Linux-进程间通信(二): FIFO
1. FIFO:
FIFO也被成为命名管道,因其通过路径关系绑定,可以用于任意进程间通信,而普通无名管道只能用于有共同祖先的进行直接通信;
命名管道也是半双工的,open管道的时候不要以读写方式打开,这种操作是未定义的;
2. FIFO创建:
#include <sys/stat.h> int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode); ret = 成功返回0,失败返回-
FIFO是一种文件类型,mode参数与open函数中的mode参数相同,并且一般文件的操作函数(close, read, write, unlink等)都以用于FIFO;
3. 非阻塞标志(O_NONBLOCK):
(1) 阻塞模式:只读open要阻塞到某个进程为写而打开此FIFO,只写open要阻塞到某个进程为读而打开此FIFO;
(2) 非阻塞模式:只读立即返回,如果没有进程为读而打开FIFO,则只写open返回-1,erron=ENXIO;
4. 一端关闭:
(1) 若读一个已经关闭写端的FIFO,则读取完数据后,会读到文件结束符,read返回0;
(2) 若写一个已经关闭读端的FIFO,则产生SIGPIPE;
5. 用途:
(1) FIFO由shell命令使用以便将数据从一条管道传送到另一条,而无需创建临时文件;
(2) FIFO用于客户进程和服务器进程进行数据传递;
6. 测试代码:两个进程间通信;
fifo_writer.c -- 向fifo中写入字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -;
int fifoid = -; char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { }; if (access(FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < ){
fifoid = mkfifo(FIFO_NAME, );
if (fifoid < ){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -;
}
} pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (pipeid < ){
perror("open pipeid error\n");
return -;
} int read_bytes = read(STDIN_FILENO, buffer, BUF_LEN);
if (read_bytes < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} const char * buff_send = buffer;
int no_write_bytes = read_bytes;
while (no_write_bytes > ){
int n = write(pipeid, buff_send, no_write_bytes);
if (n < ){
perror("write error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} no_write_bytes -= n;
buff_send += n;
} close(pipeid); return ;
}
fifo_reader.c -- 从fifo中读出字串
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h> #define FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifo_test"
#define BUF_LEN PIPE_BUF int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pipeid = -; char buffer[BUF_LEN] = { }; pipeid = open(FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY); int n = read(pipeid, buffer, BUF_LEN - );
if (n < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(pipeid);
return -;
} write(STDOUT_FILENO, buffer, n); close(pipeid); return ;
}
7. 测试代码:多个客户端与服务器通信
模型如下图所示:
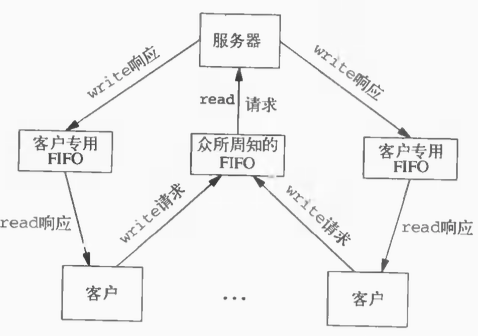
common.h--公共头文件
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include <string.h> #define SERVER_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoServer"
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME "/var/tmp/fifoClient%d"
#define BUFF_SIZE PIPE_BUF
#define MSG_LEN 64
#define CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN 64 typedef struct fifo_msg{
pid_t client_pid;
char msg[MSG_LEN];
}fifo_msg_t;
fifo_server.c
#include "common.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fifo_id = -;
int server_fifo_fd = -; if (access(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, F_OK) < ){
fifo_id = mkfifo(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, );
if (fifo_id < ){
perror("mkfifo error\n");
return -;
}
} server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_RDONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open fifo error\n");
return -;
} fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, , sizeof(client_msg));
int read_bytes = ; do {
read_bytes = read(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (read_bytes < ){
perror("read error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -;
} char *tmp_msg = client_msg.msg;
while (*tmp_msg){
*tmp_msg = toupper(*tmp_msg);
tmp_msg++;
} char client_fifo[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = { };
snprintf(client_fifo, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - , CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_msg.client_pid); int client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo, O_WRONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
} write(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
printf("write to client:%d\n", client_msg.client_pid);
close(client_fifo_fd); } while (read_bytes > ); close(server_fifo_fd);
return ;
}
fifo_client.c
#include "common.h" int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pid_t client_pid = -;
int server_fifo_fd = -;
int client_fifo_fd = -; server_fifo_fd = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY);
if (server_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open server fifo error\n");
return -;
} client_pid = getpid(); char client_fifo_name[CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN] = {};
snprintf(client_fifo_name, CLIENT_FIFO_NAME_LEN - , CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, client_pid);
if (mkfifo(client_fifo_name, ) < ){
perror("mkfifo client error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
return -;
} fifo_msg_t client_msg;
memset(&client_msg, , sizeof(client_msg));
client_msg.client_pid = client_pid; #define TRY_TIMES 3
int times = ;
for (times = ; times < TRY_TIMES; times++){
snprintf(client_msg.msg, MSG_LEN - , "client_pid:%d\n", client_pid);
write(server_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg)); client_fifo_fd = open(client_fifo_name, O_RDONLY);
if (client_fifo_fd < ){
perror("open client fifo error\n");
close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return -;
} int n = read(client_fifo_fd, &client_msg, sizeof(client_msg));
if (n > ){
printf("reveive msg from server:%s", client_msg.msg);
} close(client_fifo_fd);
} close(server_fifo_fd);
unlink(client_fifo_name);
return ;
}
Linux-进程间通信(二): FIFO的更多相关文章
- Linux 进程间通信(二) 管道
Linux 进程间通信-管道 进程是一个独立的资源分配单位,不同进程之间的资源是相互独立的,没有关联,不能在一个进程中直接访问另一个进程中的资源.但是,进程不是孤立的,不同的进程之间需要信息的交换以及 ...
- linux 进程间通信 之fifo
上一篇博客已经介绍了一种进程间通信的方式,但是那只是针对于有血缘关系的进程,即父子进程间的通信,那对于没有血缘关系的进程,那要怎么通信呢? 这就要创建一个有名管道,来解决无血缘关系的进程通信, fi ...
- Linux进程间通信(二) - 消息队列
消息队列 消息队列是Linux IPC中很常用的一种通信方式,它通常用来在不同进程间发送特定格式的消息数据. 消息队列和之前讨论过的管道和FIFO有很大的区别,主要有以下两点(管道请查阅我的另一篇文章 ...
- Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(SVR4 信号量)
Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(SVR4 信号量)
- Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(Posix 信号量)
Linux进程间通信IPC学习笔记之同步二(Posix 信号量)
- Linux 进程间通信之管道(pipe),(fifo)
无名管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允许无亲缘关系进程间的通信: 定义函数: int pipe(int f ...
- Linux进程间通信(二)
信号 信号的概念 信号是Linux进程间通信的最古老的一种方式.信号是软件中断,是一种异步通信的方式.信号可以导致一个正在运行的进程被另一个正在运行的异步进程中断,转而处理某个突发事件. 一旦产生信号 ...
- Linux进程间通信(二):信号集函数 sigemptyset()、sigprocmask()、sigpending()、sigsuspend()
我们已经知道,我们可以通过信号来终止进程,也可以通过信号来在进程间进行通信,程序也可以通过指定信号的关联处理函数来改变信号的默认处理方式,也可以屏蔽某些信号,使其不能传递给进程.那么我们应该如何设定我 ...
- Linux进程间通信之管道(pipe)、命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal)
整理自网络 Unix IPC包括:管道(pipe).命名管道(FIFO)与信号(Signal) 管道(pipe) 管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道 ...
- Linux进程间通信(四):命名管道 mkfifo()、open()、read()、close()
在前一篇文章—— Linux进程间通信 -- 使用匿名管道 中,我们看到了如何使用匿名管道来在进程之间传递数据,同时也看到了这个方式的一个缺陷,就是这些进程都由一个共同的祖先进程启动,这给我们在不相关 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL训练营01
一.数据库基础知识: 1. 数据库(database):保存有组织的数据的容器(通常是一个或者一组文件) 2. 数据库管理系统(DBMS):数据库软件,外界通过DBMS来创建和操纵数据库,具体是什么, ...
- Python 学习笔记之 Numpy 库——文件操作
1. 读写 txt 文件 a = list(range(0, 100)) a = np.array(a) # a.dtype = np.int64 np.savetxt("filename. ...
- Toward Convolutional Blind Denoising of Real Photographs
本文提出了一个针对真实图像的盲卷积去噪网络,增强了深度去噪模型的鲁棒性和实用性. 摘要 作者提出了一个 CBD-Net,由噪声估计子网络和去噪子网络两部分组成. 作者设计了一个更加真实的噪声模型,同时 ...
- js/jquery 获取本地文件的文件路劲 获取input框中type=‘file’ 中的文件路径(转载)
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/niyingxunzong/article/details/16989947 js/jquery 获取本地文件的文件路劲 获取input框中type= ...
- 预研报告——MyBatis持久层的demo
一.预研任务介绍和预研目标 任务介绍: 与 Hibernate 相比, MyBatis 是一个半自动化的持久层框架,以轻量级.效率高.原生代而好评如潮.虽然有在分享会上大致讲解,但是还是重新梳理成文字 ...
- JavaSE复习(二)集合
Collection List(存取有序,有索引,可以重复) ArrayList 底层是数组实现的,线程不安全,查找和修改快,增和删比较慢 LinkedList 底层是链表实现的,线程不安全,增和删比 ...
- Android流式布局控件
1,自定义flowlayout代码 package com.hyang.administrator.studentproject.widget; import android.content.Cont ...
- tomcat8 管理页面403 Access Denied的解决方法
安装tomcat,配置好tomcat环境变量以后,访问manager app页面,出现403 Access Denied错误,解决的方法如下: 首先在conf/tomcat-users.xml文件 ...
- 正则表达式之旅_sed_awk
谈谈正则表达式这个东西: 我想作为一个程序员,正则表达式大家绝对不陌生. 正则表达式好像一个有限则动机.主要作用是匹配,但是同时因为这个功能,我们可以扩展很多其他用法 像很多语言都引人了正则表达式:j ...
- [剑指Offer] 8.跳台阶
题目描述 一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级.求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法. [思路]与斐波那契数列类似 class Solution { public: int jumpF ...
