ACE_Select_Reactor_T 介绍 (2)
本章目录
2. ACE_Select_Reactor_T 介绍
该类继承自类ACE_Select_Reactor_Impl,实现了对IO时间、信号量、定时器的分发处理,公共的函数需要ACE_Reactor_Token进行锁定。typedef ACE_Select_Reactor_T<ACE_Select_Reactor_Token> ACE_Select_Reactor定义了常用的ACE_Select_Reactor类,可以在程序中直接使用。
2.3. 类主要成员变量
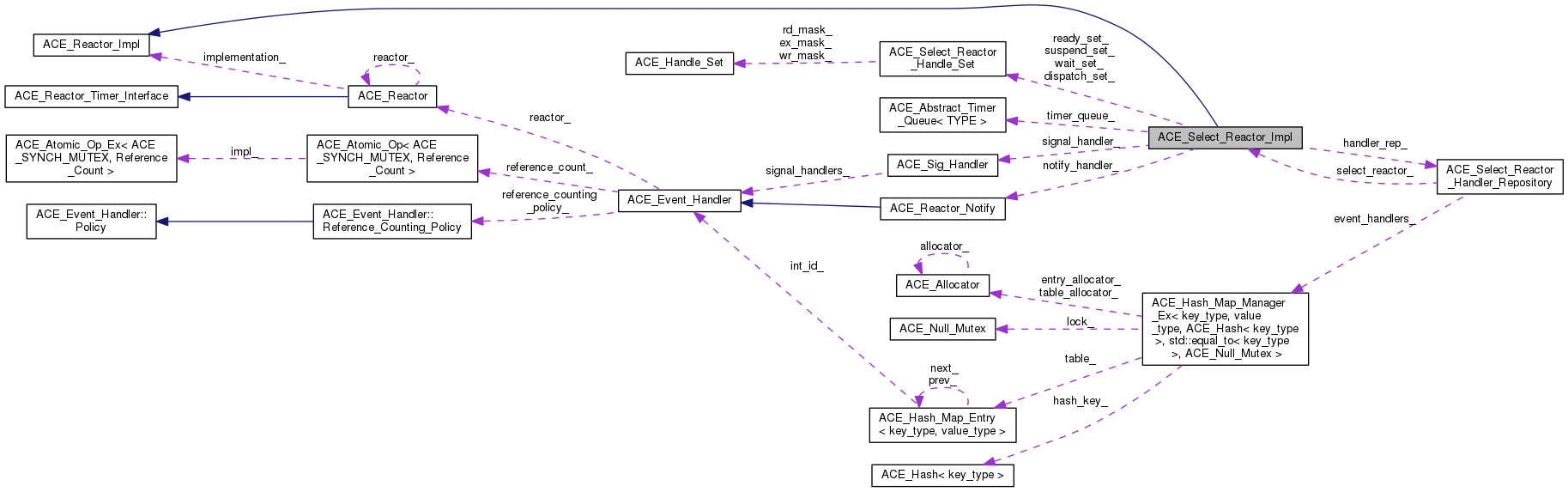
ACE_Select_Reactor_Impl继承自 ACE_Reactor_Impl,在类ACE_Select_Reactor_Impl中定义了常用的成员变量:
ace/Select_Reactor_Base.h
1 |
/// 提供<ACE_HANDLE>到<ACE_Event_Handler *>的映射 |
注解
其中ACE_Select_Reactor_Handler_Repository handler_rep_的数据结构定义,可参见 bind 函数 。
2.4. 事件处理函数调用图
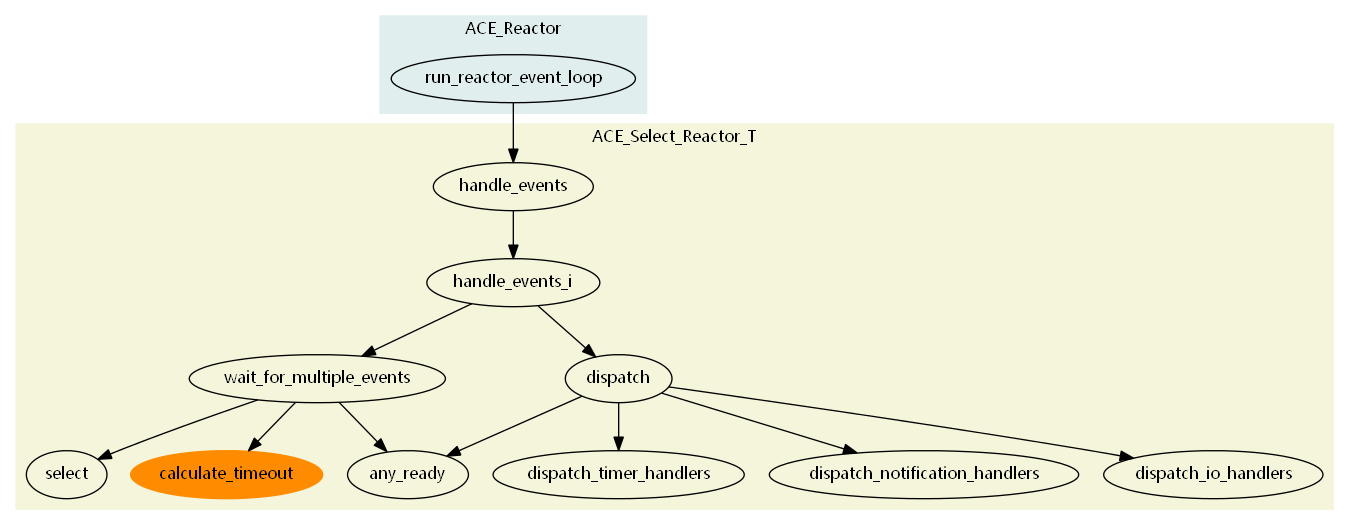
注解
calculate_timeout 函数的调用为类实现中 timer_queue_ 时间队列中最早到期时间,以便设置后续 select 调用函数的超时时间,从而实现了时间队列与IO句柄触发的整合。
2.5. 事件处理主流程
ace/Reactor.cpp
1 |
int |
行12行,Reactor调用了其实现者的 handle_events(ACE_Time_Value *max_wait_time) 函数,实现类的handle_event函数承担了主要工作的分发和处理。
2.5.1. handle_events 函数流程
ace/Select_Reactor_T.cpp handle_events 函数
1 |
template <class ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN> int |
2.5.2. handle_events_i 函数流程
ace/Select_Reactor_T.cpp handle_events_i 函数
1 |
template <class ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN> int |
行18, this->wait_for_multiple_events (this->dispatch_set_,max_wait_time) 实现了对于可分发句柄集的获取。
行21,this->dispatch (number_of_active_handles,this->dispatch_set_) 实现了对于分发句柄集的处理。
2.5.2.1. wait_for_multiple_events 函数
ace/Select_Reactor_T.cpp wait_for_multiple_events 函数
1 |
// Must be called with lock held. template <class ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN> int |
行12,,this->any_ready(dispatch_set) 实现了获取不需要select函数触发的其他类型满足触发条件的句柄
行25-26,this->timer_queue_->calculate_timeout(max_wait_time,&timer_buf) 实现了对定时器队列的超时的计算
行38-42,ACE_OS::select(width,dispatch_set.rd_mask_,dispatch_set.wr_mask_,dispatch_set.ex_mask_,this_timeout) 实现了对使用select函数返回的已触发的handle的跟踪
2.5.2.2. dispatch 函数
ace/Select_Reactor_T.cpp dispatch 函数
1 |
template <class ACE_SELECT_REACTOR_TOKEN> int |
处理顺序:
- dispatch_timer_handlers 处理分发定时器,定时器的处理优于Socket/IO的处理。 展开流程见: 定时器与Select_Reactor的分发集成。
- dispatch_notification_handlers 处理分发通知类消息。展开流程见: 通知与Select_Reactor 的分发集成。
- dispatch_io_handlers 处理分发 io handlers。展开流程见: IO句柄与Select_Reactor的分发集成。
ACE_Select_Reactor_T 介绍 (2)的更多相关文章
- ACE Reactor 源码解析
http://blogs.readthedocs.org/ ACE的学习笔记,根据源码分析了Reactor模型的实现. 因为笔记编写技术限制,这里仅列出主要目录,如有可能可以抽空复制到该Blog中 ...
- CSS3 background-image背景图片相关介绍
这里将会介绍如何通过background-image设置背景图片,以及背景图片的平铺.拉伸.偏移.设置大小等操作. 1. 背景图片样式分类 CSS中设置元素背景图片及其背景图片样式的属性主要以下几个: ...
- MySQL高级知识- MySQL的架构介绍
[TOC] 1.MySQL 简介 概述 MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统,由瑞典MySQL AB公司开发,目前属于Oracle公司. MySQL是一种关联数据库管理系统,将数据保存在不同的表中,而 ...
- Windows Server 2012 NIC Teaming介绍及注意事项
Windows Server 2012 NIC Teaming介绍及注意事项 转载自:http://www.it165.net/os/html/201303/4799.html Windows Ser ...
- Linux下服务器端开发流程及相关工具介绍(C++)
去年刚毕业来公司后,做为新人,发现很多东西都没有文档,各种工具和地址都是口口相传的,而且很多时候都是不知道有哪些工具可以使用,所以当时就想把自己接触到的这些东西记录下来,为后来者提供参考,相当于一个路 ...
- JavaScript var关键字、变量的状态、异常处理、命名规范等介绍
本篇主要介绍var关键字.变量的undefined和null状态.异常处理.命名规范. 目录 1. var 关键字:介绍var关键字的使用. 2. 变量的状态:介绍变量的未定义.已定义未赋值.已定义已 ...
- HTML DOM 介绍
本篇主要介绍DOM内容.DOM 节点.节点属性以及获取HTML元素的方法. 目录 1. 介绍 DOM:介绍DOM,以及对DOM分类和功能的说明. 2. DOM 节点:介绍DOM节点分类和节点层次. 3 ...
- HTML 事件(一) 事件的介绍
本篇主要介绍HTML中的事件知识:事件相关术语.DOM事件规范.事件对象. 其他事件文章 1. HTML 事件(一) 事件的介绍 2. HTML 事件(二) 事件的注册与注销 3. HTML 事件(三 ...
- HTML5 介绍
本篇主要介绍HTML5规范的内容和页面上的架构变动. 目录 1. HTML5介绍 1.1 介绍 1.2 内容 1.3 浏览器支持情况 2. 创建HTML5页面 2.1 <!DOCTYPE> ...
随机推荐
- Velocity 模板
Velocity 模板引擎介绍 引:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-lo-velocity1/ 在 现今的软件开发过程中,软件开发人员将更多的 ...
- luogu P1503 鬼子进村
嘟嘟嘟 线段树好题. 其实挺水的,想暴力怎么做:每一次从这个点开始向两边扩,直到遇到第一个摧毁的房屋. 那么把暴力改成倍增,然后线段树查询区间和是否为0.时间复杂度O(nlog2n). 题解好像有线段 ...
- Windows 备用数据流(ADS)的妙用___转载
NTFS交换数据流(Alternate Data Streams,简称ADS)是NTFS磁盘格式的一个特性,在NTFS文件系统下,每个文件都可以存在多个数据流.通俗的理解,就是其它文件可以“寄宿”在某 ...
- Yii 判断是不是post方式提交的数据
一.在controller里判断提交是不是通过post方式: if(Yii::$app->request->isPost){ return true; }else{ return fals ...
- oracle 完整性约束的禁用启用以及对表的影响,表的修改和复制
primary key ----表的唯一性约束,不能为空,且不能有重复值 foreign key ----俩表之间的约束,启用之时,在删除数据时需要先删除父表数据,再删除子表数据 禁用方式为:alte ...
- Oracle 行转列两种方法
1.新建一个名为TEST表 create table TEST( STUDENT varchar2(20), COURSE varchar2(20), SCORE number); INSERT IN ...
- 你不知道的javaScript笔记(4)
类型: JavaScript 有7种内置类型 空值 (null) 未定义(undefined) 布尔值(boolean) 数字(number) 字符串(string) 对象(object) 符号(sy ...
- c++:请编写一个函数,对字符串“zheshigekendiedetimu”按从大到小的顺序排列,并截取后n位数(n为函数的一个参数)。
String str="zheshigekendiedetimu"; StringBuffer buff=new StringBuffer(str); char[] arr=str ...
- solr索引大小对比
原文本 Solr建立的索引 如果进行Mysql索引应该是1:3的比例
- .scripts/mysql_install_db: 没有那个文件或目录
.scripts/mysql_install_db: 没有那个文件或目录 查了好多地方,在书上找到了解决方案,太不容易了 原因与解决方法: 系统与MYSQL版本不同,系统64位使用64位MYSQL,3 ...