每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——2.MongoDB环境变量配置和Shell操作
上一篇:每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——1.MongoDB介绍和安装
前言:为什么不是1天精通?大家都是成年人、明白人、聪明人,就不要像忽悠小孩子一样啦.......入门容易精通难,入门可能1天,精通则可能十年磨一剑才略有所成......
配置环境变量
Win10系统为例
右键单击“此电脑”——属性——高级系统设置——高级——环境变量,添加C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.0\bin;。注意:要以;隔开各种变量。
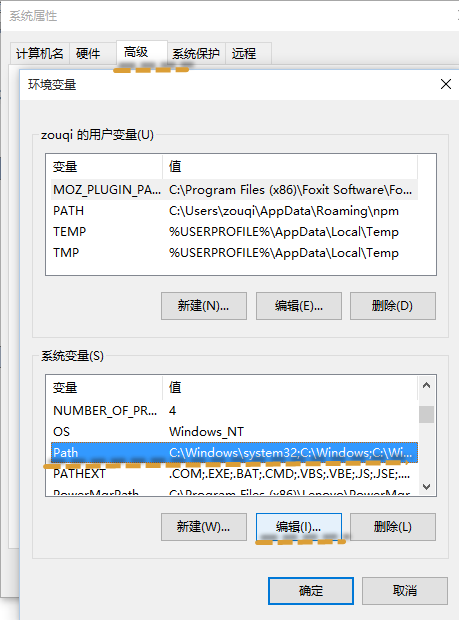
这样的话就可以直接在CMD命令窗口中输入mongo
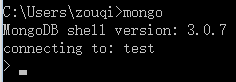
表示环境变量设置成功,并已经连接到默认数据库test中。
我们可以输入mongod --help来查看相关的帮助信息
C:\Users\zouqi>mongod --help
Options: General options:
-h [ --help ] show this usage information
--version show version information
-f [ --config ] arg configuration file specifying additional options
-v [ --verbose ] [=arg(=v)] be more verbose (include multiple times for more
verbosity e.g. -vvvvv)
--quiet quieter output
--port arg specify port number - 27017 by default
--bind_ip arg comma separated list of ip addresses to listen on
- all local ips by default
--ipv6 enable IPv6 support (disabled by default)
--maxConns arg max number of simultaneous connections - 1000000
by default
--logpath arg log file to send write to instead of stdout - has
to be a file, not directory
--logappend append to logpath instead of over-writing
--logRotate arg set the log rotation behavior (rename|reopen)
--timeStampFormat arg Desired format for timestamps in log messages.
One of ctime, iso8601-utc or iso8601-local
--pidfilepath arg full path to pidfile (if not set, no pidfile is
created)
--keyFile arg private key for cluster authentication
--setParameter arg Set a configurable parameter
--httpinterface enable http interface
--clusterAuthMode arg Authentication mode used for cluster
authentication. Alternatives are
(keyFile|sendKeyFile|sendX509|x509)
--auth run with security
--noauth run without security
--jsonp allow JSONP access via http (has security
implications)
--rest turn on simple rest api
--slowms arg (=100) value of slow for profile and console log
--profile arg 0=off 1=slow, 2=all
--cpu periodically show cpu and iowait utilization
--sysinfo print some diagnostic system information
--noIndexBuildRetry don't retry any index builds that were
interrupted by shutdown
--noscripting disable scripting engine
--notablescan do not allow table scans Windows Service Control Manager options:
--install install Windows service
--remove remove Windows service
--reinstall reinstall Windows service (equivalent to --remove
followed by --install)
--serviceName arg Windows service name
--serviceDisplayName arg Windows service display name
--serviceDescription arg Windows service description
--serviceUser arg account for service execution
--servicePassword arg password used to authenticate serviceUser Replication options:
--oplogSize arg size to use (in MB) for replication op log. default is
5% of disk space (i.e. large is good) Master/slave options (old; use replica sets instead):
--master master mode
--slave slave mode
--source arg when slave: specify master as <server:port>
--only arg when slave: specify a single database to replicate
--slavedelay arg specify delay (in seconds) to be used when applying
master ops to slave
--autoresync automatically resync if slave data is stale Replica set options:
--replSet arg arg is <setname>[/<optionalseedhostlist>]
--replIndexPrefetch arg specify index prefetching behavior (if secondary)
[none|_id_only|all] Sharding options:
--configsvr declare this is a config db of a cluster; default port
27019; default dir /data/configdb
--shardsvr declare this is a shard db of a cluster; default port SSL options:
--sslOnNormalPorts use ssl on configured ports
--sslMode arg set the SSL operation mode
(disabled|allowSSL|preferSSL|requireSSL
)
--sslPEMKeyFile arg PEM file for ssl
--sslPEMKeyPassword arg PEM file password
--sslClusterFile arg Key file for internal SSL
authentication
--sslClusterPassword arg Internal authentication key file
password
--sslCAFile arg Certificate Authority file for SSL
--sslCRLFile arg Certificate Revocation List file for
SSL
--sslDisabledProtocols arg Comma separated list of TLS protocols
to disable [TLS1_0,TLS1_1,TLS1_2]
--sslWeakCertificateValidation allow client to connect without
presenting a certificate
--sslAllowConnectionsWithoutCertificates
allow client to connect without
presenting a certificate
--sslAllowInvalidHostnames Allow server certificates to provide
non-matching hostnames
--sslAllowInvalidCertificates allow connections to servers with
invalid certificates
--sslFIPSMode activate FIPS 140-2 mode at startup Storage options:
--storageEngine arg (=mmapv1) what storage engine to use
--dbpath arg directory for datafiles - defaults to \data\db\
which is C:\data\db\ based on the current
working drive
--directoryperdb each database will be stored in a separate
directory
--noprealloc disable data file preallocation - will often
hurt performance
--nssize arg (=16) .ns file size (in MB) for new databases
--quota limits each database to a certain number of
files (8 default)
--quotaFiles arg number of files allowed per db, implies --quota
--smallfiles use a smaller default file size
--syncdelay arg (=60) seconds between disk syncs (0=never, but not
recommended)
--upgrade upgrade db if needed
--repair run repair on all dbs
--repairpath arg root directory for repair files - defaults to
dbpath
--journal enable journaling
--nojournal disable journaling (journaling is on by default
for 64 bit)
--journalOptions arg journal diagnostic options
--journalCommitInterval arg how often to group/batch commit (ms) WiredTiger options:
--wiredTigerCacheSizeGB arg maximum amount of memory to allocate
for cache; defaults to 1/2 of physical
RAM
--wiredTigerStatisticsLogDelaySecs arg (=0)
seconds to wait between each write to a
statistics file in the dbpath; 0 means
do not log statistics
--wiredTigerJournalCompressor arg (=snappy)
use a compressor for log records
[none|snappy|zlib]
--wiredTigerDirectoryForIndexes Put indexes and data in different
directories
--wiredTigerCollectionBlockCompressor arg (=snappy)
block compression algorithm for
collection data [none|snappy|zlib]
--wiredTigerIndexPrefixCompression arg (=1)
use prefix compression on row-store
leaf pages
如果你不喜欢看英文可以网上搜中文帮助介绍。
mongoDB和关系型数据库的对比
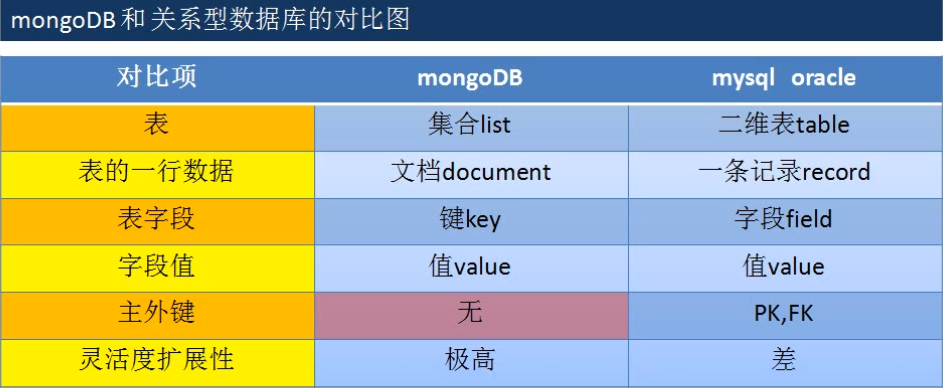
- 关系数据的表的record必须保证拥有每一个field
- mongoDBde meiyige documentde key可以不一样
- 关系型数据库查询使用SQL
- mongoDB查询使用内置find函数——》基于BSON的特殊查询工具
Shell操作
创建一个数据库——use[databaseName]
这时数据库并没有被正在创建,而是处于mongodb的一个预处理缓存池当中,如果你什么也不干就离开的花这个空数据库就会被删除。
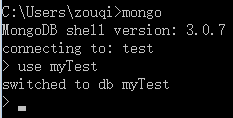
查看所有数据库——show dbs
> show dbs
demo 0.078GB
local 0.078GB
myDatabase 0.078GB
>这个时候我们看到myTest这个数据库是还没有创建的。
给指定数据库添加集合并且添加记录 ——db.[documentName].insert({...})
> db.persons.insert({name:'yujie'})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
>执行上面语句后才真正创建数据库。
> show dbs
demo 0.078GB
local 0.078GB
myDatabase 0.078GB
myTest 0.078GB
>查看数据库中的所有文档——show collections
> show collections
persons
system.indexes
>我们看到多了一个system.indexes文档,这是系统自动创建的一个索引文档,当插入记录的时候,自动创建了一个字段_id,并在这个字段上面创建了索引。我们来查看下索引:
> db.system.indexes.find()
{ "v" : 1, "key" : { "_id" : 1 }, "name" : "_id_", "ns" : "myTest.persons" }
>查看指定文档的数据——db.[documentName].find()&db.[documentName].findOne()
在这之前,我们再来往persons文档中插入一条记录
> db.persons.insert({name:'楚留香'})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
>查找persons文档中的所有记录
> db.persons.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593959250ab68d9cc7011a93"), "name" : "yujie" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59395c350ab68d9cc7011a94"), "name" : "楚留香" }
>查找persons文档中的第一条记录
> db.persons.findOne()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593959250ab68d9cc7011a93"), "name" : "yujie" }
>更新文档数据——db.[documentName].update({查询条件},{更新内容})
这里我们用到了一个update方法,我们来看下它的几个参数分别代表什么
参数1:查询的条件
参数2:更新的字段
参数3:如果不存在则插入
参数4:是否允许修改多条记录
更新name为yujie的记录
> db.persons.update({name:'yujie'},{$set:{name:'玉杰'}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })查看更新后的记录:
> db.persons.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593959250ab68d9cc7011a93"), "name" : "玉杰" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59395c350ab68d9cc7011a94"), "name" : "楚留香" }删除文档中的数据——db.[documentName].remove({...})
插入一条测试记录
> db.persons.insert({name:'test'})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })插入后:
> db.persons.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593959250ab68d9cc7011a93"), "name" : "玉杰" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59395c350ab68d9cc7011a94"), "name" : "楚留香" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593961530ab68d9cc7011a95"), "name" : "test" }
>删除文档中的数据
> db.persons.remove({name:'test'})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
>删除后结果:
> db.persons.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("593959250ab68d9cc7011a93"), "name" : "玉杰" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("59395c350ab68d9cc7011a94"), "name" : "楚留香" }
>删除数据库——db.dropDatabase()
查看所有数据库
> show dbs
demo 0.078GB
foobar 0.078GB
local 0.078GB
myDatabase 0.078GB
myTest 0.078GB
>假设我要删除foobar数据库,先使用use foobar切换到foobar数据库,然后执行 db.dropDatabase(),执行结果如下:
> db.dropDatabase()
{ "dropped" : "foobar", "ok" : 1 }
>再次查看所有数据库:
> show dbs
demo 0.078GB
local 0.078GB
myDatabase 0.078GB
myTest 0.078GB
>Shell的help
里面有所有的shell可以完成的命令帮助,全局的help数据库相关的db.help(),集合相关的db.[documentName].help()
db.help()
> db.help()
DB methods:
db.adminCommand(nameOrDocument) - switches to 'admin' db, and runs command [ just calls db.runCommand(...) ]
db.auth(username, password)
db.cloneDatabase(fromhost)
db.commandHelp(name) returns the help for the command
db.copyDatabase(fromdb, todb, fromhost)
db.createCollection(name, { size : ..., capped : ..., max : ... } )
db.createUser(userDocument)
db.currentOp() displays currently executing operations in the db
db.dropDatabase()
db.eval() - deprecated
db.fsyncLock() flush data to disk and lock server for backups
db.fsyncUnlock() unlocks server following a db.fsyncLock()
db.getCollection(cname) same as db['cname'] or db.cname
db.getCollectionInfos()
db.getCollectionNames()
db.getLastError() - just returns the err msg string
db.getLastErrorObj() - return full status object
db.getLogComponents()
db.getMongo() get the server connection object
db.getMongo().setSlaveOk() allow queries on a replication slave server
db.getName()
db.getPrevError()
db.getProfilingLevel() - deprecated
db.getProfilingStatus() - returns if profiling is on and slow threshold
db.getReplicationInfo()
db.getSiblingDB(name) get the db at the same server as this one
db.getWriteConcern() - returns the write concern used for any operations on this db, inherited from server object if set
db.hostInfo() get details about the server's host
db.isMaster() check replica primary status
db.killOp(opid) kills the current operation in the db
db.listCommands() lists all the db commands
db.loadServerScripts() loads all the scripts in db.system.js
db.logout()
db.printCollectionStats()
db.printReplicationInfo()
db.printShardingStatus()
db.printSlaveReplicationInfo()
db.dropUser(username)
db.repairDatabase()
db.resetError()
db.runCommand(cmdObj) run a database command. if cmdObj is a string, turns it into { cmdObj : 1 }
db.serverStatus()
db.setLogLevel(level,<component>)
db.setProfilingLevel(level,<slowms>) 0=off 1=slow 2=all
db.setWriteConcern( <write concern doc> ) - sets the write concern for writes to the db
db.unsetWriteConcern( <write concern doc> ) - unsets the write concern for writes to the db
db.setVerboseShell(flag) display extra information in shell output
db.shutdownServer()
db.stats()
db.version() current version of the server
>db.persons.help()
> db.persons.help()
DBCollection help
db.persons.find().help() - show DBCursor help
db.persons.count()
db.persons.copyTo(newColl) - duplicates collection by copying all documents to newColl; no indexes are copied.
db.persons.convertToCapped(maxBytes) - calls {convertToCapped:'persons', size:maxBytes}} command
db.persons.dataSize()
db.persons.distinct( key ) - e.g. db.persons.distinct( 'x' )
db.persons.drop() drop the collection
db.persons.dropIndex(index) - e.g. db.persons.dropIndex( "indexName" ) or db.persons.dropIndex( { "indexKey" : 1 } )
db.persons.dropIndexes()
db.persons.ensureIndex(keypattern[,options])
db.persons.explain().help() - show explain help
db.persons.reIndex()
db.persons.find([query],[fields]) - query is an optional query filter. fields is optional set of fields to return.
e.g. db.persons.find( {x:77} , {name:1, x:1} )
db.persons.find(...).count()
db.persons.find(...).limit(n)
db.persons.find(...).skip(n)
db.persons.find(...).sort(...)
db.persons.findOne([query])
db.persons.findAndModify( { update : ... , remove : bool [, query: {}, sort: {}, 'new': false] } )
db.persons.getDB() get DB object associated with collection
db.persons.getPlanCache() get query plan cache associated with collection
db.persons.getIndexes()
db.persons.group( { key : ..., initial: ..., reduce : ...[, cond: ...] } )
db.persons.insert(obj)
db.persons.mapReduce( mapFunction , reduceFunction , <optional params> )
db.persons.aggregate( [pipeline], <optional params> ) - performs an aggregation on a collection; returns a cursor
db.persons.remove(query)
db.persons.renameCollection( newName , <dropTarget> ) renames the collection.
db.persons.runCommand( name , <options> ) runs a db command with the given name where the first param is the collection name
db.persons.save(obj)
db.persons.stats({scale: N, indexDetails: true/false, indexDetailsKey: <index key>, indexDetailsName: <index name>})
db.persons.storageSize() - includes free space allocated to this collection
db.persons.totalIndexSize() - size in bytes of all the indexes
db.persons.totalSize() - storage allocated for all data and indexes
db.persons.update(query, object[, upsert_bool, multi_bool]) - instead of two flags, you can pass an object with fields: upsert, multi
db.persons.validate( <full> ) - SLOW
db.persons.getShardVersion() - only for use with sharding
db.persons.getShardDistribution() - prints statistics about data distribution in the cluster
db.persons.getSplitKeysForChunks( <maxChunkSize> ) - calculates split points over all chunks and returns splitter function
db.persons.getWriteConcern() - returns the write concern used for any operations on this collection, inherited from server/db if set
db.persons.setWriteConcern( <write concern doc> ) - sets the write concern for writes to the collection
db.persons.unsetWriteConcern( <write concern doc> ) - unsets the write concern for writes to the collection
>mongoDB的API
数据库和集合命名规范
- 不能是空字符串
- 不得含有' '(空格)、,、$、/,\、和\O(空字符);
- 应全部小写
- 最多64个字节
- 数据库名不能与现有系统保留库同名,如admin,local,及config
数据库i命名为db-text这样的集合也是合法的,但是不能通过db.[documentName]得到了,要改为db.getCollection("documentName"),因为db-text会被当成是减。
mongoDB的shell内置javascript引擎可以直接执行js代码
function insert(object){
db.getCollection("db-text").insert(object)
}
insert({age:29})
shell可以用eval
> db.eval("return 'mongodb'")
WARNING: db.eval is deprecated
mongodb
>
BSON是JSON的扩展,他新增了诸如日期,浮点等JSON不支持的数据类型

更多命令
db.AddUser(username,password) 添加用户
db.auth(usrename,password) 设置数据库连接验证
db.cloneDataBase(fromhost) 从目标服务器克隆一个数据库
db.commandHelp(name) 返回帮助命令
db.copyDatabase(fromdb,todb,fromhost) 复制数据库fromdb---源数据库名称,todb---目标数据库名称,fromhost---源数据库服务器地址
db.createCollection(name,{size:3333,capped:333,max:88888}) 创建一个数据集,相当于一个表
db.currentOp() 取消当前库的当前操作
db.dropDataBase() 删除当前数据库
db.eval(func,args) 运行服务器端代码
db.getCollection(cname) 取得一个数据集合,其他类似的用法:db['cname']
db.getCollenctionNames() 取得所有数据集合的名称列表
db.getLastError() 返回最后一个错误的提示消息
db.getLastErrorObj() 返回最后一个错误的对象
db.getMongo() 取得当前服务器的连接对象
db.getMongo().setSlaveOk() 允许当前连接读取备库中的成员对象
db.getName() 返回当操作数据库的名称
db.getPrevError() 返回上一个错误对象
db.getProfilingLevel()
db.getReplicationInfo() 获得重复的数据
db.getSisterDB(name) 获取服务器上面的数据库
db.killOp() 停止(杀死)在当前库的当前操作
db.printCollectionStats() 返回当前库的数据集状态
db.printReplicationInfo()
db.printSlaveReplicationInfo()
db.printShardingStatus() 返回当前数据库是否为共享数据库
db.removeUser(username) 删除用户
db.repairDatabase() 修复当前数据库
db.resetError()
db.runCommand(cmdObj) 运行数据库命令. 如果cmdObj 是 string类型, 将它转换为 {cmdObj:1}格式的对象
db.setProfilingLevel(level) 0=off,1=slow,2=all
db.shutdownServer() 关闭当前服务程序
db.version() 返回当前程序的版本信息 db.test.find({id:10}) 返回test数据集ID=10的数据集
db.test.find({id:10}).count() 返回test数据集ID=10的数据总数
db.test.find({id:10}).limit(2) 返回test数据集ID=10的数据集从第二条开始的数据集
db.test.find({id:10}).skip(8) 返回test数据集ID=10的数据集从0到第八条的数据集
db.test.find({id:10}).limit(2).skip(8) 返回test数据集ID=1=的数据集从第二条到第八条的数据
db.test.find({id:10}).sort() 返回test数据集ID=10的排序数据集
db.test.findOne([query]) 返回符合条件的一条数据
db.test.getDB() 返回此数据集所属的数据库名称
db.test.getIndexes() 返回些数据集的索引信息
db.test.group({key:...,initial:...,reduce:...[,cond:...]})
db.test.mapReduce(mayFunction,reduceFunction,<optional params>)
db.test.remove(query) 在数据集中删除一条数据
db.test.renameCollection(newName) 重命名些数据集名称
db.test.save(obj) 往数据集中插入一条数据
db.test.stats() 返回此数据集的状态
db.test.storageSize() 返回此数据集的存储大小
db.test.totalIndexSize() 返回此数据集的索引文件大小
db.test.totalSize() 返回些数据集的总大小
db.test.update(query,object[,upsert_bool]) 在此数据集中更新一条数据
db.test.validate() 验证此数据集
db.test.getShardVersion() 返回数据集共享版本号
MongoDB语法与现有关系型数据库SQL语法比较
MongoDB语法 <==> MySql语法
db.test.find({'name':'foobar'}) <==> select * from test where name='foobar'
db.test.find() <==> select * from test
db.test.find({'ID':10}).count() <==> select count(*) from test where ID=10
db.test.find().skip(10).limit(20) <==> select * from test limit 10,20
db.test.find({'ID':{$in:[25,35,45]}}) <==> select * from test where ID in (25,35,45)
db.test.find().sort({'ID':-1}) <==> select * from test order by ID desc
db.test.distinct('name',{'ID':{$lt:20}}) <==> select distinct(name) from test where ID<20
db.test.group({key:{'name':true},cond:{'name':'foo'},reduce:function(obj,prev){prev.msum+=obj.marks;},initial:{msum:0}}) <==> select name,sum(marks) from test group by name
db.test.find('this.ID<20',{name:1}) <==> select name from test where ID<20
db.test.insert({'name':'foobar','age':25})<==>insert into test ('name','age') values('foobar',25)
db.test.remove({}) <==> delete * from test
db.test.remove({'age':20}) <==> delete test where age=20
db.test.remove({'age':{$lt:20}}) <==> elete test where age<20
db.test.remove({'age':{$lte:20}}) <==> delete test where age<=20
db.test.remove({'age':{$gt:20}}) <==> delete test where age>20
db.test.remove({'age':{$gte:20}}) <==> delete test where age>=20
db.test.remove({'age':{$ne:20}}) <==> delete test where age!=20
db.test.update({'name':'foobar'},{$set:{'age':36}}) <==> update test set age=36 where name='foobar'
db.test.update({'name':'foobar'},{$inc:{'age':3}}) <==> update test set age=age+3 where name='foobar'
注意以上命令大小写敏感。
每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——2.MongoDB环境变量配置和Shell操作的更多相关文章
- 每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——1. MongoDB介绍和安装
目录:ASP.NET MVC企业级实战目录 MongoDB简介 MongoDB是一个高性能,开源,无模式的文档型数据库,是当前NoSql数据库中比较热门的一种.它在许多场景下可用于替代传统的关系型数据 ...
- 每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——3.MongoDB可视化及shell详解
本篇主要介绍MongoDB可视化操作以及shell使用及命令,备份恢复.数据导入导出. MongoVUE安装和简单使用 使用mongo.exe 管理数据库虽然可行,功能也挺强大,但每次都要敲命令,即繁 ...
- 每篇半小时1天入门MongoDB——4.MongoDB索引介绍及数据库命令操作
准备工作 继续连接到mongo C:\Users\zouqi>mongo MongoDB shell version: 3.0.7 connecting to: test 查看数据库和集合 &g ...
- Linux 环境变量配置(Nodejs/MongoDB/JDK/Nginx)
一.环境变量配置 注:配置环境变量的文件 全局变量(系统级别): /etc/bashrc /etc/profile /etc/environment 用户变量(用户级别): ~/.bash_profi ...
- JAVA JDK 环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳
JAVA JDK 环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 JERRY_Z. ~ 2020 / 9 / 13 转载请注明出处!️ 目录 JAVA JDK 环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 一.为什么j ...
- Python安装与环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳
Python安装与环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 JERRY_Z. ~ 2020 / 9 / 24 转载请注明出处!️ 目录 Python安装与环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 一.下载Py ...
- GoSDK的安装及环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳
GoSDK的安装及环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 JERRY_Z. ~ 2020 / 10 / 29 转载请注明出处!️ 目录 GoSDK的安装及环境变量配置 入门详解 - 精简归纳 一.进入G ...
- smarty半小时快速上手入门教程
http://www.jb51.net/article/56754.htm http://www.yiibai.com/smarty/smarty_functions.html http://www. ...
- idea部署Maven入门(一)——环境变量的配置和下载
介绍: 1 Maven是用来管理jar包的一种工具, 2 Maven主要是构建java项目和java web项目 3 maven项目管理所依赖的jar ...
随机推荐
- 求解释一个蛋疼的bug
大婶儿们出来解决个问题,看看有碰见过的没 截图中的 if (order.EShopOrder_PayStatus == 0 && order.EShopOrder_Status == ...
- Linux - 进程间通信 - 命名管道
1.命名管道的特点: (1)是管道,可用于非血缘关系的进程间的通信 (2)使用命名管道时,梁金成需要用路径表示通道. (3)命名管道以FIFO的文件形式存储于文件系统中.(FIFO:总是按照先进先出的 ...
- JS中Object常用的一些属性和方法
1⃣️属性 刚接触prototype.constructor.proto这三个玩意儿的时候,是不是有点儿傻傻分不清楚的感觉?下面来简单的说下... 举
- bzoj2560 串珠子
Description 铭铭有n个十分漂亮的珠子和若干根颜色不同的绳子.现在铭铭想用绳子把所有的珠子连接成一个整体. 现在已知所有珠子互不相同,用整数1到n编号.对于第i个珠子和第j个珠子,可以选择不 ...
- 蓝桥杯-骰子游戏-java
/* (程序头部注释开始) * 程序的版权和版本声明部分 * Copyright (c) 2016, 广州科技贸易职业学院信息工程系学生 * All rights reserved. * 文件名称: ...
- PHP中的对象遍历技巧
PHP中的对象遍历 对象的遍历,主要是指遍历对象中的,对外部可见属性.实际上就是用访问限制符public声明的属性,这点大家肯定很熟悉了.并且,在php中,遍历对象居然与遍历数组一样,都可以用使用fo ...
- 用PHP删除ftp下载导致的文件空行
使用FTP上传下载文件,如果没有设置传输方式为二进制,可能会导致文件出现空行的情况,例如: 使用PHP对文件的空行进行删除,使用正则: <?php $file = './abc.inc.php' ...
- H5游戏见缝插针开发
中秋节马上就要来临,公司开发了一个h5小游戏叉月饼,其实就是游戏“见缝插针”的翻版.这个游戏的开发任务落到了我的头上... 一 游戏介绍 游戏场景基本如下所示: 二 所用工具 这次的开 ...
- 一分钟应对勒索病毒WannaCry
一.WannaCry 勒索病毒 勒索病毒WannaCry肆虐全球,利用Windows操作系统漏洞,因链式反应迅猛自动传播,校园电脑.个人电脑.政府机关都是重灾区.中毒电脑所有文档被加密,将被勒索高达3 ...
- Java 7 Fork/Join 框架
在 Java7引入的诸多新特性中,Fork/Join 框架无疑是重要的一项.JSR166旨在标准化一个实质上可扩展的框架,以将并行计算的通用工具类组织成一个类似java.util中Collection ...
