Leetcode | N-Queens I & II
N-Queens I
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
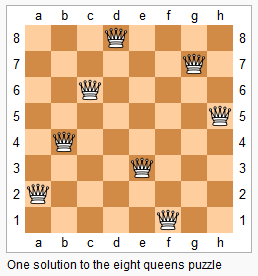
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where 'Q' and '.' both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
For example,
There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle:
[
[".Q..", // Solution 1
"...Q",
"Q...",
"..Q."], ["..Q.", // Solution 2
"Q...",
"...Q",
".Q.."]
]
Wiki:任两个皇后都不能处于同一条横行、纵行或斜线上。八皇后问题可以推广为更一般的n皇后摆放问题:这时棋盘的大小变为n×n,而皇后个数也变成n。当且仅当 n = 1 或 n ≥ 4 时问题有解。
回溯,用了一个数组col[i]来表示第i列是不是已经放了queen。
对于(row1, col1)和(row2, col2)这两个位置,如果它们在同一对角线上,那么有abs(row1-row2) = abs(col1-col2)。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string> > solveNQueens(int n) {
if (n == || n == ) {
return ret;
}
vector<string> sol(n, string(n, '.'));
vector<bool> col(n, false);
bt(n, , col, sol);
return ret;
}
void bt(int n, int r, vector<bool> &col, vector<string> &sol) {
if (r >= n) {
ret.push_back(sol);
return;
}
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
if (col[i]) continue;
bool diag = false;
for (int j = r - ; j >= ; --j) {
for (int m = ; m < n; ++m) {
if (abs(j - r) == abs(m - i) && sol[j][m] == 'Q') {
diag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if (!diag) {
col[i] = true;
sol[r][i] = 'Q';
bt(n, r + , col, sol);
col[i] = false;
sol[r][i] = '.';
}
}
}
private:
vector<vector<string> > ret;
};
N-Queens II
Follow up for N-Queens problem.
Now, instead outputting board configurations, return the total number of distinct solutions.
和N-Queens I 类似,同样需要回溯。
前面回溯的时候需要用到一个额外的数组col[i],而且用到了sol这个数组来判断对角线元素。
网上的解决方案更巧妙些,用到一个数组sol[i],存的是第i行可解的列号。
当处理到第r行时,检查前r-1行,看sol[0...r-1]有没有等于i的,有就代表了该列已经有queen了。然后再检查对角线上的。
class Solution {
public:
int totalNQueens(int n) {
if (n == || n == ) {
return ;
}
vector<int> sol(n, -);
total = ;
bt(n, , sol);
return total;
}
void bt(int n, int r, vector<int> &sol) {
if (r >= n) {
total++;
return;
}
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
bool valid = true;
for (int j = r - ; j >= ; --j) {
for (int m = ; m < n; ++m) {
if (sol[j] == i || abs(j - r) == abs(sol[j] - i)) {
valid = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (valid) {
int t = sol[r];
sol[r] = i;
bt(n, r + , sol);
sol[r] = t;
}
}
}
private:
int total;
};
第三次写,在返回值统计。至此leetcode三遍刷完。
class Solution {
public:
int totalNQueens(int n) {
if (n <= ) return ;
vector<int> colSetted(n, -);
return recurse(n, , colSetted);
}
int recurse(int n, int row, vector<int> &colSetted) {
if (row >= n) {
return ;
}
int count = ;
for (int i = ; i < n; ++i) {
if (colSetted[i] == -) {
bool couldSet = true;
for (int j = ; j < n; ++j) {
if (colSetted[j] != - && abs(row - colSetted[j]) == abs(i - j)) {
couldSet = false;
break;
}
}
if (couldSet) {
colSetted[i] = row;
count += recurse(n, row + , colSetted);
colSetted[i] = -;
}
}
}
return count;
}
};
Leetcode | N-Queens I & II的更多相关文章
- LeetCode Single Number I / II / III
[1]LeetCode 136 Single Number 题意:奇数个数,其中除了一个数只出现一次外,其他数都是成对出现,比如1,2,2,3,3...,求出该单个数. 解法:容易想到异或的性质,两个 ...
- [array] leetcode - 40. Combination Sum II - Medium
leetcode - 40. Combination Sum II - Medium descrition Given a collection of candidate numbers (C) an ...
- LeetCode 137. Single Number II(只出现一次的数字 II)
LeetCode 137. Single Number II(只出现一次的数字 II)
- LeetCode:路径总和II【113】
LeetCode:路径总和II[113] 题目描述 给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,找到所有从根节点到叶子节点路径总和等于给定目标和的路径. 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点. 示例:给定如下二叉树, ...
- LeetCode:组合总数II【40】
LeetCode:组合总数II[40] 题目描述 给定一个数组 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合. candi ...
- [Leetcode] n queens ii n皇后问题
Follow up for N-Queens problem. Now, instead outputting board configurations, return the total numbe ...
- [Leetcode][Python]52: N-Queens II
# -*- coding: utf8 -*-'''__author__ = 'dabay.wang@gmail.com' 52: N-Queens IIhttps://oj.leetcode.com/ ...
- [LeetCode] Number of Islands II 岛屿的数量之二
A 2d grid map of m rows and n columns is initially filled with water. We may perform an addLand oper ...
- LeetCode:Word Ladder I II
其他LeetCode题目欢迎访问:LeetCode结题报告索引 LeetCode:Word Ladder Given two words (start and end), and a dictiona ...
- LeetCode:Path Sum I II
LeetCode:Path Sum Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such ...
随机推荐
- Java中成员变量和局部变量的区别
java面向对象过程中,最基本的两类变量就是成员变量和局部变量 成员变量是写在类中并且写在方法外部,一般写在每个类的头部,用于初始化或者方法操作,作用域是整个类被实例化到被销毁,中间变量都可以被外部方 ...
- python基础——函数的参数
python基础——函数的参数 定义函数的时候,我们把参数的名字和位置确定下来,函数的接口定义就完成了.对于函数的调用者来说,只需要知道如何传递正确的参数,以及函数将返回什么样的值就够了,函数内部的复 ...
- Android Studio安装与配置
谷歌已经停止支持eclipse开发android了,转向android studio是大势所趋,笔者由于电脑配置的原因, 以前迟迟不愿意向android studio,现如今因为开始学习materia ...
- C#控制管理VisualSVN Server 分类: C# 2014-05-29 15:51 796人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
VisualSVN Server可以用WMI接口管理(Windows Management Instrumentation). VisualSVN Server安装的计算机中,位于%VISUALSVN ...
- phpcms分页使用
#pages { padding: 14px 10px; font-family: 宋体; } .text-c { text-align: center; } #pages span { displa ...
- JAVA反射机制(转)
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法: 对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性: 这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为java语言 ...
- Codeforces Gym 100513G G. FacePalm Accounting
G. FacePalm Accounting Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/gym/100513 ...
- Hark的数据结构与算法练习之鸡尾酒排序
算法说明 鸡尾酒排序又叫定向冒泡排序,鸡尾酒搅拌排序,搅拌排序,涟漪排序,回来排序,快乐小时排序. 鸡尾酒排序是交换排序的一种,它是冒泡排序的一个轻微的变种.冒泡是从低向高比较排序,鸡尾酒从低向高,从 ...
- Spring的自定义标签
当Spring拿到一个元素时首先要做的是根据命名空间进行解析,如果是默认的命名空间,则使用parseDefaultElement方法进行元素解析,否则使用parseCustom Element方法进行 ...
- js:数据结构笔记10--图和图算法
图:是由边和定点的集合组成: 按照图的定点对是否有序可以分为:有向图和无向图: 路径:所有顶点都由边连接构成:路径长度为第一个定点到最后一个顶点之间的数量: 环:指向自身的顶点,长度为0:圈:至 ...
