HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(17)-BottomNavigationBar
目录:
引言
BottomNavigationBar底部导航栏,可以说所有的app是这样的页面架构,原因很简单,操作简单,模块化清晰,页面切换流畅,而且每页都可以展示不同的风格。相信开发者已经很熟悉Android的底部导航栏的开发以及开发流程,那么接下来将对比Android来讲解鸿蒙的底部导航栏的实现步骤。
功能介绍
鸿蒙BottomNavigationBar底部导航栏,根据所需要底部button的数量,动态生成对应的底部button,并且可以设置默认字体颜色,选中字体颜色,默认icon,选中icon属性。模拟器效果图如下:
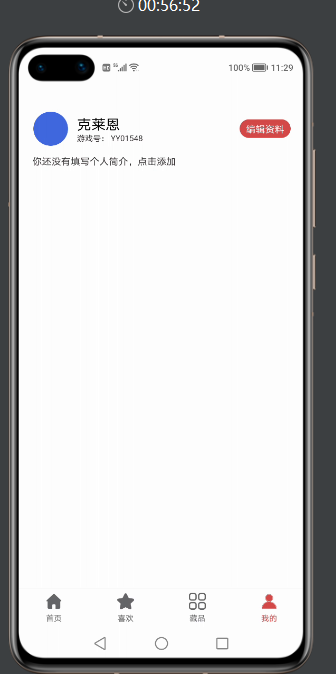
看了效果图,是不是都想知道在实际工作中,是如何使用的呢?接下来给大家详细介绍下BottomNavigationBar如何使用。
BottomNavigationBar使用指南
Ø 新建工程, 添加组件Har包依赖
在应用模块中添加HAR,只需要将mylibrarybottom-debug.har复制到entry\libs目录下即可。
Ø 修改相关文件
1. 修改主页面的布局文件ability_main.xml:

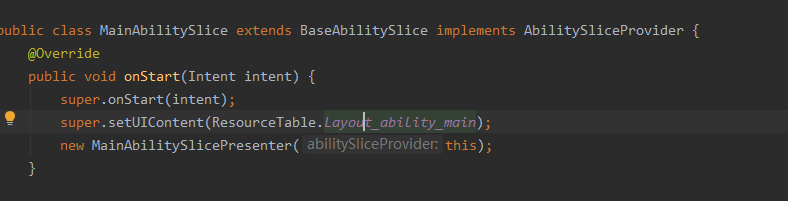
2. 修改MainAbilitySlice代码:
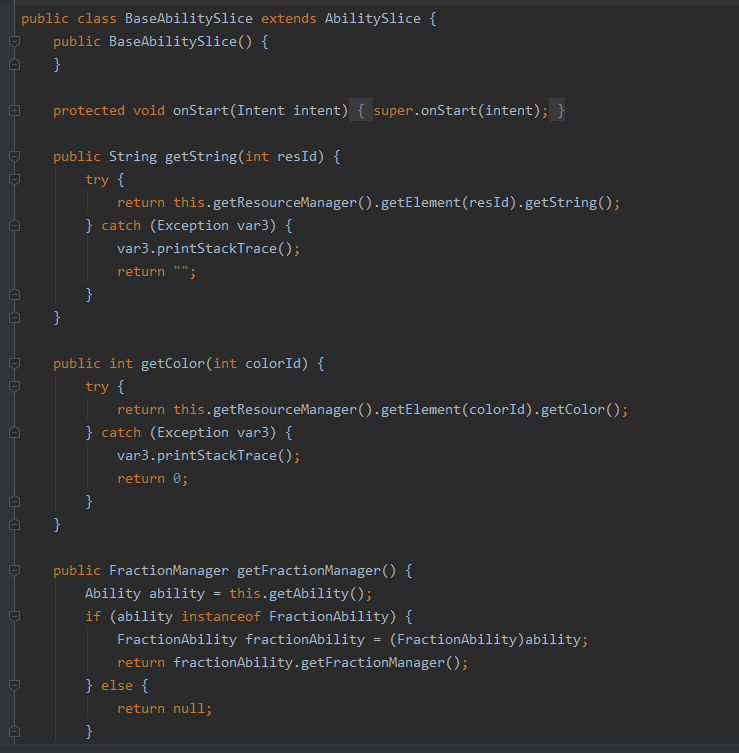
3. 修改BaseAbilitySlinct代码:
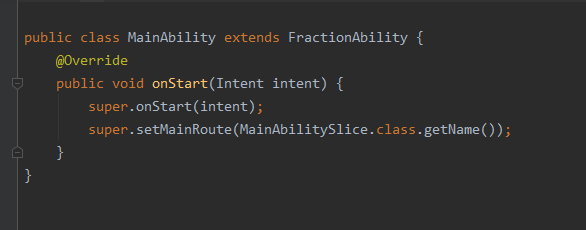
4. MainAbility的代码:
配置好1-4步,接下来就看如何给对应的底部导航栏添加Fraction
1. initBottom 方法如下:
private void initBottom() {
tabBottomLayout = (BottomNavigationBar) mAbilitySliceProvider.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_bottom_navigation_bar);
bottomInfoList = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取string.json文件中定义的字符串
String home = mAbilitySliceProvider.getString(ResourceTable.String_home);
String favorite = mAbilitySliceProvider.getString(ResourceTable.String_favorite);
String category = mAbilitySliceProvider.getString(ResourceTable.String_category);
String profile = mAbilitySliceProvider.getString(ResourceTable.String_mine);
// 首页
BottomBarInfo<Integer> homeInfo = new BottomBarInfo<>(home,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma1,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma2,
defaultColor, tintColor);
homeInfo.fraction = HomeFraction.class;
// 收藏
BottomBarInfo<Integer> favoriteInfo = new BottomBarInfo<>(favorite,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma1,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma2,
defaultColor, tintColor);
favoriteInfo.fraction = SecondFraction.class;
// 分类
BottomBarInfo<Integer> categoryInfo = new BottomBarInfo<>(category,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma1,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma2,
defaultColor, tintColor);
categoryInfo.fraction = ThirdFraction.class;
// 我的
BottomBarInfo<Integer> profileInfo = new BottomBarInfo<>(profile,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma1,
ResourceTable.Media_category_norma2,
defaultColor, tintColor);
profileInfo.fraction = MineFraction.class;
// 将每个条目的数据放入到集合
bottomInfoList.add(homeInfo);
bottomInfoList.add(favoriteInfo);
bottomInfoList.add(categoryInfo);
bottomInfoList.add(profileInfo);
// 设置底部导航栏的透明度
tabBottomLayout.setBarBottomAlpha(0.85f);
// 初始化所有的条目
tabBottomLayout.initInfo(bottomInfoList);
initFractionBarComponent();
tabBottomLayout.addBarSelectedChangeListener((index, prevInfo, nextInfo) ->
// 显示fraction
mFractionBarComponent.setCurrentItem(index));
// 设置默认选中的条目,该方法一定要在最后调用
tabBottomLayout.defaultSelected(homeInfo);
2. 创建fraction类,继承BaseFraction
1. 引入需要展示页面的布局文件
@Override
public int getUIComponent() {
return ResourceTable.Layout_layout_fraction_home;
}2. 操作布局文件中的控件
@Override
public void initComponent(Component component) {
text = (Text) component.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_text);
}BottomNavigationBar开发指南
底部导航栏,在应用中真的非常常见,核心思想就是底部有几个选项,然后点击其中任意一个,切换至对应的页面。接下来主要介绍下核心实现步骤。
主要封装的原则是,动态的,通过外界传递,固定过的则封装起来。其中底部导航栏的图片、文字、文字的颜色是变的,其它的可以封装起来,外界只需要把每个条目的图片、文字以及文字的颜色传入进来即可,内部来实现底部导航栏。在封装的时候,需要面向接口编程,同时使用泛型。
定义接口IBarLayout
1、定义一个IBarLayout接口,第一个泛型就是底部导航栏中的每个条目,第二个泛型是每个条目的数据。在接口里面提供一些方法,可以根据数据查找条目,可以添加监听,可以设置默认选中的条目,可以初始化所有的条目,当某个条目被选中后需要通过回调方法。
代码如下:
public interface IBarLayout<Bar extends ComponentContainer, D> {
/**
* 根据数据查找条目
*
* @param info 数据
* @return 条目
*/
Bar findBar(D info);
/**
* 添加监听
*
* @param listener
*/
void addBarSelectedChangeListener(OnBarSelectedListener<D> listener);
/**
* 默认选中的条目
*
* @param defaultInfo
*/
void defaultSelected(D defaultInfo);
/**
* 初始化所有的条目
*
* @param infoList
*/
void initInfo(List<D> infoList);
interface OnBarSelectedListener<D> {
/**
* 当某个条目被选中后的回调,该方法会被调用多次
*
* @param index 点击后选中条目的下标
* @param preInfo 点击前选中的条目
* @param nextInfo 点击后选中的条目
*/
void onBarSelectedChange(int index, D preInfo, D nextInfo);
}
}2、再定义一个单个条目的接口IBar,泛型就是每个条目的数据,接口里面定义方法,可以设置条目的数据,可以动态修改某个条目的大小
代码如下:
/**
* 单个条目的接口
*/
public interface IBar<D> extends IBarLayout.OnBarSelectedListener<D> {
/**
* 设置条目的数据
*
* @param data
*/
void setBarInfo(D data);
/**
* 动态修改某个条目的大小
*
* @param height
*/
void resetHeight(int height);
}每个条目所对应的实体类BottomBarInfo
每个条目都有自己的图片、文字、文字的颜色,我们把这些属性定义在一个实体类中。由于颜色可以是整型,也可以是字符串,这里定义泛型,泛型就是文字的颜色。具体是哪种类型的颜色,由调用者来决定。
注意下BarType这个枚举,我们的底部导航栏支持两种类型,IMAGE代表下图,某个条目只显示图片,也可以让某个条目凸出来,只需要将条目的高度变高即可。
public class BottomBarInfo<Color> extends TopBottomBarInfo {
public enum BarType {
/**
* 显示图片和文案
*/
IMAGE_TEXT,
/**
* 只显示图片
*/
IMAGE
}
/**
* 条目的名称
*/
public String name;
public BarType tabType;
public Class<? extends Fraction> fraction;
public BottomBarInfo(String name, int defaultImage, int selectedImage) {
this.name = name;
this.defaultImage = defaultImage;
this.selectedImage = selectedImage;
this.tabType = BarType.IMAGE;
}
public BottomBarInfo(String name, int defaultImage, int selectedImage, Color defaultColor, Color tintColor) {
this.name = name;
this.defaultImage = defaultImage;
this.selectedImage = selectedImage;
this.defaultColor = defaultColor;
this.tintColor = tintColor;
this.tabType = BarType.IMAGE_TEXT;
}
}单个条目的封装
定义BottomBar,继承相对布局,实现之前定义的IBar接口,泛型就是每个条目所对应的实体类,由于目前并不知道泛型的具体类型,所以泛型直接使用问号来代替。BottomBar就是单个条目。
我们需要将component对象放入到BottomBar中,所以第二个参数传this,第三个参数为true。
public class BottomBar extends DependentLayout implements IBar<BottomBarInfo<?>> {
/**
* 当前条目所对应的数据
*/
private BottomBarInfo<Color> tabInfo;
private Text mTabName;
private Image mTabImage;
public BottomBar(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public BottomBar(Context context, AttrSet attrSet) {
this(context, attrSet, "");
}
public BottomBar(Context context, AttrSet attrSet, String styleName) {
super(context, attrSet, styleName);
Component component = LayoutScatter.getInstance(context).parse(ResourceTable.Layout_layout_bar_bottom, this, true);
mTabImage = (Image) component.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_image);
mTabName = (Text) component.findComponentById(ResourceTable.Id_name);
mTabImage.setScaleMode(Image.ScaleMode.INSIDE);
}
/**
* 设置条目的数据
*
* @param data
*/
@Override
public void setBarInfo(BottomBarInfo<?> data) {
tabInfo = (BottomBarInfo<Color>) data;
inflateInfo(false, true);
}
/**
* 初始化条目
*
* @param selected true 选中
* @param init true 初始化
*/
private void inflateInfo(boolean selected, boolean init) {
if (tabInfo.tabType == BottomBarInfo.BarType.IMAGE_TEXT) {
if (init) {
// 图片和名称都可见
mTabName.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
mTabImage.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(tabInfo.name)) {
// 设置条目的名称
mTabName.setText(tabInfo.name);
}
}
if (selected) {
// 显示选中的图片
mTabImage.setPixelMap(tabInfo.selectedImage);
mTabName.setTextColor(new Color(parseColor(tabInfo.tintColor)));
} else {
// 显示未选中的图片
mTabImage.setPixelMap(tabInfo.defaultImage);
mTabName.setTextColor(new Color(parseColor(tabInfo.defaultColor)));
}
} else if (tabInfo.tabType == BottomBarInfo.BarType.IMAGE) {
if (init) {
// 仅仅显示图片,将名称隐藏
mTabName.setVisibility(HIDE);
mTabImage.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
}
if (selected) {
// 显示选中的图片
mTabImage.setPixelMap(tabInfo.selectedImage);
} else {
// 显示未选中的图片
mTabImage.setPixelMap(tabInfo.defaultImage);
}
}
}
private int parseColor(Object color) {
if (color instanceof String) {
return Color.getIntColor((String) color);
} else {
return (int) color;
}
}
/**
* 动态修改某个tab的高度
*
* @param height tab的高度
*/
@Override
public void resetHeight(int height) {
ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig config = getLayoutConfig();
config.height = height;
setLayoutConfig(config);
mTabName.setVisibility(HIDE);
}
/**
* 当某个条目被选中后的回调,该方法会被调用多次
*
* @param index 点击后选中条目的下标
* @param preInfo 点击前选中的条目
* @param nextInfo 点击后选中的条目
*/
@Override
public void onBarSelectedChange(int index, BottomBarInfo<?> preInfo, BottomBarInfo<?> nextInfo) {
if (nextInfo.tabType == BottomBarInfo.BarType.IMAGE) {
// 当前条目的类型是IMAGE类型,则不做任何处理
return;
}
if (preInfo == nextInfo) {
// 假设当前选中的是条目1,同时点击的也是条目1,那就不需要做任何操作了
return;
}
if (preInfo != tabInfo && nextInfo != tabInfo) {
/**
* 假设有三个条目,条目1、条目2、条目3,preInfo是条目1,nextInfo是条目3,tabInfo是条目2,
* 点击前选中的是条目1,点击后选中的条目3,此时条目2就不需要做任何操作了
*/
return;
}
if (preInfo == tabInfo) {
// 将点击前的条目反选
inflateInfo(false, false);
} else {
// 选中被点击的条目
inflateInfo(true, false);
}
}
public BottomBarInfo<Color> getTabInfo() {
return tabInfo;
}
public Text getTabName() {
return mTabName;
}
public Image getImage() {
return mTabImage;
}
}底部导航栏的封装
定义BottomNavigationBar,继承栈布局。第一个泛型就是底部导航栏的条目,第二个泛型就是每个条目的数据。
public class BottomNavigationBar extends StackLayout implements IBarLayout<BottomBar, BottomBarInfo<?>> {
private static final int ID_TAB_BOTTOM = 0XFF;
/**
* 事件监听的集合
*/
private List<OnBarSelectedListener<BottomBarInfo<?>>> tabSelectedListeners = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 当前选中的条目
*/
private BottomBarInfo<?> selectedInfo;
/**
* 底部导航栏的透明度
*/
private float barBottomAlpha = 1;
/**
* 底部导航栏的高度
*/
private float barBottomHeight = 50;
/**
* 底部导航栏线条的高度
*/
private float barBottomLineHeight = 0.5f;
/**
* 底部导航栏线条的颜色
*/
private RgbColor barBottomLineColor = new RgbColor(223, 224, 225);
/**
* 所有的tab
*/
private List<BottomBarInfo<?>> infoList;
public BottomNavigationBar(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public BottomNavigationBar(Context context, AttrSet attrSet) {
this(context, attrSet, "");
}
public BottomNavigationBar(Context context, AttrSet attrSet, String styleName) {
super(context, attrSet, styleName);
}
/**
* 根据数据查找条目
*
* @param info 条目的数据
* @return 条目
*/
@Override
public BottomBar findBar(BottomBarInfo<?> info) {
ComponentContainer componentContainer = (ComponentContainer) findComponentById(ID_TAB_BOTTOM);
for (int i = 0; i < componentContainer.getChildCount(); i++) {
Component component = componentContainer.getComponentAt(i);
if (component instanceof BottomBar) {
BottomBar bottomBar = (BottomBar) component;
if (bottomBar.getTabInfo() == info) {
return bottomBar;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 添加监听
*
* @param listener 监听
*/
@Override
public void addBarSelectedChangeListener(OnBarSelectedListener<BottomBarInfo<?>> listener) {
tabSelectedListeners.add(listener);
}
/**
* 默认选中的条目
*
* @param defaultInfo 默认选中条目的信息
*/
@Override
public void defaultSelected(BottomBarInfo<?> defaultInfo) {
onSelected(defaultInfo);
}
/**
* 初始化所有的条目
*
* @param infoList 所有条目的信息
*/
@Override
public void initInfo(List<BottomBarInfo<?>> infoList) {
if (infoList == null || infoList.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
this.infoList = infoList;
// 移除之前已经添加的组件,防止重复添加
removeComponent();
selectedInfo = null;
// 添加背景
addBackground();
// 添加条目
addBottomBar();
// 添加线条
addBottomLine();
}
/**
* 添加线条
*/
private void addBottomLine() {
Component line = new Component(getContext());
// 目前不支持直接设置背景颜色,只能通过Element来设置背景
ShapeElement element = new ShapeElement();
element.setShape(ShapeElement.RECTANGLE);
element.setRgbColor(barBottomLineColor);
line.setBackground(element);
LayoutConfig config = new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,
DisplayUtils.vp2px(getContext(), barBottomLineHeight));
// 位于底部
config.alignment = LayoutAlignment.BOTTOM;
config.setMarginBottom(DisplayUtils.vp2px(getContext(), barBottomHeight - barBottomLineHeight));
line.setAlpha(barBottomAlpha);
addComponent(line, config);
}
/**
* 添加条目
*/
private void addBottomBar() {
// 每个条目的宽度就是屏幕宽度除以条目的总个数
int width = DisplayUtils.getDisplayWidthInPx(getContext()) / infoList.size();
// 高度是固定的值,这里需要做屏幕适配,将vp转换成像素
int height = DisplayUtils.vp2px(getContext(), barBottomHeight);
StackLayout stackLayout = new StackLayout(getContext());
stackLayout.setId(ID_TAB_BOTTOM);
for (int i = 0; i < infoList.size(); i++) {
BottomBarInfo<?> info = infoList.get(i);
// 创建布局配置对象
LayoutConfig config = new LayoutConfig(width, height);
// 设置底部对齐
config.alignment = LayoutAlignment.BOTTOM;
// 设置左边距
config.setMarginLeft(i * width);
BottomBar bottomBar = new BottomBar(getContext());
tabSelectedListeners.add(bottomBar);
// 初始化每个条目
bottomBar.setBarInfo(info);
// 添加条目
stackLayout.addComponent(bottomBar, config);
// 设置点击事件
bottomBar.setClickedListener(component -> onSelected(info));
}
LayoutConfig layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,
ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_CONTENT);
layoutConfig.alignment = LayoutAlignment.BOTTOM;
addComponent(stackLayout, layoutConfig);
}
/**
* 点击条目后给外界回调
*
* @param nextInfo 点击后需要选中的条目
*/
private void onSelected(BottomBarInfo<?> nextInfo) {
for (OnBarSelectedListener<BottomBarInfo<?>> listener : tabSelectedListeners) {
listener.onBarSelectedChange(infoList.indexOf(nextInfo), selectedInfo, nextInfo);
}
if (nextInfo.tabType == BottomBarInfo.BarType.IMAGE_TEXT) {
selectedInfo = nextInfo;
}
}
/**
* 添加背景
*/
private void addBackground() {
Component component = new Component(getContext());
// 目前还不能直接设置背景颜色,只能通过Element来设置背景
ShapeElement element = new ShapeElement();
element.setShape(ShapeElement.RECTANGLE);
RgbColor rgbColor = new RgbColor(255, 255, 255);
element.setRgbColor(rgbColor);
component.setBackground(element);
component.setAlpha(barBottomAlpha);
LayoutConfig config = new LayoutConfig(ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,
DisplayUtils.vp2px(getContext(), barBottomHeight));
config.alignment = LayoutAlignment.BOTTOM;
addComponent(component, config);
}
/**
* 移除之前已经添加的组件,防止重复添加
*/
private void removeComponent() {
for (int i = getChildCount() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
removeComponentAt(i);
}
tabSelectedListeners.removeIf(listener ->
listener instanceof BottomBar);
}
/**
* 设置底部导航栏的透明度
*
* @param barBottomAlpha 底部导航栏的透明度
*/
public void setBarBottomAlpha(float barBottomAlpha) {
this.barBottomAlpha = barBottomAlpha;
}
/**
* 设置底部导航栏的高度
*
* @param barBottomHeight 底部导航栏的高度
*/
public void setBarBottomHeight(float barBottomHeight) {
this.barBottomHeight = barBottomHeight;
}
/**
* 设置底部导航栏线条的高度
*
* @param barBottomLineHeight 底部导航栏线条的高度
*/
public void setBarBottomLineHeight(float barBottomLineHeight) {
this.barBottomLineHeight = barBottomLineHeight;
}
/**
* 设置底部导航栏线条的颜色
*
* @param barBottomLineColor 底部导航栏线条的颜色
*/
public void setBarBottomLineColor(RgbColor barBottomLineColor) {
this.barBottomLineColor = barBottomLineColor;
}
}initInfo(List<BottomBarInfo<?>> infoList)该方法由外界调用,外界将所有的条目信息传递过来,我们将条目添加到底部导航栏。首先移除之前已经添加的组件,防止重复添加,然后添加背景,添加条目,添加线条。
更多原创,请关注:软通动力HarmonyOS学院https://harmonyos.51cto.com/column/30
作者:软通田可辉
想了解更多内容,请访问51CTO和华为合作共建的鸿蒙社区:https://harmonyos.51cto.com/
HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(17)-BottomNavigationBar的更多相关文章
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(15)-LoadingView功能介绍
目录: 1. LoadingView组件功能介绍2. Lottie使用方法3. Lottie开发实现4.<HarmonyOS三方件开发指南>系列文章合集 1. LoadingView组件功 ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(12)——cropper图片裁剪
鸿蒙入门指南,小白速来!0基础学习路线分享,高效学习方法,重点答疑解惑--->[课程入口] 目录:1. cropper组件功能介绍2. cropper使用方法3. cropper组件开发实现4. ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(13)-SwipeLayout侧滑删除
鸿蒙入门指南,小白速来!0基础学习路线分享,高效学习方法,重点答疑解惑--->[课程入口] 目录:1. SwipeLayout组件功能介绍2. SwipeLayout使用方法3. SwipeLa ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(14)-Glide组件功能介绍
<HarmonyOS三方件开发指南>系列文章合集 引言 在实际应用开发中,会用到大量图片处理,如:网络图片.本地图片.应用资源.二进制流.Uri对象等,虽然官方提供了PixelMap进行图 ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(16)-VideoCache 视频缓存
目录: 1.引言 2.功能介绍 3.VideoCache使用指南 4.VideoCache开发指南 5.<HarmonyOS三方件开发指南>系列文章合集 引言 对于视频播放器这个app大家 ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(19)-BGABadgeView徽章组件
目录: 1.引言 2.功能介绍 3.BGABadgeView 使用指南 4.BGABadgeView 开发指南 5.<HarmonyOS三方件开发指南>系列文章合集 引言 现在很多的APP ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(4)——Logger组件
目录: 1. Logger功能介绍 2. Logger使用方法 3. Logger开发实现 4. 源码上传地址 1. Logger功能介绍1.1. ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(5)——Photoview组件
PhotoView使用说明 1. PhotoView功能介绍1.1 组件介绍: PhotoView是一个继承自Image的组件,不同之处在于:它可以进行图击放大功能,手势缩放功能(暂无 ...
- HarmonyOS三方件开发指南(7)——compress组件
目录:1. 组件compress功能介绍2. 组件compress使用方法3. 组件compress开发实现 1. 组件compress功能介绍1.1. 组件介绍: compress是 ...
随机推荐
- 伦尼斯酒庄(Chateau Renice)再次赞助亚洲50大餐厅赛事
连续几年来,伦尼斯酒庄(Chateau Renice)一直是亚洲50大最佳餐厅评选赛(Asia's 50 Best Restaurant Awards)的赞助商.2020年伦尼斯酒庄酒庄(Chatea ...
- 27_MySQL数字函数(重点)
/* SALES部门中工龄超过20年的,底薪增加10% SALES部门中工龄不满20年的,底薪增加5% ACCOUNTING部门,底薪增加300元 RESEARCH部门里低于部门平均底薪的,底薪增加2 ...
- web项目中各工具的作用
一.HTML:用于搭建基础网页,展示网页的内容 Hyper Text Markup Language 超文本标记语言 ,是最基础的网页开发语言. * 超文本: * 超文本是用超链接的方法,将各种不同空 ...
- js中函数调用时,对参数个数和类型没有要求
因为js是一种弱类型的编程语言,对数据类型的要求没有其他编程语言的要求严格,所以在定义函数的时候不需要像java一样对其传入参数的类型进行定,也对传入参数的个数没有要求. js函数的参数与大多数其他语 ...
- ubuntu系统共享桌面的使用和配置
内容转载自我的博客 目录 1. ubuntu共享桌面 2. 局域网登录远程桌面 2.1 ubuntu使用remmina登录远程桌面 2.2 在windows登录远程桌面 2.3 Android使用RD ...
- 女朋友看了会生气的回答 URI和URL有什么区别?
URL是什么 URL 代表着是统一资源定位符(Uniform Resource Locator).作用是为了告诉使用者 某个资源在 Web 上的地址.这个资源可以是一个 HTML 页面,一个 CSS ...
- Ext.Net一般处理程序上传文件
引言 最近公司项目全部转向前端化,故所有aspx页面业务逻辑尽可能的转到用户控件前台页面完成.以方便每次发布项目时只是替换前端页面不会影响客户体验. 既然转到前台逻辑,那么必须走后台的业务也就单独封装 ...
- 如何快速开发Winform应用系统
在实际的业务中,往往还有很多需要使用Winform来开发应用系统的,如一些HIS.MIS.MES等系统,由于Winform开发出来的系统界面友好,响应快速,开发效率高等各方面原因,还有一些原因是独立的 ...
- 漏洞复现-fastjson1.2.24-RCE
0x00 实验环境 攻击机:Win 10.Win Server2012 R2(公网环境,恶意java文件所在服务器) 靶机也可作为攻击机:Ubuntu18 (公网环境,docker ...
- SHELL编程概念&变量剖析
一.shell软件概念和应用场景 1) 学习Linux技术,不是为了学习系统安装.命令操作.用户权限.配置IP.网络管理,学习Linux技术重点:基于Linux系统部署和维护各种应用软件.程序(Apa ...
