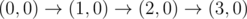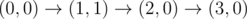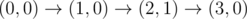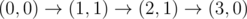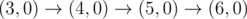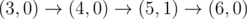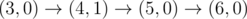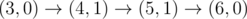Codeforces 821E Okabe and El Psy Kongroo(矩阵快速幂)
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Okabe likes to take walks but knows that spies from the Organization could be anywhere; that's why he wants to know how many different walks he can take in his city safely. Okabe's city can be represented as all points (x, y) such that x and y are non-negative. Okabe starts at the origin (point (0, 0)), and needs to reach the point (k, 0). If Okabe is currently at the point (x, y), in one step he can go to (x + 1, y + 1), (x + 1, y), or (x + 1, y - 1).
Additionally, there are n horizontal line segments, the i-th of which goes from x = ai to x = bi inclusive, and is at y = ci. It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n. The i-th line segment forces Okabe to walk with y-value in the range 0 ≤ y ≤ ci when his xvalue satisfies ai ≤ x ≤ bi, or else he might be spied on. This also means he is required to be under two line segments when one segment ends and another begins.
Okabe now wants to know how many walks there are from the origin to the point (k, 0) satisfying these conditions, modulo 109 + 7.
The first line of input contains the integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ k ≤ 1018) — the number of segments and the destination xcoordinate.
The next n lines contain three space-separated integers ai, bi, and ci (0 ≤ ai < bi ≤ 1018, 0 ≤ ci ≤ 15) — the left and right ends of a segment, and its y coordinate.
It is guaranteed that a1 = 0, an ≤ k ≤ bn, and ai = bi - 1 for 2 ≤ i ≤ n.
Print the number of walks satisfying the conditions, modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
1 3
0 3 3
4
2 6
0 3 0
3 10 2
4
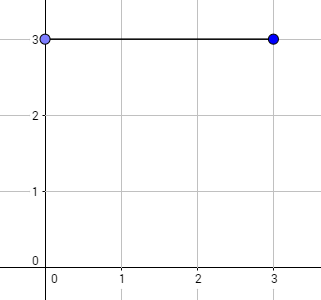
The graph above corresponds to sample 1. The possible walks are:
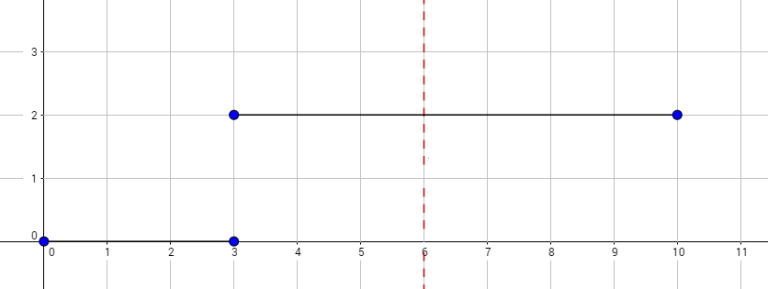
The graph above corresponds to sample 2. There is only one walk for Okabe to reach (3, 0). After this, the possible walks are:
题目链接:CF 821E
很好的一道题,用dp[x][y]表示到坐标$(x,y)$的方案数,容易可以想到简单的递推:$dp[x][y]=dp[x-1][y]+dp[x-1][y-1]+dp[x-1][y+1]$,但是由于x太大不能直接写dp,看这个式子,发现当前的dp[x]只跟dp[x-1]有关系,因此实际上只需要两个一维数组就可以完成这种迭代,那如何加速迭代呢?用矩阵快速幂,把dp[x-1][y]放到矩阵A的第一行,dp[x][y]显然是转移之后的矩阵A的第一行,如何转移?y从上一次的y-1,y+1,y进行转移,因此构造中间矩阵B,B[i][j]=i走到j是否可行,然后一条线段一条线段地进行转移,当上一次转移线段的高度为3,当前线段高度为2,那显然3这个高度已经越界了,因此转移之前要把A矩阵的越界位置方案数置0,然后用当前的高度作为行数进行转移,否则会多算,最后注意一下长度不能超过k,不然也会多算
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <bitset>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LC(x) (x<<1)
#define RC(x) ((x<<1)+1)
#define MID(x,y) ((x+y)>>1)
#define fin(name) freopen(name,"r",stdin)
#define fout(name) freopen(name,"w",stdout)
#define CLR(arr,val) memset(arr,val,sizeof(arr))
#define FAST_IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef long long LL;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int N = 110;
const int M = 16;
const LL mod = 1000000007LL;
int row;
struct Mat
{
LL A[M][M];
void zero()
{
CLR(A, 0);
}
Mat operator*(Mat b)
{
Mat c;
c.zero();
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
{
for (int k = 0; k < row; ++k)
{
if (A[i][k])
{
for (int j = 0; j < row; ++j)
{
if (b.A[k][j])
c.A[i][j] = (c.A[i][j] + A[i][k] * b.A[k][j]) % mod;
}
}
}
}
return c;
}
friend Mat operator^(Mat a, LL b)
{
Mat r;
r.zero();
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i)
r.A[i][i] = 1;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
r = r * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return r;
}
};
LL a[N], b[N];
int c[N]; int main(void)
{
int n, i, j;
LL k;
while (~scanf("%d%I64d", &n, &k))
{
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%I64d%I64d%d", &a[i], &b[i], &c[i]);
if (b[n - 1] > k)
b[n - 1] = k;
Mat A,B;
A.zero();
A.A[0][0] = 1;
B.zero();
for (j = 0; j <= 15; ++j) //列
{
B.A[j][j] = 1;
if (j - 1 >= 0)
B.A[j][j - 1] = 1;
if (j + 1 <= 15)
B.A[j][j + 1] = 1;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
row = c[i] + 1;
for (j = c[i] + 1; j < M; ++j)
A.A[0][j] = 0;
A = A * (B ^ (b[i] - a[i]));
}
printf("%I64d\n", A.A[0][0]);
}
return 0;
}
Codeforces 821E Okabe and El Psy Kongroo(矩阵快速幂)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo 矩阵快速幂优化dp
E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- CF821 E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo 矩阵快速幂
LINK 题意:给出$n$条平行于x轴的线段,终点$k$坐标$(k <= 10^{18})$,现在可以在线段之间进行移动,但不能超出两条线段的y坐标所夹范围,问到达终点有几种方案. 思路:刚开始 ...
- Codeforces 821E Okabe and El Psy Kongroo
题意:我们现在位于(0,0)处,目标是走到(K,0)处.每一次我们都可以从(x,y)走到(x+1,y-1)或者(x+1,y)或者(x+1,y+1)三个位子之一.现在一共有N段线段,每条线段都是平行于X ...
- codeforces E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo(dp+矩阵快速幂)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/821/problem/E 题意:我们现在位于(0,0)处,目标是走到(K,0)处.每一次我们都可以从(x,y)走到(x+1,y- ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo DP+矩阵快速幂加速
E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo Okabe likes to take walks but knows that spies from the Organization ...
- Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2) E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo dp+矩阵快速幂
E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo Okabe likes to take walks but knows that spies from the Organization c ...
- CF821E 【Okabe and El Psy Kongroo】
首先我们从最简单的dp开始 \(dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j]+dp[i-1][j+1]+dp[i-1][j-1]\) 然后这是一个O(NM)的做法,肯定行不通,然后我们考虑使用矩阵加速 \( ...
- [codeforces821E]Okabe and El Psy Kongroo
题意:(0,0)走到(k,0),每一部分有一条线段作为上界,求方案数. 解题关键:dp+矩阵快速幂,盗个图,注意ll 关于那条语句为什么不加也可以,因为我的矩阵C,就是因为多传了了len的原因,其他位 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 13 D. Iterated Linear Function (矩阵快速幂)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/678/D 简单的矩阵快速幂模版题 矩阵是这样的: #include <bits/stdc++.h&g ...
随机推荐
- jQuery 使用问题
attr('checked', 'checked')调用多次仅第一次生效 使用attr()获取这些属性的返回值为String类型,如果被选中(或禁用)就返回checked.selected或disab ...
- Ubuntu 配置多域名站点
思路 -- 跟Windows 一样 1添加Nginx 指向项目的入口 配置域名 2修改本地host文件域名指向 实现: 1 进入Nginx 配置文件 默认地址为 /etc/nginx/sites-e ...
- python入门(续)
类和方法 创建类 class A(object): def add(self, a,b ): return a+b count = A() print(count.add(3,5)) 初始化工作 cl ...
- YUM工具使用
一.yum命令概述: 1.简介: yum命令时在Fedora和RedHat以及SUSE中基于rpm的软件包管理器,它可以使系统管理人员交互和自动化地更细与管理RPM软件包,能够从指定的服务器自动下载R ...
- mybatis动态列名
mybatis动态列名 <select id="getUser" resultType="java.util.Map" parameterType=&qu ...
- Java线程和多线程(十)——TimerTask
Java中的java.util.Timer是一个工具类,可以用于调度一个线程在将来的某一个时刻执行特定的任务.Java Timer类可以将一个任务定时执行一次,或者是以后以每隔一定的时间间隔来触发一次 ...
- 详解mysql体系结构和存储引擎
概述 之前整理的一些mysql方面内容,适合做备忘,因为我基本不会去记这些概念性的东西,大家做个了解就可以了. 一.定义数据库和实例 1.数据库: 物理操作系统文件或其他形式文件类型的集合. 在MyS ...
- itop-4412开发板学习-内核信号量
1. 翻翻书看下,linux提供两种信号量,内核信号量,由内核控制路径使用,System V IPC信号量,由用户态进程使用.下面的就是内核部分的信号量.内核信号量类似于自旋锁,当锁关闭着时,不允许内 ...
- I两种冒泡算法
两种冒泡算法: 第一个循环,I 定位当前坐标,第二个循环 把 I 之后的每个数都与 I 比较(比 I 小的都去坐标I),第二个循环之后 坐标 I 为数组里最小的数值. 效率比较高的冒泡算法: stat ...
- python语句和语法
python语句和语法 python程序结构: 1.程序由模块构成. 2.模块包含语句. 3.语句包含表达式. 4.表达式建立并处理对象. python的语法实质上是有语句和表达式组成的.表达式处理对 ...