pyhton课堂随笔-基本画图
- %matplotlib inline
- import matplotlib as mpl
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- import pandas as pd
#首先导入基本的画图包,第一句是必要的
- house = pd.read_csv('./housing.csv') # 读取数据,数据文件存放在c根目录下盘可直接这样访问,如果放在文件夹里。可像平常一样加上目录名称
- house.describe().loc[['min', 'std', 'max', 'mean'], ['RM', 'MEDV']].round(2) 求均值方差等
可得到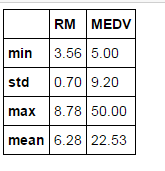
- for i in range(4):
- print (house.iloc[:, i].corr(house.iloc[:, i+4]).round(2)) # 可得到相关系数
- fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize = (16, 4))
- for n in range(4):
- axes[n].scatter(house.iloc[:, n],house.iloc[:, n+4]) ## 这里开始画图
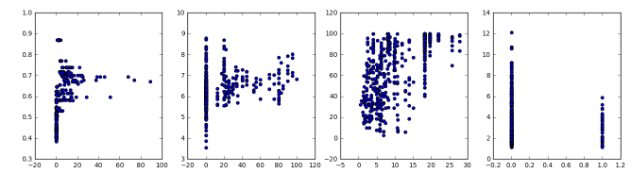
- 基本概念
- figure:画布
- axes: 坐标轴,或者理解成所画的图形
- 一张画布(figure)可以有很多图(axes)
- 其他
- label: 坐标上的标注
- tickets: 刻度
- legend:图例
- loc = 0: 自动寻找最好的位置
- ncol = 3:分三列
- fontsize
- frameon = True: 边框
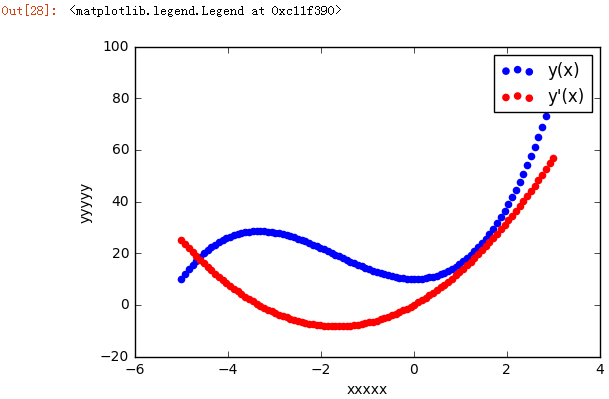
- fig, ax = plt.subplots()
- ax.plot(x, y1, color = "blue", label = "y(x)")
- ax.plot(x, y2, color = "red", label = "y'(x)")
- ax.set_xlabel("xxxxx")
- ax.set_ylabel("yyyyy")
- ax.legend() # 基本画线图

- fig, ax = plt.subplots()
- ax.scatter(x, y1, color = "blue", label = "y(x)")
- ax.scatter(x, y2, color = "red", label = "y'(x)")
- ax.set_xlabel("xxxxx")
- ax.set_ylabel("yyyyy")
- ax.legend() #基本画点图
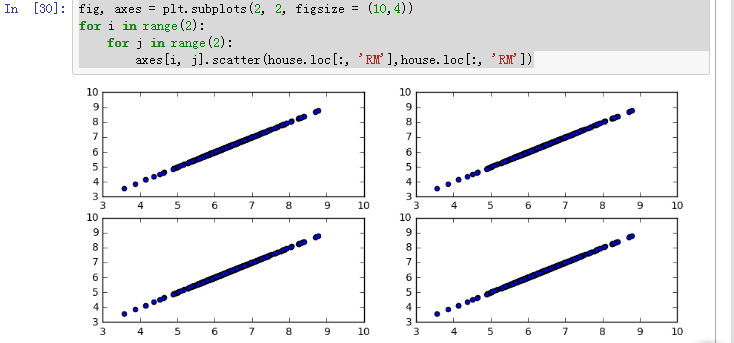
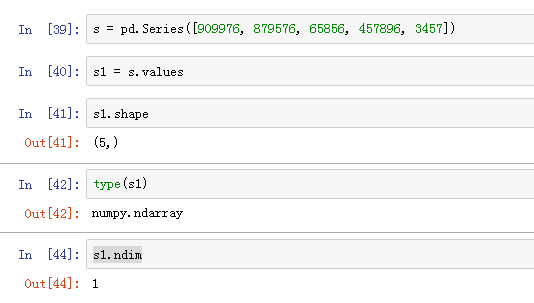
- fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize = (10,4))
- for i in range(2):
- for j in range(2):
- axes[i, j].scatter(house.loc[:, 'RM'],house.loc[:, 'RM'])
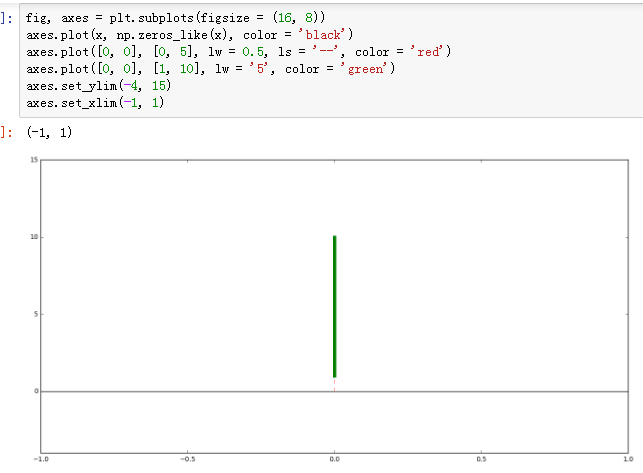
- fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize = (16, 8))
- axes.plot(x, np.zeros_like(x), color = 'black')
- axes.plot([0, 0], [0, 5], lw = 0.5, ls = '--', color = 'red')
- axes.plot([0, 0], [1, 10], lw = '', color = 'green')
- axes.set_ylim(4, 15)
- axes.set_xlim(-1, 1)
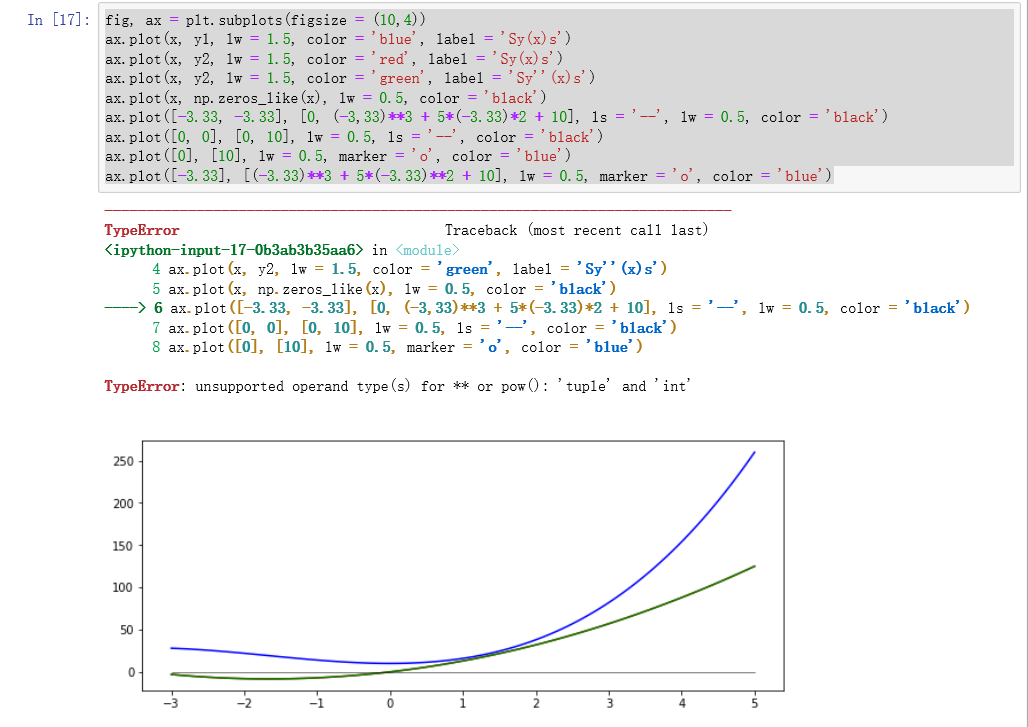
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- ax.plot(x, y1, lw = 1.5, color = 'blue', label = 'Sy(x)s')
- ax.plot(x, y2, lw = 1.5, color = 'red', label = 'Sy(x)s')
- ax.plot(x, y2, lw = 1.5, color = 'green', label = 'Sy''(x)s')
- ax.plot(x, np.zeros_like(x), lw = 0.5, color = 'black')
- ax.plot([-3.33, -3.33], [0, (-3,33)**3 + 5*(-3.33)*2 + 10], ls = '--', lw = 0.5, color = 'black')
- ax.plot([0, 0], [0, 10], lw = 0.5, ls = '--', color = 'black')
- ax.plot([0], [10], lw = 0.5, marker = 'o', color = 'blue')
- ax.plot([-3.33], [(-3.33)**3 + 5*(-3.33)**2 + 10], lw = 0.5, marker = 'o', color = 'blue')
- fig = plt.figure(figsize = (8, 2.5), facecolor = "#f1f1f1")
- left, bottom, width, height = 0.1, 0.1, 0.8, 0.8
- ax = fig.add_axes((left, bottom, width, height), facecolor = "#e1e1e1")
- x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 1000)
- y1 = np.cos(40*x)
- y2 = np.exp(-x*2)
- ax.plot(x, y1*y2)
- ax.plot(x, y2, 'g')
- ax.plot(x, -y2, 'g')
- ax.set_xlabel("x")
- ax.set_ylabel("y")
- fig.savefig("graph.png", dpi = 100, facecolor = "#f1f1f1")
- fig.savefig("graph.pdf", dpi = 300, facecolor = "#f1f1f1")

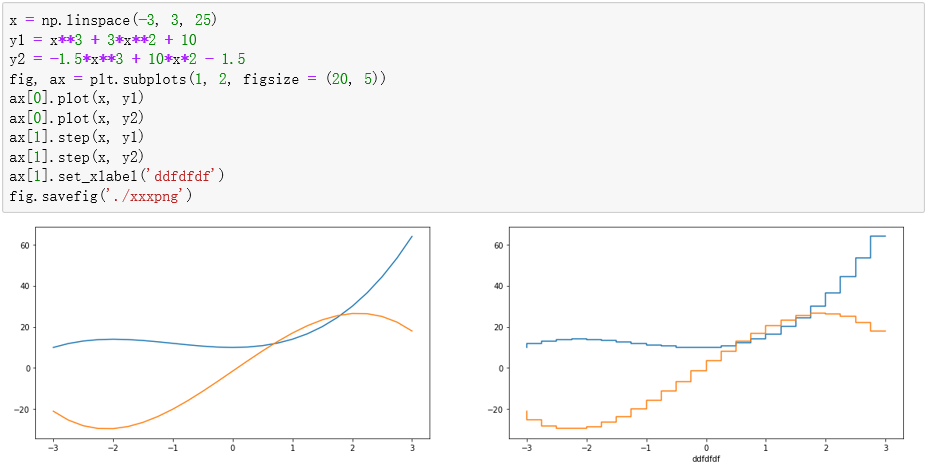
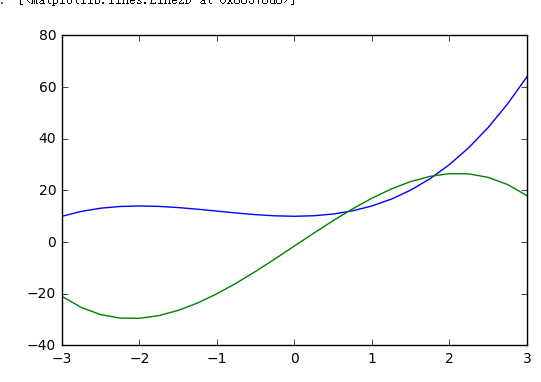
- x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 25)
- y1 = x**3 + 3*x**2 + 10
- y2 = -1.5*x**3 + 10*x*2 - 1.5
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (20, 5))
- ax[0].plot(x, y1)
- ax[0].plot(x, y2)
- ax[1].step(x, y1)
- ax[1].step(x, y2)
- ax[1].set_xlabel('ddfdfdf')
- fig.savefig('./xxxpng')
- fignum = 0
- x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 25)
- y1 = x**3 + 3*x**2 + 10
- y2 = -1.5*x**3 + 10*x*2 - 1.5
- fig, ax = plt.subplots()
- ax.plot(x, y1)
- ax.plot(x, y2)
- def hide_label(fig, ax):
- global fignum
- ax.set_xtickets([])
- ax.set_yticks([])
- ax.xaxis.set
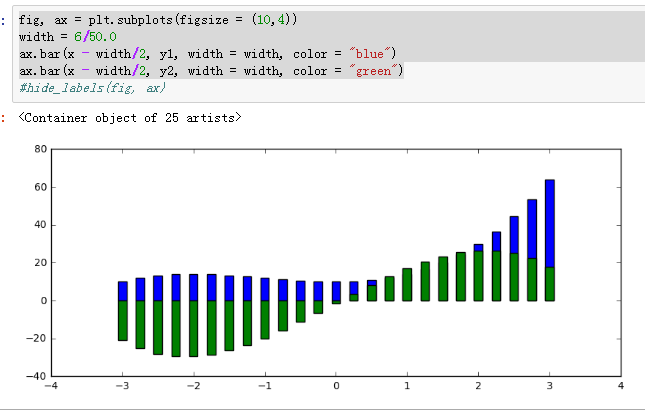
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- width = 6/50.0
- ax.bar(x - width/2, y1, width = width, color = "blue")
- ax.bar(x - width/2, y2, width = width, color = "green")
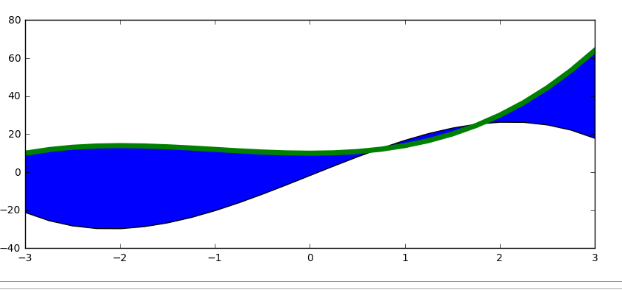
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- ax.fill_between(x, y1, y2)
- ax.plot(x, y1, color = 'green', lw = 5)
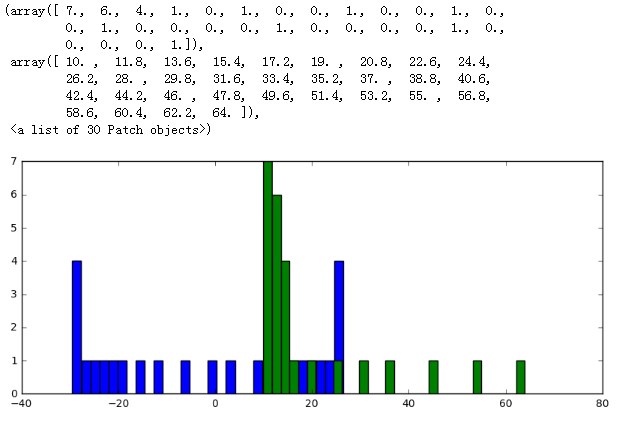
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- ax.hist(y2, bins = 30)
- ax.hist(y1, bins = 30)
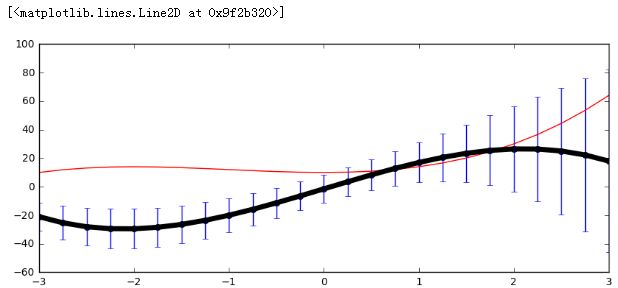
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- ax.errorbar(x, y2, yerr = y1, fmt = 'o-')
- ax.plot(x, y1, color = 'red')
- ax.plot(x, y2, color = 'black', lw = 5)
- fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize = (10,4))
- x = np.linspace(0, 5, 50)
- ax.scatter(x, -1 + x + 0.25*x**2 + 2*np.random.rand(len(x)))
- ax.scatter(x, np.sqrt(x) + 2*np.random.rand(len(x)))
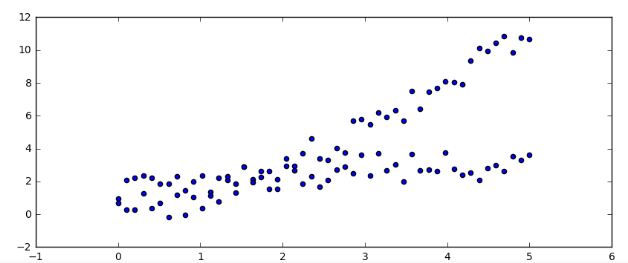

- s.plot(kind = 'bar')
- s.plot(kind = 'pie') # 画饼状图
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- %matplotlib inline
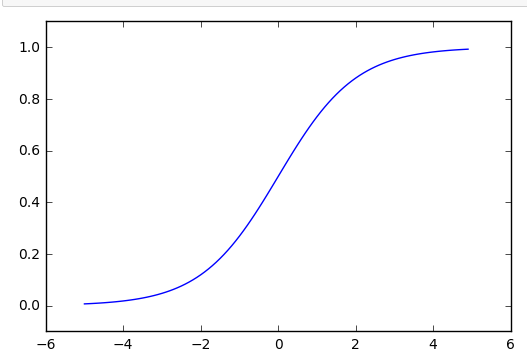
- def sigmoid(x):
- return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
- x = np.arange(-5.0, 5.0 ,0.1)
- y = sigmoid(x)
- plt.plot(x ,y)
- plt.ylim(-0.1, 1.1)
- plt.show()
- a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
- b = np.array([[1 ,2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
- np.dot(a, b)
- #X--------Y
- W2 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4] ,[5, 6]])
- W1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
- W3 = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
- b1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
- b2 = np.array([1, 2])
- b3 = np.array([1, 2])
- X = np.array([1.0, 2.0])
- A1 = np.dot(X ,W1) + b1
- A2 = np.dot(A1, W2) + b2
- Y = np.dot(A2, W3) + b3
- #and门
- def and_gate(x1, x2):
- if (20*x1 + 20*x2 -30) > 0:
- return 1
- else:
- return 0
- x1, x2 = 1, 1
- and_gate(x1, x2)
pyhton课堂随笔-基本画图的更多相关文章
- Matlab随笔之画图函数总结
原文:Matlab随笔之画图函数总结 MATLAB函数画图 MATLAB不但擅长於矩阵相关的数值运算,也适合用在各种科学目视表示(Scientific visualization).本节将介绍MATL ...
- 课堂随笔 set (集合)
1.什么是集合:set (集合)为无序不重复的序列. 2.如何创建一个集合:(1)set() 这样就创建了一个空的集合(2)s1={11,22,33}这样也创建了一个集合.(3)s2=set([ ...
- jQuery选择器课堂随笔
$(function(){ //并集选择器 /* $("h2,ul").css("background","pink");* ...
- HTMl课堂随笔
html: 1.超文本标记语言(Hyper Text Markup Lan) 2.不是一种编程语言,而是一种标记语言(Markup Language) 3.标记语言是一套标记标签(Markup Tag ...
- 课堂随笔03--for循环及两个循环中断关键字
for (int i = 1; i <= 8;i++) {} for循环可嵌套,执行指定次数,可用作计数. 用两个for循环嵌套,可以方便控制行列的输出. break:中断循环 continu ...
- 课堂随笔02--c#中string作为引用类型的特殊性
using System; namespace Test { class Test1 { static void Main(string[] args) { string str1 = "1 ...
- 课堂随笔04--关于string类的一些基本操作
//定义一个空字符串 string strA = string.Empty; strA = "abcdesabcskkkkk"; //获取字符串的长度 int i = strA.L ...
- 使用 LVS 实现负载均衡原理及安装配置详解(课堂随笔)
一.负载均衡LVS基本介绍 LB集群的架构和原理很简单,就是当用户的请求过来时,会直接分发到Director Server上,然后它把用户的请求根据设置好的调度算法,智能均衡地分发到后端真正服务器(r ...
- linux基础—课堂随笔09_数组
数组:(6.14 第一节) 取分区利用率,大于百分之八十则发出警报 取分区第一列 取分区使用率: 脚本: 检查脚本语法: ——end 数组切片: 1.跳过前两个取后面 2.跳过前两个取三个 生成10个 ...
随机推荐
- flask hook
@app.before_first_requestdef before_first_request(): """在第一次请求之前会访问该函数""&qu ...
- openGL实现图形学扫描线种子填充算法
title: "openGL实现图形学扫描线种子填充算法" date: 2018-06-11T19:41:30+08:00 tags: ["图形学"] cate ...
- nist-sha
nist目前支持的sha运算,sha1系列,输出mac160bit. sha2系列,支持sha2-224,sha2-256,sha2-384,sha2-512,sha2-512/224,sha2-51 ...
- Remastersys打包你自己的ubuntu成iso文件
采用Remastersys3.0.4.ubuntu版本是ubuntu14.04 LTS amd64. (1)软件下载安装: 下载: 到http://www.easy-vdr.de/downloads/ ...
- vb配置下位机CAN寄存器小结
2011-12-14 18:44:32 效果图 1,完成设计(由于没有eeprom等存储设备,所以每次上电后需要通过串口配置某些寄存器).在设计中,列出技术评估难度,并进行尝试,参看<我的设计& ...
- c语言的一些易错知识积累
1. #ifdef 和#if defined 的区别: 后者可以组成复杂的预编译条件,而如果判断的是单个宏定义的时候,两种用法的效果都是一样的. 2.#if 0 { code }#endif ...
- 1.2:Properties
文章著作权归作者所有.转载请联系作者,并在文中注明出处,给出原文链接. 本系列原更新于作者的github博客,这里给出链接. 上一节我们了解了一个Shader的基本结构,这一节,我们从 Propert ...
- C类网络子网掩码速查
子网掩码 网络位数 子网数量 可用主机数 255.255.255.252 30 64 2 255.255.255.248 29 32 6 255.255.255.240 28 16 14 255.25 ...
- 连接centos服务器gui
https://blog.csdn.net/jack_nichao/article/details/78289398 配置好后下载vnc viewer 进行连接. Ubuntu:https://www ...
- Excel导出采用mvc的ExcelResult继承遇到的问题
ExcelResult继承:ViewResult(只支持excel版本2003及兼容2003的版本)通过视图模板生成excel /// <summary> /// ms-excel视图 / ...
