[LeetCode] 802. Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. If we reach a node that is terminal (that is, it has no outgoing directed edges), we stop.
Now, say our starting node is eventually safe if and only if we must eventually walk to a terminal node. More specifically, there exists a natural number K so that for any choice of where to walk, we must have stopped at a terminal node in less than K steps.
Which nodes are eventually safe? Return them as an array in sorted order.
The directed graph has N nodes with labels 0, 1, ..., N-1, where N is the length of graph. The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of labels j such that (i, j) is a directed edge of the graph.
Example:
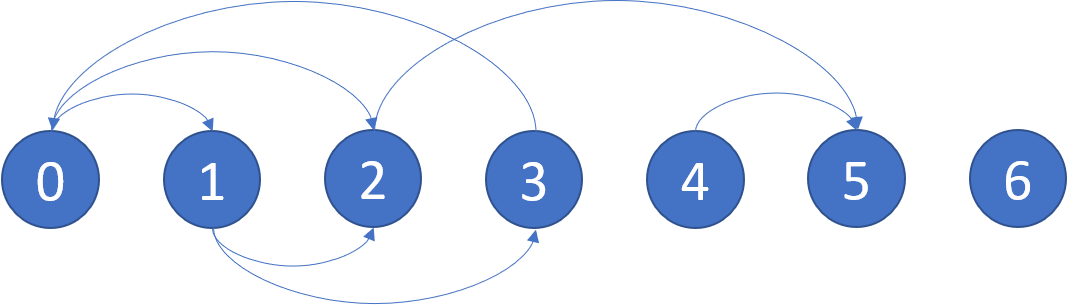
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
Output: [2,4,5,6]
Here is a diagram of the above graph.
Note:
graphwill have length at most10000.- The number of edges in the graph will not exceed
32000. - Each
graph[i]will be a sorted list of different integers, chosen within the range[0, graph.length - 1].
在一个有向图中,如果从一个节点出发走过很多步之后到达了终点(出度为0的节点,无路可走了),则认为这个节点是最终安全的节点。如果根本停不下来,那就是在一个环上,就是不安全节点。要在自然数K步内停止,到达安全节点,返回满足要求的排序好的所有安全节点的索引值。实质是在一个有向图中找出不在环路上的节点。
解法:DFS,可采用染色的方法对节点进行分类:0表示该结点还没有被访问;1表示已经被访问过了,并且发现是safe的;2表示被访问过了,但发现是unsafe的。我们采用DFS的方法进行遍历,并返回该结点是否是safe的:如果发现它已经被访问过了,则直接返回是否是safe的标记;否则就首先将其标记为unsafe的,然后进行DFS搜索(此时该结点会处在DFS的路径上,所以后面的DFS一旦到了该结点,就会被认为是形成了环,所以直接返回false)。当整个DFS的搜索都已经结束,并且都没有发现该结点处在环上时,说明该结点是safe的,所以此时将其最终标记为safe即可。空间复杂度是O(n),时间复杂度是O(n)
解法2: 迭代,记录下每个节点的出度,如果出度为0那必然是环路外的节点,然后将该点以及指向该点的边删除,继续寻找出度为0的点
class Solution {
public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes(int[][] graph) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(graph == null || graph.length == 0) return res;
int nodeCount = graph.length;
int[] color = new int[nodeCount];
for(int i = 0;i < nodeCount;i++){
if(dfs(graph, i, color)) res.add(i);
}
return res;
}
public boolean dfs(int[][] graph, int start, int[] color){
if(color[start] != 0) return color[start] == 1;
color[start] = 2;
for(int newNode : graph[start]){
if(!dfs(graph, newNode, color)) return false;
}
color[start] = 1;
return true;
}
}
Python:
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
n = len(graph)
out_degree = collections.defaultdict(int)
in_nodes = collections.defaultdict(list)
queue = []
ret = []
for i in range(n):
out_degree[i] = len(graph[i])
if out_degree[i]==0:
queue.append(i)
for j in graph[i]:
in_nodes[j].append(i)
while queue:
term_node = queue.pop(0)
ret.append(term_node)
for in_node in in_nodes[term_node]:
out_degree[in_node] -= 1
if out_degree[in_node]==0:
queue.append(in_node)
return sorted(ret)
Python:
# Time: O(|V| + |E|)
# Space: O(|V|)
import collections class Solution(object):
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
WHITE, GRAY, BLACK = 0, 1, 2 def dfs(graph, node, lookup):
if lookup[node] != WHITE:
return lookup[node] == BLACK
lookup[node] = GRAY
for child in graph[node]:
if lookup[child] == BLACK:
continue
if lookup[child] == GRAY or \
not dfs(graph, child, lookup):
return False
lookup[node] = BLACK
return True lookup = collections.defaultdict(int)
return filter(lambda node: dfs(graph, node, lookup), xrange(len(graph)))
Python:
class Solution(object):
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not graph: return [] n = len(graph)
# 用字段存储每个节点的父节点
d = {u:[] for u in range(n)}
degree = [0] * n
for u in range(n):
for v in graph[u]:
d[v].append(u)
degree[u] = len(graph[u]) Q = [u for u in range(n) if degree[u]==0]
res = []
while Q:
node = Q.pop()
res.append(node)
for nodes in d[node]:
degree[nodes] -= 1
if degree[nodes] == 0:
Q.append(nodes)
return sorted(res)
C++:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> eventualSafeNodes(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
vector<int> res;
if (graph.size() == 0) {
return res;
}
int size = graph.size();
vector<int> color(size, 0); // 0: not visited; 1: safe; 2: unsafe.
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (dfs(graph, i, color)) { // the i-th node is safe
res.push_back(i);
}
}
return res;
}
private:
bool dfs(vector<vector<int>> &graph, int start, vector<int> &color) {
if (color[start] != 0) {
return color[start] == 1;
}
color[start] = 2; // mark it as unsafe because it is on the path
for (int next : graph[start]) {
if (!dfs(graph, next, color)) {
return false;
}
}
color[start] = 1; // mark it as safe because no loop is found
return true;
}
};
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总
[LeetCode] 802. Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- LeetCode 802. Find Eventual Safe States
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/ 题目: In a directed graph, we start a ...
- 【LeetCode】802. Find Eventual Safe States 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]802. Find Eventual Safe States 解题报告(Python) 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemi ...
- LC 802. Find Eventual Safe States
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- 【leetcode】802. Find Eventual Safe States
题目如下: 解题思路:本题大多数人采用DFS的方法,这里我用的是另一种方法.我的思路是建立一次初始值为空的safe数组,然后遍历graph,找到graph[i]中所有元素都在safe中的元素,把i加入 ...
- 802. Find Eventual Safe States
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/description/ class Solution { public: vector ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 802 找到最终的安全状态 (DFS)
802. 找到最终的安全状态 在有向图中, 我们从某个节点和每个转向处开始, 沿着图的有向边走. 如果我们到达的节点是终点 (即它没有连出的有向边), 我们停止. 现在, 如果我们最后能走到终点,那么 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode802. 找到最终的安全状态 | Find Eventual Safe States
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- LeetCode 277. Find the Celebrity (找到明星)$
Suppose you are at a party with n people (labeled from 0 to n - 1) and among them, there may exist o ...
随机推荐
- CentOS7.5安装SVN和可视化管理工具iF.SVNAdmin
一.安装Apache和PHP 由于iF.SVNAdmin使用php写的,因此我们需要安装php yum install httpd php 二.安装SVN服务器(其中,mod_dav_svn是Apac ...
- P4560 [IOI2014]Wall 砖墙
题目描述 给定一个长度为 nn且初始值全为 00的序列.你需要支持以下两种操作: Add L, R, hL,R,h:将序列 [L, R][L,R]内所有值小于 hh的元素都赋为 hh,此时不改变高度大 ...
- 异常检测(Anomaly detection): 什么是异常检测及其一些应用
异常检测的例子: 如飞机引擎的两个特征:产生热量与振动频率,我们有m个样本画在图中如上图的叉叉所示,这时来了一个新的样本(xtest),如果它落在上面,则表示它没有问题,如果它落在下面(如上图所示), ...
- 小米BL不解锁刷机
关于小米NOTE顶配近期解锁的问题中发现还有很多人不会用9008模式刷机,现出个简单教程方便米粉们救砖.硬件:小米NOTE顶配手机 win10系统的电脑 手机与电脑相连的数据线软件:老版本的mifla ...
- 02-Flutter移动电商实战-建立项目和编写入口文件
环境搭建请参考之前写的一篇文章:Flutter_初体验_创建第一个应用 1.创建项目 采用AndroidStudio构建本项目,FIle>New>New Flutter Project… ...
- 看图轻松理解数据结构与算法系列(NoSQL存储-LSM树) - 全文
<看图轻松理解数据结构和算法>,主要使用图片来描述常见的数据结构和算法,轻松阅读并理解掌握.本系列包括各种堆.各种队列.各种列表.各种树.各种图.各种排序等等几十篇的样子. 关于LSM树 ...
- 洛谷 P1012 拼数
P1012 拼数 标签 字符串 排序 NOIp提高组 1998 云端 难度 普及- 时空限制 1s / 128MB 题目描述 设有n个正整数(n≤20),将它们联接成一排,组成一个最大的多位整数. 例 ...
- 2019qbxt游记
Day 1 2019.8.6 来到qbxt的第一天,虽然早就对宾馆的等级做好了准备,但是还是十分的失望,外观是真的很简陋,不过里面还好的,,可以凑合. 我竟然和lbh一个宿舍!!!这次外出学习必将不安 ...
- 一个100%Go语言的Web-Term-SSH 堡垒机项目
SSH-Fortress 1. What does it do? Make your cluster servers be more safe by expose your SSH connectio ...
- GoCN每日新闻(2019-10-05)
国庆专辑:GopherChina祝大家国庆节快乐GoCN每日新闻(2019-10-05) 1. Gophercon UK 2019 https://www.bilibili.com/video/av ...
