[集合]Collection集合框架源码分析
Collection接口
在java的集合类库中,基本接口是Collection,该接口的在集合中的源码定义如下(将源码中的注释删掉了):
public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {
// Query Operations
// 查询操作相关方法
// 返回集合的元素个数
int size();
// 如果这个集合没有包含任何元素了就返回true,即判断集合是否为空
boolean isEmpty();
// 如果这个集合至少包含一个指定的元素就返回true,
//如果指定的元素和集合中的元素不兼容,会抛出 ClassCastException
// 如果指定的元素为空并且该集合不允许元素为空时,会抛出 NullPointerException
boolean contains(Object o);
// 返回集合中元素的迭代器,它不保证元素的有序性 (除非该集合本身的实现可以保证元素的顺序)
Iterator<E> iterator();
// 返回一个包含集合中所有元素的数组,元素的顺序性和 iterator 一样,由集合实现类本身决定
// 这个方法返回的数组时安全的,因为集合不用保留对返回数组的引用,我们可以任意修改而不影响集合本身
Object[] toArray();
// 返回包含该集合中所有元素的数组,数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型,
// 如果指定的数组适合集合的大小,直接返回其中,否则重新创建数组
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
// Modification Operations
// 往集合中添加一个元素,如果集合允许更改就返回true,如果集合不允许元素重复并且已经包含了此元素,则返回false
boolean add(E e);
// 从集合中删除指定元素的单个实例 如果集合允许改变就返回true
boolean remove(Object o);
// Bulk Operations
// 批量操作相关
// 如果该集合包含指定集合的所有元素 则返回true
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
// 添加指定集合的所有元素到该集合中
// 如果在添加操作的过程中修改了指定的集合 ,则此操作的行为是不确定的,不安全
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
// 在该集合中删除指定集合的所有元素,反方法成功返回后,该集合中将不再包含任何指定集合中的元素
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
// 删除满足给定条件的所有元素,如果在迭代期间发生运行时异常,那么将返回给调用者
// 注意:这是JDK1.8 的新特性,在接口中也有方法实现,实现类调用时的默认实现逻辑
default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
boolean removed = false;
final Iterator<E> each = iterator();
while (each.hasNext()) {
if (filter.test(each.next())) {
each.remove();
removed = true;
}
}
return removed;
}
// 从集合中删除不包含在指定集合中的所有元素
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
// 清空集合中的所有元素,该方法返回后,集合将为空
void clear();
// Comparison and hashing
// 比较和散列
// 将指定的对象与集合进行比较
boolean equals(Object o);
// 返回在这个集合的hashCode值
int hashCode();
// 在此集合中的元素上创建Spliterator/
// jdk 1.8 的新特性
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);
}
// 返回以此集合为源的顺序Stream。/
// jdk 1.8 的新特性
default Stream<E> stream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);
}
// 以此集合作为源返回可能并行的Stream。 此方法允许返回顺序流。/
// jdk1.8 新特性
default Stream<E> parallelStream() {
return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);
}
}
上面的源码中第17行的 iterator () 返回了一个迭代器对象 Iterator,可以使用这个迭代器一次访问集合中的元素。 Iterator 是一个接口,看看它在源码中的定义:
public interface Iterator<E> {
// 如果这个迭代器对象还有元素的话就返回true
boolean hasNext();
// 返回这个迭代器中的下一个元素
E next();
// 从底层集合中移除此迭代器返回的最后一个元素。 每次调用next时,只能调用一次此方法。
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
// 对集合中剩余的每个元素执行给定的操作,知道处理完所有元素或者引发异常
// jdk 1.8 新特性
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
}
看完了这个迭代器,我们应该对集合元素的遍历方法有所思考,我们可以反复的调用hasNext,next 方法逐个的访问集合元素,我们还可以使用“for each” 带迭代器的循环访问任何实现了Iterable接口的对象,Iterable接口中定义的方法 都是为了迭代元素而存在的
public interface Iterable<T> {
Iterator<T> iterator();
// 1.8 新特性
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (T t : this) {
action.accept(t);
}
}
// 1.8 新特性
default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);
}
}
而Collection接口扩展了 Iterable 接口,因此凡是 Collection 接口的实现,我们都可以使用“for each” 循环来遍历所有的元素。在JDK 1.8 中,我们甚至可以调用 forEachRemaining 方法并提供一个Lambda 表达式定义处理剩余元素的逻辑,知道结束。这3中迭代集合元素的方法我们会根据实际需求来选择。还有一个很重的问题就是元素被访问的顺序,它取决于集合的实现类型,后面我们将会对每一种实现类型详细分析。另外当我们使用迭代器来删除集合中的元素时,必须使用next方法先返回要删除的元素,然remove该元素,也就是这两个方法必须一前一后,否则将会抛出 IllegalStateException 异常。
Collection接口中声明了很多对于集合来说很有用的方法,那么每一个Collection接口的实现类都应该具有这些通用的功能,但是每一种实现类都要重复这些逻辑,岂不烦人?于是在Collection接口的具体实现类之上提供了一个Collection的抽象实现 AbstractCollection,在该抽象类中,它将size,iterator 方法抽象化了,由具体集合实现类去完成。但是实现了集合的相关通用方法,当然,如果子类有更高效的实现的话,是可以覆盖的。
在AbstractCollection抽象类中实现的通用方法主要有:
- public boolean contains(Object o)
public boolean contains(Object o) {
// 得到一个迭代器对象,用于遍历集合的元素
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
// 如果需要判断的对象是 null 值
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null) // 集合包含null 返回true
return true;
} else { // 判断的对象不为null
while (it.hasNext()) // 循环遍历结合查找匹配
if (o.equals(it.next())) // 使用传入对象的equals方法判断
return true;
}
return false; // 没有找到,,返回false
}
- public Object[] toArray()
public Object[] toArray() {
// Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements
// 创建一个和集合元素个数相同的对象数组,用于存储元素数据
Object[] r = new Object[size()];
// 返回迭代器
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
// 循环将集合元素放入对象数组中
for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {
if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expected 元素少于预期的个数
return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); // 将包含所有的元素的对象数组返回
r[i] = it.next();
}
// 当迭代器返回的元素多于预期时,重新分配在toArray中使用的数组,并完成从迭代器填充它。否则返回该数组
return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r;
}
- public boolean remove(Object o)
// 调用 Iterator 迭代器的方法执行删除操作
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 得到一个迭代器对象,用于遍历集合的元素
Iterator<E> it = iterator();
//如果要删除的元素是 null
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext()) {
if (it.next()==null) {
it.remove();
return true;
}
}
} else {
while (it.hasNext()) { // 使用传入对象的equals方法判断,找到并删除
if (o.equals(it.next())) {
it.remove();
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
以上就是 AbstractCollection主要实现的通用方法,其他的一些方法都是调用这些基本方法实现,或者是等具体的实现类实现的,点击查看更多方法。另外在该抽象类中还定义了如果使用数组实现的数组大小上限:
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
实现了Collection的接口
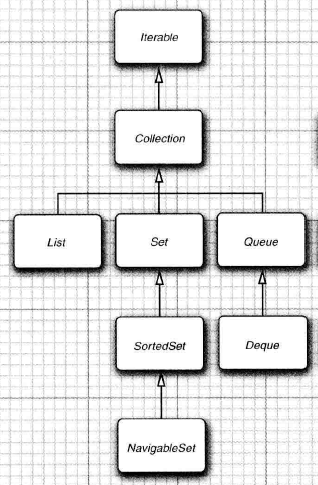
其中List是一个有序集合。元素会增加到容器中的特定位置。可以采用两种方式访问元素,使用迭代器访问,或者使用一个随机索引来访问,后一种方法为随机访问,这样可以按照任意顺序访问元素,而迭代器则必须顺序的访问元素。下面列出List与之父接口Collection不同的一些方法源码:
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
// 将该列表的每个元素替换为 将运算符应用于该元素的结果
// jdk 1.8 特性
default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();
while (li.hasNext()) {
li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
}
}
// 根据传入的规则将列表排序
// jdkk 1.8 特性
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Object[] a = this.toArray();
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();
for (Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
}
// 返回true的条件是 两个list的元素个数和顺序都相等
boolean equals(Object o);
/**
* 计算法则:
* int hashCode = 1;
* for (E e : list)
* hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
*/
int hashCode();
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
// 返回此列表中元素的列表迭代器
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
// 返回指定索引的视图,也就是该列表的子列表,子列表和源列表的操作是可见的
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
}
List与Collection不同的方法定义
Set接口等同于Collection(虽然也是继承自Collection接口),其方法的定义都与Collection差不多,但是Set接口方法的行为有更加严谨的要求,Set接口的add方法中不允许有重复的元素。Set方法中equals方法的定义:只要两个Set中含有相同的元素就为true,而不考虑元素的顺序。hashCode方法的定义:保证两个包含相同元素的 Set返回同样的散列码。因为Set中hashCode的计算是所有元素的hashCode之和。在此就不列出Set接口的代码了,具体我们在看具体实现的时候再说。
SortedSet接口:队列与双端队列的定义,我们可以在方便的在尾部添加元素,头部删除元素, 这样有两个端头的队列,叫做双端队列,但是不能在队列的中间位置插入一个元素。在javase中队列的实现有ArrayDQueue和LinkedList。将在后面介绍。
public interface SortedSet<E> extends Set<E> {
Comparator<? super E> comparator();
SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement);
SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement);
SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement);
E first();
E last();
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator<E>(
this, Spliterator.DISTINCT | Spliterator.SORTED | Spliterator.ORDERED) {
@Override
public Comparator<? super E> getComparator() {
return SortedSet.this.comparator();
}
};
}
}
Queue与Deque接口:
Collection的具体实现
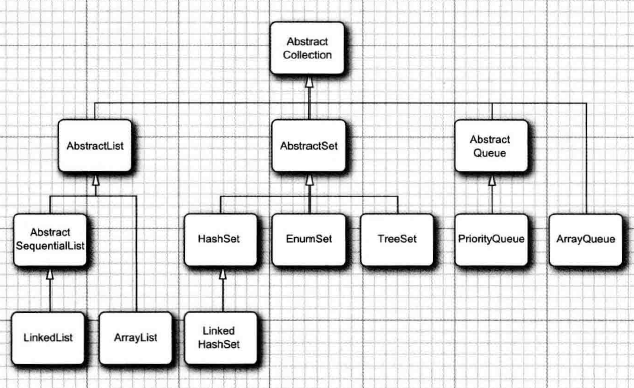
ArrayList:底层基于数组实现,添加元素时判断数组容量,可以动态扩容,相应的功能实现看代码
定义:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { .... }
构造函数及其相关属性:
// 底层基于数组实现,定义用于存放元素的 对象数组
transient Object[] elementData; // 默认的容量大小
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 创建指定大小的ArrayList时(指定为0)用于初始化一个指定容量的空的对象数组
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 创建ArrayList时不指定初始化容量 创建的默认 为空的对象数组
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 创建指定大小的ArrayList
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) { // 指定容量等于0 时,创建空的对象数组
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else { // 参数不合法
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
} // 创建默认的对象数组
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} // 根据传入的集合对象创建ArrayList
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); // 复制数据到对象数组中
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 传入集合为空时
}
}
添加一个元素及其扩容策略:
public boolean add(E e) {
// 1. 保证容量的合理范围
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 2. 如果当前对象数组的大小小于 默认容量10 ,那么将容量增加到10
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
// 根据当前容量判断是否需要扩容
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
// 如果 当前容量小于对象数组的长度,扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity); // 扩容方法
}
// 计算当前容量是否小于最小要求10
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
// 扩容策略
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 当前对象数组的长度
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 新的容量等于 当前数组的长度 + 当前数组长度 / 2 ;也就是1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) // 扩容容量是否满足最低要求
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) // 新容量超过允许的数组最大值
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 再加大数组的允许范围
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? // Integer 的最大值
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
删除一个元素
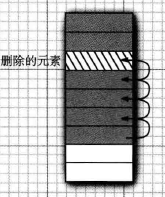
public E remove(int index) {
// 下标的范围检查
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index); // 即将删除的元素的值,临时保存,为返回用
int numMoved = size - index - 1; // 删除该元素,其他元素移动的次数
if (numMoved > 0) // 移动次数大于0 ,合法
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, // 通过拷贝的方式删除一个元素
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue; // 返回删除的元素
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
用于元素操作的内部类
// 这三个内部类通过定义就可以看到,它们都是继承了相应的接口
// 针对基于数组实现的ArrayList 方便相应的操作,在这就不一一解释了,都是见名知意的,
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { } private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { } private class SubList extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess { }
LinkedList:底层基于链表实现。
定义:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { ... }
构造函数及其相关属性:LinkedList基于链表实现,在其内部定义了一个Node类用户存放数据和维持节点之间的关系。
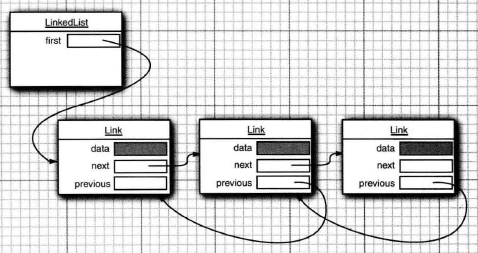
// 记录元素的个数
transient int size = 0; // 链表的第一个节点
transient Node<E> first; // 最后一个节点
transient Node<E> last; // 构造哦一个空的链表
public LinkedList() { } // 根据传入的集合类构建一个链表
// 具体的addAll 在添加元素的时候分析
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
} // 构造链表的几点,是LinkedList的静态内部类
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 真实数据
Node<E> next; // 下一个节点
Node<E> prev; // 前一个节点 // 节点的构造函数
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
添加一个元素:包括在头,尾,中间任意节点插入元素
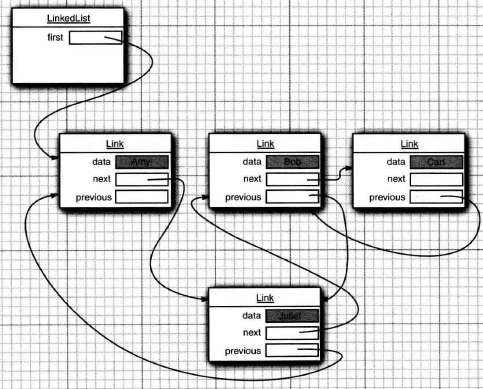
// 在链表的头结点添加一个元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
} private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); // 根据传入的数据新创建一个节点,将头节点作为下一节点
first = newNode; //更新头结点为新创建的节点
if (f == null) // 如果头结点为空,也就是空链表的时候
last = newNode; // 头等于尾
else
f.prev = newNode; // 原来的头结点的上一节点为新创建的节点
size++;
modCount++;
} // 在链表的末尾添加一个元素
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
} void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); // 根据传入的数据新创建一个节点,将原始尾节点作为前一节点
last = newNode; // 更新尾节点
if (l == null) // 为空链表时
first = newNode; // 头等于尾
else
l.next = newNode; // 原始尾节点的下一个等于新创建的节点
size++;
modCount++;
} // 在任意位置插入元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index); // 索引的范围检查 if (index == size) // 如果 索引是最后个 直接加入
linkLast(element);
else // 否则
linkBefore(element, node(index)); // 在给定索引的元素前面插入该元素
} void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; // 给定索引的前一节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); // 创建一个以给定索引的前一节点,以及给定索引为下一节点的新节点
succ.prev = newNode; // 给定索引的节点为新建节点
if (pred == null) // 给定索引的前一节点为空的情况
first = newNode;
else // 否则 给定索引的前一节点的下一节点为新建的节点
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
删除一个元素:包括在头,尾,中间任意节点插入元素
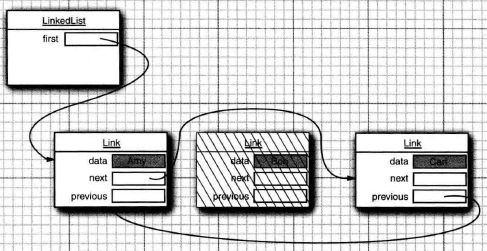
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null) // 没有元素时 ,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null) // 没有元素时 ,抛出异常
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item; // 保存即将删除元素的数据 返回用
final Node<E> next = f.next; // 即将删除元素的下一个
f.item = null; // 删除元素
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next; // 更新头加点
if (next == null) // 为空时
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
根据索引查找元素:此方法LinkedList做了优化,看代码
// 获取指定索引的元素
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
} // 优化
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 查找的索引小于 总个数的 1/2
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) // 遍历到索引的位置
x = x.next;
return x;
} else { // 查找的索引大于 总个数的 1/2
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) // 从尾到头遍历查找元素
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
在LinkedList的实现中我们可以看到,它利用元素的插入和删除,但是对于索引访问元素的操作,需要从头开始遍历,虽然做了微小的优化,但是还是不如数组实现的访问速度。
Vector:当我们在需要使用动态数组时,还有一个Vector可以满足我们的要求,它也是基于数组实现的有序集合,但是它与ArrayList的最大区别是Vector的所有方法都实现了同步,可以由两个线程安全的访问Vector对象,但是由一个线程访问Vector时,代码要在同步操作上耗费大量的时间。因为此性能较低,我们也不常用,在此不做讨论。
HashSet: 基于散列表的Set,Set中没有重复的元素,元素是否重复是基于散列码比较的,将元素散列在表的各个位置上,所以访问元素的顺序是随机的。适合不关心集合中元素的顺序时使用。
散列表:在java中使用的是链表数组实现的,每个列表叫做bucket,元素根据对象的散列码与bucket总数取余,决定元素的存储位置。如果bucket容量满时,将会出现hash冲突,性能下降,因此对于bucket总数的设置有学问,一般设置为预计插入元素个数的75%~150%,最好设置为素数,以防hash聚集。当我们设置的bucket总数小于预计插入元素时,此时会发生在散列,再散列就是创建一个数量更大的新的bucket,并将原bucket的数据复制过来,再弃用原bucket。何时进行在散列的判断,称为负载因子。java实现中默认为0.75.散列码(hashCode)是根据对象的内存地址转换而来的整数.
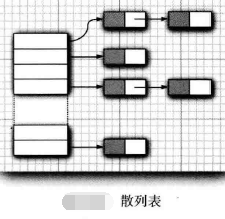
定义:
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { ...
}
构造方法与属性定义:
// 底层基于HashMap实现
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map; private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
} // 根据传入的集合类,创建HashMap,如果元素的个数少于默认值,那么创建时指定为默认值,
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
} // 创建时指定容量和负载因子
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
} // 指定容量
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
} // 为包调用的构造函数,仅为实现类LinkedHashSet使用
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
HashSet中对元素的操作都是基于HashMap实现的,因此具体实现将在HashMap中详细介绍。
TreeSet:与HashSet类似,但是它是有序的Set,可以以任意顺序将数据插入到集合中,当我们遍历这个集合时,元素总是以排好的顺序输出。如名所示,TreeSet的排序使用树完成的(当前使用的是红黑树),根据特性可知,插入元素到TreeSet中比HashSet要慢,但是比数组实现的ArrayList和基于链表的LinkedList要快,TreeSet中元素比较是使用Comparable接口的comparator方法。实际应用中会根据实际需求是否需要对元素排序而在HashSet和TreeSet中选择。
定义:
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { ...
}
在TreeSet的定义中可以看到,它使用了 NavigableSet 接口,在这个接口中增加了几个便于定位元素和反向变遍历的方法。
构造函数与相关属性:通过构造方法不难看出,TreeSet的实现都是调用TreeMap实现的,同样,在后面再详细介绍。
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}
ArrayDeque:基于数组实现的双端队列
定义:
public class ArrayDeque<E> extends AbstractCollection<E>
implements Deque<E>, Cloneable, Serializable { ...
}
构造函数与属性
// 用于存放元素的 对象数组
transient Object[] elements; // 队头的下标
transient int head; // 队尾的下标
transient int tail; // 队列默认的容量
private static final int MIN_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 8; public ArrayDeque() {
elements = new Object[16];
} public ArrayDeque(int numElements) {
allocateElements(numElements);
} public ArrayDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
allocateElements(c.size());
addAll(c);
}
PriorityQueue:优先级队列。利用基于数组实现的堆的数据结构,元素的顺序和插入的顺序无关,而是和本身的优先级相关。与TreeSet类似,元素优先级的判断是根据实现了Comparable接口的comparator()方法判断的。对于元素的插入,利用二叉树的自调整 ,总是将自小的元素移动到根。而在元素删除的时候,总是删除数组最后的元素,也是数组优先级最大的元素。
Map接口
Map用来存放 key/value 对,可以可以根据提供的key,找到相应的value。其接口的定义如下 ():
public interface Map<K,V> {
// 元素个数
int size();
// 是否为空
boolean isEmpty();
// 是否包含指定的key
boolean containsKey(Object key);
// 是否包含指定的value
boolean containsValue(Object value);
// 根据key 返回value
V get(Object key);
// 加入一个键值对
V put(K key, V value);
// 根据key,删除value
V remove(Object key);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
// 清空map中的所有元素
void clear();
// 将map中的所有值包含在一个Set中返回,在此处该该Set的定义是视图,但是由Map支持,因此在Map中的修改和Set中的修改将是同步的,
Set<K> keySet();
// 同样的,返回map中所有的值,但是此时是放在集合对象中,同样修改也是相互影响的。多说一句,为什么键和值的返回类型不一样?
// 这个和Map的实现有关,在map中,键的存放和Set一样,也是基于hashCode的,而值的存储可以放在Collection中,可以基于数组实现。
Collection<V> values();
// 将Map中的元素包装为视图在Set中返回,其泛型是Entry,是Map的内部接口,其中定义了对Map的键值的相关操作方法,接口定义如下
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
// 操作Map中键值的接口定义
interface Entry<K,V> {
// 获取键
K getKey();
// 获取值
V getValue();
// 更新值操作
V setValue(V value);
// 判断对象相等
boolean equals(Object o);
// 散列码
int hashCode();
// 一下方法为jdk8 中的新特性
public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
}
public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());
}
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());
}
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());
}
}
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
// 一下为JDK8 中的新特性
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
}
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
}
default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Objects.requireNonNull(function);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
// ise thrown from function is not a cme.
v = function.apply(k, v);
try {
entry.setValue(v);
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
}
}
default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
V v = get(key);
if (v == null) {
v = put(key, value);
}
return v;
}
default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
remove(key);
return true;
}
default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
put(key, newValue);
return true;
}
default V replace(K key, V value) {
V curValue;
if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) {
curValue = put(key, value);
}
return curValue;
}
default V computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);
V v;
if ((v = get(key)) == null) {
V newValue;
if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) {
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
}
}
return v;
}
default V computeIfPresent(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue;
if ((oldValue = get(key)) != null) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (newValue != null) {
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
} else {
remove(key);
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
}
default V compute(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue = get(key);
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (newValue == null) {
// delete mapping
if (oldValue != null || containsKey(key)) {
// something to remove
remove(key);
return null;
} else {
// nothing to do. Leave things as they were.
return null;
}
} else {
// add or replace old mapping
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
}
}
default V merge(K key, V value,
BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
Objects.requireNonNull(value);
V oldValue = get(key);
V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value :
remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);
if(newValue == null) {
remove(key);
} else {
put(key, newValue);
}
return newValue;
}
}
Map具体的实现类:
HashMap: 采用数组+链表+红黑树实现,当链表的长度超过8 时,转而使用红黑树。
定义:
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { ...
}
构造函数及其属性:
// 允许的最大容量
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; // 默认的容量大小
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 // 将链表转为红黑树的阈值,当链表的个数大于8 时,转为红黑树
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; // 红黑树转为链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; // 红黑树的默认容量大小
static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; // 负载因子,真实的元素个数占总容量的比例,超过后就会扩容
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 传入容量大小和负载因子创建hashMap
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)// 容量小于0
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) // 超出最大容量 那么容量就是 2^30
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) // 负载因子的合法性
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
} public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
} public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
} public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
putMapEntries(m, false);
}
数据的封装:当我们将一个键值对放入hashmap的时候,键值对实际上被封装为一个Node,该Node实现了Map接口中的Entry,源码如下:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; // 这个node对象的hash值
final K key; // 键
V value; // 值
Node<K,V> next; // 链表中的下一个
// 构造函数
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
// hashCode的计算方法 ^异或运算:两个数转为二进制,然后从高位开始比较,如果相同则为0,不相同则为1。
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); // 键 ^值
}
// 更新Node对象的值
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
// 判断存入的对象是否相等的方法 ,地址相同或者键值都相同返回true
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) // 比较地址
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) { // 比较键和值的equals方法
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
数据的存放对象:
// 存放数据的是Node类型的数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table; // hash表的负载因子
final float loadFactor; // 实际存放元素的个数,以此判断是否需要扩容 (threshold = capacity * loadFactor)
int threshold; // 修改次数
transient int modCount; // 键值对的数量
transient int size; // 保持缓存?
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
放入一个键值对的操作:第一插入元素时对数组扩容,分配空间
// 放入一个键值映射,
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true); // 如果键对应的值已经存在了,那么就替换旧值
} /**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key 键的hash值 ,计算方法在Node中定义,看上面的Node源码
* @param key the key 键
* @param value the value to put 值
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value 是否不改变已经存在的值
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. 表的模式? false处于创建模式
* @return previous value, or null if none 返回该key对应的以前的值,如果没有,那么返回 null
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; // tab为存放数据的数组, p 为根据 key 计算得到的数组下标对应的node,n为数组当前的长度,
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) // 如果存放对象的 数组为空,或者长度为0
n = (tab = resize()).length; // 对数组进行第一次扩容, 这里说明hashmap 数组的初始化是在第一次放入元素时,而不是在创建的时候
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) // 数组的长度 n - 1 和 键的hash值 与运算得到数组下标,如果该值为空,直接放入,位与运算 & :两个数都转为二进制,然后从高位开始比较,如果两个数都为1则为1,否则为0。
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else { // 如果不为空,那么放入链表?
Node<K,V> e; K k;
if (p.hash == hash && // 放入的元素和已有的元素 key hash相等且 equals返回true
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p; // key相等时,e = 当前下标对应的元素。
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) // 如果是红黑树的节点,按照红黑树的方法插入
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else { // hash冲突的解决办法
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) { // e = 下标对应的元素的下一节点为null
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); // 那么下一个就是等于新创建的节点 加入链表
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st // 当链表的长度大于等于 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8,转而使用红黑树,注意有一个 -1的操作,也就是7的时候就转了。
treeifyBin(tab, hash); // 红黑树的操作
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash && // 创建的 key与 传入的key 相同
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e; // 插入链表
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) // 根据参数判断是否替换
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e); // 不替换,加入链表后面
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) // 判断是否需要扩容,
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
取出一个元素的操作:
// 根据key取出元素
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
} final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 && // 检查数组有效性
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node // 第一个就相等
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode) // 是否为红黑树
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do { // 循环链表查找key对应的节点
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
扩容机制:
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; // 原来的数组
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length; // 原数组的容量
int oldThr = threshold; // 原来的扩容限制值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) { // 如果原来的容量大于0
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { // 如果原来的容量大于等于最大容量限制 2^30
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 那么扩容限制设置为 最大值
return oldTab; // 返回原来的数组
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) // 否则如果新容量为原来的两倍并且小于最大容量
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold // 新的扩容限制也设为原来的两倍
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold // 如果原来的扩容限制大于0
newCap = oldThr; // 那么新的容量等于 原来的扩容限制
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; // 否则新的容量设置为默认 16
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); // 新的扩容限制 newThr 等于 = 默认的加载因子 0.75f * 默认的容量 16
}
if (newThr == 0) { // 如果新扩容限制 = 0
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; // 计算得到
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr; // 设置新的扩容限制
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; // 根据新的容量创建数组
table = newTab;
// 如果原来的数组不为空,那么需要将原来数组的数据复制到新数组
if (oldTab != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null; // 置空,便于垃圾回收
if (e.next == null) // 如果为链表是,判断当前下标如果不再有元素
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; // 放入的位置是该元素的hash 和 新的容量 - 1 与运算 的得到的下标
else if (e instanceof TreeNode) // 如果为红黑树的时候 ,
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); // 红黑树拆分
else { // preserve order // 不为红黑树,但是当前数组的下标对应的链表中还有元素
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
// 循环复制链表中的元素到新数组
do {
next = e.next;
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
遍历:HashMap有一个内部类EntrySet,其中定义了操作 map中数据的系列方法,我们的数据都是放在 Entry里面的。entrySet方法就是将Entry放在Set中返回了,我们再一次迭代该Set就完成了hashMap的遍历。
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() {
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> es;
return (es = entrySet) == null ? (entrySet = new EntrySet()) : es;
}
final class EntrySet extends AbstractSet<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final int size() { return size; }
public final void clear() { HashMap.this.clear(); }
public final Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> iterator() {
return new EntryIterator();
}
public final boolean contains(Object o) {
if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry))
return false;
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Node<K,V> candidate = getNode(hash(key), key);
return candidate != null && candidate.equals(e);
}
public final boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>) o;
Object key = e.getKey();
Object value = e.getValue();
return removeNode(hash(key), key, value, true, true) != null;
}
return false;
}
public final Spliterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> spliterator() {
return new EntrySpliterator<>(HashMap.this, 0, -1, 0, 0);
}
public final void forEach(Consumer<? super Map.Entry<K,V>> action) {
Node<K,V>[] tab;
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (size > 0 && (tab = table) != null) {
int mc = modCount;
for (int i = 0; i < tab.length; ++i) {
for (Node<K,V> e = tab[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
action.accept(e);
}
if (modCount != mc)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
final class EntryIterator extends HashIterator
implements Iterator<Map.Entry<K,V>> {
public final Map.Entry<K,V> next() { return nextNode(); }
}
WeakHashMap:
IdentityHashMap:
LinkedHashMap:
TreeMap:使用树构建的有序映射。排序的依据是Comparable接口。
SortedMap:
EnumMap:
HashTable:
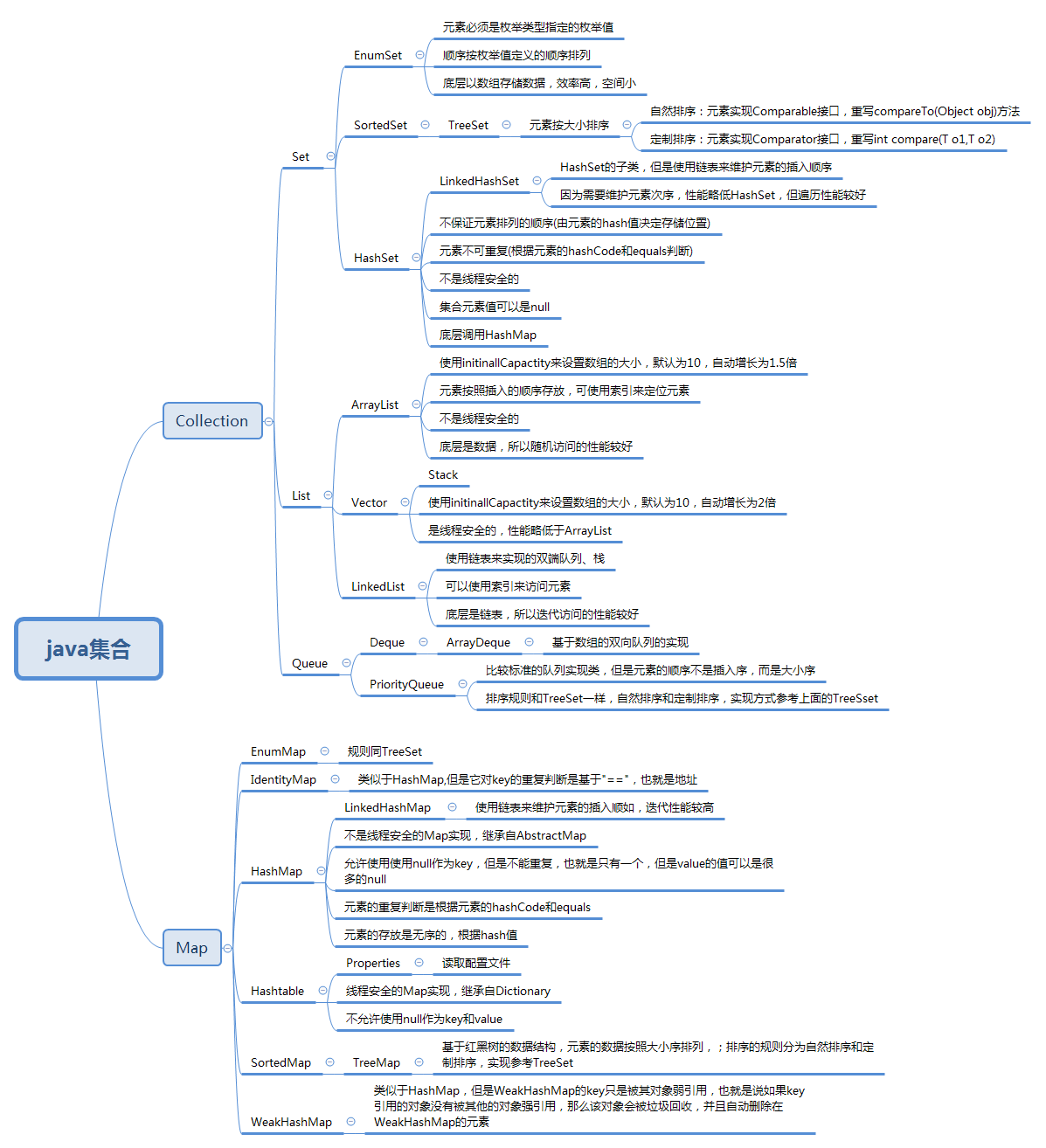
最后附上一张整个集合框架的概览图:
[集合]Collection集合框架源码分析的更多相关文章
- List-LinkedList、set集合基础增强底层源码分析
List-LinkedList 作者 : Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 继上一章继续讲解,上章内容: List-ArreyLlist集合基础增强底层源码分析:https:// ...
- java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析
java集合系列之LinkedList源码分析 LinkedList数据结构简介 LinkedList底层是通过双端双向链表实现的,其基本数据结构如下,每一个节点类为Node对象,每个Node节点包含 ...
- java集合系列之ArrayList源码分析
java集合系列之ArrayList源码分析(基于jdk1.8) ArrayList简介 ArrayList时List接口的一个非常重要的实现子类,它的底层是通过动态数组实现的,因此它具备查询速度快, ...
- Java集合系列[4]----LinkedHashMap源码分析
这篇文章我们开始分析LinkedHashMap的源码,LinkedHashMap继承了HashMap,也就是说LinkedHashMap是在HashMap的基础上扩展而来的,因此在看LinkedHas ...
- List-ArrayList集合基础增强底层源码分析
List集合基础增强底层源码分析 作者:Stanley 罗昊 [转载请注明出处和署名,谢谢!] 集合分为三个系列,分别为:List.set.map List系列 特点:元素有序可重复 有序指的是元素的 ...
- YII框架源码分析(百度PHP大牛创作-原版-无广告无水印)
YII 框架源码分析 百度联盟事业部——黄银锋 目 录 1. 引言 3 1.1.Yii 简介 3 1.2.本文内容与结构 3 2.组件化与模块化 4 2.1.框架加载和运行流程 4 ...
- 介绍开源的.net通信框架NetworkComms框架 源码分析
原文网址: http://www.cnblogs.com/csdev Networkcomms 是一款C# 语言编写的TCP/UDP通信框架 作者是英国人 以前是收费的 售价249英镑 我曾经花了 ...
- Android Small插件化框架源码分析
Android Small插件化框架源码分析 目录 概述 Small如何使用 插件加载流程 待改进的地方 一.概述 Small是一个写得非常简洁的插件化框架,工程源码位置:https://github ...
- Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)简述
Spark RPC系列: Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)运行时序 Spark RPC框架源码分析(二)运行时序 Spark RPC框架源码分析(三)运行时序 一. Spark rpc框架概述 S ...
- Spark RPC框架源码分析(二)RPC运行时序
前情提要: Spark RPC框架源码分析(一)简述 一. Spark RPC概述 上一篇我们已经说明了Spark RPC框架的一个简单例子,Spark RPC相关的两个编程模型,Actor模型和Re ...
随机推荐
- Crack IDEA
使用破解补丁 Crack IDEA→在http://idea.lanyus.com/上可以找到最新的破解补丁,下载并放到软件的bin目录下 →更改bin目录下的两个文件:Idea.exe.vmopti ...
- code1064 虫食算
dfs搜索每个字母对应的数字 剪枝: 1.当一列上三个数a b c都已知时,如果 (a+b)%n!=c && (a+b+1)%n!=c 剪枝(+1是考量进位,注意&&) ...
- SQL游标 数据库编程样例
--处理file与folder中的order -- 声明变量 DECLARE @fileid AS INT, @folderid AS INT, @order AS INT, @oldFolderId ...
- vmware workstation 12 密钥
VMware Workstation 12序列号:5A02H-AU243-TZJ49-GTC7K-3C61N
- Log4j配置(转)
原文:http://www.blogjava.net/zJun/archive/2006/06/28/55511.html Log4J的配置文件(Configuration File)就是用来设置记录 ...
- Qt之QML开发常用知识
小技巧: 1. QML的内部逻辑可以直接调试 2. ctrl+ alt + space,在写QML时,可以直接调出工具条 3. 属性以小写字母开发 4. 属性改变事件,基本都是on+Property+ ...
- ssh的配置[待写]
开机自启:/etc/rc.local /etc/init.d/ssh start 将 /etc/ssh/sshd_confg中PermitRootLogin no 改为yes,重新启动ssh服务.
- read与write
函数原型 ssize_t read(int filedes, void *buf, size_t count); ssize_t write(int filedes, void* buf, siz ...
- ThinkJS 中的Logic层
第一个为什么需要Logic层: 当在 Action 里处理用户的请求时,经常要先获取用户提交过来的数据,然后对其校验,如果校验没问题后才能进行后续的操作:当参数校验完成后,有时候还要进行权限判断等,这 ...
- Linq转换操作之OfType,Cast,AsEnumerable,ToLookup源码分析
Linq转换操作之OfType,Cast,AsEnumerable,ToLookup源码分析 一:Tolookup 1. 从方法的注解上可以看到,ToLookup也是一个k,v的形式,那么问题来了,它 ...
