在Spring Boot中使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解, @EnableConfigurationProperties
但 Spring Boot 提供了另一种方式 ,能够根据类型校验和管理application中的bean。 这里会介绍如何使用@ConfigurationProperties。
继续使用mail做例子。配置放在mail.properties文件中。属性必须命名规范才能绑定成功。举例:
1 protocol and PROTOCOL will be bind to protocol field of a bean
2 smtp-auth , smtp_auth , smtpAuth will be bind to smtpAuth field of a bean
3 smtp.auth will be bind to … hmm to smtp.auth field of a bean!
Spring Boot 使用一些松的规则来绑定属性到@ConfigurationProperties bean 并且支持分层结构(hierarchical structure)。
开始创建一个@ConfigurationProperties bean:

package com.dxz.property; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties(locations = "classpath:mail.properties", ignoreUnknownFields = false, prefix = "mail")
public class MailProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String from;
private String username;
private String password;
private Smtp smtp; // ... getters and setters
public String getHost() {
return host;
} public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
} public int getPort() {
return port;
} public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public String getFrom() {
return from;
} public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
} public String getUsername() {
return username;
} public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
} public String getPassword() {
return password;
} public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
} public Smtp getSmtp() {
return smtp;
} public void setSmtp(Smtp smtp) {
this.smtp = smtp;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "MailProperties [host=" + host + ", port=" + port + ", from=" + from + ", username=" + username
+ ", password=" + password + ", smtp=" + smtp + "]";
} public static class Smtp {
private boolean auth;
private boolean starttlsEnable; public boolean isAuth() {
return auth;
} public void setAuth(boolean auth) {
this.auth = auth;
} public boolean isStarttlsEnable() {
return starttlsEnable;
} public void setStarttlsEnable(boolean starttlsEnable) {
this.starttlsEnable = starttlsEnable;
} }
}

如下属性中创建 ( mail.properties ):

mail.host=localhost
mail.port=25
mail.smtp.auth=false
mail.smtp.starttls-enable=false
mail.from=me@localhost
mail.username=duan
mail.password=duan123456

上例中我们用@ConfigurationProperties注解就可以绑定属性了。ignoreUnknownFields = false告诉Spring Boot在有属性不能匹配到声明的域的时候抛出异常。开发的时候很方便! prefix 用来选择哪个属性的prefix名字来绑定。
请注意setters 和 getters 需要在@ConfigurationProperties bean中创建! 与@Value注解相反。
我们需要用属性来配置 application。 有至少两种方式来创建@ConfigurationProperties。即可以搭配@Configuration 注解来提供 @Beans 也可以单独使用并注入 @Configuration bean。
方案1:定义spring的一个实体bean装载配置文件信息,其它要使用配置信息是注入该实体bean

package com.dxz.property3; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
@ConfigurationProperties(locations = "classpath:mail.properties", ignoreUnknownFields = false, prefix = "mail")
public class MailProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String from;
private String username;
private String password;
private Smtp smtp; // ... getters and setters
public String getHost() {
return host;
} public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
} public int getPort() {
return port;
} public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public String getFrom() {
return from;
} public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
} public String getUsername() {
return username;
} public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
} public String getPassword() {
return password;
} public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
} public Smtp getSmtp() {
return smtp;
} public void setSmtp(Smtp smtp) {
this.smtp = smtp;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "MailProperties [host=" + host + ", port=" + port + ", from=" + from + ", username=" + username
+ ", password=" + password + ", smtp=" + smtp + "]";
} public static class Smtp {
private boolean auth;
private boolean starttlsEnable; public boolean isAuth() {
return auth;
} public void setAuth(boolean auth) {
this.auth = auth;
} public boolean isStarttlsEnable() {
return starttlsEnable;
} public void setStarttlsEnable(boolean starttlsEnable) {
this.starttlsEnable = starttlsEnable;
} }
}

启动及测试类:

package com.dxz.property3; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController
@SpringBootApplication
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(MailProperties.class)
public class TestProperty3 { @Autowired
private MailProperties mailProperties; @RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello() {
System.out.println("mailProperties" + mailProperties);
return "hello world";
} public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(TestProperty1.class, args);
new SpringApplicationBuilder(TestProperty3.class).web(true).run(args); }
}

结果:
mailPropertiesMailProperties [host=localhost, port=25, from=me@localhost, username=duan, password=duan123456, smtp=com.dxz.property3.MailProperties$Smtp@37cebacb]
方案2:@Bean+@ConfigurationProperties
我们还可以把@ConfigurationProperties还可以直接定义在@bean的注解上,这是bean实体类就不用@Component和@ConfigurationProperties了

package com.dxz.property4;
public class MailProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String from;
private String username;
private String password;
private Smtp smtp;
// ... getters and setters
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Smtp getSmtp() {
return smtp;
}
public void setSmtp(Smtp smtp) {
this.smtp = smtp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MailProperties [host=" + host + ", port=" + port + ", from=" + from + ", username=" + username
+ ", password=" + password + ", smtp=" + smtp + "]";
}
public static class Smtp {
private boolean auth;
private boolean starttlsEnable;
public boolean isAuth() {
return auth;
}
public void setAuth(boolean auth) {
this.auth = auth;
}
public boolean isStarttlsEnable() {
return starttlsEnable;
}
public void setStarttlsEnable(boolean starttlsEnable) {
this.starttlsEnable = starttlsEnable;
}
}
}

配置类(启动类)

package com.dxz.property4; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; @SpringBootApplication
public class TestProperty4 { @Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(locations = "classpath:mail.properties", prefix = "mail")
public MailProperties mailProperties(){
MailProperties mp = new MailProperties();
System.out.println("zheli " + mp);
return mp; } public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(TestProperty1.class, args);
new SpringApplicationBuilder(TestProperty4.class).web(true).run(args); }
}

测试类:

package com.dxz.property4; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController
@RequestMapping("/task")
public class TaskController { @Autowired
MailProperties mailProperties; @RequestMapping(value = {"/",""})
public String hellTask(){
System.out.println("mailProperties" +mailProperties);
return "hello task !!";
} }

结果:
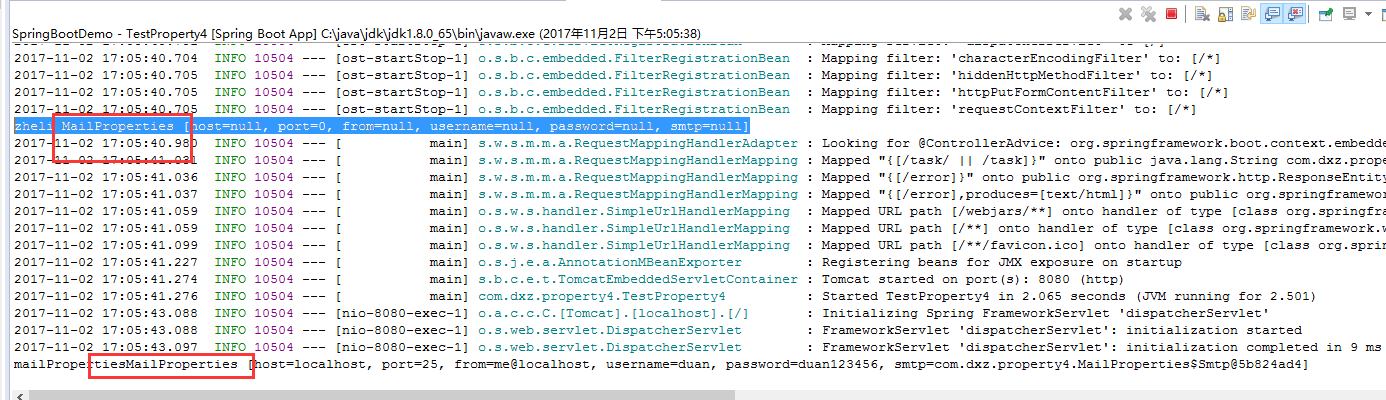
方案3:@ConfigurationProperties + @EnableConfigurationProperties
我们和上面例子一样注解属性,然后用 Spring的@Autowire来注入 mail configuration bean:

package com.dxz.property; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; @ConfigurationProperties(locations = "classpath:mail.properties", ignoreUnknownFields = false, prefix = "mail")
public class MailProperties {
private String host;
private int port;
private String from;
private String username;
private String password;
private Smtp smtp; // ... getters and setters
public String getHost() {
return host;
} public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
} public int getPort() {
return port;
} public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
} public String getFrom() {
return from;
} public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
} public String getUsername() {
return username;
} public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
} public String getPassword() {
return password;
} public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
} public Smtp getSmtp() {
return smtp;
} public void setSmtp(Smtp smtp) {
this.smtp = smtp;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "MailProperties [host=" + host + ", port=" + port + ", from=" + from + ", username=" + username
+ ", password=" + password + ", smtp=" + smtp + "]";
} public static class Smtp {
private boolean auth;
private boolean starttlsEnable; public boolean isAuth() {
return auth;
} public void setAuth(boolean auth) {
this.auth = auth;
} public boolean isStarttlsEnable() {
return starttlsEnable;
} public void setStarttlsEnable(boolean starttlsEnable) {
this.starttlsEnable = starttlsEnable;
} }
}

启动类及测试类:

package com.dxz.property; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.builder.SpringApplicationBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MailProperties.class)
public class TestProperty1 { @Autowired
private MailProperties mailProperties; @RequestMapping(value = "/hello", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String hello() {
System.out.println("mailProperties" + mailProperties);
return "hello world";
} public static void main(String[] args) {
//SpringApplication.run(TestProperty1.class, args);
new SpringApplicationBuilder(TestProperty1.class).web(true).run(args); }
}

结果:
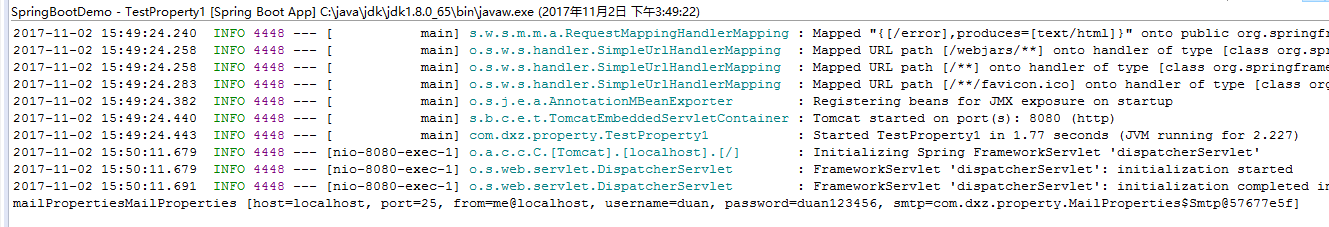
请注意@EnableConfigurationProperties注解。该注解是用来开启对@ConfigurationProperties注解配置Bean的支持。也就是@EnableConfigurationProperties注解告诉Spring Boot 能支持@ConfigurationProperties。如果不指定会看到如下异常:
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type [com.dxz.property.MailProperties] found for dependency: expected at least 1 bean which qualifies as autowire candidate for this dependency. Dependency annotations: {@org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired(required=true)}
注意: 还有其他办法 (Spring Boot 总是有其他办法!) 让@ConfigurationProperties beans 被添加 – 用@Configuration或者 @Component注解, 这样就可以在 component scan时候被发现了。
总结:
@ConfigurationProperties很方便使用。 比用@Value注解好吗? 在特定的方案中是的,这只是一个选择问题。
看下Spring Boot的文档有更多的关于typesafe configuration 属性
转自原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/duanxz/p/4520571.html
在Spring Boot中使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解, @EnableConfigurationProperties的更多相关文章
- 在Spring Boot中使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
但 Spring Boot 提供了另一种方式 ,能够根据类型校验和管理application中的bean. 这里会介绍如何使用@ConfigurationProperties.继续使用mail做例子. ...
- Spring Boot 中使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解
@ConfigurationProperties 主要作用:绑定 application.properties 中的属性 例如: @Configuration public class DataSou ...
- 在Spring Boot中使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解 (二十六)
@ConfigurationProperties主要作用:就是绑定application.properties中的属性 java代码 @Configuration public class DataS ...
- 利用 Spring Boot 中的 @ConfigurationProperties,优雅绑定配置参数
使用 @Value("${property}") 注释注入配置属性有时会很麻烦,尤其是当你使用多个属性或你的数据是分层的时候. Spring Boot 引入了一个可替换的方案 -- ...
- Spring Boot中使用MyBatis注解配置详解(1)
之前在Spring Boot中整合MyBatis时,采用了注解的配置方式,相信很多人还是比较喜欢这种优雅的方式的,也收到不少读者朋友的反馈和问题,主要集中于针对各种场景下注解如何使用,下面就对几种常见 ...
- 如何优雅地在 Spring Boot 中使用自定义注解,AOP 切面统一打印出入参日志 | 修订版
欢迎关注个人微信公众号: 小哈学Java, 文末分享阿里 P8 资深架构师吐血总结的 <Java 核心知识整理&面试.pdf>资源链接!! 个人网站: https://www.ex ...
- Spring Boot 中使用 @Transactional 注解配置事务管理
事务管理是应用系统开发中必不可少的一部分.Spring 为事务管理提供了丰富的功能支持.Spring 事务管理分为编程式和声明式的两种方式.编程式事务指的是通过编码方式实现事务:声明式事务基于 AOP ...
- Spring Boot中使用@Transactional注解配置事务管理
事务管理是应用系统开发中必不可少的一部分.Spring 为事务管理提供了丰富的功能支持.Spring 事务管理分为编程式和声明式的两种方式.编程式事务指的是通过编码方式实现事务:声明式事务基于 AOP ...
- Spring boot中相关的注解
一.相关类中使用的注解 @RestController:REST风格的控制器 @RequestMapping:配置URL和方法之间的映射 @SpringBootApplication:应用程序入口类 ...
随机推荐
- IO流-基础
//创建输出流对象 FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("d:\\a.txt"); /* * 创建输出流对象做了哪些事情: * A:调用系统资源创建了一个 ...
- bzoj 1295 最长距离 - 最短路
Description windy有一块矩形土地,被分为 N*M 块 1*1 的小格子. 有的格子含有障碍物. 如果从格子A可以走到格子B,那么两个格子的距离就为两个格子中心的欧几里德距离. 如果从格 ...
- 0x17二叉堆之超市
题目链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/147/ 容易想到一个贪心策略:在最优解中,对于每个时间(天数) t,应该在保证不卖出过期商品的前提下,尽量卖出 ...
- Qt Quick Dialogs
一.如下图.. 二. 1.FileDialog //定义FileDialog{ id:fileDialog; title: "open a picture"; nameFilter ...
- topcoder srm 380 div1
problem1 link 分类讨论.高度没有太大关系.主要看长度. problem2 link 二分答案$mid$.计算每种$card$不足的部分,加起来,小于等于$min(jokers,mid)$ ...
- Transaction
SqlTransaction——事务详解 事务是将一系列操作作为一个单元执行,要么成功,要么失败,回滚到最初状态.在事务处理术语中,事务要么提交,要么中止.若要提交事务,所有参与者都必须保证对数据的任 ...
- Vue学习三:v-on:click命令及v-html命令学习
本文为博主原创,未经允许不得转载: 第一部分: v-on:click 命令讲解及使用方法 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh"> ...
- ComponentOne使用技巧——从Winform穿越到WPF
概述 WPF 和 Winform 是两个单独的平台,但二者又都是基于 .NET 4.0 以上版本开发的,所以很多.NET开发人员就开始研究如何在WPF中使用Winform.微软已经架设了两个开发平台的 ...
- springmvc异步上传图片并回调页面函数插入图片url代码示例
<tr> <td class="search_td">属性值图片值:</td> <td> <input type=" ...
- Ubuntu14.04 clang3.8 Installation Guide
Reference Installing clang 3.8 on Ubuntu 14.04.3. Ubuntu14.04 clang3.8 Installation Guide 1.add the ...
