virtio guest side implementation: PCI, virtio device, virtio net and virtqueue
With the publishing of OASIS virtio specification version 1.0, virtio made another big step in becoming an official standard from a De-Facto standard for virtual i/o device in paravirtualization environment.
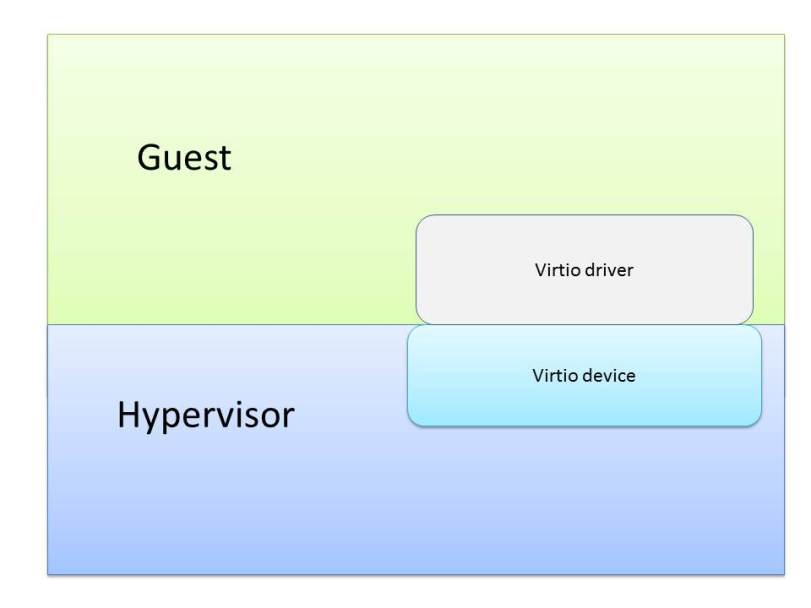
virtio device
For virtio, device emulation is done in hypervisor/host. They are commonly implemented as PCI devices, virtio over memory mapped device (MMIO) or channel i/o is also seen.
Take QEMU as example, it emulates the control plane of virtio PCI device like device status, feature bits and device configuration space, while the implementation of virtqueue backend data plane has three options so far:
- Virtio backend running inside QEMU
virtqueue notification and actual data access are done directly by QEMU. virtio.c contains the major implementation.
- Virtio backend inside host kernel, vhost
QEMU help setup kick/irq eventfd, vhost utilizes them to communicates with drivers in guest directly for virtqueue notification. Linux kernel module vhost sends/receives data via virtqueue with guest without exiting to host user space. vhost-worker is the kernel thread handling the notification and data buffer, the arrangement that enables it to access whole QEMU/guest address space is that: QEMU issues VHOST_SET_OWNER ioctl call to saves the mm context of qemu process in vhost_dev, then vhost-worker thread take on the specified mm context. Check use_mm() kernel function.
- Virtio backend running in separate userspace process
virtio device driver
Guest OS implements the drivers for driving virtio device presented by underlying hypervisor. Here we walk through the virtio PCI network card driver example in Linux kernel.
Virtio PCI
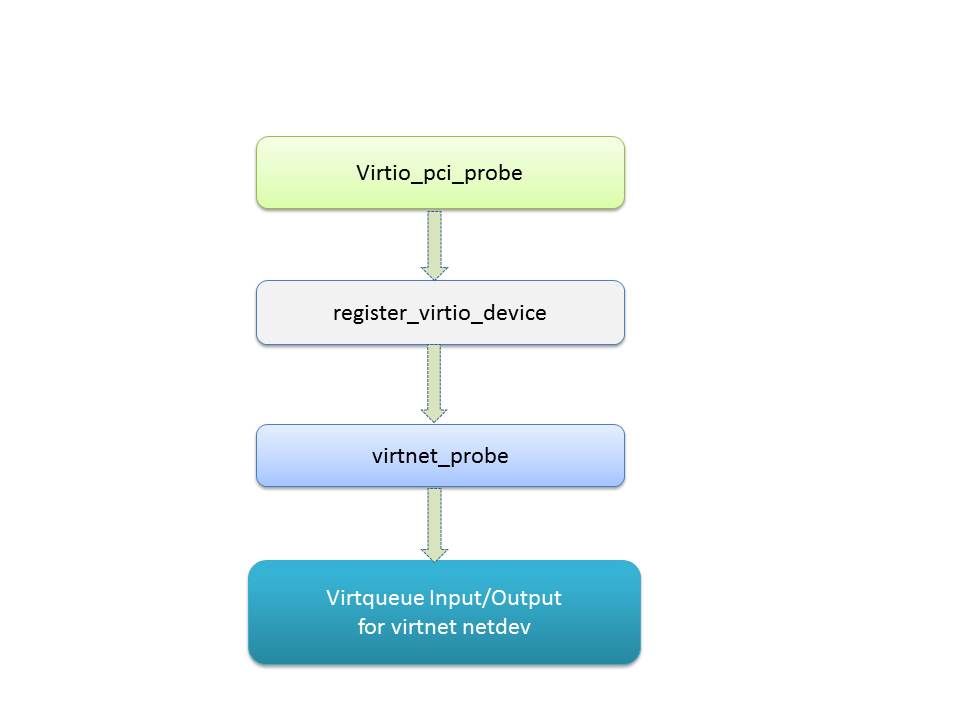
As that for a regular PCI device, virtio pci driver fills data and call back functions into standard pci_driver structure, among them the most important parts are the pci_device_id table and probe function. All virtio devices use vendor id of ox1af4. virtio_pci_probe() will be called if a virtio pci device with that specific vendor id is detected on PCI bus. The probe function allocates a virtio_pci_device structure which saves the necessary information like pci_dev pointer, MSI-X config and virtqueues list. virtio_device structure is also part of virtio_pci_device, “struct virtio_config_ops virtio_pci_config_ops” provides a set of virtio device status/feature/configuration/virtqueue callback functions and it will be linked into virtio_device.
At the end of virtio PCI probe processing, PCI subsystem vendor and device id will be assigned to the new virtio_device as its vendor and device id, then the newly created virtio_device which is inside virtio_pci_device structure will be register onto virtio bus: “int register_virtio_device(struct virtio_device *dev)”
Virtio netdev
virtio_net_driver is a Linux kernel driver module registered with virtio_bus. Note that virtio_bus has been registered during kernel initialization : core_initcall(virtio_init); and the code is built in kernel and not a loadable module.
The virtio_driver probe fucntion virtnet_probe() will be called once a virtio device with device ID VIRTIO_ID_NET has been detected. To work as a network device, net_device structure is created via alloc_etherdev_mq() , various network features are checked. Within the probe function, TX/RX virtqueue will be created/initialized, the find_vqs() callback function in virtio_pci_config_ops of virtio_device will called during this process. virtnet_info works as the private data of virtio net_device to link net_device and virtio_device together.
net_device_ops virtnet_netdev is also configured for the new net device which will be ready to function as a network interface card for sending/receiving data.
Virtio netdev RX/TX
At least 2 virtqueues will be created for virtio net_device interface, one for TX and the other one for RX. If host supports flow steering feature VIRTIO_NET_F_MQ, then more than one pair of queues may be created. Supporting of VIRTIO_NET_F_CTRL_VQ adds another virtqueue which is used by driver to send commands to manipulate various features of device which would not easily map into the PCI configuration space.
In RX direction, virtnet_receive() is called by virtnet_poll() or virtnet_busy_poll() depending on kernel CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL option setting. virtqueue_get_buf() is the next layer function which gets the data from host. As special requirement for virtio driver, it needs to add in buffer for host to put data there. Function try_fill_recv() serves that purpose, virtqueue_add_inbuf() is called eventually to expose input buffers to the other end.
For virtnet device driver, the TX processing starts with the call back function start_xmit() within virtnet_netdev , it first frees up any pending old buffer via free_old_xmit_skbs(), then goes into xmit_skb()which calls virtqueue_add_outbuf() located in virtio_ring.c. virtqueue_get_buf()is also called by free_old_xmit_skbs() to get used buffer and release the virtqueue ring descriptor back to desc free list.
Virtqueue
virtqueue is the fundamental building block of virtio, it is the mechanism for bulk data transport on virtio devices. From virtqueque point of view, both virtio netdev RX and TX queues are virtually the same. Each virtqueue consists of three parts: Descriptor table, Available ring and Used ring.
Each descriptor could refer to a buffer that driver uses for virtio device, the addr field of it points to a physical address of guest.
Available ring stores index of entries in descriptor table for which guest informs host/hypervisor that the buffer descriptor points to is available for use. In the perspective of guest virtio netdev TX queue, the buff is filled with data to be processed by host. While for guest virtio netdev RX queue, the buffer is empty and should be filled by host. virtqueue_add() which is called by both virtqueue_add_outbuf() & virtqueue_add_inbuf() operates on the available ring. Guest performs write operation on available ring data structure, host reads it only.
Used ring is where the virtio device (host) returns buffer once it is done with them. it is only written to by the device, and read by the driver (guest). For both virtio netdev RX/TX queues, detach_buf() which is called by virtqueue_get_buf() will take the descriptors indicated by used ring and put them back to descriptor table free list.
Refer to Virtual I/O Device (VIRTIO) Version 1.0 and virtio: Towards a De-Facto Standard For Virtual I/O Devices for authentic information about virtio.
https://jipanyang.wordpress.com/2014/10/27/virtio-guest-side-implementation-pci-virtio-device-virtio-net-and-virtqueue/
virtio guest side implementation: PCI, virtio device, virtio net and virtqueue的更多相关文章
- Virtio: An I/O virtualization framework for Linux
The Linux kernel supports a variety of virtualization schemes, and that's likely to grow as virtuali ...
- [qemu] 在前端驱动使用virtio的情况下,如何让后端使用vhost-user [未解决]
首先,如果你更关心原理和知识,请读读这个 http://chuansong.me/n/2186528 (值得细细的逐字读). 在<<深入浅出dpdk>>中提到,vhost-us ...
- QEMU KVM Libvirt手册(8): 半虚拟化设备virtio
KVM本身并不提供半虚拟化功能,是通过virtio来实现的 The benefits of virtio drivers are of lower overhead and higher perfor ...
- virtio后端驱动详解
2016-10-08 virtIO是一种半虚拟化驱动,广泛用于在XEN平台和KVM虚拟化平台,用于提高客户机IO的效率,事实证明,virtIO极大的提高了VM IO 效率,配备virtIO前后端驱动的 ...
- Virtio SCSI设备介绍
Qemu的存储栈 在KVM虚拟化环境中,当客户机的内核存储系统像在物理机上一样通过页缓存.文件系统.通用块设备层运行到实际设备驱动时,这时驱动对设备寄存器的访问会触发CPU从客户机代码切换到物理机内的 ...
- 【原创】Linux虚拟化KVM-Qemu分析(九)之virtio设备
背景 Read the fucking source code! --By 鲁迅 A picture is worth a thousand words. --By 高尔基 说明: KVM版本:5.9 ...
- 【原创】Linux虚拟化KVM-Qemu分析(十)之virtio驱动
背景 Read the fucking source code! --By 鲁迅 A picture is worth a thousand words. --By 高尔基 说明: KVM版本:5.9 ...
- virtio 驱动的数据结构理解
ps:本文基于4.19.204内核 Q:vqueue的结构成员解释: A:结构如下,解析附后: struct virtqueue { struct list_head list;//caq:一个vir ...
- KVM下virtio驱动虚拟机XML配置文件分析
[root@opennebula qemu]# pwd /etc/libvirt/qemu [root@opennebula qemu]# ls networks one-12.xml one-12. ...
随机推荐
- https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/6755717.html
知识预览 一 进程与线程的概念 二 threading模块 三 multiprocessing模块 四 协程 五 IO模型 回到顶部 一 进程与线程的概念 1.1 进程 考虑一个场景:浏览器,网易云音 ...
- .Vue.js大全
Vue起步 1.下载核心库vue.js bower info vue npm init --yes cnpm install vue --save vue2.0和1.0相比,最大的变化就是引入了Vir ...
- 初识idea
http://blog.csdn.net/bitcarmanlee/article/details/54951589 http://blog.csdn.net/haishu_zheng/article ...
- Hidden String---hdu5311(字符串处理)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5311 题意:从给出的串 s 中找到3个子串然后把他们连在一起问是否能够成anniversary #in ...
- springboot集成shiro和开涛的动态url问题
我出现的问题就是一旦/**=authc不管放到前面还是后面都会把所有的资源全部拦截,css和js都访问不到,只需要把开涛的动态url代码改一下就行了(如上图)
- Harbor实现容器镜像仓库的管理和运维
本次分享主要讲述了在开发运维中的管理容器镜像方法.为了便于说明原理,较多地使用Harbor作为例子. 内容主要包括: 开发和生产环境中镜像仓库的权限控制: 镜像远程同步(复制)的原理: 大规模应用镜像 ...
- C#超级方便的ExpandoObject类别
这东西是.NET Framework 4.5 的新东西..发现这个,大概就跟发现新大陆一样的兴奋,让我再次赞叹Anders Hejlsberg 之神.. 这边有MSDN : http://msdn.m ...
- JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA 15 Ultimate Edition版本激活破解
由于JetBrains系列新版本注册激活发生了变化,所以原来的激活方式已经不能在使用. 只能用新的方式来破解了.此方式支持所有系列的新版版.包括IDEA15,PHPSTORM10,WEBSTO ...
- CSS3自定义滚动条样式 之 -webkit-scrollbar
有没有觉得浏览器自带的原始滚动条很不美观,同时也有看到很多网站的自定义滚动条显得高端,就连chrome32.0开发板都抛弃了原始的滚动条,美观多了.那webkit浏览器是如何自定义滚动条的呢? 前言 ...
- python继承,判断类型,多态
1.python中继承 如果已经定义了Person类,需要定义新的Student和Teacher类时,可以直接从Person类继承: class Person(object): def __init_ ...
