Laravel开发:Laravel核心——Ioc服务容器源码解析(服务器解析)
make解析
服务容器对对象的自动解析是服务容器的核心功能,make 函数、build 函数是实例化对象重要的核心,先大致看一下代码:
public function make($abstract)
{
$abstract = $this->getAlias($abstract); if (isset($this->deferredServices[$abstract])) {
$this->loadDeferredProvider($abstract);
} return parent::make($abstract);
}
public function make($abstract)
{
return $this->resolve($abstract);
} public function resolve($abstract, $parameters = [])
{
$abstract = $this->getAlias($abstract); $needsContextualBuild = ! empty($parameters) || ! is_null(
$this->getContextualConcrete($abstract)
); // If an instance of the type is currently being managed as a singleton we'll
// just return an existing instance instead of instantiating new instances
// so the developer can keep using the same objects instance every time.
if (isset($this->instances[$abstract]) && ! $needsContextualBuild) {
return $this->instances[$abstract];
} $concrete = $this->getConcrete($abstract); // We're ready to instantiate an instance of the concrete type registered for
// the binding. This will instantiate the types, as well as resolve any of
// its "nested" dependencies recursively until all have gotten resolved.
if ($this->isBuildable($concrete, $abstract)) {
$object = $this->build($concrete);
} else {
$object = $this->make($concrete);
} // If we defined any extenders for this type, we'll need to spin through them
// and apply them to the object being built. This allows for the extension
// of services, such as changing configuration or decorating the object.
foreach ($this->getExtenders($abstract) as $extender) {
$object = $extender($object, $this);
} // If the requested type is registered as a singleton we'll want to cache off
// the instances in "memory" so we can return it later without creating an
// entirely new instance of an object on each subsequent request for it.
if ($this->isShared($abstract) && ! $needsContextualBuild) {
$this->instances[$abstract] = $object;
} $this->fireResolvingCallbacks($abstract, $object); $this->resolved[$abstract] = true; return $object;
}
在讲解解析流程之前,我们先说说使用make函数进行解析的分类:
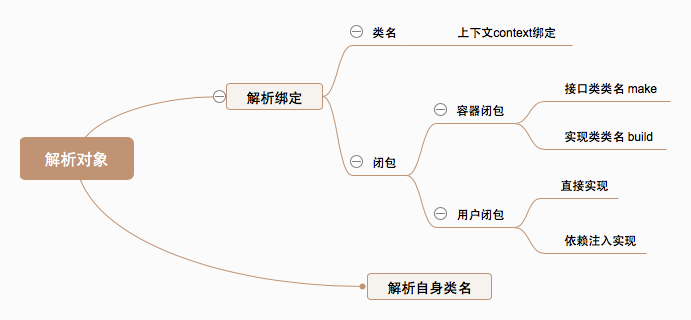
我们详细的讲一下上图。这里我把使用make函数进行解析的情况分为大致两种:
解析对象没有绑定过任何类,例如:
$app->make('App\Http\Controllers\HomeController');
解析对象绑定过实现类
对于绑定过实现类的对象可以分为两种:
绑定的是类名,例如:
$app->when('App\Http\Controllers\HomeController')
->needs('App\Http\Requests\InRequest')
->give('App\Http\Requests\TestsRequest');
绑定的是闭包
对于绑定的是闭包的又可以分为:
用户绑定闭包,例如:
$app->singleton('auth',function($app){
return new AuthManager($app)
});//对象类直接实现方法
$app->singleton(EloquentFactory::class, function ($app) {
return EloquentFactory::construct(
$app->make(FakerGenerator::class), database_path('factories')
);//对象类依赖注入
});
服务容器外包一层闭包函数(make/build),例如:
$app->singleton(
Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class,
App\Http\Kernel::class
);//包装make $app->singleton(
App\ConSole\Kernel::class,
);//包装build
我们在这里先大致讲一下服务容器解析的流程,值得注意的是其中 build 函数有可能会递归调用 make:
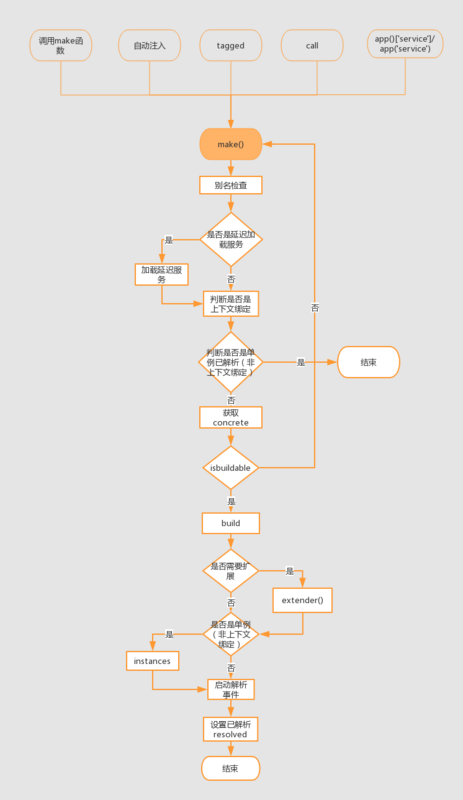
获取服务名称。
加载延迟服务。判断当前的接口是否是延迟服务提供者,若是延迟服务提供者,那么还要对服务提供者进行注册与启动操作。
解析单例。如果接口服务是已经被解析过的单例对象,而且并非上下文绑定,那么直接取出对象。
获取注册的实现。实现方式可能是上下文绑定的,也可能是 binding 数组中的闭包,也有可能就是接口本身。
build 解析。首先判断是否需要递归。是,则递归 make;否,则调用 build 函数;直到调用 build 为止
执行扩展。若当前解析对象存在扩展,运行扩展函数。
创造单例对象。若 shared 为真,且不存在上下文绑定,则放入单例数组中
回调
标志解析
下面我们开始详细分解代码逻辑。由于 getAlias 函数已经在 上一篇 讲过,这里不会再说。而loadDeferredProvider 函数作用是加载延迟服务,与容器解析关系不大,我们放在以后再说。
获取注册的实现
获取解析类的真正实现,函数优先去获取上下文绑定的实现,否则获取 binding 数组中的实现,获取不到就是直接返回自己作为实现:
protected function getConcrete($abstract)
{
if (! is_null($concrete = $this->getContextualConcrete($abstract))) {
return $concrete;
} if (isset($this->bindings[$abstract])) {
return $this->bindings[$abstract]['concrete'];
} return $abstract;
}
一般来说,上下文绑定的服务是通过依赖注入来实现的:
$this->app->when(PhotoController::class)
->needs(Filesystem::class)
->give(function () {
return Storage::disk('local');
}); class PhotoController{
protected $file; public function __construct(Filesystem $file){
$this->file = $file;
}
}
服务容器会在解析 PhotoController 的时候,通过放射获取参数类型 Filesystem,并且会把 Filesystem 自动解析为 Storage::disk('local')。如何实现的呢?首先,从 上一篇 文章我们知道,当进行上下文绑定的时候,实际上是维护 contextual 数组,通过上下文绑定,这个数组中存在:
contextual[PhotoController][Filesystem] = function () { return Storage::disk('local'); }
若是服务容器试图构造 PhotoController 类,那么由于其构造函数依赖于 Filesystem,所以容器必须先生成 Filesystem 类,然后再注入到 PhotoController 中。
在构造 Filesystem 之前,服务容器会先把 PhotoController 放入 buildStack 中,继而再去解析 Filesystem。
解析 Filesystem 时,运行 getContextualConcrete 函数:
protected function getContextualConcrete($abstract)
{
if (! is_null($binding = $this->findInContextualBindings($abstract))) {
return $binding;
} if (empty($this->abstractAliases[$abstract])) {
return;
} foreach ($this->abstractAliases[$abstract] as $alias) {
if (! is_null($binding = $this->findInContextualBindings($alias))) {
return $binding;
}
}
} protected function findInContextualBindings($abstract)
{
if (isset($this->contextual[end($this->buildStack)][$abstract])) {
return $this->contextual[end($this->buildStack)][$abstract];
}
}
从上面可以看出,getContextualConcrete 函数把当前解析的类(Filesystem)作为 abstract,buildStack 最后一个类(PhotoController)作为 concrete,寻找 this->contextual[concrete] [abstract] (contextual[PhotoController] [Filesystem])中的值,在这个例子里面这个数组值就是那个匿名函数。
build 解析
对于服务容器来说,绑定是可以递归的,例如:
$app->bind('a','b');
$app->bind('b','c');
$app->bind('c',function(){
return new C;
})
遇到这样的情况,bind 绑定中 getClosure 函数开始发挥作用,该函数会给类包一层闭包,闭包内调用 make 函数,服务容器会不断递归调用 make 函数,直到最后一层,也就是绑定 c 的匿名函数。但是另一方面,有一些绑定方式并没有调用 bind 函数,例如上下文绑定 context:
$this->app->when(E::class)
->needs(F::class)
->give(A::class);
当make(E::class)的时候,getConcrete 返回 A 类,而不是调用 make 函数的闭包,所以并不会启动递归流程得到 C 的匿名函数,所以造成 A 类完全无法解析,isBuildable 函数就是解决这种问题的,当发现需要解析构造的对象很有可能是递归的,那么就递归调用 make 函数,否则才会调用build。
...
if ($this->isBuildable($concrete, $abstract)) {
$object = $this->build($concrete);
} else {
$object = $this->make($concrete);
}
... protected function isBuildable($concrete, $abstract)
{
return $concrete === $abstract || $concrete instanceof Closure;
}
执行扩展
获取扩展闭包,并运行扩展函数:
protected function getExtenders($abstract)
{
$abstract = $this->getAlias($abstract); if (isset($this->extenders[$abstract])) {
return $this->extenders[$abstract];
} return [];
}
回调
先后启动全局的解析事件回调函数,再启动针对类型的事件回调函数:
protected function fireResolvingCallbacks($abstract, $object)
{
$this->fireCallbackArray($object, $this->globalResolvingCallbacks); $this->fireCallbackArray(
$object, $this->getCallbacksForType($abstract, $object, $this->resolvingCallbacks)
); $this->fireAfterResolvingCallbacks($abstract, $object);
} protected function getCallbacksForType($abstract, $object, array $callbacksPerType)
{
$results = []; foreach ($callbacksPerType as $type => $callbacks) {
if ($type === $abstract || $object instanceof $type) {
$results = array_merge($results, $callbacks);
}
} return $results;
} protected function fireAfterResolvingCallbacks($abstract, $object)
{
$this->fireCallbackArray($object, $this->globalAfterResolvingCallbacks); $this->fireCallbackArray(
$object, $this->getCallbacksForType($abstract, $object, $this->afterResolvingCallbacks)
);
build 解析
make 函数承担了解析的大致框架,build 主要的职责就是利用反射将类构造出来,先看看主要代码:
public function build($concrete)
{
// If the concrete type is actually a Closure, we will just execute it and
// hand back the results of the functions, which allows functions to be
// used as resolvers for more fine-tuned resolution of these objects.
if ($concrete instanceof Closure) {
return $concrete($this, $this->getLastParameterOverride());
} $reflector = new ReflectionClass($concrete); // If the type is not instantiable, the developer is attempting to resolve
// an abstract type such as an Interface of Abstract Class and there is
// no binding registered for the abstractions so we need to bail out.
if (! $reflector->isInstantiable()) {
return $this->notInstantiable($concrete);
} $this->buildStack[] = $concrete; $constructor = $reflector->getConstructor(); // If there are no constructors, that means there are no dependencies then
// we can just resolve the instances of the objects right away, without
// resolving any other types or dependencies out of these containers.
if (is_null($constructor)) {
array_pop($this->buildStack); return new $concrete;
} $dependencies = $constructor->getParameters(); // Once we have all the constructor's parameters we can create each of the
// dependency instances and then use the reflection instances to make a
// new instance of this class, injecting the created dependencies in.
$instances = $this->resolveDependencies(
$dependencies
); array_pop($this->buildStack); return $reflector->newInstanceArgs($instances);
}
我们下面详细的说一下各个部分:
闭包函数执行
if ($concrete instanceof Closure) {
return $concrete($this, $this->getLastParameterOverride());
}
这段代码很简单,但是作用很大。前面说过闭包函数有很多种类:
用户绑定时提供的直接提供实现类的方式:
$app->singleton('auth',function($app){
return new AuthManager($app)
});//对象类直接实现方法
这种情况 concrete(this) 直接就可以解析构造出具体实现类,服务容器解析完毕。
用户绑定时提供的带有依赖注入的实现:
$app->singleton(EloquentFactory::class, function ($app) {
return EloquentFactory::construct(
$app->make(FakerGenerator::class), database_path('factories')
);//对象类依赖注入
这种情况下,concrete(this) 会转而去解析 FakerGenerator::class,递归调用 make 函数。
bind函数使用 getClosure 包装而来:
function($container, $parameters = []){
method = make/build;
return $container->$method($concrete, $parameters);
}
这种情况,concrete(this) 将会继续递归调用 make 或者 build。
反射
当 build 的参数是类名而不是闭包的时候,就要利用反射构建类对象,如果构建的类对象不需要依赖任何其他参数,那么:
$reflector = new ReflectionClass($concrete);
$constructor = $reflector->getConstructor();
if (is_null($constructor)) {
return new $concrete;
}
如果需要依赖注入,那么就要用反射机制来获取 __construct 函数所需要注入的依赖,如果在make的时候带入参数值,那么直接利用传入的参数值;如果依赖是类对像,那么递归调用 make 函数;如果依赖是变量值,那么就从上下文中或者参数默认值中去获取:
...$dependencies = $constructor->getParameters();
$instances = $this->resolveDependencies($dependencies);
... protected function resolveDependencies(array $dependencies)
{
$results = []; foreach ($dependencies as $dependency) { if ($this->hasParameterOverride($dependency)) {
$results[] = $this->getParameterOverride($dependency); continue;
} $results[] = is_null($class = $dependency->getClass())
? $this->resolvePrimitive($dependency)
: $this->resolveClass($dependency);
} return $results;
}
解析变量值参数,如果变量值在上下文绑定中设置过,则去取上下文绑定的值,否则通过反射去取参数默认值,如果没有默认值,那么就要终止报错:
protected function resolvePrimitive(ReflectionParameter $parameter)
{
if (! is_null($concrete = $this->getContextualConcrete('$'.$parameter->name))) {
return $concrete instanceof Closure ? $concrete($this) : $concrete;
} if ($parameter->isDefaultValueAvailable()) {
return $parameter->getDefaultValue();
} $this->unresolvablePrimitive($parameter);
} protected function hasParameterOverride($dependency)
{
return array_key_exists(
$dependency->name, $this->getLastParameterOverride()
);
} protected function getParameterOverride($dependency)
{
return $this->getLastParameterOverride()[$dependency->name];
} protected function getLastParameterOverride()
{
return count($this->with) ? end($this->with) : [];
}
解析类参数,利用服务容器进行依赖注入:
protected function resolveClass(ReflectionParameter $parameter)
{
try {
return $this->make($parameter->getClass()->name);
}
catch (BindingResolutionException $e) {
if ($parameter->isOptional()) {
return $parameter->getDefaultValue();
} throw $e;
}
}
buildstack 解析栈
值的注意的是服务容器里面有个 buildStack,每次利用反射对参数进行依赖注入的时候,都要向这个数组中压入当前的解析对象,前面说过这部分是为了上下文绑定而设计的:
...
$this->buildStack[] = $concrete;//压入数组栈中
...
$instances = $this->resolveDependencies($dependencies);//解析依赖注入的参数
array_pop($this->buildStack);//弹出数组栈
...
解析标签
使用标签绑定的类,将会使用 tagged 来解析:
public function tagged($tag)
{
$results = []; if (isset($this->tags[$tag])) {
foreach ($this->tags[$tag] as $abstract) {
$results[] = $this->make($abstract);
}
} return $results;
}
call方法注入
服务容器中,我们直接使用或者间接的使用 make 来构造服务对象,但是在实际的应用场景中,会有这样的需求:我们拥有一个对象或者闭包函数,想要调用它的一个函数,但是它函数里面却有其他类的参数,这个就需要进行 call 方法注入
public function call($callback, array $parameters = [], $defaultMethod = null)
{
return BoundMethod::call($this, $callback, $parameters, $defaultMethod);
}
在 上一篇 文章中,我们说过,call 函数中的 callback 参数有以下几种形式:
闭包 Closure
class@method
类静态函数,class::method
类静态函数: [ className/classObj, method ];类非静态函数: [ classObj, method ]
若 defaultMethod 不为空,className
首先,我们先看看 call 方法注入的流程图:
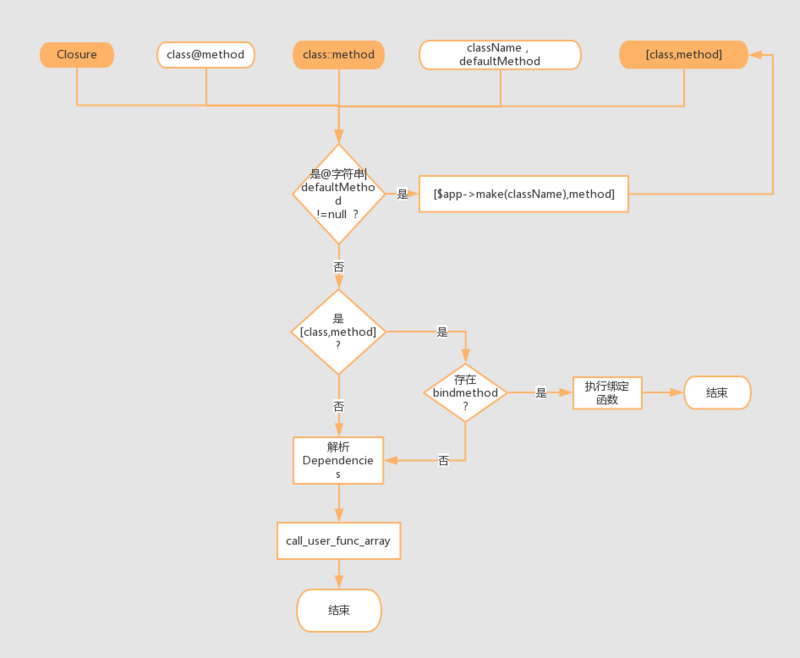
从流程图中我们可以看出来,虽然调用 call 的形式有 5 种,但是实际最终的形式是三种,第二种和第五种被转化为了第四种。
接下来,我们详细的解析源码:
call
先看一下 call 方法的主体:
public static function call($container, $callback, array $parameters = [], $defaultMethod = null)
{
if (static::isCallableWithAtSign($callback) || $defaultMethod) {
return static::callClass($container, $callback, $parameters, $defaultMethod);
} return static::callBoundMethod($container, $callback, function () use ($container, $callback, $parameters) {
return call_user_func_array(
$callback, static::getMethodDependencies($container, $callback, $parameters)
);
});
}
可以看出来,call 方法注入主要有 4 个大的步骤:
对于 className@method 和 className-defaultMethod,实例化 className 为类对象,转化为 [ classObj, method ]。
判断 [ classObj / classname, method ] 是否存在被绑定的方法,如果有则调用。
利用服务容器解析依赖的参数。
调用 call_user_func_array。
实例化类对象
在这里 className@method 和 className-defaultMethod 两种情况被转化为 [ classObj, method ], className会被实例化为类对象,并重新调用 call:
protected static function isCallableWithAtSign($callback)
{
return is_string($callback) && strpos($callback, '@') !== false;
} protected static function callClass($container, $target, array $parameters = [], $defaultMethod = null)
{
$segments = explode('@', $target); $method = count($segments) == 2
? $segments[1] : $defaultMethod; if (is_null($method)) {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('Method not provided.');
} return static::call(
$container, [$container->make($segments[0]), $method], $parameters
);
}
执行绑定方法
针对 [ className/classObj, method ], 调用被绑定的方法:
protected static function callBoundMethod($container, $callback, $default)
{
if (! is_array($callback)) {
return value($default);
} $method = static::normalizeMethod($callback); if ($container->hasMethodBinding($method)) {
return $container->callMethodBinding($method, $callback[0]);
} return value($default);
} protected static function normalizeMethod($callback)
{
$class = is_string($callback[0]) ? $callback[0] : get_class($callback[0]); return "{$class}@{$callback[1]}";
} public function hasMethodBinding($method)
{
return isset($this->methodBindings[$method]);
} public function callMethodBinding($method, $instance)
{
return call_user_func($this->methodBindings[$method], $instance, $this);
}
那么这个被绑定的方法 methodBindings 从哪里来呢,就是 上一篇 文章提的 bindMethod:
public function bindMethod($method, $callback)
{
$this->methodBindings[$method] = $callback;
}
从上面可以看出来,methodBindings 中 callback 参数一定是 classname@method 形式的。
实例化依赖
这一步就要通过反射来获取函数方法需要注入的参数类型,然后利用服务容器对参数类型进行解析构建:
protected static function getMethodDependencies($container, $callback, array $parameters = [])
{
$dependencies = []; foreach (static::getCallReflector($callback)->getParameters() as $parameter) {
static::addDependencyForCallParameter($container, $parameter, $parameters, $dependencies);
} return array_merge($dependencies, $parameters);
}
getCallReflector 函数利用反射来获取参数类型,值得注意的是class::method是需要拆分处理的:
protected static function getCallReflector($callback)
{
if (is_string($callback) && strpos($callback, '::') !== false) {
$callback = explode('::', $callback);
} return is_array($callback)
? new ReflectionMethod($callback[0], $callback[1])
: new ReflectionFunction($callback);
}
利用传入的参数,利用服务容器构建解析参数类型,或者获取参数默认值:
protected static function addDependencyForCallParameter($container, $parameter,
array &$parameters, &$dependencies)
{
if (array_key_exists($parameter->name, $parameters)) {
$dependencies[] = $parameters[$parameter->name]; unset($parameters[$parameter->name]);
} elseif ($parameter->getClass()) {
$dependencies[] = $container->make($parameter->getClass()->name);
} elseif ($parameter->isDefaultValueAvailable()) {
$dependencies[] = $parameter->getDefaultValue();
}
}
call_user_func_array
关于这个函数可以参考 Laravel学习笔记之Callback Type
call_user_func_array(
$callback, static::getMethodDependencies($container, $callback, $parameters)
);
本文转自:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000009402317#articleHeader10
Laravel开发:Laravel核心——Ioc服务容器源码解析(服务器解析)的更多相关文章
- Laravel开发:Laravel核心——Ioc服务容器源码解析(服务器绑定)
服务容器的绑定 bind 绑定 bind 绑定是服务容器最常用的绑定方式,在 上一篇文章中我们讨论过,bind 的绑定有三种: 绑定自身 绑定闭包 绑定接口 今天,我们这篇文章主要从源码上讲解 Ioc ...
- Laravel开发:Laravel核心——Ioc服务容器
服务容器 在说 Ioc 容器之前,我们需要了解什么是 Ioc 容器. Laravel 服务容器是一个用于管理类依赖和执行依赖注入的强大工具. 在理解这句话之前,我们需要先了解一下服务容器的来龙去脉: ...
- 核心概念 —— 服务容器
1.简介 Laravel 服务容器是一个用于管理类依赖和执行依赖注入的强大工具.依赖注入听上去很花哨,其实质是通过构造函数或者某些情况下通过 set 方法将类依赖注入到类中. 让我们看一个简单的例子: ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析系列文章导读
1. 简介 Spring 是一个轻量级的企业级应用开发框架,于 2004 年由 Rod Johnson 发布了 1.0 版本.经过十几年的迭代,现在的 Spring 框架已经非常成熟了.Spring ...
- Laravel框架下路由的使用(源码解析)
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是关于Laravel框架下路由的使用(源码解析),有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你有所帮助. 前言 我的解析文章并非深层次多领域的解析攻略.但是参考着开发文 ...
- 最简 Spring IOC 容器源码分析
前言 BeanDefinition BeanFactory 简介 Web 容器启动过程 bean 的加载 FactoryBean 循环依赖 bean 生命周期 公众号 前言 许多文章都是分析的 xml ...
- 小白都能看懂的Spring源码揭秘之IOC容器源码分析
目录 前言 IOC 只是一个 Map 集合 IOC 三大核心接口 IOC 初始化三大步骤 定位 加载 注册 总结 前言 在 Spring 框架中,大家耳熟能详的无非就是 IOC,DI,Spring M ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 创建原始 bean 对象
1. 简介 本篇文章是上一篇文章(创建单例 bean 的过程)的延续.在上一篇文章中,我们从战略层面上领略了doCreateBean方法的全过程.本篇文章,我们就从战术的层面上,详细分析doCreat ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 余下的初始化工作
1. 简介 本篇文章是"Spring IOC 容器源码分析"系列文章的最后一篇文章,本篇文章所分析的对象是 initializeBean 方法,该方法用于对已完成属性填充的 bea ...
随机推荐
- Python 操作mongodb 简单实例
1.建立数据库用户 要读写 mongo数据库,默认没有用户名和密码也可以对数据库进行读写操作,但是从安全的角度,最好给要操作的数据库建立用户名和密码. 打开mongo数据库服务,打开mongo.exe ...
- Maven 使用 二——nexus
上篇博客介绍了创建maven项目的两种方式,当中一种是使用命令行的方式来创建,这种情况非常少,一般我们都有IDE开发环境.所以接下来,我们还是在一个详细的IDE中来说,我使用的是Eclipse. 一. ...
- 二分求幂 - A^B(王道*)
题目描述: 求A^B的最后三位数表示的整数,说明:A^B的含义是“A的B次方” 输入: 输入数据包含多个测试实例,每个实例占一行,由两个正整数A和B组成(1<=A,B<=10000),如果 ...
- MyISAM的key_buffer_size和InnoDB的innodb_buffer_pool_size
一.MyISAM的key_buffer_size MyISAM的索引方式是非聚集索引,主索引和其他索引没有本质区别,在data域都是存储了具体记录行的地址.key_buffer_size规定了系统将多 ...
- socket websocket
1.websocket客户端 websocket允许通过JavaScript建立与远程服务器的连接,从而实现客户端与服务器间双向的通信.在websocket中有两个方法: 1.send() 向远程服务 ...
- rpm安装找不到.so库文件(linux动态库连接的相关知识)(转)
1.找不到库文件的原因 库文件不存在 这种情况一般是因为所需要的包没装,只要安装相应的包就可以解决 存在而系统不知道 这种情况一般出现在自己编译软件时候 确保库文件所在的路径已加入系统,在/etc/l ...
- Java 8 List
排序 依据自定义对象的某个属性进行排序. List<Student> students = Arrays.asList(student1, student2, student3); stu ...
- Loadrunner11之VuGen常用函数lr_user_data_point(一)
Loadrunner11之VuGen常用函数lr_user_data_point(一) 上一篇 / 下一篇 2011-11-15 00:15:33 / 精华(1) / 置顶(1) / 个人分类:性能 ...
- Redis 配置文件及命令详解
==基本配置 daemonize no 是否以后台进程启动 databases 16 创建database的数量(默认选中的是database 0) save 900 1 #刷新快照到硬盘中,必须满足 ...
- C语言学习笔记(四) 流程控制
流程控制 流程控制,说通俗一点就是程序代码执行的顺序.不管对于哪门语言来说,流程控制都是很重要的一部分内容: 流程控制的分类,可以分为三大类: 1.顺序 这个很好理解,顺序执行就是代码从上往下一行行的 ...
