springMVC整理03--处理数据模型 & 试图解析器 & @ResponseBody & HttpEntity
1.处理模型数据
SpringMVC 中的模型数据是非常重要的,因为 MVC 中的控制(C)请求处理业务逻辑来生成数据模型(M),而视图(V)就是为了渲染数据模型的数据。当有一个查询的请求,控制器(C)会把请求拦截下来,然后把根据请求的内容对它进行分配适合的处理方法,在处理方法上进行处理查询的业务逻辑,得到了数据,再把数据封装成数据模型对象,最后把数据模型(M)对象传给了视图(V),让视图去渲染数据模型。SpringMVC 提供了以下几种途径输出模型数据:
- ModelAndView:处理方法返回值类型为 ModelAndView 时,方法体即可通过该对象添加模型数据。
- @ModelAttribute:方法入参标注该注解后,入参的对象就会放到数据模型中。
- Map 及 Model:入参为 org.springframework.ui.Model、org.springframework.uiModelMap 或 java.util.Map 时,处理方法返回时,Map 中的数据会自动添加到模型中。
- @SessionAttributes:将模型中的某个属性暂存到 HttpSession 中,以便多个请求之间可以共享这个属性。
1.1 Map 和 和 Model 入参
/**
* 当参数为 Map 时
* SpirngMVC 会传入 一个 BindingAwareModelMap
* 往 BindingAwareModelMap 里面存入的值 会在后面存入 request 域中
* 相当于在方法返回前执行了一个 request.setAttribute 的操作
*/
@RequestMapping("/map.html")
public String map(Map<String, Object> map) {
System. out .println(map.getClass().getName());
map.put("name", "aaa");
map.put("id", 123);
return "/model.jsp";
}
/**
* 参数为 Model 类型的,作用和 Map 一样
*/
@RequestMapping("/model.html")
public String model(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("id",123);
model.addAttribute("name","aaa");
return "/model.jsp";
}
测试页面:
name=${name}<br/>
id=${id}<br/>
运行结果:访问 map.html 或 model.html 的时候,页面上显示: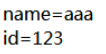 name=aaa id=123
name=aaa id=123
1.2ModelAndView
ModelAndView 既包含数据模型,又包含视图信息
@RequestMapping("/modelandview.html")
public ModelAndView testModeAndView(){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//将 Model 数据作为 request.attribute Foward 到下一个页面。
modelAndView.addObject("id",123);
modelAndView.addObject("name","abc");
modelAndView.setViewName("/model.jsp");//设置要返回的页面
return modelAndView;
}
1.3 @SessionAttributes
若希望在多个请求之间共用某个模型属性数据,则可以在控制器类上标注一个 @SessionAttributes,SpringMVC 将在模型中对应的属性暂存到 HttpSession 中。
@SessionAttributes 只能标注在类上。
@SessionAttributes 除了可以通过属性名指定需要放到会话中的属性外,还可以通过模型属性的对象类型指定哪些模型属性需要放到会话中.
– @SessionAttributes(types=Dept.class) 会将隐含模型中所有类型为 Dept.class 的属性添加到session 中。
– @SessionAttributes(value={“user”,”admin”})会将模型中名为 user 和 admin 的属性添加到session 中
– @SessionAttributes(types={Dept.class, Employee.class})会将模型中所有类型为 Dept 和Employee 的属性添加到 session 中
– @SessionAttributes(value={“user”,”admin”}, types={Dept.class})会将模型中名为 user和 admin和类型为 Dept 的对象放到 session 中。
在类上添加 @SessionAttributes 注解
@SessionAttributes(types = Dept.class, value = {"user", "admin"})
@Controller
public class ModelController {
测试方法:
@RequestMapping("/session.html")
public ModelAndView testSettion(Map<String, Object> map) {
map.put("admin", "I am admin");
map.put("user", "I am user");
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setName("session name");
map.put("dept", dept);
//@SessionAttributes 注解里没有声明 other 这个属性,所以不会在 session 中
map.put("other", "I'm other");
return new ModelAndView("/model.jsp", "result", map);
}
测试页面:
request 中的属性:<br/>
admin:${requestScope.admin}<br/>
user:${requestScope.user}<br/>
dept.name:${requestScope.dept.name}<br/>
other:${requestScope.other}<br/>
session 中的属性:<br/>
admin:${sessionScope.admin}<br/>
user:${sessionScope.user}<br/>
dept.name:${sessionScope.dept.name}<br/>
other:${sessionScope.other}<br/>
运行效果:

可以看到模型中的属性都放到了request的域中。@SessionAttributes中没有声明other,所以 session 中的 other 是空的。
1.4 @ModelAttribute
1.4.1 方法参数上使用@ ModelAttribute
在参数前使用@ModelAttribute,在进去方法时可以通过参数给对象赋值,如下面的代码,当请求/model1.html?id=1 的时候,会给 dept 的 id 属性赋值。在方法中可以对 dept 做进一步的处理。@ModelAttribute 可以自动将被注解的对象作为数据模型返回给页面。
@RequestMapping("/model1.html")
public String testModelAttribute(@ModelAttribute Dept dept) {
dept.setId(123);
dept.setName("test");
//使用@ModelAttribute 注解 dept
//相当于执行了 request.setAttribute("dept",dept);
//页面上可以直接取数据
return "/model.jsp";
}
测试页面 model.jsp,使用 EL 表达式取值 :
<body>
dept.id=${dept.id}<br/>
dept.name=${dept.name}
</body
运行结果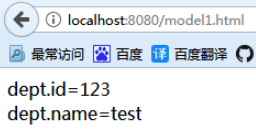
1.4.2 定义方法时使用@ ModelAttribute
在方法上使用@ModelAttribute 后,执行这个 Controller 的任意一个方法之前,都会调用这个方法给对象赋值。
/**
* 在方法上使用@ModelAttribute,调用这个 Controller 任意一个方法之前
* 都会执行这个方法给模型赋值
*/
@ModelAttribute("dept")
public Dept getDept() {
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId(456);
dept.setName("name");
return dept;
}
/**
* 在调用这个方法前,会执行 getDept()
* 如果请求中有参数,会覆盖掉 getDept()的值
* dept 会作为数据模型返回到页面上
*/
@RequestMapping("/model2.html")
public String testModelAttribute2(@ModelAttribute Dept dept) {
System. out .println(dept.getId());
System. out .println(dept.getName());
return "/model.jsp";
}
2. 视图和视图解析器
对于Controller的目标方法,无论其返回值是String、View、ModelMap或是ModelAndView,SpringMVC 都会在内部将它们封装为一个 ModelAndView 对象进行返回。
Spring MVC 借助视图解析器(ViewResolver)得到最终的视图对象(View),最终的视图可以是 JSP 也可是 Excell、 JFreeChart 等各种表现形式的视图。
View ---View 接口表示一个响应给用户的视图,例如 jsp 文件,pdf 文件,html 文件等。
视图的作用是渲染模型数据,将模型里的数据以某种形式呈现给客户。
为了实现视图模型和具体实现技术的解耦,Spring 在 org.springframework.web.servlet 包中定义了一个高度抽象的 View 接口。
视图对象由视图解析器负责实例化。由于视图是无状态的,所以他们不会有线程安全的问题。所谓视图是无状态的,是指对于每一个请求,都会创建一个 View 对象。
JSP 是最常见的视图技术。
2.1 ViewResolver
ViewResolver 的主要作用是把一个逻辑上的视图名称解析为一个真正的视图,SpringMVC
中用于把 View 对象呈现给客户端的是 View 对象本身,而 ViewResolver 只是把逻辑视图名称
解析为对象的 View 对象。
2.1.1 InternalResourceViewResolver
InternalResourceViewResolver 可以在视图名称前自动加前缀或后缀:
<!-- 配置视图解析器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/"></property><!--前缀-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property><!--后缀-->
</bean>
如果配置了上面的解析器,Controller中返回字符串就不需要写/index.jsp了,直接返回“index”,就会按照/index.jsp 去解析
2.1.2 MappingJackson2JsonView
2.1.3 FreeMarkViewResolver
FreeMaker 后面会进行介绍,
FreeMarker 与 spring 整合需要导入 jar:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarker</groupId>
<artifactId>freemarker</artifactId>
<version>2.3.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId>
<version>4.3.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
使用 FreeMarker 模板生成静态网页,需要在 springMVC-servlet.xml 中配置:
<bean id="freemarkerConfig"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker.FreeMarkerConfigurer">
<!--模板存放路径-->
<property name="templateLoaderPath" value="/WEB-INF/ftl/" />
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</bean>
在 WEB-INF/ftl 下创建模板文件 hello.ftl:
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${hello}</h1>
</body>
通过模板生成静态网页:
@Controller
public class FreeMarkerController { {
@Autowired
private FreeMarkerConfigurer freeMarkerConfigurer;
@RequestMapping( "/freemarker.html")
@ResponseBody
public String genHtml() throws Exception { {
// 1 、从 g spring 容器中获得 r FreeMarkerConfigurer 对象。
// 2 、从 r FreeMarkerConfigurer 对象中获得 n Configuration 对象。
Configuration configuration = freeMarkerConfigurer.getConfiguration();
// 3 、使用 n Configuration 对象获得 e Template 对象。
Template template = configuration.getTemplate( "hello.ftl");
// 4 、创建数据集
Map dataModel = new HashMap <>();
dataModel. put( "hello", "1000");
// 5 、创建输出文件的 r Writer 对象。
Writer out = new FileWriter( new File( "F:/spring- - freemarker.html"));
// 6 、调用模板对象的 s process 方法,生成文件。
template.process( dataModel, out);
// 7 、关闭流。
out. close();
return "OK";
} }
} }
在 F 盘下就能看到 spring-freemark.html 文件了

以上是生成静态网页的配置。
如果想像读取 jsp 一样动态展示 freeMarker 的页面,可以配置视图解析器:
<bean id="viewResolverFtl"
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker.FreeMarkerViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass"
value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.freemarker.FreeMarkerView"/>
<property name="contentType" value="text/html; charset=utf-8"/>
<property name="cache" value="true" />
<property name="suffix" value=".ftl" />
<property name="order" value="0"/>
</bean>
order 越小,视图解析器的优先级就越高。
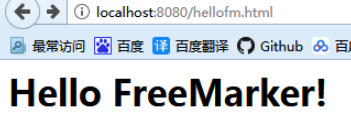
@RequestMapping( "/hellofm.html")
public String sayHello( ModelMap map) { {
// 传递属性到页面
map.addAttribute( "hello", " Hello FreeMarker!");
return "/hello"; // 去找 hello.ftl
} }
运行结果:
2.1.4 BeanNameViewResolver
引入 servlet 的 jar
<!--servlet 依赖 jar 包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</dependency>
自定义一个视图,然后声明成 bean,Controller 中返回这个 bean 的名字,就可以显示当前的视图:
public class HelloView implements View { {
public String getContentType() { {
return "text/html";
} }
public void render(Map< < String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { {
// 向相应中写入数据
response. getWriter().print( "Welcome to View:Hello");
} }
} }
springMVC-servlet.xml 中配置:
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.BeanNameViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="10" /><!--优先级靠后-->
</bean>
<bean id="helloView" class="view.HelloView"/>
Controller
@RequestMapping( "helloview.html")
public String hello() { {
// 因为当前没有 helloView.jsp
// 所以视图解析器依次执行,找到 w id=helloView 的视图并显示
return "helloView";
}
运行结果:
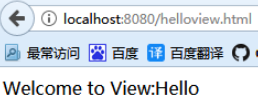
2.2 自定义 View
处理 json 数据需要 json 的 jar 包
<!-- Jackson Json 处理工具包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency>
public class JsonView extends AbstractView { {
/**
* 该 w View 对应的输出类型
*/
@Override
public String getContentType() { {
return "application/json; charset=UTF- - 8";
} }
// 向响应中写入数据
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(Map< < String, Object > model,
HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception { {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
// 设置 e Date 类型的格式,默认是显示毫秒数
mapper.setDateFormat( new SimpleDateFormat( "yyyy- - MM- - dd HH:mm:ss"));
// 需要注意的是放入 l model 的对象一定要实现 e Serializable 接口才能转化成 json
String jsonStr = mapper.writeValueAsString( model);
response. setContentType(getContentType());
response. setHeader( "Cache- - Control", "no- - cache");
response. setCharacterEncoding( "UTF- - 8");
PrintWriter out = null;
try { {
out = response. getWriter();
out.print( jsonStr);
out.flush();
} catch ( IOException e e) { {
} finally { {
if ( out != null) { {
out.close();
out = null;
} }
} }
} }
} }
测试代码:
@RequestMapping( "myview.html")
public ModelAndView myView() { {
Map< < String, Object > result = new HashMap <>();
result. put( "key1", "123");
result. put( "key2", new String[]{ { "a", "b"} });
result. put( "key3", new Date());
return new ModelAndView( new JsonView(), result);
} }
如果是 map 中的值是其它对象类型的,传给 ModelAndView 的数据必须有一个 modelName
2.3 转发和重定向
public String showView2() {
//转发前面加 forward:
return "index.html";
}
@RequestMapping("/redirect.html")
public String showView3() {
//重定向前面加 redirect:
return "redirect:index.html";
}
3. @ReponseBody
该注解用于将 Controller 的方法返回的对象,通过适当的 HttpMessageConverter 转换为指定格式后,写入到 Response 对象的 body 数据区。使用时机:返回的数据不是 html 标签的页面,而是其他某种格式的数据时(如 json、xml 等)使用。
3.1 返回 json 数据
处理 json 数据需要 json 的 jar 包
<!-- Jackson Json 处理工具包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</dependency
返回 json 类型的数据,需要在 spring 配置文件中加入如下配置:
<!--配置返回值转换器-->
<bean id="contentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean"
class="org.springframework.web.accept.ContentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<!--是否支持后缀匹配-->
<property name="favorPathExtension" value="true"/>
<!--是否支持参数匹配-->
<property name="favorParameter" value="true"/>
<!--是否 accept-header 匹配-->
<property name="ignoreAcceptHeader" value="false"/>
<property name="mediaTypes">
<map>
<!--表示.json 结尾的请求返回 json-->
<entry key="json" value="application/json"/>
<!--表示.xml 结尾的返回 xml-->
<entry key="xml" value="application/xml"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
测试 favorPathExtension 请求后缀分别是.xml 和.json
测试 favorParameter 请求中参数 format=json 和 format=xml
测试 ignoreAcceptHeader,请求的 Header 中 Accept=application/json 或 Accept=application/xml
如果要返回 Xml,需要将要转换为 xml 的实体类上添加注解,如:
@XmlRootElement
public class Dept {
在<mvc:annotation-driven/>标签中指定 content-negotation-manager
<mvc:annotation-driven
content-negotiation-manager="contentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean"/>
测试类:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/json")
public class JsonController {
@RequestMapping("/get ")
@ResponseBody//会自动将返回值转换成 json
public Dept getJson() {
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId(1);
dept.setName("张三");
return dept;
}
}
测试结果:
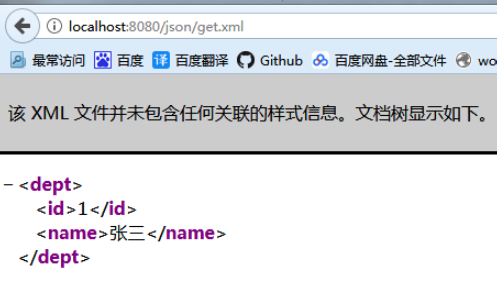

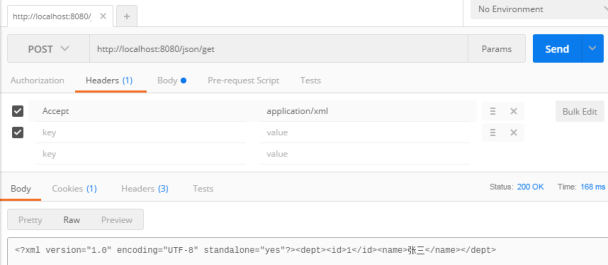
3.2 实现 RESTFUL
@RestController//相当于本类中所有的方法都加了@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class RestTestController {
//通过 method 限制请求的方式
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod. GET )
public Dept getDept(@PathVariable Integer id) {
//模拟从数据库中查出一条数据
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId(id);
dept.setName("张三");
return dept;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod. POST )
public Dept addDept(Dept dept) {
//模拟插入数据后生成主键
dept.setId(1);
System. out .println(dept.getName());
return dept;
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod. PUT , consumes = "application/json")
public Dept updateDept(@RequestBody Dept dept) {
System. out .println(dept.getName());
//执行修改的业务略
dept.setName("修改");//模拟修改名字
return dept;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod. DELETE )
public String deleteDept(@PathVariable Integer id) {
//执行删除的业务略
System. out .println(id);
return "删除成功";
}
}
通过 postman 可以测试请求(ajax 方式无法测试 PUT 和 DELETE)。测试 put 的时候,请求的 body 设置为 raw,Headers 的 ContentType=application/json,否则会报 415:
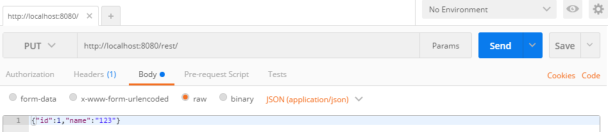
注意类名上方的@RestController,相当于在类中每个方法上都添加了@ReponseBody。deleteDept 方法返回了一句 String 类型的提示信息,默认的 String 类型的返回值,编码是ISO-8859-1,中文会乱码,解决方案是在配置文件中修改编码:
修改<mvc:annotation-driven>节点,添加<mvc:message-converters>
<mvc:annotation-driven
content-negotiation-manager="contentNegotiationManagerFactoryBean">
<!--String 返回值默认编码是 ISO-8859-1,需要-->
<mvc:message-converters>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter">
<constructor-arg value="UTF-8" />
</bean>
</mvc:message-converters>
</mvc:annotation-driven>
4 HttpEntity
HttpEntity 和@RequestBody 和@ResponseBody 类似,除了可以得到 request 和 response的 body 以外,还可以操作 header。
@RequestMapping("/entity.html")
public ResponseEntity<Dept> getEntity(RequestEntity<Dept> requestEntity) {
//获取请求头
String requestHeader = requestEntity.getHeaders().getFirst("MyRequestHeader");
System. out .println(requestHeader);
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setId(1);
dept.setName("张三");
HttpHeaders responseHeaders = new HttpHeaders();//创建响应头
responseHeaders.set("MyResponseHeader", "MyValue");//自定义响应头
//响应对象
ResponseEntity<Dept> responseEntity =
new ResponseEntity<>(dept, responseHeaders, HttpStatus. OK );
return responseEntity;
}
测试的页面:
<input type="button" onclick=" testEntity ()" value="测试 HttpEntity"/>
<script type="text/javascript">
function testEntity (){
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "/json/entity.html",
headers:{"MyRequestHeader":"abc"},
success: function(data, status, xhr){//xhr 可以看到响应的头
alert(data.id);
alert(status);
alert("Header="+xhr.getResponseHeader("MyResponseHeader"));
},
error: function(data, status, xhr){
alert(data.id);
alert(status);
alert("Header="+xhr.getResponseHeader("MyResponseHeader"));
}
});
}
</script>
springMVC整理03--处理数据模型 & 试图解析器 & @ResponseBody & HttpEntity的更多相关文章
- springMVC源码分析--RequestParamMethodArgumentResolver参数解析器(三)
之前两篇博客springMVC源码分析--HandlerMethodArgumentResolver参数解析器(一)和springMVC源码解析--HandlerMethodArgumentResol ...
- SpringMVC听课笔记(六:视图和试图解析器)
1.spring mvc解析视图 2. 视图和视图解析器 3. 视图 4.常用的视图类 5.视图解析器 1) 2) 3) 4)JSTL 需要注意的是,配置了mvc:view-controller,为 ...
- springMVC源码分析--ViewResolver视图解析器(一)
SpringMVC用于处理视图最重要的两个接口是ViewResolver和View.ViewResolver的主要作用是把一个逻辑上的视图名称解析为一个真正的视图,SpringMVC中用于把View对 ...
- springMVC源码分析--HandlerMethodArgumentResolver参数解析器(一)
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver是用来为处理器解析参数的,主要用在HandlerMethod中,每个Resolver对应一种类型的参数,其实现类特别的多. HandlerMe ...
- SSM-SpringMVC-11:SpringMVC中ParameterMethodNameResolver参数方法名称解析器
------------吾亦无他,唯手熟尔,谦卑若愚,好学若饥------------- 或许曾经的我们也见过一种方式http://localhost:8080/项目名/后台servlet?actio ...
- SSM-SpringMVC-10:SpringMVC中PropertiesMethodNameResolver属性方法名称解析器
------------吾亦无他,唯手熟尔,谦卑若愚,好学若饥------------- 上次的以继承MultiActionController可以实现一个处理器中多个处理方法,但是局限出来了,他们的 ...
- springMVC整理04--文件上传 & 拦截器 & 异常处理
1. 文件上传 SpringMVC 的文件上传非常简便,首先导入文件上传依赖的 jar: <!-- 文件上传所依赖的 jar 包 --> <dependency> <g ...
- SpringMVC系列(七)视图解析器和视图
在springmvc.xml里面配置视图解析器 <!-- 配置视图解析器: 如何把 handler 方法返回值解析为实际的物理视图 --> <bean class="org ...
- SpringMVC源码阅读:视图解析器
1.前言 SpringMVC是目前J2EE平台的主流Web框架,不熟悉的园友可以看SpringMVC源码阅读入门,它交代了SpringMVC的基础知识和源码阅读的技巧 本文将通过源码(基于Spring ...
随机推荐
- List,DataTable实现行转列的通用方案
最近在做报表统计方面的需求,涉及到行转列报表.根据以往经验使用SQL可以比较容易完成,这次决定挑战一下直接通过代码方式完成行转列.期间遇到几个问题和用到的新知识这里整理记录一下. 阅读目录 问题介绍 ...
- 跨界 - Omi 发布多端统一框架 Omip 打通小程序与 Web
Omip 今天,Omi 不仅仅可以开发桌面 Web.移动 H5,还可以直接开发小程序!直接开发小程序!直接开发小程序! Github Omi 简介 Omi 框架是微信支付线研发部研发的下一代前端框架, ...
- H5 36-背景定位属性
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- D2. Great Vova Wall (Version 2)
l链接 [https://codeforces.com/contest/1092/problem/D2] 题意 和D1一样只是不能竖直放了 分析 水平放的话,就只可能是相邻等时才可以,而且你会发现 只 ...
- Survey项目总结
1.Ioc深入理解 Inverse of control org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.SchedulerFactoryBean org.mybatis. ...
- threading模块,python下的多线程
一.GIL全局解释器锁 In CPython, the global interpreter lock, or GIL, is a mutex that prevents multiple nativ ...
- PHP导出CSV文件出现乱码的解决方法
在做项目时碰到使用外语的情况下,我们就会使用UTF-8编码.但是,在用PHP导出CSV文件时,如果写入的数据是使用UTF-8编码的日语.韩语之类的外文,就会出现乱码. 要解决PHP生成CSV文件的乱码 ...
- 学习笔记:filter_var()函数
PHP 过滤器用于对来自非安全来源的数据(比如用户输入)进行验证和过滤 filter_var() 函数通过指定的过滤器过滤变量. 如果成功,则返回已过滤的数据,如果失败,则返回 false. 语法 f ...
- 【学亮IT手记】MySql行列转换案例
create table score( name ), math int, english int ); ,); ,); ,); ,); SHOW tables; SELECT * from scor ...
- SpringMVC+Spring+Mybatis+AngularJS 多规格保存示例代码
insert时拿到最新增加的id值 绑定参数 js 实体类 Service实现类 Controller
