt[now] + ;
now = sam.son[now][id];
}
}
// printf("%d ", len);
sam.cmp[now] = max(sam.cmp[now], len);
int res = now;
while (sam.fa[res] && sam.cmp[now]) {
if (sam.cmp[sam.fa[res]] == sam.mxCnt[sam.fa[res]]) break;
sam.cmp[sam.fa[res]] = sam.mxCnt[sam.fa[res]];
res = sam.fa[res];
}
}
// printf("\n");
}
LL ans = ;
for (int i = ; i <= sam.t; ++i) {
ans += sam.mxCnt[i] - sam.cmp[i];
}
static int f = ;
printf("Case %d: %lld\n", ++f, ans);
} int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) work();
return ;
}
后缀自动机 && 题目的更多相关文章
- HIHOcoder 1457 后缀自动机四·重复旋律7
思路 后缀自动机题目,题目本质上是要求求出所有不同的子串的和,SAM每个节点中存放的子串互不相同,所以对于每个节点的sum,可以发现是可以递推的,每个点对子节点贡献是sum[x]*10+c*sz[x] ...
- 后缀自动机(SAM)奶妈式教程
后缀自动机(SAM) 为了方便,我们做出如下约定: "后缀自动机" (Suffix Automaton) 在后文中简称为 SAM . 记 \(|S|\) 为字符串 \(S\) 的长 ...
- 后缀自动机/回文自动机/AC自动机/序列自动机----各种自动机(自冻鸡) 题目泛做
题目1 BZOJ 3676 APIO2014 回文串 算法讨论: cnt表示回文自动机上每个结点回文串出现的次数.这是回文自动机的定义考查题. #include <cstdlib> #in ...
- 不在B中的A的子串数量 HDU - 4416 (后缀自动机模板题目)
题目: 给定一个字符串a,又给定一系列b字符串,求字符串a的子串不在b中出现的个数. 题解: 先将所有的查询串放入后缀自动机(每次将sam.last=1)(算出所有子串个数) 然后将母串放入后缀自动机 ...
- BZOJ 后缀自动机四·重复旋律7
后缀自动机四·重复旋律7 时间限制:15000ms 单点时限:3000ms 内存限制:512MB 描述 小Hi平时的一大兴趣爱好就是演奏钢琴.我们知道一段音乐旋律可以被表示为一段数构成的数列. 神奇的 ...
- 【Codeforces235C】Cyclical Quest 后缀自动机
C. Cyclical Quest time limit per test:3 seconds memory limit per test:512 megabytes input:standard i ...
- 【hihocoder#1413】Rikka with String 后缀自动机 + 差分
搞了一上午+接近一下午这个题,然后被屠了个稀烂,默默仰慕一晚上学会SAM的以及半天4道SAM的hxy大爷. 题目链接:http://hihocoder.com/problemset/problem/1 ...
- HDU 5442 后缀自动机+kmp
题目大意: 给定一个字符串,可理解成环,然后选定一位置,逆时针或顺时针走一遍,希望得到字典序最大,如果同样大,希望找到起始位置最小的,如果还相同,就默认顺时针 比赛一直因为处理最小位置出错,一结束就想 ...
- hdu5853 (后缀自动机)
Problem Jong Hyok and String 题目大意 给你n个字符串,有q个询问. 定义set(s)={(i,j)} 表示 s在第i个字符串中出现,且末尾位置为j. 对于一个询问,求se ...
随机推荐
- javascript总结44: DOM对象的dataset属性方式
1 DOM设置属性的特殊方式: DOM对象的dataset属性方式获取data-xxx方式定义的属性 由于我们经常需要在标签上自定义属性来存储数据或状态,但是如果用传统的方式操作起来比较繁琐,而且不熟 ...
- CodeForces 540A Combination Lock (水题)
题意:给定一个串数,表示一种密码锁,再给定一串密码,问你滑动最少的次数,把第一行变成第二行. 析:很简单么,反正只有0-9这个10个数字,那么就是把每一个数从正着滑和倒着滑中找出一个最小的即可,正着滑 ...
- Hadoop中Writable类
1.Writable简单介绍 在前面的博客中,经常出现IntWritable,ByteWritable.....光从字面上,就可以看出,给人的感觉是基本数据类型 和 序列化!在Hadoop中自带的or ...
- 团体程序设计天梯赛L2-003 月饼 2017-03-22 18:17 42人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
L2-003. 月饼 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 陈越 月饼是中国人在中秋佳节时吃的一种传统食品,不同地区有许多不 ...
- Gym - 101498G(Super Subarray )
In this problem, subarray is defined as non-empty sequence of consecutive elements. We define a suba ...
- IIS 发布webservice 需要用户名和密码访问 解决
今天,我在IIS上发布了一个自己写的webservice,然后我在远程通过浏览器来访问这个webservice的时候出现一个登录界面如下 之前我朋友发布webservice的时候也出现过一次,那次好 ...
- Linux Shell 编程学习笔记
1:Shell Script中if语句的条件部分要以分号来分隔 2:要注意条件测试部分中的空格.在方括号的两侧都有空格 3:echo "Hi, ${a}s" 单引号中的变量不会进行 ...
- 201621123023《Java程序设计》第1周学习总结
第1周-Java基本概念 一.本周学习总结 关键词:java发展历史.JVM/JRE/JDK.编辑器 java是一门面向对象的语言,相比于C语言我感觉java更方便.java是运行在JVM上的,不同的 ...
- 1.Javascript简介
web前端有三层: HTML:从语义的角度,描述页面的结构 CSS:从审美的角度,描述样式(美化页面) JavaScript:从交互的角度,描述行为(提升用户体验) 历史背景介绍 布兰登 艾奇 199 ...
- 526. Beautiful Arrangement
Suppose you have N integers from 1 to N. We define a beautiful arrangement as an array that is const ...
