深入探究 Golang 反射:功能与原理及应用
Hi 亲爱的朋友们,我是 k 哥。今天,咱们来一同探讨下 Golang 反射。
Go 出于通用性的考量,提供了反射这一功能。借助反射功能,我们可以实现通用性更强的函数,传入任意的参数,在函数内通过反射动态调用参数对象的方法并访问它的属性。举例来说,下面的bridge接口为了支持灵活调用任意函数,在运行时根据传入参数funcPtr,通过反射动态调用funcPtr指向的具体函数。
func bridge(funcPtr interface{}, args ...interface{})
再如,ORM框架函数为了支持处理任意参数对象,在运行时根据传入的参数,通过反射动态对参数对象赋值。
type User struct {
Name string
Age int32
}
user := User{}
db.FindOne(&user)
本文将深入探讨Golang反射包reflect的功能和原理。同时,我们学习某种东西,一方面是为了实践运用,另一方面则是出于功利性面试的目的。所以,本文还会为大家介绍反射的典型应用以及高频面试题。
1 关键功能
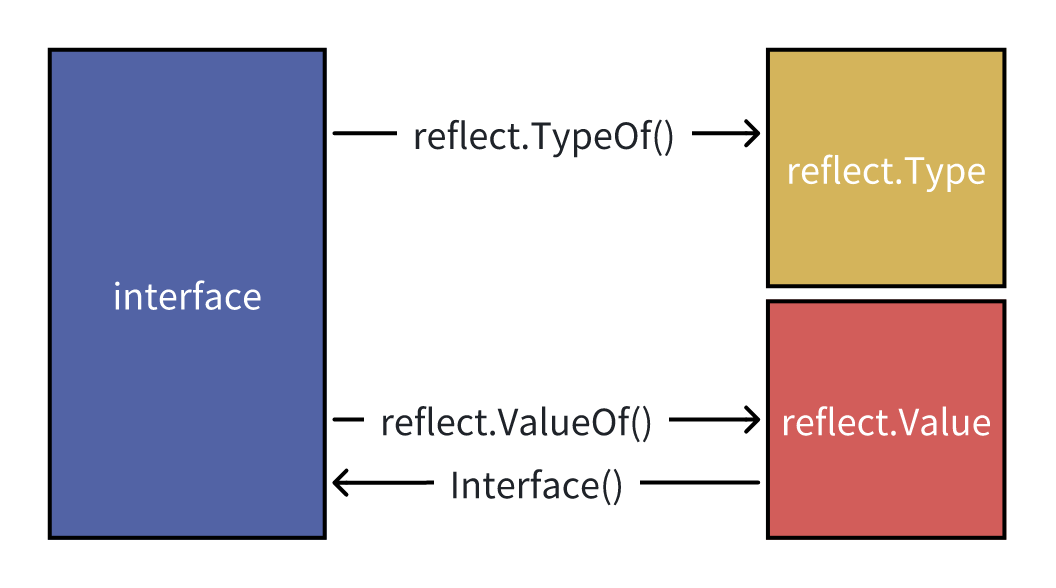
reflect包提供的功能比较多,但核心功能是把interface变量转化为反射类型对象reflect.Type和reflect.Value,并通过反射类型对象提供的功能,访问真实对象的方法和属性。本文只介绍3个核心功能,其它方法可看官方文档。
1.对象类型转换。通过TypeOf和ValueOf方法,可以将interface变量转化为反射类型对象Type和Value。通过Interface方法,可以将Value转换回interface变量。
type any = interface{}
// 获取反射对象reflect.Type
// TypeOf returns the reflection Type that represents the dynamic type of i.
// If i is a nil interface value, TypeOf returns nil.
func TypeOf(i any) Type
// 获取反射对象reflect.Value
// ValueOf returns a new Value initialized to the concrete value stored in the interface i.
// ValueOf(nil) returns the zero Value.
func ValueOf(i any) Value
// 反射对象转换回interface
func (v Value) Interface() (i any)
示例如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
age := 18
fmt.Println("type: ", reflect.TypeOf(age)) // 输出type: int
value := reflect.ValueOf(age)
fmt.Println("value: ", value) // 输出value: 18
fmt.Println(value.Interface().(int)) // 输出18
}
2.变量值设置。通过reflect.Value的SetXX相关方法,可以设置真实变量的值。reflect.Value是通过reflect.ValueOf(x)获得的,只有当x是指针的时候,才可以通过reflec.Value修改实际变量x的值。
// Set assigns x to the value v. It panics if Value.CanSet returns false.
// As in Go, x's value must be assignable to v's type and must not be derived from an unexported field.
func (v Value) Set(x Value)
func (v Value) SetInt(x int64)
...
// Elem returns the value that the interface v contains or that the pointer v points to. It panics if v's Kind is not Interface or Pointer. It returns the zero Value if v is nil.
func (v Value) Elem() Value
示例如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
age := 18
// 通过reflect.ValueOf获取age中的reflect.Value
// 参数必须是指针才能修改其值
pointerValue := reflect.ValueOf(&age)
// Elem和Set方法结合,相当于给指针指向的变量赋值*p=值
newValue := pointerValue.Elem()
newValue.SetInt(28)
fmt.Println(age) // 值被改变,输出28
// reflect.ValueOf参数不是指针
pointerValue = reflect.ValueOf(age)
newValue = pointerValue.Elem() // 如果非指针,直接panic: reflect: call of reflect.Value.Elem on int Value
}
3.方法调用。Method和MethodByName可以获取到具体的方法,Call可以实现方法调用。
// Method returns a function value corresponding to v's i'th method.
// The arguments to a Call on the returned function should not include a receiver;
// the returned function will always use v as the receiver. Method panics if i is out of range or if v is a nil interface value.
func (v Value) Method(i int) Value
// MethodByName returns a function value corresponding to the method of v with the given name.
func (v Value) MethodByName(name string) Value
// Call calls the function v with the input arguments in. For example, if len(in) == 3, v.Call(in) represents the Go call v(in[0], in[1], in[2]).
// Call panics if v's Kind is not Func. It returns the output results as Values
func (v Value) Call(in []Value) []Value
示例如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type User struct {
Age int
}
func (u User) ReflectCallFunc(name string) {
fmt.Printf("age %d ,name %+v\n", u.Age, name)
}
func main() {
user := User{18}
// 1. 通过reflect.ValueOf(interface)来获取到reflect.Value
getValue := reflect.ValueOf(user)
methodValue := getValue.MethodByName("ReflectCallFunc")
args := []reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf("k哥")}
// 2. 通过Call调用方法
methodValue.Call(args) // 输出age 18 ,name k哥
}
2 原理
Go语言反射是建立在Go类型系统和interface设计之上的,因此在聊reflect包原理之前,不得不提及Go的类型和interface底层设计。
2.1 静态类型和动态类型
在Go中,每个变量都会在编译时确定一个静态类型。所谓静态类型(static type),就是变量声明时候的类型。比如下面的变量i,静态类型是interface
var i interface{}
所谓动态类型(concrete type,也叫具体类型),是指程序运行时系统才能看见的,变量的真实类型。比如下面的变量i,静态类型是interface,但真实类型是int
var i interface{}
i = 18
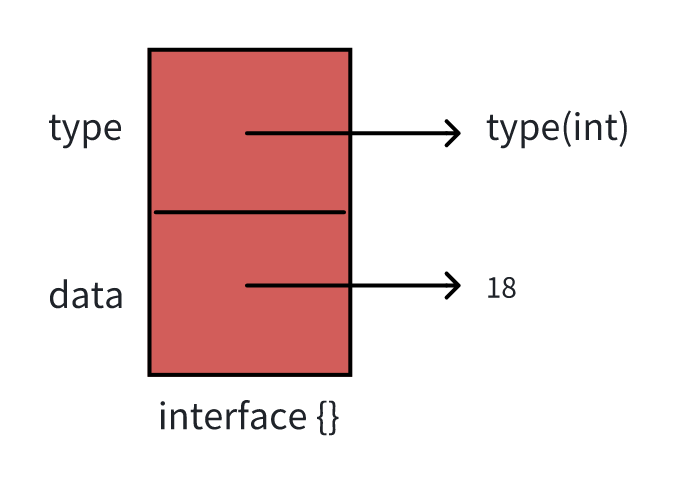
2.2 interface底层设计
对于任意一个静态类型是interface的变量,Go运行时都会存储变量的值和动态类型。比如下面的变量age,会存储值和动态类型(18, int)
var age interface{}
age = 18
2.3 reflect原理
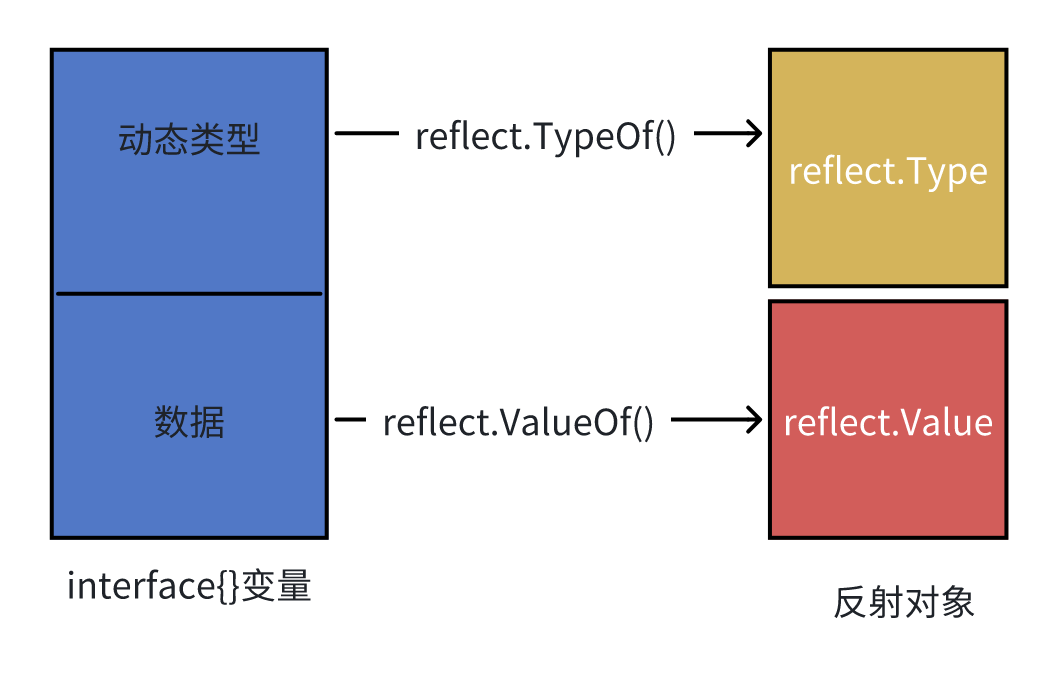
reflect是基于interface实现的。通过interface底层数据结构的动态类型和数据,构造反射对象。
reflect.TypeOf获取interface底层的动态类型,从而构造出reflect.Type对象。通过Type,可以获取变量包含的方法、字段等信息。
// TypeOf returns the reflection Type that represents the dynamic type of i.
// If i is a nil interface value, TypeOf returns nil.
func TypeOf(i interface{}) Type {
eface := *(*emptyInterface)(unsafe.Pointer(&i)) // eface为interface底层结构
return toType(eface.typ) // eface.typ就是interface底层的动态类型
}
func toType(t *rtype) Type {
if t == nil {
return nil
}
return t
}
reflect.ValueOf获取interface底层的Type和数据,封装成reflect.Value对象。
type Value struct {
// typ holds the type of the value represented by a Value.
typ *rtype // 动态类型
// Pointer-valued data or, if flagIndir is set, pointer to data.
// Valid when either flagIndir is set or typ.pointers() is true.
ptr unsafe.Pointer // 数据指针
// flag holds metadata about the value.
// The lowest bits are flag bits:
// - flagStickyRO: obtained via unexported not embedded field, so read-only
// - flagEmbedRO: obtained via unexported embedded field, so read-only
// - flagIndir: val holds a pointer to the data
// - flagAddr: v.CanAddr is true (implies flagIndir)
// - flagMethod: v is a method value.
// The next five bits give the Kind of the value.
// This repeats typ.Kind() except for method values.
// The remaining 23+ bits give a method number for method values.
// If flag.kind() != Func, code can assume that flagMethod is unset.
// If ifaceIndir(typ), code can assume that flagIndir is set.
flag // 标记位,用于标记此value是否是方法、是否是指针等
}
type flag uintptr
// ValueOf returns a new Value initialized to the concrete value
// stored in the interface i. ValueOf(nil) returns the zero Value.
func ValueOf(i interface{}) Value {
if i == nil {
return Value{}
}
return unpackEface(i)
}
// unpackEface converts the empty interface i to a Value.
func unpackEface(i interface{}) Value {
// interface底层结构
e := (*emptyInterface)(unsafe.Pointer(&i))
// NOTE: don't read e.word until we know whether it is really a pointer or not.
// 动态类型
t := e.typ
if t == nil {
return Value{}
}
// 标记位,用于标记此value是否是方法、是否是指针等
f := flag(t.Kind())
if ifaceIndir(t) {
f |= flagIndir
}
return Value{t, e.word, f} // t为类型,e.word为数据,
}
3 应用
工作中,反射常见应用场景有以下两种:
1.不知道接口调用哪个函数,根据传入参数在运行时通过反射调用。例如以下这种桥接模式:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
// 函数内通过反射调用funcPtr
func bridge(funcPtr interface{}, args ...interface{}) {
n := len(args)
inValue := make([]reflect.Value, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
inValue[i] = reflect.ValueOf(args[i])
}
function := reflect.ValueOf(funcPtr)
function.Call(inValue)
}
func call1(v1 int, v2 int) {
fmt.Println(v1, v2)
}
func call2(v1 int, v2 int, s string) {
fmt.Println(v1, v2, s)
}
func main() {
bridge(call1, 1, 2) // 输出1 2
bridge(call2, 1, 2, "test") // 输出1 2 test
}
2.不知道传入函数的参数类型,函数需要在运行时处理任意参数对象,这种需要对结构体对象反射。典型应用场景是ORM,orm示例如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type User struct {
Name string
Age int32
}
func FindOne(x interface{}) {
sv := reflect.ValueOf(x)
sv = sv.Elem()
// 对于orm,改成从db里查出来再通过反射设置进去
sv.FieldByName("Name").SetString("k哥")
sv.FieldByName("Age").SetInt(18)
}
func main() {
user := &User{}
FindOne(user)
fmt.Println(*user) // 输出 {k哥 18}
}
4 高频面试题
1.reflect(反射包)如何获取字段 tag?
通过反射包获取tag。步骤如下:
通过reflect.TypeOf生成反射对象reflect.Type
通过reflect.Type获取Field
通过Field访问tag
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name" otherTag:"name"`
age string `json:"age"`
}
func main() {
user := User{}
userType := reflect.TypeOf(user)
field := userType.Field(0)
fmt.Println(field.Tag.Get("json"), field.Tag.Get("otherTag")) // 输出name name
field = userType.Field(1)
fmt.Println(field.Tag.Get("json")) // 输出age
}
2.为什么 json 包不能导出私有变量的 tag?
从1中的例子中可知,反射可以访问私有变量age的tag。json包之所以不能导出私有变量,是因为json包的实现,将私有变量的tag跳过了。
func typeFields(t reflect.Type) structFields {
// Scan f.typ for fields to include.
for i := 0; i < f.typ.NumField(); i++ {
sf := f.typ.Field(i)
// 非导出成员(私有变量),忽略tag
if !sf.IsExported() {
// Ignore unexported non-embedded fields.
continue
}
tag := sf.Tag.Get("json")
if tag == "-" {
continue
}
}
}
3.json包里使用的时候,结构体里的变量不加tag能不能正常转成json里的字段?
如果是私有成员,不能转,因为json包会忽略私有成员的tag信息。比如下面的demo中,User结构体中的a和b都不能json序列化。
如果是公有成员。
- 不加tag,可以正常转为json里的字段,json的key跟结构体内字段名一致。比如下面的demo,User中的C序列化后,key和结构体字段名保持一致是C。
- 加了tag,从struct转json的时候,json的key跟tag的值一致。比如下面的demo,User中的D序列化后是d。
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
)
type User struct {
a string // 小写无tag
b string `json:"b"` //小写+tag
C string //大写无tag
D string `json:"d"` //大写+tag
}
func main() {
u := User{
a: "1",
b: "2",
C: "3",
D: "4",
}
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", u) // 输出{a:1 b:2 C:3 D:4}
jsonInfo, _ := json.Marshal(u)
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", string(jsonInfo)) // 输出{"C":"3","d":"4"}
}

深入探究 Golang 反射:功能与原理及应用的更多相关文章
- 一种实现C++反射功能的想法(一)
Java的反射机制很酷, 只需知道类的名字就能够加载调用. 这个功能很实用, 想象一下, 用户只需指定类的名称, 就可以动态绑定类型, 而且只需通过字符串指定, 字符串的使用可以使得用户的修改只需修改 ...
- UDP反射DDoS攻击原理和防范
东南大学:UDP反射DDoS攻击原理和防范 2015-04-17 中国教育网络 李刚 丁伟 反射攻击的防范措施 上述协议安装后由于有关服务默认处于开启状态,是其被利用的一个重要因素.因此,防范可以从配 ...
- Java之反射 — 用法及原理
Java之反射 - 用法及原理 定义 Java反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法:对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性:这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象 ...
- Go For Web:一篇文章带你用 Go 搭建一个最简单的 Web 服务、了解 Golang 运行 web 的原理
前言: 本文作为解决如何通过 Golang 来编写 Web 应用这个问题的前瞻,对 Golang 中的 Web 基础部分进行一个简单的介绍.目前 Go 拥有成熟的 Http 处理包,所以我们去编写一个 ...
- golang反射初试
golang反射来自Go AST(Abstract Syntax Tree). reflect操作更多像traverse AST. t := reflect.TypeOf(obj) 使用TypeOf( ...
- 【Android 界面效果29】研究一下Android滑屏的功能的原理,及scrollTo和scrollBy两个方法
Android中的滑屏功能的原理是很值得我们去研究的,在知道这两个原理之前,有必要先说说View的两个重要方法,它们就是scrollTo 和scrollBy. Android View视图是没有边界的 ...
- js基础进阶--图片上传时实现本地预览功能的原理
欢迎访问我的个人博客:http://www.xiaolongwu.cn 前言 最近在项目上加一个图片裁剪上传的功能,用的是cropper插件,注意到选择本地图片后就会有预览效果,这里整理一下这种预览效 ...
- Excel阅读模式/聚光灯开发技术之二 超级逐步录入提示功能开发原理简述—— 隐鹤 / HelloWorld
Excel阅读模式/聚光灯开发技术之二 超级逐步录入提示功能开发原理简述———— 隐鹤 / HelloWorld 1. 引言 自本人第一篇博文“Excel阅读模式/单元格行列指示/聚光灯开发技术要 ...
- golang 反射应用(二)
golang反射应用(二) package test import ( "reflect" "testing" ) //定义适配器 func TestRefle ...
- 使用反射功能在Unity运行状态通过Inspector面板修改字段和调用方法
使用反射功能在Unity运行状态通过Inspector面板修改字段和调用方法 效果展示 一个很简单的组件脚本 运行状态在Inspector面板可以随便修改字段和调用方法 方法调用日志 设计由来 最近在 ...
随机推荐
- Tkinter禁止用户调整窗口尺寸大小
禁止用户调整窗口尺寸大小的方式: root.resizable(False,False) 例子: from tkinter import * from tkinter import ttk impor ...
- HTML——超链接标签
一.超链接标签的基本使用 超链接是浏览者和服务器的交互的主要手段,也叫超级链接或a链接,是网页中指向一个目标的连接关系,这个目标可以是网页.网页中的具体位置.图片.邮件地址.文件.应用程序等. 超链接 ...
- Android 13 - Media框架(30)- ACodec(六)
关注公众号免费阅读全文,进入音视频开发技术分享群! 前一节我们了解了input buffer写入的流程,知道了起播写前几笔数据时会先获取graphic buffer,这一节我们就一起来了解下deque ...
- Android 11(R) MultiMedia(十五)MediaCodec同步模式实现一个简易播放器
这一节是实践,学习android原生SimplePlayer并自己码一遍,果然学到很多. MyPlayer.h #include <media/stagefright/foundation/AH ...
- Jenkins自动化集成
gitlab连接Jenkins 创建token后 , 现在的网页上就会出现一个token: token只出现一次,注意保存 将这个token在Jenkins上配置,现在开始配置Jenkins Jenk ...
- 主成分分析(PCA)介绍
目录 计算过程 投影分量计算 假设你有一家理发店,已经记录了过去一年中所有顾客的头发长度和发型偏好的数据.现在你想从这些数据中提取一些主要的信息,比如顾客最常选择的发型类型,以及不同发型之间的相关性等 ...
- Java访问权限修饰符(public , private , protected)
访问权限修饰符包括:public.protected.private和默认修饰符(friendly/包访问权限). 可以修饰在类.字段.方法前面. public:公开权限,所有类都可以访问. prot ...
- GO语言 GOLANG 上传微信电子小票图片
GO语言 GOLANG 上传微信电子小票图片.GO HTTP POST 图片文件.GO 上传图片文件.multipart/form-data.image/jpeg.image/png. GO 环境: ...
- C#.NET 使用Windows证书库中的证书
public static X509Certificate2 GetCertificate(string commonName, StoreName storeName) { X509Certific ...
- xxlJob Cron表达式 0 0 8,13 * * ?
xxlJob Cron表达式 0 0 8,13 * * ? Cron有如下两种语法格式:(1)Seconds Minutes Hours DayofMonth Month DayofWeek Yea ...
