利用jieba,word2vec,LR进行搜狐新闻文本分类
一、简介
1)jieba
中文叫做结巴,是一款中文分词工具,https://github.com/fxsjy/jieba
2)word2vec
单词向量化工具,https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/word2vec.html
3)LR
LogisticRegression中文叫做逻辑回归模型,是一种基础、常用的分类方法
二、步骤
0)建立jupyter notebook
桌面新建名字为基于word2vec的文档分类的文件夹,并进入该文件夹,按住shift,鼠标点击右键,然后选择在此处打开命令窗口,然后在dos下输入:jupyter notebook
新建一文件:word2vecTest.ipynb
1)数据准备
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1mR87V40bUtWgUBIoqn4lOw 密码:lqe4
训练集共有24000条样本,12个分类,每个分类2000条样本。
测试集共有12000条样本,12个分类,每个分类1000条样本。
下载并解压到基于word2vec的文档分类文件夹内:
查看数据发现文件分两列:
import pandas as pd
train_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_train.txt', sep='\t', header=None)
train_df.head()

查看train每个分类的名字以及样本数量:
for name, group in train_df.groupby(0):
print(name,'\t', len(group)) #或者通过columns来查看
train_df.columns = ['Subject', 'Content']
train_df['Subject'].value_counts().sort_index()

同样的方法查看test每个分类的名字以及样本数量:
test_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_test.txt', sep='\t', header=None)
for name, group in test_df.groupby(0):
print(name, '\t', len(group))

关于groupby函数,我们通过查看name和group加以理解(变量group是一个GroupBy对象,它实际上还没有进行任何计算):
for name, group in df_train.groupby(0):
print(name)
print(group)

其中科技即打印出来的name,后面的内容即group对象内容,包含两列,第一列为科技,第二列为内容(注意:该train数据集包含了12个分类,这里只是展示了name为科技的图片,其他name结构类似)
2)分词
安装jieba:pip install jieba
对训练集的24000条样本循环遍历,使用jieba库的cut方法获得分词列表赋值给变量cutWords。
判断分词是否为停顿词,如果不为停顿词,则添加进变量cutWords中,查看一下stopwords.txt文件:

从上我们发现:这些停顿词语都是没用用的词语,对我们文本分类没什么作用,所以在分词的时候,将其从分词列表中剔除
import jieba, time
train_df.columns = ['分类', '文章']
#stopword_list = [k.strip() for k in open('stopwords.txt', encoding='utf-8').readlines() if k.strip() != '']
#上面的语句不建议这么写,因为readlines()是一下子将所有内容读入内存,如果文件过大,会很耗内存,建议这么写
stopword_list = [k.strip() for k in open('stopwords.txt', encoding='utf-8') if k.strip() != ''] cutWords_list = [] i = 0
startTime = time.time()
for article in train_df['文章']:
cutWords = [k for k in jieba.cut(article) if k not in stopword_list]
i += 1
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('前%d篇文章分词共花费%.2f秒' % (i, time.time() - startTime))
cutWords_list.append(cutWords)
本人电脑配置低(在linux下速度很快,本人用ubuntu,前5000篇文章分词共花费373.56秒,快了近三分之二),用时:

然后将分词结果保存为本地文件cutWords_list.txt,代码如下:
with open('cutWords_list.txt', 'w') as file:
for cutWords in cutWords_list:
file.write(' '.join(cutWords) + '\n')
为了节约时间,将cutWords_list.txt保存到本地,链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1zQiiJGp3helJraT3Sfxv5w 提取码:g6c7
载入分词文件:
with open('cutWords_list.txt') as file:
cutWords_list = [ k.split() for k in file ]
查看分词结果文件:cutWords_list.txt,可以看出中文分词工具jieba分词效果还不错:

3)word2vec模型
安装命令:pip install gensim
调用gensim.models.word2vec库中的LineSentence方法实例化行模型对象(为避免warning信息输出,导入warning 模块):
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
from gensim.models import Word2Vec
word2vec_model = Word2Vec(cutWords_list, size=100, iter=10, min_count=20)
sentences:可以是一个list,对于大语料集,建议使用BrownCorpus,Text8Corpus或lineSentence构建
size:是指特征向量的维度,默认为100。大的size需要更多的训练数据,但是效果会更好,推荐值为几十到几百
min_count:可以对字典做截断,词频少于min_count次数的单词会被丢弃掉, 默认值为5
调用Word2Vec模型对象的wv.most_similar方法查看与摄影含义最相近的词
wv.most_similar方法有2个参数,第1个参数是要搜索的词,第2个关键字参数topn数据类型为正整数,是指需要列出多少个最相关的词汇,默认为10,即列出10个最相关的词汇
wv.most_similar方法返回值的数据类型为列表,列表中的每个元素的数据类型为元组,元组有2个元素,第1个元素为相关词汇,第2个元素为相关程度,数据类型为浮点型
word2vec_model.wv.most_similar('摄影')

wv.most_similar方法使用positive和negative这2个关键字参数的简单示例。查看女人+先生-男人的结果,代码如下:
word2vec_model.most_similar(positive=['女人', '先生'], negative=['男人'], topn=1)

查看两个词的相关性,如下图所示:
word2vec_model.similarity('男人', '女人')
word2vec_model.similarity('摄影', '摄像')

保存Word2Vec模型为word2vec_model.w2v文件,代码如下:
word2vec_model.save( 'word2vec_model.w2v' )
4)特征工程
对于每一篇文章,获取文章的每一个分词在word2vec模型的相关性向量。然后把一篇文章的所有分词在word2vec模型中的相关性向量求和取平均数,即此篇文章在word2vec模型中的相关性向量(用一篇文章分词向量的平均数作为该文章在模型中的相关性向量)
实例化Word2Vec对象时,关键字参数size定义为100,则相关性矩阵都为100维
getVector函数获取每个文章的词向量,传入2个参数,第1个参数是每篇文章分词的结果,第2个参数是word2vec模型对象
每当完成1000篇文章词向量转换的时候,打印花费时间
最终将24000篇文章的词向量赋值给变量X,即X为特征矩阵
对比文章转换为相关性向量的4种方法花费时间。为了节省时间,只对比前5000篇文章转换为相关性向量的花费时间
4.1 ) 第1种方法,用for循环常规计算
def getVector_v1(cutWords, word2vec_model):
count = 0
article_vector = np.zeros( word2vec_model.layer1_size )
for cutWord in cutWords:
if cutWord in word2vec_model:
article_vector += word2vec_model[cutWord]
count += 1 return article_vector / count startTime = time.time()
vector_list = []
i = 0
for cutWords in cutWords_list[:5000]:
i += 1
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('前%d篇文章形成词向量花费%.2f秒' % (i, time.time() - startTime))
vector_list.append( getVector_v1(cutWords, word2vec_model) )
X = np.array(vector_list)
print('Total Time You Need To Get X:%.2f秒' % (time.time() - startTime) )

4.2)第2种方法,用pandas的mean方法计算
import time
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def getVector_v2(cutWords, word2vec_model):
vector_list = [ word2vec_model[k] for k in cutWords if k in word2vec_model]
vector_df = pd.DataFrame(vector_list)
cutWord_vector = vector_df.mean(axis=0).values
return cutWord_vector startTime = time.time()
vector_list = []
i = 0
for cutWords in cutWords_list[:5000]:
i += 1
if i % 1000 ==0:
print('前%d篇文章形成词向量花费%.2f秒' %(i, time.time()-startTime))
vector_list.append( getVector_v2(cutWords, word2vec_model) )
X = np.array(vector_list)
print('Total Time You Need To Get X:%.2f秒' % (time.time() - startTime) )

4.3)用numpy的mean方法计算
import time
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def getVector_v2(cutWords, word2vec_model):
vector_list = [ word2vec_model[k] for k in cutWords if k in word2vec_model]
vector_df = pd.DataFrame(vector_list)
cutWord_vector = vector_df.mean(axis=0).values
return cutWord_vector startTime = time.time()
vector_list = []
i = 0
for cutWords in cutWords_list[:5000]:
i += 1
if i % 1000 ==0:
print('前%d篇文章形成词向量花费%.2f秒' %(i, time.time()-startTime)) vector_list.append( getVector_v2(cutWords, word2vec_model) )
X = np.array(vector_list)
print('Total Time You Need To Get X:%.2f秒' % (time.time() - startTime) )

4.4)第4种方法,用numpy的add、divide方法计算
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd def getVector_v4(cutWords, word2vec_model):
i = 0
index2word_set = set(word2vec_model.wv.index2word)
article_vector = np.zeros((word2vec_model.layer1_size))
for cutWord in cutWords:
if cutWord in index2word_set:
article_vector = np.add(article_vector, word2vec_model.wv[cutWord])
i += 1
cutWord_vector = np.divide(article_vector, i)
return cutWord_vector startTime = time.time()
vector_list = []
i = 0
for cutWords in cutWords_list[:5000]:
i += 1
if i % 1000 == 0:
print('前%d篇文章形成词向量花费%.2f秒' %(i, time.time()-startTime)) vector_list.append( getVector_v4(cutWords, word2vec_model) ) X = np.array(vector_list)
print('Total Time You Need To Get X:%.2f秒' % (time.time() - startTime) )

因为形成特征矩阵的花费时间较长,为了避免以后重复花费时间,把特征矩阵保存为文件。使用ndarray对象的dump方法,需要1个参数,数据类型为字符串,为保存文件的文件名,加载数据也很方便,代码如下(保存X之前要用方法四对所有cutWords_list元素进行处理,5000只是用来比较四种方法快慢):
X.dump('articles_vector.txt')
#加载数据可以用下面的代码
X = np.load('articles_vector.txt')
5)模型训练、模型评估
1)标签编码
调用sklearn.preprocessing库的LabelEncoder方法对文章分类做标签编码
import pandas as pd from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
train_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_train.txt', sep='\t', header=None)
train_df.columns = ['分类', '文章']
labelEncoder = LabelEncoder()
y = labelEncoder.fit_transform(train_df['分类'])
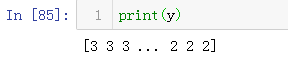
2)LR模型
调用sklearn.linear_model库的LogisticRegression方法实例化模型对象
调用sklearn.model_selection库的train_test_split方法划分训练集和测试集
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_X, test_X, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0) logistic_model = LogisticRegression()
logistic_model.fit(train_X, train_y)
logistic_model.score(test_X, test_y)

3)保存模型
调用sklearn.externals库中的joblib方法保存模型为logistic.model文件
模型持久化官方文档示例:http://sklearn.apachecn.org/cn/0.19.0/modules/model_persistence.html
from sklearn.externals import joblib
joblib.dump(logistic_model, 'logistic.model') #加载模型
logistic_model = joblib.load('logistic.model')
4)交叉验证
调用sklearn.model_selection库的ShuffleSplit方法实例化交叉验证对象
调用sklearn.model_selection库的cross_val_score方法获得交叉验证每一次的得分
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
cv_split = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=5, train_size=0.7, test_size=0.2)
logistic_model = LogisticRegression()
score_ndarray = cross_val_score(logistic_model, X, y, cv=cv_split)
print(score_ndarray)
print(score_ndarray.mean())
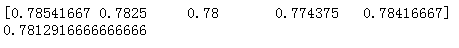
6)模型测试
调用sklearn.externals库的joblib对象的load方法加载模型赋值给变量logistic_model
调用DataFrame对象的groupby方法对每个分类分组,从而每种文章类别的分类准确性
调用自定义的getVector方法将文章转换为相关性向量
自定义getVectorMatrix方法获得测试集的特征矩阵
调用StandardScaler对象的transform方法将预测标签做标签编码,从而获得预测目标值
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import jieba
def getVectorMatrix(article_series):
return np.array([getVector_v4(jieba.cut(k), word2vec_model) for k in article_series]) logistic_model = joblib.load('logistic.model') test_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_test.txt', sep='\t', header=None)
test_df.columns = ['分类', '文章']
for name, group in test_df.groupby('分类'):
featureMatrix = getVectorMatrix(group['文章'])
target = labelEncoder.transform(group['分类'])
print(name, logistic_model.score(featureMatrix, target))
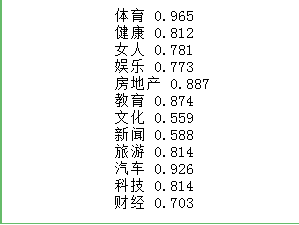
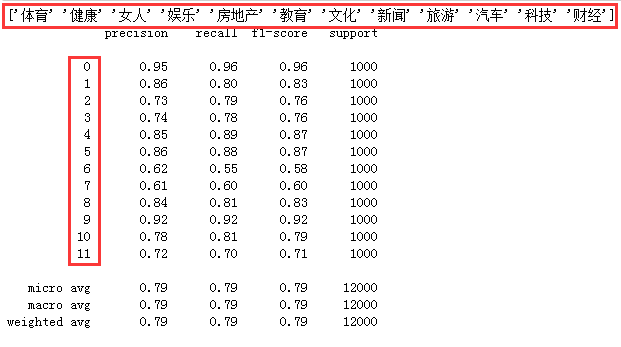
我们来看看各个分类的精确率和召回率:
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
test_df = pd.read_csv('sohu_test.txt', sep='\t', header=None)
test_df.columns = ['分类', '文章']
test_label = labelEncoder.transform(test_df['分类'])
y_pred = logistic_model.predict( getVectorMatrix(test_df['文章']) )
print(labelEncoder.inverse_transform([[x] for x in range(12)]))
print(classification_report(test_label, y_pred))
7)结论
word2vec模型应用的第1个小型项目,训练集数据共有24000条,测试集数据共有12000条。
经过交叉验证,模型平均得分为0.78左右。
测试集的验证效果中,体育、教育、健康、旅游、汽车、科技、房地产这7个分类得分较高,即容易被正确分类。
女人、娱乐、新闻、文化、财经这5个分类得分较低,即难以被正确分类。
想要学习如何提高文档分类的准确率,请查看我的另外一篇文章《基于jieba,TfidfVectorizer,LogisticRegression进行搜狐新闻文本分类》
8)致谢
本文参考简书:https://www.jianshu.com/p/96b983784dae
感谢作者的详细过程,再次感谢!
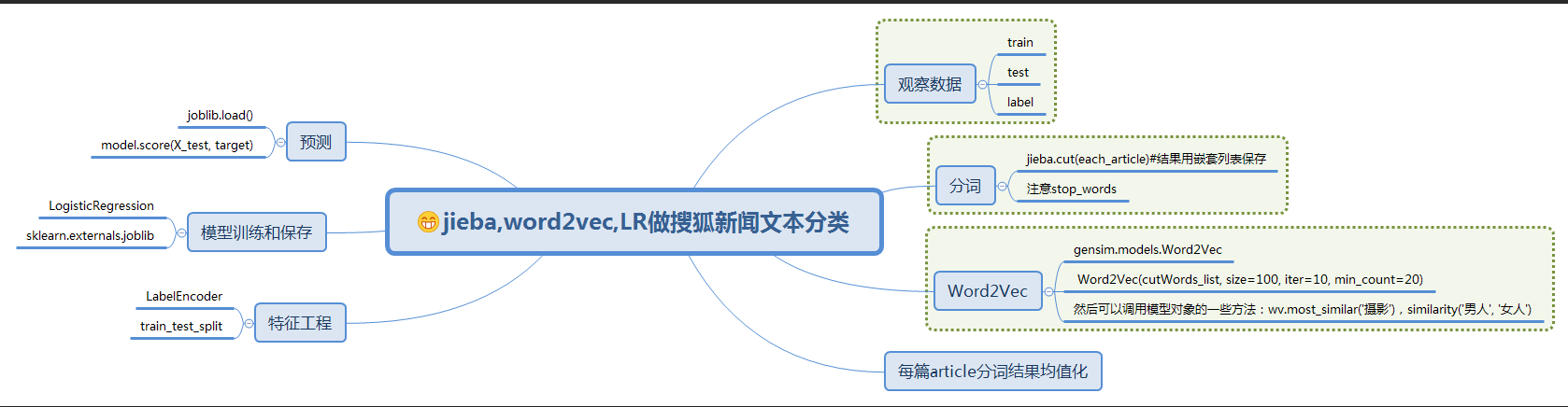
9)流程图
10)感兴趣的可以查看利用TfIdf进行向量化后的新闻文本分类,效果有一定的提升
利用jieba,word2vec,LR进行搜狐新闻文本分类的更多相关文章
- 基于jieba,TfidfVectorizer,LogisticRegression进行搜狐新闻文本分类
一.简介 此文是对利用jieba,word2vec,LR进行搜狐新闻文本分类的准确性的提升,数据集和分词过程一样,这里就不在叙述,读者可参考前面的处理过程 经过jieba分词,产生24000条分词结果 ...
- 利用朴素贝叶斯分类算法对搜狐新闻进行分类(python)
数据来源 https://www.sogou.com/labs/resource/cs.php介绍:来自搜狐新闻2012年6月—7月期间国内,国际,体育,社会,娱乐等18个频道的新闻数据,提供URL ...
- sohu_news搜狐新闻类型分类
数据获取 数据是从搜狐新闻开放的新闻xml数据,经过一系列的处理之后,生成的一个excel文件 该xml文件的处理有单独的处理过程,就是用pandas处理,该过程在此省略 import numpy a ...
- 使用百度NLP接口对搜狐新闻做分类
一.简介 本文主要是要利用百度提供的NLP接口对搜狐的新闻做分类,百度对NLP接口有提供免费的额度可以拿来练习,主要是利用了NLP里面有个文章分类的功能,可以顺便测试看看百度NLP分类做的准不准.详细 ...
- 利用搜狐新闻语料库训练100维的word2vec——使用python中的gensim模块
关于word2vec的原理知识参考文章https://www.cnblogs.com/Micang/p/10235783.html 语料数据来自搜狐新闻2012年6月—7月期间国内,国际,体育,社会, ...
- 【NLP】3000篇搜狐新闻语料数据预处理器的python实现
3000篇搜狐新闻语料数据预处理器的python实现 白宁超 2017年5月5日17:20:04 摘要: 关于自然语言处理模型训练亦或是数据挖掘.文本处理等等,均离不开数据清洗,数据预处理的工作.这里 ...
- 搜狗输入法弹出搜狐新闻的解决办法(sohunews.exe)
狗输入法弹出搜狐新闻的解决办法(sohunews.exe) 1.找到搜狗输入法的安装目录(一般是C:\program files\sougou input\版本号\)2.右键点击sohunews.ex ...
- 搜狐新闻APP是如何使用HUAWEI DevEco IDE快速集成HUAWEI HiAI Engine
6月12日,搜狐新闻APP最新版本在华为应用市场正式上线啦! 那么,这一版本的搜狐新闻APP有什么亮点呢? 先抛个图,来直接感受下—— 模糊图片,瞬间清晰! 效果杠杠的吧. 而藏在这项神操作背后的 ...
- 世界更清晰,搜狐新闻客户端集成HUAWEI HiAI 亮相荣耀Play发布会!
6月6日,搭载有“很吓人”技术的荣耀Play正式发布,来自各个领域的大咖纷纷为新机搭载的惊艳技术站台打call,其中,搜狐公司董事局主席兼首席执行官张朝阳揭秘:华为和搜狐新闻客户端在硬件AI方面做 ...
随机推荐
- mysql严格模式的开启、关闭
关于mysql严格模式的开启.关闭 由于项目中对一些默认值设置问题,以及种种原因,mysql数据库需要使用非严格模式开发(mysql最近的版本默认是开启严格模式的). linux下mysql服务下操作 ...
- import logging报错raise notimplementederror 'emit must be implemented ' ^
在导入logging的时候出现这个错误 大概看了一下,就是因为python内置里面已经有logging这个模块,所以不需要再安装 在site-packages里面找到关于logging的文件,删掉 重 ...
- 【XSY2745】装饰地板 状压DP 特征多项式
题目大意 你有\(s_1\)种\(1\times 2\)的地砖,\(s_2\)种\(2\times 1\)的地砖. 记铺满\(m\times n\)的地板的方案数为\(f(m,n)\). 给你\(m, ...
- MT【293】拐点处切线
(2018浙江高考压轴题)已知函数$f(x)=\sqrt{x}-\ln x.$(2)若$a\le 3-4\ln 2,$证明:对于任意$k>0$,直线$y=kx+a$ 与曲线$y=f(x)$有唯一 ...
- 【正睿oi省选十连测】第一场
四小时写了两个暴力??自闭 [原来这就是神仙们的分量Orz rank 56/75 可以说是无比垃圾了 下周目标:进步十名?[大雾 T1 题意:有n个点的图 点有点权Ai 也有点权Bi = A_1 + ...
- LGP2801 教主的魔法
题目链接 : P2801 教主的魔法 这是第一次A分块的题 就是模板题了 每个块内排序 每个整块仅需维护整块的修改量 询问操作: 对于边缘块 直接暴力找在[l, r]内 且比给定值大的有几个 对于整块 ...
- zabbix agent 自定义 UserParameter
有时候我们想让被监控端执行一个zabbix没有预定义的检测,zabbix的用户自定义参数功能提供了这个方法.我们可以在客户端配置文件zabbix_angentd.conf里面配置UserParamet ...
- 如何将Drawable转为Bitmap?
本文选自StackOverflow(简称:SOF)精选问答汇总系列文章之一,本系列文章将为读者分享国外最优质的精彩问与答,供读者学习和了解国外最新技术.本文将讲解如何将Drawable转为Bitmap ...
- 转----ui输入测试数据
jin'tHackChecker黑测工作室 - 专注于软件安全测试技术研究!(www.AutomationQA.com)常用安全测试用例 建立整体的威胁模型,测试溢出漏洞.信息泄漏.错误处理.SQL ...
- ELK部署详解--kibana
kibana.yml # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use.#端口server ...
