Effective Java Chapter4 Classes and Interface
MInimize the accessibility of classes and members
这个叫做所谓的 information hiding ,这么做在于让程序耦合度更低,增加程序的健壮性等等,反正就是很有必要和有用。
四个修饰等级 private :只能当前class中调用
package-praivate 声明class,没有修饰的时候是默认 package-praivate,表示在一个 package里面使用
protect subclass里面调用
public 任意地方调用
任何field能够private 就private,java的封装原则。其次如果一个class 中有方法是继承superclass 那么class的leve就不能低于protect,意思即class的level必须高于等于它的field和method的等级。
摘录一段话 解释setter和getter的作用
Image if a field should never be null. If you have a setter method you could check for null and throw and IllegalArgumentException if null is ever passed. However if the field is public than any user of your class could set the field to any value including null. Your code then might get a NullPointerException because it was always expecting the field to never be null
Minimize mutability
如果一个类可以被设计成immutable class 最好就设计成immutable class
不可变对象有很多优点:
1. 构造、测试和使用都很简单。
2. 线程安全且没有同步问题,不需要担心数据会被其它线程修改。因为在多线程同时进行的情况下,一个可变对象的值很可能被其他进程改变,这样会造成不可预期的结果,而使用不可变对象就可以避免这种情况。
3. 当用作类的属性时不需要保护性拷贝。
缺点是,每次创建不可变类的时候内存消耗比较大 ,例如 每次对String的修改是new 一个String ,而每次对StringBuffer的修改就是直接利用StringBUffer里面的方法修改。
理解便是,immutable class 是一种不会变得状态,任何我们想要一个物体保持不变的状态都需要将其变成immutable class。
设计 immutable class的方法 http://www.cnblogs.com/pcideas/articles/5160689.html
public final class Complex {
private final double re;//元素值使用private final 修饰
private final double im;
public Complex (double re,double im){
this.re=re;
this.im=im;
}
public double realPart(){return re;}//基本元素 可以直接返回。
public double imaginaryPary(){return im;}
public Complex add(Complex c){
return new Complex(re+c.re,im+c.im);//非基本元素需要defensivecopy 所谓new?
}
public Complex substract(Complex c){
return new Complex(re-c.re,im-c.im);
}
}
建立一个 immutable class 的关键几个要点。
1 成员用 private final来修饰
2 不提供任何可以修改成员的方法 比如setter
3 对读取成员数据,如果成员是基本类型 可以直接 返回,比如上面句子的 return re;但是如果成员不是基本数据,比如 Date 或者 Complex 等,就需要返回他的defensive copy,如果直接返回引用,也是相当于提供一个可以修改该成员的方法,很危险。
4 若有必要,重写equeal ,用来比较是否相等。
public class Complex {//final取消掉 特意的写成静态方法就是为了能够继承?
private final double re;
private final double im;
private Complex (double re,double im){//设置成私有
this.re=re;
this.im=im;
}
public static Complex valueOf(double re,double im){
return new Complex(re,im);
}//提供静态方法
public double realPart(){return re;}
public double imaginaryPary(){return im;}
public Complex add(Complex c){
return new Complex(re+c.re,im+c.im);
}
public Complex substract(Complex c){
return new Complex(re-c.re,im-c.im);
}
}
代码也可以改成这个,但是。。。好处在哪里日后再想。
Favor composition over inheritance
public class InstrumentedHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E> {
private int count=0;
public InstrumentedHashSet(){}
public InstrumentedHashSet (int intitCap,float loadFactor){super(intitCap,loadFactor);}
@Override public boolean add(E e){
count++;
return super.add(e);
}
@Override public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E>c){
count+=c.size();
return super.addAll(c);
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
InstrumentedHashSet ih = new InstrumentedHashSet();
ih.addAll(Arrays.asList("1","2","3"));
System.out.println(ih.getCount());
}
}
//输出 6
为什么会输出6而不是3 呢,InstrumentedHashSet 中的方法addall 调用,其实是父类循环调用 add方法。所以每次add也会count++ addall count+=3,最后输出6
现在做一个调整
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set; public class ForwardingSet<E> implements Set<E>{//这个被称之为wrapper类,包装类
private final Set<E> s;//在里面命名一个s,之后所有的返回值是return s.XX,这样s的结构我们没有extends
public ForwardingSet(Set<E> s){
this.s=s;
}
@Override
public boolean add(E e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.add(e);
} @Override
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.addAll(c);
} @Override
public void clear() {
s.clear(); } @Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.contains(o);
} @Override
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.containsAll(c);
} @Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.isEmpty();
} @Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.iterator();
} @Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.remove(o);
} @Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.removeAll(c);
} @Override
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.retainAll(c);
} @Override
public int size() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.size();
} @Override
public Object[] toArray() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.toArray();
} @Override
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.toArray(a);
} } import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set; public class InstrumentedHashSet<E> extends ForwardingSet<E> {
private int count=0;
public InstrumentedHashSet(Set<E> s){super (s);} @Override public boolean add(E e){
count++;
return super.add(e);
}
@Override public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E>c){
count+=c.size();
return super.addAll(c);
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
} } public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
InstrumentedHashSet ih = new InstrumentedHashSet(new HashSet());
ih.addAll(Arrays.asList("1","2","3"));
System.out.println(ih.getCount()); } }
通过上面那个问题我们发现,如果直接继承一个类,并重写它的方法,然而我们也许不清楚里面的逻辑结构怎样,或者说之后版本改动成什么样子,我们在写父类的扩展方法时候加入了我们自己的逻辑,但是也许我们的逻辑和继承类的逻辑有冲突,就比如例子中的add 和addAll,继承类中addAll是直接循环调用自己的add方法,使我们得出了6的错误答案。
这样包装概念就出来了,我们先写一个Forwarding类 这个类implement Set<E> 接口 之后 在这个类里面实例一个我们需要的功能类(private final Set<E> s;),就像一层膜 隔开了功能类本身的逻辑运算和外部我们自己添加的运算,使我们不被内部类的结构所影响。 好像是只要在内部实例而不是继承一个类,都叫composition?
在类中直接使用 继承应该多考虑,当两者关系是 isA 的时候比较合适, 比如 Class employee entends people 。其他优先考虑接口 包装,等。
prefer interfaces to abstract classes
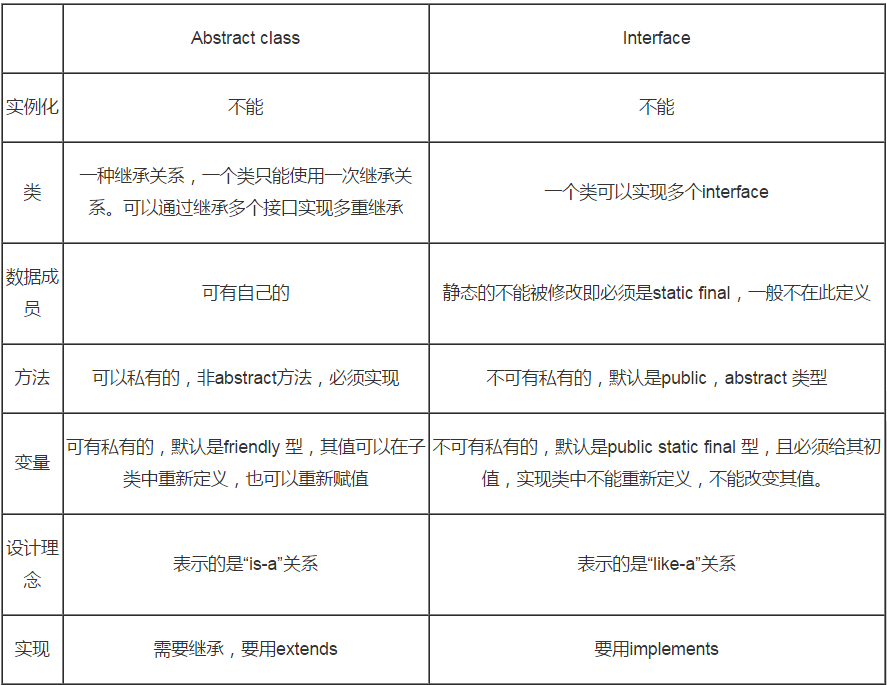
先看两者的区别,在设计使 我们要多考虑interface 摘录 effective java 里面的几句话
Existing classed can be easily retrofitted to implement a new interface .
Interfaces are ideal for defining mixins
Inerfaces allow the construction of nonhierarchical type frameworks
interfaces enable safe,powerful functionality enhancements 之后是注意的几个点
It is far easier to evolve an abstract class than an interface //因为interface 定义了一个方法就必须实现,不然compiler 错误,相对abstract class 比较灵活,
Once an interface is realsed and widely implemented,it is almost impossible to change.//所以定义一个interface要很小心
prefer class hierachies to tagged classes
class Figure {//这个是taged class ,就是各种信息糅杂在一起
enum Shape {
RECTANGLE, CIRCLE
};
// Tag field - the shape of this figure
final Shape shape;
// These fields are used only if shape is RECTANGLE
double length;
double width;
// This field is used only if shape is CIRCLE
double radius;
// Constructor for circle
Figure(double radius) {
shape = Shape.CIRCLE;
this.radius = radius;
}
// Constructor for rectangle
Figure(double length, double width) {
shape = Shape.RECTANGLE;
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
double area() {
switch (shape) {
case RECTANGLE:
return length * width;
case CIRCLE:
return Math.PI * (radius * radius);
default:
throw new AssertionError();
}
}
abstract class Figure { //这是hierachies class 好像是分层?
abstract double area();
}
class Circle extends Figure {
final double radius;
Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
double area() {
return Math.PI * (radius * radius);
}
}
class Rectangle extends Figure {
final double length;
final double width;
Rectangle(double length, double width) {
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
double area() {
return length * width;
}
}
class Square extends Rectangle {
Square(double side) {
super(side, side);
}
}
如果你要一个圆,计算一个圆,使用tagged classes 就会有多余的信息 constructor for rectangle(){},而且如果我现在要再加一个图形,比如扇形,也会发现要对Figure进行修改,破坏了Java的封装原则?
所以要使用分层的概念, 需要的共同的东西拿出来,然后再分别设计,比如计算图形函数 area()都是需要的,提出来作为一个abstract,之后扩展成所需要的图形。大概这样的意思。
Use function objects to represent strategies
直接记录一个 java策略模式。
//前言,个人认为理解和写策略模式的三要素 一 策略的申明(implement 或者 abstract) 二策略的具体实现(继承上者的Class) 三(使用策略的环境) 策略的实际意义应该在于包装算法?
public interface CountPrice { //一 策略的声明
public void priceNumber(int price);
}
public class PriceA implements CountPrice {//策略(算法)的不同实现
@Override
public void priceNumber(int price) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("这是价格策略A 价格为:"+price);
}
}
public class PriceB implements CountPrice {
@Override
public void priceNumber(int price) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("这是价格策略B 价格为:"+price*0.8);
}
}
public class PriceC implements CountPrice {
@Override
public void priceNumber(int price) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("这是价格策略C 价格为:"+price*0.5);
}
}
public class Context {//策略的具体环境
private CountPrice cprice;//标记我们需要某个算法
public Context (CountPrice cprice){//其实不要在这里面构造策略比较好,比较策略这种东西,是看我们需要用的时候再用就好了,构造函数这么重要的东西,还是不要放策略比较好,我现在是刚想到这点,还是懒得改了。
this.cprice=cprice;
}
public void setCountPrice(CountPrice cprice){//选择策略
this.cprice=cprice;
}
public void sayPrice(int price){
cprice.priceNumber(price);
}
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Context ct = new Context(new PriceC());
ct.sayPrice(500);
ct.setCountPrice(new PriceB());
ct.sayPrice(500);
ct.setCountPrice(new PriceA());
ct.sayPrice(500);
}
}
}
输出:
这是价格策略C 价格为:250.0
这是价格策略B 价格为:400.0
这是价格策略A 价格为:500
Favor static member classes over nonstatic
抄录一个 stackover 的回答 大概就是这样
The main difference between static and non-static inner classes is that a non-static inner class has access to other members of the outer class, even if they are private. Non-static inner classes are a "part" of the outer class. You cannot create nor can they exist without an instance of an outer class. A consequence of this is that an instance of a non-static inner classes are destroyed when the outer class's instance is destroyed.
Static inner classes, on the other hand, are just like normal outer classes. The live and die on their own. You don't need an instance of the outer class for the inner class to exist. That means they also have their own life cycle. They get destroyed when the garbage collector decides to destroy them.
Effective Java Chapter4 Classes and Interface的更多相关文章
- Effective Java —— 使类和成员的可访问性最小化
本文参考 本篇文章参考自<Effective Java>第三版第十五条"Minimize the accessibility of classes and members&quo ...
- Effective Java —— 谨慎覆盖clone
本文参考 本篇文章参考自<Effective Java>第三版第十三条"Always override toString",在<阿里巴巴Java开发手册>中 ...
- Effective Java —— 用静态工厂方法代替构造器
本文参考 本篇文章参考自<Effective Java>第三版第一条"Consider static factory methods instead of constructor ...
- Effective Java
Effective Java 创建和销毁对象---考虑用静态工厂方法代替构造器 构造器是创建一个对象实例最基本也最通用的方法,大部分开发者在使用某个class的时候,首先需要考虑的就是如何构造和初始化 ...
- Effective Java Index
Hi guys, I am happy to tell you that I am moving to the open source world. And Java is the 1st langu ...
- [Effective Java]第八章 通用程序设计
声明:原创作品,转载时请注明文章来自SAP师太技术博客( 博/客/园www.cnblogs.com):www.cnblogs.com/jiangzhengjun,并以超链接形式标明文章原始出处,否则将 ...
- effective java 第2章-创建和销毁对象 读书笔记
背景 去年就把这本javaer必读书--effective java中文版第二版 读完了,第一遍感觉比较肤浅,今年打算开始第二遍,顺便做一下笔记,后续会持续更新. 1.考虑用静态工厂方法替代构造器 优 ...
- Effective Java通俗理解(持续更新)
这篇博客是Java经典书籍<Effective Java(第二版)>的读书笔记,此书共有78条关于编写高质量Java代码的建议,我会试着逐一对其进行更为通俗易懂地讲解,故此篇博客的更新大约 ...
- Effective Java通俗理解(下)
Effective Java通俗理解(上) 第31条:用实例域代替序数 枚举类型有一个ordinal方法,它范围该常量的序数从0开始,不建议使用这个方法,因为这不能很好地对枚举进行维护,正确应该是利用 ...
随机推荐
- (转)python 全栈开发,Day74(基于双下划线的跨表查询,聚合查询,分组查询,F查询,Q查询)
昨日内容回顾 # 一对多的添加方式1(推荐) # book=Book.objects.create(title="水浒传",price=100,pub_date="164 ...
- Confluence 6 查看所有空间
有下面 2 种方法在 Confluence 中查看空间: 空间目录(The space directory) – 在 Confluence 的头部选择 空间(Spaces )> 空间目录(Spa ...
- 架构探险笔记4-使框架具备AOP特性(上)
对方法进行性能监控,在方法调用时统计出方法执行时间. 原始做法:在内个方法的开头获取系统时间,然后在方法的结尾获取时间,最后把前后台两次分别获取的系统时间做一个减法,即可获取方法执行所消耗的总时间. ...
- LOJ6072苹果树
虽然结合了很多算法,但是一步一步地推一下还不算太难的一道题. 首先考虑枚举枚举有用的苹果的集合,然后去算生成树个数. 先考虑怎么计算生成树个数. 发现可以使用matrix-tree. 所有有用点可以和 ...
- dsu on tree练习
dsu on tree主要是处理一些有根树子树询问的操作, 作用与点分治和线段树合并类似. 一般无根树询问所有树链信息的直接就点分了, 有根树的话一般用线段树合并或dsu on tree, 线段树合并 ...
- 【IDEA】【4】遇到的问题
前言: 1,jar包未导入到项目中 2,报错 cannot resolve symbol 3,左边栏只能看到文件看不到项目结构 4,报错 No valid Maven installation fou ...
- 轻量级RPC
①自定义一个协议接口继承VersionedProtocol ②自定义协议类实现上面的接口,完善功能需求 ③服务端 ④客户端 二:模拟一个namenode
- python-flask-Flask-SQLAlchemy与Flask-Migrate联合进行数据化迁移
使用步骤: 1. 引入Flask-SQLAlchemy from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy db = SQLAlchemy() 2. 注册 Flask-SQ ...
- hdu 1025LIS思路同1257 二分求LIS
题目: Constructing Roads In JGShining's Kingdom Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit ...
- ADO.NET json数组多条记录执行在DAL层循环(执行存储过程)
public int UpdateRegdate(tj_book_patient regdatejson) { int temp; SqlParameter[] ps = new SqlParamet ...
