Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 2) D. Legacy 线段树建模+最短路
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Rick and his co-workers have made a new radioactive formula and a lot of bad guys are after them. So Rick wants to give his legacy to Morty before bad guys catch them.
There are n planets in their universe numbered from 1 to n. Rick is in planet number s (the earth) and he doesn't know where Morty is. As we all know, Rick owns a portal gun. With this gun he can open one-way portal from a planet he is in to any other planet (including that planet). But there are limits on this gun because he's still using its free trial.

By default he can not open any portal by this gun. There are q plans in the website that sells these guns. Every time you purchase a plan you can only use it once but you can purchase it again if you want to use it more.
Plans on the website have three types:
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from planet v to planet u.
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from planet v to any planet with index in range [l, r].
- With a plan of this type you can open a portal from any planet with index in range [l, r] to planet v.
Rick doesn't known where Morty is, but Unity is going to inform him and he wants to be prepared for when he finds and start his journey immediately. So for each planet (including earth itself) he wants to know the minimum amount of money he needs to get from earth to that planet.
The first line of input contains three integers n, q and s (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 105, 1 ≤ s ≤ n) — number of planets, number of plans and index of earth respectively.
The next q lines contain the plans. Each line starts with a number t, type of that plan (1 ≤ t ≤ 3). If t = 1 then it is followed by three integers v, u and w where w is the cost of that plan (1 ≤ v, u ≤ n, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109). Otherwise it is followed by four integers v, l, r and wwhere w is the cost of that plan (1 ≤ v ≤ n, 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109).
In the first and only line of output print n integers separated by spaces. i-th of them should be minimum money to get from earth to i-th planet, or - 1 if it's impossible to get to that planet.
- 3 5 1
2 3 2 3 17
2 3 2 2 16
2 2 2 3 3
3 3 1 1 12
1 3 3 17
- 0 28 12
- 4 3 1
3 4 1 3 12
2 2 3 4 10
1 2 4 16
- 0 -1 -1 12
In the first sample testcase, Rick can purchase 4th plan once and then 2nd plan in order to get to get to planet number 2.
题目链接:点击传送
题意:给你n个点,q个操作,s为起点
t表示操作类型,1 v->u的权值为w ,2 v -> [l,r](区间所有点)的权值为w ,3 [l,r] -> v 的权值为w;
思路:
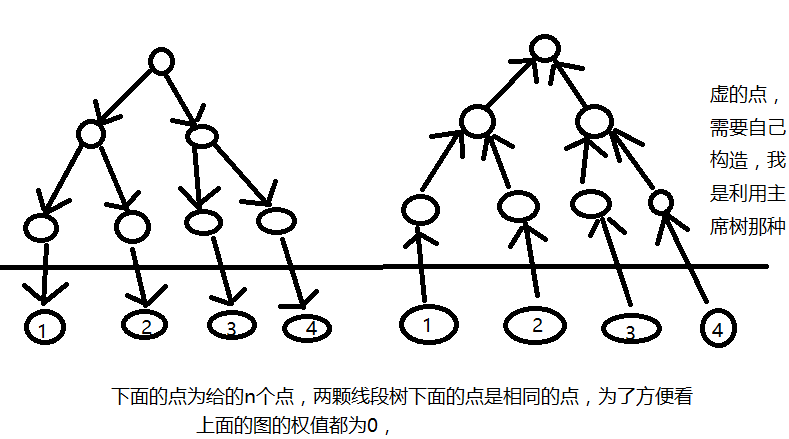
根据线段树的区间进行修改即可;
- #pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
- #include<iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cmath>
- #include<string>
- #include<queue>
- #include<algorithm>
- #include<stack>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<vector>
- #include<list>
- #include<set>
- #include<map>
- using namespace std;
- #define ll long long
- #define pi (4*atan(1.0))
- #define eps 1e-4
- #define bug(x) cout<<"bug"<<x<<endl;
- const int N=1e5+,M=1e6+,inf=;
- const ll INF=1e17+,mod=1e9+;
- struct is
- {
- int v,next;
- ll w;
- }edge[M*];
- int head[N*],edg,vis[M];
- void init()
- {
- memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
- memset(head,-,sizeof(head));
- edg=;
- }
- void add(int u,int v,ll w)
- {
- edg++;
- edge[edg].v=v;
- edge[edg].w=w;
- edge[edg].next=head[u];
- head[u]=edg;
- }
- struct SGT
- {
- int ls[N*][],rs[N*][],root[];
- int tot;
- void build(int l,int r,int &pos,int type)
- {
- pos=tot++;
- if(l==r)
- {
- if(type)
- add(l,pos,);
- else
- add(pos,l,);
- return;
- }
- int mid=(l+r)>>;
- build(l,mid,ls[pos][type],type);
- build(mid+,r,rs[pos][type],type);
- if(type)
- add(ls[pos][type],pos,),add(rs[pos][type],pos,);
- else
- add(pos,ls[pos][type],),add(pos,rs[pos][type],);
- }
- void up(int v,int L,int R,ll c,int l,int r,int pos)
- {
- if(L<=l&&r<=R)
- {
- //cout<<"add"<<v<<" "<<pos<<endl;
- add(pos,v,c);
- return;
- }
- int mid=(l+r)>>;
- if(L<=mid)
- up(v,L,R,c,l,mid,ls[pos][]);
- if(R>mid)
- up(v,L,R,c,mid+,r,rs[pos][]);
- }
- void down(int v,int L,int R,ll c,int l,int r,int pos)
- {
- if(L<=l&&r<=R)
- {
- //cout<<"add"<<v<<" "<<pos<<endl;
- add(v,pos,c);
- return;
- }
- int mid=(l+r)>>;
- if(L<=mid)
- down(v,L,R,c,l,mid,ls[pos][]);
- if(R>mid)
- down(v,L,R,c,mid+,r,rs[pos][]);
- }
- };
- SGT tree;
- struct mmp
- {
- int s;
- ll dis;
- mmp(){}
- mmp(int ss,ll d){s=ss,dis=d;}
- bool operator <(const mmp &b)const
- {
- return dis>b.dis;
- }
- };
- ll ans[N*];
- priority_queue<mmp>q;
- void dij(int s)
- {
- ans[s]=;
- q.push(mmp(s,0LL));
- while(!q.empty())
- {
- mmp now = q.top();
- q.pop();
- if(vis[now.s])continue;
- vis[now.s]=;
- for(int i = head[now.s]; i !=-; i = edge[i].next)
- {
- int v=edge[i].v;
- ll w=edge[i].w;
- if(ans[v] > ans[now.s] + w)
- {
- q.push(mmp(v,ans[now.s]+w));
- ans[v]=ans[now.s]+w;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- int main()
- {
- init();
- int n,q,s;
- scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&q,&s);
- for(int i=;i<=n*;i++)
- ans[i]=INF;
- tree.tot=n+;
- tree.build(,n,tree.root[],);
- tree.build(,n,tree.root[],);
- for(int i=;i<=q;i++)
- {
- int t,v,u,l,r;
- ll w;
- scanf("%d%d",&t,&v);
- if(t==)
- scanf("%d%lld",&u,&w),add(v,u,w);
- else if(t==)
- scanf("%d%d%lld",&l,&r,&w),tree.down(v,l,r,w,,n,tree.root[]);
- else
- scanf("%d%d%lld",&l,&r,&w),tree.up(v,l,r,w,,n,tree.root[]);
- }
- dij(s);
- for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
- {
- if(ans[i]>=INF)printf("-1 ");
- else printf("%lld ",ans[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- return ;
- }
Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 2) D. Legacy 线段树建模+最短路的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 1) B. Legacy 线段树建图跑最短路
B. Legacy 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/786/problem/B Description Rick and his co-workers have ...
- 【转】Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 1) B. Legacy 线段树建图&&最短路
B. Legacy 题目连接: http://codeforces.com/contest/786/problem/B Description Rick and his co-workers have ...
- Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 2) D. Legacy (线段树建图dij)
D. Legacy time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
- Codeforces Round #406 (Div. 2) 787-D. Legacy
Rick and his co-workers have made a new radioactive formula and a lot of bad guys are after them. So ...
- Codeforces Round #603 (Div. 2) E. Editor 线段树
E. Editor The development of a text editor is a hard problem. You need to implement an extra module ...
- Codeforces Codeforces Round #316 (Div. 2) C. Replacement 线段树
C. ReplacementTime Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/570/problem ...
- Codeforces Round #765 Div.1 F. Souvenirs 线段树
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/765/problem/F 题意概述: 给出一个序列,若干组询问,问给出下标区间中两数作差的最小绝对值. 分析: 这个题揭示着数据 ...
- Codeforces Round #278 (Div. 1) Strip (线段树 二分 RMQ DP)
Strip time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input output s ...
- Codeforces 787D. Legacy 线段树建模+最短路
D. Legacy time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard input out ...
随机推荐
- 前端js如何生成一个对象,并转化为json字符串
https://www.cnblogs.com/May-day/p/6841958.html 一,直接上代码 <script src="../../Content/jquery-2.0 ...
- storm介绍,核心组件,编程模型
一.流式计算概念 利用分布式的思想和方法,对海量“流”式数据进行实时处理,源自业务对海量数据,在“时效”的价值上的挖掘诉求,随着大数据场景应用场景的增长,对流式计算的需求愈发增多,流式计算的一般架构图 ...
- Centos上执行Shell的四种方式
注意:我这里说的shell脚本是Bash Shell,其他类型的shell脚本不保证有效 1,方式一:进入shell文件所在目录 ./my.sh执行 ./my.sh ./的意思是说在当前的工作目录下执 ...
- springmvc学习笔记一框架的理解
SpringMVC现在在很多公司都很流行,所以这个框架对我们来说,是很重要的. 首先我们对比mvc来分析springmvc这个框架是怎么设计,以及它的工作的流程. 首先来看mvc: 1. 用户发起r ...
- Javascript-逻辑或(||)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- bootstrap modal 垂直居中对齐
bootstrap modal 垂直居中对齐 文章参考 http://www.bubuko.com/infodetail-666582.html http://v3.bootcss.com/Jav ...
- JSP—内置对象
JSP内置对象是Web容器创建的一组对象,不用声明,直接使用 out 输出对象 类型 javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter 作用域 Page request 请求对象 类型 java ...
- mysql_connect
in this passage, we slove the problem about Mysql_connect. first, let' see an example: resource mysq ...
- WebStorm使用快速入门
WebStorm建立在开源IntelliJ平台之上,JetBrains已经开发和完善了超过15年.其提供了统一的UI,可与许多流行的版本控制系统配合使用,确保在git,GitHub,SVN,Mercu ...
- swift 之 as、as!、as?
1,as使用场合(1)从派生类转换为基类,向上转型(upcasts) class Animal {} class Cat: Animal {} let cat = Cat() let animal = ...
