『TensorFlow』分布式训练_其三_多机分布式
本节中的代码大量使用『TensorFlow』分布式训练_其一_逻辑梳理中介绍的概念,是成熟的多机分布式训练样例
一、基本概念
Cluster、Job、task概念:三者可以简单的看成是层次关系,task可以看成每台机器上的一个进程,多个task组成job;job又有:ps、worker两种,分别用于参数服务、计算服务,组成cluster。
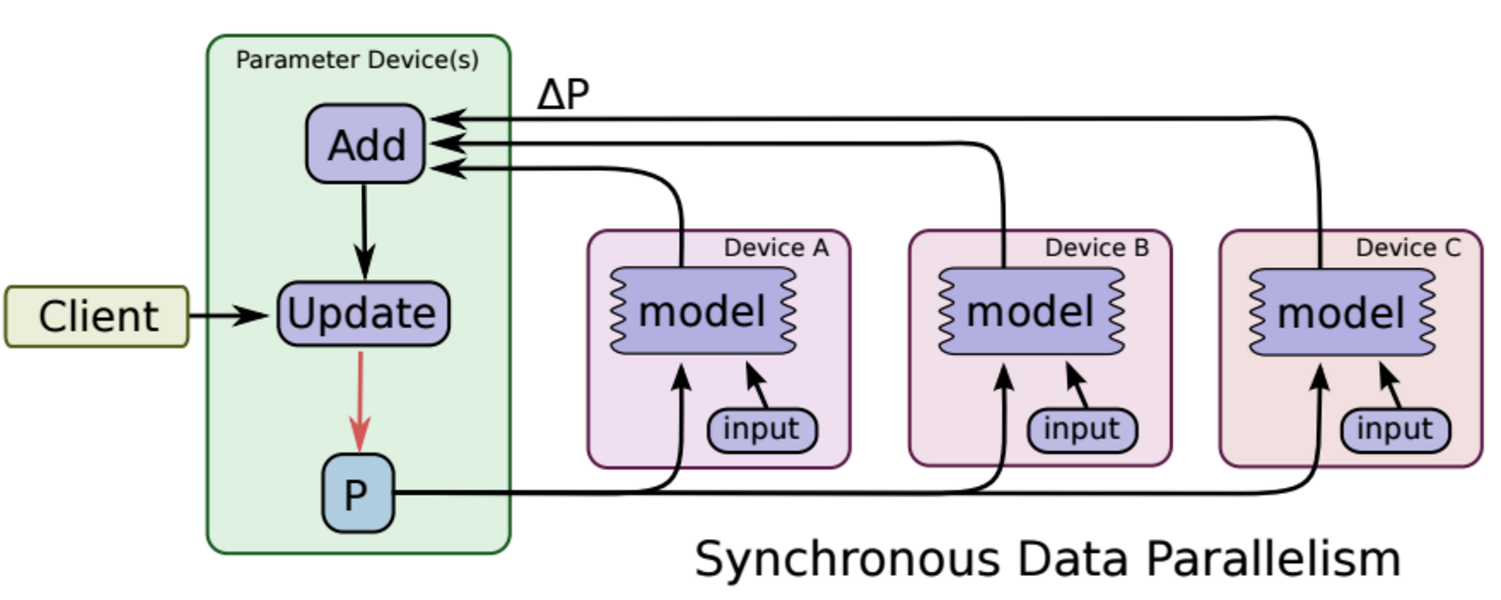
同步更新
各个用于并行计算的电脑,计算完各自的batch 后,求取梯度值,把梯度值统一送到ps服务机器中,由ps服务机器求取梯度平均值,更新ps服务器上的参数。
如下图所示,可以看成有四台电脑,第一台电脑用于存储参数、共享参数、共享计算,可以简单的理解成内存、计算共享专用的区域,也就是ps job;另外三台电脑用于并行计算的,也就是worker task。
这种计算方法存在的缺陷是:每一轮的梯度更新,都要等到A、B、C三台电脑都计算完毕后,才能更新参数,也就是迭代更新速度取决与A、B、C三台中,最慢的那一台电脑,所以采用同步更新的方法,建议A、B、C三台的计算能力都不想。
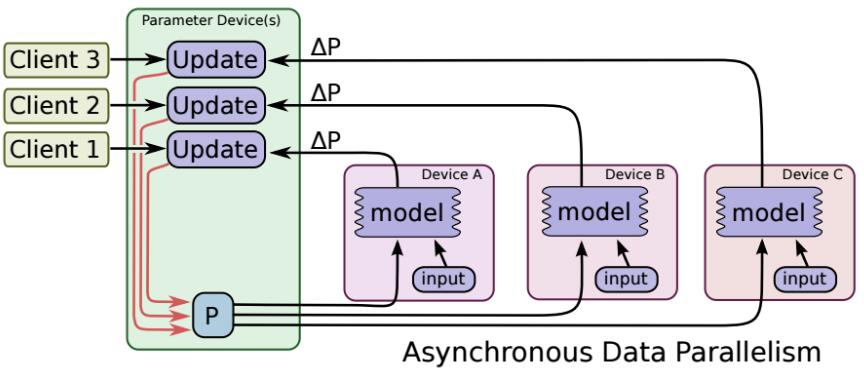
异步更新
ps服务器收到只要收到一台机器的梯度值,就直接进行参数更新,无需等待其它机器。这种迭代方法比较不稳定,收敛曲线震动比较厉害,因为当A机器计算完更新了ps中的参数,可能B机器还是在用上一次迭代的旧版参数值。
二、抽象接口
1、定义分布式集群对象
tf.train.ClusterSpec
# coding=utf-8
# 多台机器,每台机器有一个显卡、或者多个显卡,这种训练叫做分布式训练
import tensorflow as tf
# 现在假设我们有A、B、C、D四台机器,首先需要在各台机器上写一份代码,并跑起来,各机器上的代码内容大部分相同
# 除了开始定义的时候,需要各自指定该台机器的task之外。
# 以机器A为例子,A机器上的代码如下:
cluster=tf.train.ClusterSpec({
"worker": [
"A_IP:2222", # 格式 IP地址:端口号,第一台机器A的IP地址 ,在代码中需要用这台机器计算的时候,就要定义:/job:worker/task:0
"B_IP:1234" # 第二台机器的IP地址 /job:worker/task:1
"C_IP:2222" # 第三台机器的IP地址 /job:worker/task:2
],
"ps": [
"D_IP:2222", # 第四台机器的IP地址 对应到代码块:/job:ps/task:0
]})
然后我们需要写四分代码,这四分代码文件大部分相同,但是有几行代码是各不相同的(可以通过命令行参数使得字面相同各自选择if分支不同)。
2、在各台机器上,定义server
比如A机器上的代码server要定义如下:
server=tf.train.Server(cluster,job_name='worker',task_index=0) # 找到‘worker’名字下的,task0,也就是机器A
3、在代码中,指定device
device不仅可以指定卡,还可以将计算图中的不同节点指定不同机器
with tf.device('/job:ps/task:0'): # 参数定义在机器D上
w=tf.get_variable('w',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
b=tf.get_variable('b',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(5))
with tf.device('/job:worker/task:0/cpu:0'): # 在机器A cpu上运行
addwb=w+b
with tf.device('/job:worker/task:1/cpu:0'): # 在机器B cpu上运行
mutwb=w*b
with tf.device('/job:worker/task:2/cpu:0'): # 在机器C cpu上运行
divwb=w/b
不过在深度学习训练图计算中,对于每个worker task来说,计算任务都是相同的,所以我们会把所有图计算、变量定义等代码,都写到下面这个语句下:
with tf.device(tf.train.replica_device_setter(worker_device='/job:worker/task:indexi',cluster=cluster)):
函数replica_deviec_setter会自动把变量参数定义部分定义到ps服务中(如果ps有多个任务,那么自动分配)。
下面举个例子,假设现在有两台机器A、B,A用于计算服务,B用于参数服务,那么代码如下:
# 上面是因为worker计算内容各不相同,不过再深度学习中,一般每个worker的计算内容是一样的,
# 因为都是计算神经网络的每个batch的前向传导,所以一般代码是重用的
import tensorflow as tf
# 现在假设我们有A、B台机器,首先需要在各台机器上写一份代码,并跑起来,各机器上的代码内容大部分相同
# ,除了开始定义的时候,需要各自指定该台机器的task之外。以机器A为例子,A机器上的代码如下:
cluster=tf.train.ClusterSpec({
"worker": [
"192.168.11.105:1234", # 格式 IP地址:端口号,在代码中需要用这台机器计算的时候,就要定义:/job:worker/task:0
],
"ps": [
"192.168.11.130:2223" # 第四台机器的IP地址 对应到代码块:/job:ps/task:0
]}) # 不同的机器,下面这一行代码各不相同,server可以根据job_name、task_index两个参数,查找到集群cluster中对应的机器 isps=False
if isps:
server=tf.train.Server(cluster,job_name='ps',task_index=0) # 找到‘ps’名字下的,task0,也就是机器A
server.join()
else:
server=tf.train.Server(cluster,job_name='worker',task_index=0) # 找到‘worker’名字下的,task0,也就是机器B
with tf.device(tf.train.replica_device_setter(worker_device='/job:worker/task:0',cluster=cluster)):
w=tf.get_variable('w',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
b=tf.get_variable('b',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(5))
addwb=w+b
mutwb=w*b
divwb=w/b saver = tf.train.Saver()
summary_op = tf.merge_all_summaries()
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(init_op=init_op, summary_op=summary_op, saver=saver)
with sv.managed_session(server.target) as sess:
while 1:
print sess.run([addwb,mutwb,divwb])
把该代码在机器A上运行,程序会进入等候状态,等候用于ps参数服务的机器启动,才会运行。
因此接着我们需要在机器B上运行如下代码:
# 上面是因为worker计算内容各不相同,不过再深度学习中,一般每个worker的计算内容是一样的,
# 因为都是计算神经网络的每个batch前向传导,所以一般代码是重用的
#coding=utf-8
#多台机器,每台机器有一个显卡、或者多个显卡,这种训练叫做分布式训练
import tensorflow as tf
# 现在假设我们有A、B、C、D四台机器,首先需要在各台机器上写一份代码,并跑起来,各机器上的代码内容大部分相同
# ,除了开始定义的时候,需要各自指定该台机器的task之外。以机器A为例子,A机器上的代码如下:
cluster=tf.train.ClusterSpec({
"worker": [
"192.168.11.105:1234", # 格式 IP地址:端口号,在代码中需要用这台机器计算的时候,就要定义:/job:worker/task:0
],
"ps": [
"192.168.11.130:2223" # 第四台机器的IP地址 对应到代码块:/job:ps/task:0
]}) # 不同的机器,下面这一行代码各不相同,server可以根据job_name、task_index两个参数,查找到集群cluster中对应的机器 isps=True
if isps:
server=tf.train.Server(cluster,job_name='ps',task_index=0) # 找到‘ps’名字下的,task0,也就是机器A
server.join()
else:
server=tf.train.Server(cluster,job_name='worker',task_index=0) # 找到‘worker’名字下的,task0,也就是机器B
with tf.device(tf.train.replica_device_setter(worker_device='/job:worker/task:0',cluster=cluster)):
w=tf.get_variable('w',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
b=tf.get_variable('b',(2,2),tf.float32,initializer=tf.constant_initializer(5))
addwb=w+b
mutwb=w*b
divwb=w/b saver = tf.train.Saver()
summary_op = tf.merge_all_summaries()
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(init_op=init_op, summary_op=summary_op, saver=saver)
with sv.managed_session(server.target) as sess: while 1:
print sess.run([addwb,mutwb,divwb])
附录1:分布式训练需要熟悉的函数
tf.train.Servertf.train.Supervisortf.train.SessionManagertf.train.ClusterSpectf.train.replica_device_settertf.train.MonitoredTrainingSessiontf.train.MonitoredSessiontf.train.SingularMonitoredSessiontf.train.Scaffoldtf.train.SessionCreatortf.train.ChiefSessionCreatortf.train.WorkerSessionCreator
附录2:分布式训练例程
tensorflow/tools/dist_test/python/mnist_replica.py
# Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Distributed MNIST training and validation, with model replicas.
A simple softmax model with one hidden layer is defined. The parameters
(weights and biases) are located on one parameter server (ps), while the ops
are executed on two worker nodes by default. The TF sessions also run on the
worker node.
Multiple invocations of this script can be done in parallel, with different
values for --task_index. There should be exactly one invocation with
--task_index, which will create a master session that carries out variable
initialization. The other, non-master, sessions will wait for the master
session to finish the initialization before proceeding to the training stage.
The coordination between the multiple worker invocations occurs due to
the definition of the parameters on the same ps devices. The parameter updates
from one worker is visible to all other workers. As such, the workers can
perform forward computation and gradient calculation in parallel, which
should lead to increased training speed for the simple model.
""" from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function import math
import sys
import tempfile
import time import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string("data_dir", "/tmp/mnist-data",
"Directory for storing mnist data")
flags.DEFINE_boolean("download_only", False,
"Only perform downloading of data; Do not proceed to "
"session preparation, model definition or training")
flags.DEFINE_integer("task_index", None,
"Worker task index, should be >= 0. task_index=0 is "
"the master worker task the performs the variable "
"initialization ")
flags.DEFINE_integer("num_gpus", 1, "Total number of gpus for each machine."
"If you don't use GPU, please set it to '0'")
flags.DEFINE_integer("replicas_to_aggregate", None,
"Number of replicas to aggregate before parameter update "
"is applied (For sync_replicas mode only; default: "
"num_workers)")
flags.DEFINE_integer("hidden_units", 100,
"Number of units in the hidden layer of the NN")
flags.DEFINE_integer("train_steps", 200,
"Number of (global) training steps to perform")
flags.DEFINE_integer("batch_size", 100, "Training batch size")
flags.DEFINE_float("learning_rate", 0.01, "Learning rate")
flags.DEFINE_boolean(
"sync_replicas", False,
"Use the sync_replicas (synchronized replicas) mode, "
"wherein the parameter updates from workers are aggregated "
"before applied to avoid stale gradients")
flags.DEFINE_boolean(
"existing_servers", False, "Whether servers already exists. If True, "
"will use the worker hosts via their GRPC URLs (one client process "
"per worker host). Otherwise, will create an in-process TensorFlow "
"server.")
flags.DEFINE_string("ps_hosts", "localhost:2222",
"Comma-separated list of hostname:port pairs")
flags.DEFINE_string("worker_hosts", "localhost:2223,localhost:2224",
"Comma-separated list of hostname:port pairs")
flags.DEFINE_string("job_name", None, "job name: worker or ps") FLAGS = flags.FLAGS IMAGE_PIXELS = 28 def main(unused_argv):
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.data_dir, one_hot=True)
if FLAGS.download_only:
sys.exit(0) if FLAGS.job_name is None or FLAGS.job_name == "":
raise ValueError("Must specify an explicit `job_name`")
if FLAGS.task_index is None or FLAGS.task_index == "":
raise ValueError("Must specify an explicit `task_index`") print("job name = %s" % FLAGS.job_name)
print("task index = %d" % FLAGS.task_index) # 解析集群参数
# ps作业的ip端口,可以有多个ps作业,之间用逗号分割
ps_spec = FLAGS.ps_hosts.split(",")
# worker作业的ip端口,可以有多个worker作业,之间用逗号分割
worker_spec = FLAGS.worker_hosts.split(",") # Get the number of workers.
num_workers = len(worker_spec)
# 分布式集群对象,字典形式接收作业类型对应的任务主机&端口
cluster = tf.train.ClusterSpec({"ps": ps_spec, "worker": worker_spec}) if not FLAGS.existing_servers:
# Not using existing servers. Create an in-process server.
# 任务内部服务器(ps或者worker的上层抽象)的抽象对象,接收集群对象,接收当前任务信息
server = tf.train.Server(
cluster, job_name=FLAGS.job_name, task_index=FLAGS.task_index)
# 如果本次程序运行于ps任务,则启动监听(join持续等待,不会返回)
if FLAGS.job_name == "ps":
server.join() # 选择本任务所处GPU
if FLAGS.num_gpus > 0:
# Avoid gpu allocation conflict: now allocate task_num -> #gpu
# for each worker in the corresponding machine
gpu = (FLAGS.task_index % FLAGS.num_gpus)
worker_device = "/job:worker/task:%d/gpu:%d" % (FLAGS.task_index, gpu)
elif FLAGS.num_gpus == 0:
# Just allocate the CPU to worker server
cpu = 0
worker_device = "/job:worker/task:%d/cpu:%d" % (FLAGS.task_index, cpu) """ 构建网络 """
# The device setter will automatically place Variables ops on separate
# parameter servers (ps). The non-Variable ops will be placed on the workers.
# The ps use CPU and workers use corresponding GPU
# 设备设定器将自动将变量OPS放置在单独的参数服务器(PS)上。不可变的OPS将放在worker身上。
with tf.device(
# 设备放置器,可以返回被tf.device接受的设备名称
tf.train.replica_device_setter(
worker_device=worker_device,
ps_device="/job:ps/cpu:0",
cluster=cluster)):
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name="global_step", trainable=False) # Variables of the hidden layer
hid_w = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal(
[IMAGE_PIXELS * IMAGE_PIXELS, FLAGS.hidden_units],
stddev=1.0 / IMAGE_PIXELS),
name="hid_w")
hid_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([FLAGS.hidden_units]), name="hid_b") # Variables of the softmax layer
sm_w = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal(
[FLAGS.hidden_units, 10],
stddev=1.0 / math.sqrt(FLAGS.hidden_units)),
name="sm_w")
sm_b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name="sm_b") # Ops: located on the worker specified with FLAGS.task_index
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_PIXELS * IMAGE_PIXELS])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10]) hid_lin = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(x, hid_w, hid_b)
hid = tf.nn.relu(hid_lin) y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.xw_plus_b(hid, sm_w, sm_b))
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(tf.clip_by_value(y, 1e-10, 1.0))) opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(FLAGS.learning_rate) # 如果使用同步训练机制
if FLAGS.sync_replicas:
# 如果并行副本数(期望)没有指定
if FLAGS.replicas_to_aggregate is None:
# 勒令并行数等于worker数
replicas_to_aggregate = num_workers
else:
# 用户指定了就用指定的
replicas_to_aggregate = FLAGS.replicas_to_aggregate
# 同步优化器,接收本地优化器
opt = tf.train.SyncReplicasOptimizer(
opt,
replicas_to_aggregate=replicas_to_aggregate,
total_num_replicas=num_workers,
name="mnist_sync_replicas") # 优化器或者同步优化器单步优化节点(注意此句在if外)
train_step = opt.minimize(cross_entropy, global_step=global_step) # 如果是worker,则编号0的worker设置为chief worker
is_chief = (FLAGS.task_index == 0) # 同步训练机制下的初始化操作
if FLAGS.sync_replicas:
# local_step初始化(chief_worker会改写此句,所以实际上本句针对非chief_worker)
local_init_op = opt.local_step_init_op
if is_chief:
# chief_worker使用的时global_step,也需要初始化
local_init_op = opt.chief_init_op
# 为未初始化的Variable初始化
ready_for_local_init_op = opt.ready_for_local_init_op # Initial token and chief queue runners required by the sync_replicas mode
# 同步标记队列实例
chief_queue_runner = opt.get_chief_queue_runner()
# 同步标记队列初始值设定
sync_init_op = opt.get_init_tokens_op() # 全局变量初始化
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
train_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp() if FLAGS.sync_replicas:
# 管理同步训练相关操作
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(
is_chief=is_chief,
logdir=train_dir,
init_op=init_op,
local_init_op=local_init_op,
ready_for_local_init_op=ready_for_local_init_op,
recovery_wait_secs=1,
global_step=global_step)
else:
# 管理异步训练相关操作
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(
is_chief=is_chief,
logdir=train_dir,
init_op=init_op,
recovery_wait_secs=1,
global_step=global_step)
# 配置分布式会话
# 没有可用GPU时使用CPU
# 不打印设备放置信息
# 过滤未绑定在ps或者worker的操作
sess_config = tf.ConfigProto(
allow_soft_placement=True,
log_device_placement=False,
device_filters=["/job:ps",
"/job:worker/task:%d" % FLAGS.task_index]) # chief会初始化所有worker的会话,否则等待chief返回会话
# The chief worker (task_index==0) session will prepare the session,
# while the remaining workers will wait for the preparation to complete.
if is_chief:
print("Worker %d: Initializing session..." % FLAGS.task_index)
else:
print("Worker %d: Waiting for session to be initialized..." %
FLAGS.task_index) if FLAGS.existing_servers:
server_grpc_url = "grpc://" + worker_spec[FLAGS.task_index]
print("Using existing server at: %s" % server_grpc_url) sess = sv.prepare_or_wait_for_session(server_grpc_url, config=sess_config)
else:
sess = sv.prepare_or_wait_for_session(server.target, config=sess_config) print("Worker %d: Session initialization complete." % FLAGS.task_index) # 同步更新模式的chief worker
if FLAGS.sync_replicas and is_chief:
# Chief worker will start the chief queue runner and call the init op.
# 初始化同步标记队列
sess.run(sync_init_op)
# 启动相关线程,运行各自服务
sv.start_queue_runners(sess, [chief_queue_runner]) # Perform training
time_begin = time.time()
print("Training begins @ %f" % time_begin) local_step = 0
while True:
# Training feed
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(FLAGS.batch_size)
train_feed = {x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys} _, step = sess.run([train_step, global_step], feed_dict=train_feed)
local_step += 1 now = time.time()
print("%f: Worker %d: training step %d done (global step: %d)" %
(now, FLAGS.task_index, local_step, step)) if step >= FLAGS.train_steps:
break time_end = time.time()
print("Training ends @ %f" % time_end)
training_time = time_end - time_begin
print("Training elapsed time: %f s" % training_time) # Validation feed
val_feed = {x: mnist.validation.images, y_: mnist.validation.labels}
val_xent = sess.run(cross_entropy, feed_dict=val_feed)
print("After %d training step(s), validation cross entropy = %g" %
(FLAGS.train_steps, val_xent)) if __name__ == "__main__":
tf.app.run()
『TensorFlow』分布式训练_其三_多机分布式的更多相关文章
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其一:论文及开源项目文档介绍
一.论文介绍 读论文系列:Object Detection ECCV2016 SSD 一句话概括:SSD就是关于类别的多尺度RPN网络 基本思路: 基础网络后接多层feature map 多层feat ...
- 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_训练网络其三:训练Model
Github地址:Mask_RCNN 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_论文学习 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_项目文档翻译 『计算机视觉』Mask-RCNN_推断网络其一:总览 『计算机视觉』M ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其五:TFR数据读取&数据预处理
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 一.TFR数据读取 创建slim.dataset.Dataset对象 在train_ssd_network.py获取数据操作如下,首先需要slim.dataset.Dat ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其八:网络训练
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 作者使用了分布式训练的写法,这使得训练部分代码异常臃肿,我给出了部分注释.我对于多机分布式并不很熟,而且不是重点,所以不过多介绍,简单的给出一点训练中作者的优化手段,包含 ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其三:锚框生成
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 上一节中我们定义了vgg_300的网络结构,实际使用中还需要匹配SSD另一关键组件:被选取特征层的搜索网格.在项目中,vgg_300网络和网格生成都被统一进一个class ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其四:数据介绍及TFR文件生成
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 一.数据格式介绍 数据文件夹命名为VOC2012,内部有5个子文件夹,如下, 我们的检测任务中使用JPEGImages文件夹和Annotations文件夹. JPEGIm ...
- 『TensorFlow』网络操作API_中_损失函数及分类器
一.误差值 度量两个张量或者一个张量和零之间的损失误差,这个可用于在一个回归任务或者用于正则的目的(权重衰减). l2_loss tf.nn.l2_loss(t, name=None) 解释:这个函数 ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其二:基于VGG的SSD网络前向架构
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 参考自集智专栏 一.SSD基础 在分类器基础之上想要识别物体,实质就是 用分类器扫描整张图像,定位特征位置 .这里的关键就是用什么算法扫描,比如可以将图片分成若干网格,用 ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其七:损失函数
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 一.损失函数介绍 SSD损失函数分为两个部分:对应搜索框的位置loss(loc)和类别置信度loss(conf).(搜索框指网络生成的网格) 详细的说明如下: i指代搜索 ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其六:标签整理
Fork版本项目地址:SSD 一.输入标签生成 在数据预处理之后,图片.类别.真实框格式较为原始,不能够直接作为损失函数的输入标签(ssd向前网络只需要图像就行,这里的处理主要需要满足loss的计算) ...
随机推荐
- 网络_TCP连接的建立与释放
三报文握手 1.概述 TCP是面向连接的协议.TCP建立连接的过程叫做握手,握手需要在客户和服务器之间交换三个TCP报文段,即我们说的"三次握手"(严格讲是一次握手过程中交换了三个 ...
- 中文目录对 sublime text 有什么影响?
用了这软件好几个月了,一直没出现问题.最近做精简时,发现一个奇怪的问题. 相同的配置,为什么两个程序表现得不一样? 难道是哪里的配置不一样? 难道是插件被我精简得太厉害了? 难道是插件有依赖文件被我删 ...
- Lintcode455-StudentID-Easy
Implement a class Class with the following attributes and methods: A public attribute students which ...
- Codeforces 776E The Holmes Children
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/776/E ${\because gcd(i,n-i)=1\Leftrightarrow gcd(i,n)= ...
- 算法时间复杂度的表示法O(n²)、O(n)、O(1)、O(nlogn)等是什么意思?
Java中 Set 和 List 集合 的contains()方法,检查数组链表中是否包含某元素检查数组链表中是否包含某元素,使用 Set 而不使用 List 的原因是效率问题, 前者的 set ...
- vs 2013 编译cocos2d-x-3.9
下载地址:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1IkQsMU6NoERAAQLcCUMcXQ 提取码: p1pb 下载完成后,解压 进入build 目录 使用vs 2013 打开工 ...
- VC.文件时间
1. #include <stdio.h> #include <windows.h> void GetFileTimeZ(char *_pcFullFileName, FILE ...
- Android打开相机进行人脸识别,使用虹软人脸识别引擎
上一张效果图,渣画质,能看就好 功能说明: 人脸识别使用的是虹软的FreeSDK,包含人脸追踪,人脸检测,人脸识别,年龄.性别检测功能,其中本demo只使用了FT和FR(人脸追踪和人脸识别),封装了开 ...
- 学习笔记5—Python 将多维数据转为一维数组 (总结)
<code class="language-python">import operator from functools import reduce a = [[1,2 ...
- 用友软件系统管理员账号admin密码忘记了,如何解决?
1.打开数据库. 2.点开 数据库-UFSystem. 3.找到dbo.UA_user表,鼠标右键,点打开表. 4.打开后,找到admin,cPassword列即可找到系统管理员密码.