LeetCode 周赛 336,多少人直接 CV?
本文已收录到 AndroidFamily,技术和职场问题,请关注公众号 [彭旭锐] 提问。
大家好,我是小彭。
今天早上是 LeetCode 第 336 场周赛,你参加了吗?这场周赛整体质量比较高,但是最后一题是老题,CV 能过。但是输入数据范围被降低了,这操作也是没谁了。

2587. 统计范围内的元音字符串数(Easy)
题目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-vowel-strings-in-range/
题目描述
给你一个下标从 0 开始的字符串数组 words 和两个整数:left 和 right 。
如果字符串以元音字母开头并以元音字母结尾,那么该字符串就是一个 元音字符串 ,其中元音字母是 'a'、'e'、'i'、'o'、'u' 。
返回 words[i] 是元音字符串的数目,其中 i 在闭区间 [left, right] 内。

题解(模拟)
简单模拟题。
class Solution {
fun vowelStrings(words: Array<String>, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
val set = hashSetOf('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u')
var count = 0
for (index in left..right) {
val word = words[index]
if (set.contains(word[0]) && set.contains(word[word.length - 1])) count++
}
return count
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$
- 空间复杂度:$O(1)$
2588. 重排数组以得到最大前缀分数(Medium)
题目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/rearrange-array-to-maximize-prefix-score/
题目描述
给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums 。你可以将 nums 中的元素按 任意顺序 重排(包括给定顺序)。
令 prefix 为一个数组,它包含了 nums 重新排列后的前缀和。换句话说,prefix[i] 是 nums 重新排列后下标从 0 到 i 的元素之和。nums 的 分数 是 prefix 数组中正整数的个数。
返回可以得到的最大分数。

题解(贪心)
贪心思路:负数会降低前缀和,为了延缓前缀和变小的速度,正权值应该放在尽可能前的位置,负权值放在尽可能后的位置,即对数组降序排序。
class Solution {
fun maxScore(nums: IntArray): Int {
// 3 2 1 0 -1 -3 -3
// 3 5 6 6 5 2 -1
nums.sortDescending()
var preSum = 0L
for (index in nums.indices) {
preSum += nums[index]
if (preSum <= 0L) return index
}
return nums.size
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(nlgn + n)$ 排序加线性遍历;
- 空间复杂度:$O(lgn)$ 排序递归栈空间。
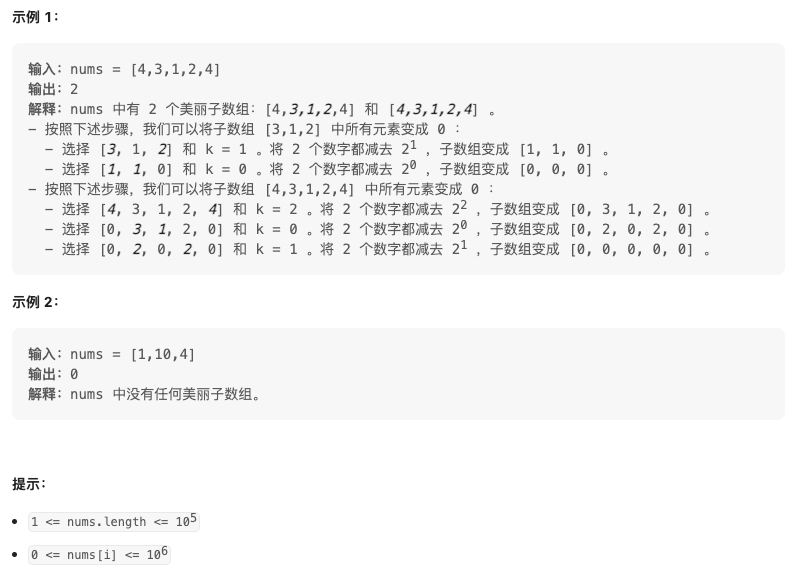
2589. 统计美丽子数组数目(Medium)
题目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-the-number-of-beautiful-subarrays/
题目描述
给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组nums 。每次操作中,你可以:
- 选择两个满足
0 <= i, j < nums.length的不同下标i和j。 - 选择一个非负整数
k,满足nums[i]和nums[j]在二进制下的第k位(下标编号从 0 开始)是1。 - 将
nums[i]和nums[j]都减去2k。
如果一个子数组内执行上述操作若干次后,该子数组可以变成一个全为 0 的数组,那么我们称它是一个 美丽 的子数组。
请你返回数组 nums 中 美丽子数组 的数目。
子数组是一个数组中一段连续 非空 的元素序列。
题解一(滑动窗口)
分析题目操作:当两个数在某一位都是 1 时,可以执行一次消除操作。因此,在满足题目要去的子数组中,所有位上 1 出现的次数要么是 0,要么是大于 0 的偶数,符合异或的性质。于是,我们可以将题目转换为求 “异或值为 0 的子数组” 个数,与以下题目类似:
朴素的解法我们考虑枚举所有子数组:
class Solution {
fun beautifulSubarrays(nums: IntArray): Long {
val n = nums.size
var count = 0L
for (left in 0 until n) {
var xorSum = 0
for (right in left until n) {
xorSum = xorSum xor nums[right]
if (xorSum == 0) count++
}
}
return count
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$ 其中 $n$ 是 $nums$ 数组的长度,在这道题中将超出时间限制;
- 空间复杂度:$O(1)$。
题解二(前缀和 + 散列表)
“和为 k 的子数组” 有 $O(n)$ 的解法:
class Solution {
fun beautifulSubarrays(nums: IntArray): Long {
val n = nums.size
var count = 0L
// xorSun - index
val xorSumMap = HashMap<Int, Int>().apply {
this[0] = 1
}
var preXorSum = 0
for (num in nums) {
preXorSum = preXorSum xor num
if (xorSumMap.containsKey(preXorSum)) {
count += xorSumMap[preXorSum]!!
}
xorSumMap[preXorSum] = xorSumMap.getOrDefault(preXorSum, 0) + 1
}
return count
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$ 线性遍历;
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$ 散列表空间。
2590. 完成所有任务的最少时间(Hard)
题目地址
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-time-to-complete-all-tasks/
题目描述
你有一台电脑,它可以 同时 运行无数个任务。给你一个二维整数数组 tasks ,其中 tasks[i] = [starti, endi, durationi] 表示第 i 个任务需要在 闭区间 时间段 [starti, endi] 内运行 durationi 个整数时间点(但不需要连续)。
当电脑需要运行任务时,你可以打开电脑,如果空闲时,你可以将电脑关闭。
请你返回完成所有任务的情况下,电脑最少需要运行多少秒。

题解一(贪心)
这道题其实是 LCP 原题:LCP 32. 批量处理任务
区间任务问题一般有按照 “开始时间” 排序或 “结束时间” 排序两种排序方法:
- 按照开始时间排序: 对于任务 task,我们无法判断应该优选选择较早点时间还是较晚的时间。
- 按照结束时间排序: 对于任务 task,如果优先选择越晚的开始时间(推迟开机),那么越有可能被后续任务覆盖。可以用反证法证明:假设推迟到最晚时间 $task_{end}$ 不是最优解,即存在非最晚时间 $task_{end - 1}$ 是最优解,那么对于下一个任务来说,如果它的开始时间晚于 $task_{end - 1}$,那么它就错过了一次开机时间,说明 $task_{end - 1}$ 不可能是最优解。
另外,由于任务的开机时间允许不连续,所以我们需要用一个额外的数组存储开机时间。在处理每个任务时,我们先讲已开始时间去掉,再将剩下的时间安排在尽可能晚的时间。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照结束时间排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
val used = BooleanArray(2001)
var time = 0
for (task in tasks) {
var count = task[2]
// 消除已开机时间
for (index in task[0]..task[1]) {
if (used[index]) count--
}
if (count <= 0) continue
time += count
// 推迟最晚开机时间
for (index in task[1] downTo task[0]) {
if (used[index]) continue
used[index] = true
if (--count == 0) break
}
}
return time
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(nlgn + nm)$ 其中 n 是任务个数,m 是任务的平均时间;
- 空间复杂度:$O(lgn + U)$ 其中 $U$ 是数据范围 2000,排序递归栈空间 + $used$ 数组空间。
题解二(朴素线段树)
回顾题解一中的 2个关键操作:
- 1、消除已开机时间: 计算 [start, end] 之间为 true 的时间点个数(等价于区间和);
- 2、推迟最晚开机时间: 逆序将 [start, end] 中最后 count 个时间点标记为 true(等价于区间更新)。
因此,我们发现题目可能存在线段树、树状数组之类优化手段:类似的区间求和问题,我们先回顾一下解决方案:
- 1、静态数组求区间和:「前缀和数组」、「树状数组」、「线段树」
- 2、频繁单点更新,求区间和:「树状数组」、「线段树」
- 3、频繁区间更新,求具体位置:「差分数组」
- 4、频繁区间更新,求区间和:「线段树 + 懒更新」
这道题涉及 “区间更新” 和 “区间求和”,所以属于线段树的覆盖范围。相对于在函数中重复传递节点所代表的区间范围(例如 update(i: int, l: int, r: int, L: int, R: int)),使用 Node 节点记录更为方便。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照结束时间排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
// 线段树
val tree = SegmentTree(2001)
for (task in tasks) {
// 消除已开机时间
val count = task[2] - tree.query(task[0], task[1])
if (count <= 0) continue
// 推迟最晚开机时间
tree.update(task[0], task[1], count)
}
// 根节点即为所有开机时间
return tree.query(1, 2000)
}
private class SegmentTree(private val n: Int) {
// 线段树节点(区间范围与区间值)
private class Node(val left: Int, val right: Int, var value: Int)
// 线段树数组
private val tree = Array<Node?>(n * 4) { null } as Array<Node>
// 左子节点索引
private val Int.left get() = 2 * this + 1
// 右子节点索引
private val Int.right get() = 2 * this + 2
init {
// 建树
buildNode(0, 0, n - 1)
}
private fun buildNode(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int) {
// 叶子节点
if (left == right) {
tree[index] = Node(left, right, 0)
return
}
val mid = (left + right) ushr 1
// 构建左子节点
buildNode(index.left, left, mid)
// 构建右子节点
buildNode(index.right, mid + 1, right)
// 合并左右子节点
tree[index] = Node(left, right, tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value)
}
// 开机(推迟到最晚时间)
fun update(left: Int, right: Int, count: Int) {
update(0, left, right, count)
}
// return:有效修改个数
private fun update(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int, count: Int): Int {
// 1、当前节点不处于区间内
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、叶子结点
if (tree[index].left == tree[index].right) {
// 开机
if (0 == tree[index].value) {
tree[index].value = 1
return 1
} else {
return 0
}
}
// 3、更新右子树(贪心思路:推迟开机)
var realUpdate = update(index.right, left, right, count)
if (count - realUpdate > 0) {
// 4、更新左子树
realUpdate += update(index.left, left, right, count - realUpdate)
}
// 5、合并左右子节点
tree[index].value = tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value
return realUpdate
}
// 查询
fun query(left: Int, right: Int): Int {
return query(0, left, right)
}
private fun query(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
// 1、当前节点不处于区间范围内
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、当前节点完全处于区间范围内
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right) return tree[index].value
// 3、合并左右子节点
return query(index.left, left, right) + query(index.right, left, right)
}
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(nlgn + U + nU + nlgU)$ 线段树单次区间和操作是 $O(lgU)$,单次区间更新是 $O(U)$。其中 $O(nlgn)$ 是排序时间,$O(U)$ 是建树时间,$O(nU)$ 是 $n$ 次区间更新,$O(nlgU)$ 是 $n$ 次区间查询;
- 空间复杂度:$O(lgn + U)$ 排序递归栈空间 + 线段树空间。
题解三(线段树 + Lazy)
朴素线段树的性能瓶颈在于:区间更新需要改动从根节点到叶子节点中所有与目标区间有交集的节点,因此单次区间更新操作的时间复杂度是 $O(n)$。
懒更新线段树的核心思想是:当一个节点代表的区间完全包含于目标区间内时,我们没有必要继续向下递归更新,而是在当前节点上标记 Lazy Tag 。只有将来更新该节点的某个子区间时,才会将懒更新 pushdown 到子区间。
class Solution {
fun findMinimumTime(tasks: Array<IntArray>): Int {
// 按照结束时间排序
Arrays.sort(tasks) { e1, e2 ->
e1[1] - e2[1]
}
// 线段树
val tree = SegmentTree(2001)
for (task in tasks) {
// 消除已开机时间
val count = task[2] - tree.query(task[0], task[1])
if (count <= 0) continue
// 推迟最晚开机时间
tree.update(task[0], task[1], count)
}
// 根节点即为所有开机时间
return tree.query(1, 2000)
}
private class SegmentTree(private val n: Int) {
// 线段树节点(区间范围与区间值)
private class Node(val left: Int, val right: Int, var value: Int, var lazy: Boolean = false)
// 线段树数组
private val tree = Array<Node?>(n * 4) { null } as Array<Node>
// 左子节点索引
private val Int.left get() = 2 * this + 1
// 右子节点索引
private val Int.right get() = 2 * this + 2
init {
// 建树
buildNode(0, 0, n - 1)
}
private fun buildNode(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int) {
// 叶子节点
if (left == right) {
tree[index] = Node(left, right, 0)
return
}
val mid = (left + right) ushr 1
// 构建左子节点
buildNode(index.left, left, mid)
// 构建右子节点
buildNode(index.right, mid + 1, right)
// 合并左右子节点
tree[index] = Node(left, right, tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value)
}
// 开机(推迟到最晚时间)
fun update(left: Int, right: Int, count: Int) {
update(0, left, right, count)
}
// return:有效修改个数
private fun update(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int, count: Int): Int {
// 1、当前节点不处于区间内
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
val size = tree[index].right - tree[index].left + 1
val unUsedSize = size - tree[index].value
if (unUsedSize == 0) return 0 // 整个区间已开机
// 2、当前节点完全处于区间范围之内
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right && unUsedSize <= count) {
// 整个区间可以改为开机
lazyUpdate(index)
return unUsedSize
}
// pushdown
if (tree[index].lazy) {
lazyUpdate(index.left)
lazyUpdate(index.right)
tree[index].lazy = false
}
// 3、更新右子树(贪心思路:推迟开机)
var realUpdate = update(index.right, left, right, count)
if (count - realUpdate > 0) {
// 4、更新左子树
realUpdate += update(index.left, left, right, count - realUpdate)
}
// 5、合并左右子节点
tree[index].value = tree[index.left].value + tree[index.right].value
return realUpdate
}
private fun lazyUpdate(index: Int) {
tree[index].value = tree[index].right - tree[index].left + 1
tree[index].lazy = true
}
// 查询
fun query(left: Int, right: Int): Int {
return query(0, left, right)
}
private fun query(index: Int, left: Int, right: Int): Int {
// 1、当前节点不处于区间范围内
if (tree[index].left > right || tree[index].right < left) return 0
// 2、当前节点完全处于区间范围内
if (tree[index].left >= left && tree[index].right <= right) return tree[index].value
// pushdown
if (tree[index].lazy) {
lazyUpdate(index.left)
lazyUpdate(index.right)
tree[index].lazy = false
}
// 3、合并左右子节点
return query(index.left, left, right) + query(index.right, left, right)
}
}
}
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(nlgn + U + nlgU)$ 线段树单次区间和操作是 $O(lgU)$,单次区间更新是 $O(lgU)$;
- 空间复杂度:$O(lgn + U)$ 排序递归栈空间 + 线段树空间。
LeetCode 周赛 336,多少人直接 CV?的更多相关文章
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-111开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 111 (题号941-944)(2019年1月19日,补充题解,主要是943题) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-111 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-71开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 71 () Contest 72 () Contest 73 (2019年1月30日模拟) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-91开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 91 (2018年10月24日,周三) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-91/ 模拟比赛情况记录:第一题柠檬摊的那题6分钟 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-121开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 121 (题号981-984)(2019年1月27日) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-121 总结:2019年2月22日 ...
- LeetCode周赛#208
本周周赛的题面风格与以往不太一样,但不要被吓着,读懂题意跟着模拟,其实会发现并不会难到哪里去. 1599. 经营摩天轮的最大利润 #模拟 题目链接 题意 摩天轮\(4\)个座舱,每个座舱最多可容纳\( ...
- 拼写单词[哈希表]----leetcode周赛150_1001
题目描述: 给你一份『词汇表』(字符串数组) words 和一张『字母表』(字符串) chars. 假如你可以用 chars 中的『字母』(字符)拼写出 words 中的某个『单词』(字符串),那么我 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-41开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 41 ()(题号) Contest 42 ()(题号) Contest 43 ()(题号) Contest 44 (2018年12月6日,周四上午)(题号653—656) 链接:htt ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-51开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 51 (2018年11月22日,周四早上)(题号681-684) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/leetcode-weekly-contest-51 ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest-81开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
Contest 81 (2018年11月8日,周四,凌晨) 链接:https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-81 比赛情况记录:结果:3/4, ranki ...
- 【Leetcode周赛】从contest1开始。(一般是10个contest写一篇文章)
注意,以前的比赛我是自己开了 virtual contest.这个阶段的目标是加快手速,思考问题的能力和 bug-free 的能力. 前面已经有了100个contest.计划是每周做三个到五个cont ...
随机推荐
- WPF中向下拉框中绑定枚举体
1.枚举绑定combox的ItemsSourceItemsSource绑定的是个集合值,要想枚举绑定ItemsSource,首先应该想到的是把枚举值变成集合. 方法一:使用资源里的ObjectData ...
- 2020年第11届蓝桥杯C/C++B组 第一轮省赛
# JJU-干干 试题 A: 跑步训练 代码: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* run this program using ...
- python 深拷贝及浅拷贝区别
深拷贝及浅拷贝区别 浅拷贝copy: 可变类型:(列表,字典,集合)copy函数对可变类型的第一层对象进行拷贝,对拷贝的对象开辟新的内存空间进行存储,不会拷贝对象内部的子对象 不可变类型:(数字,字符 ...
- mysql 的小问题
首先按下win+R 执行 services.msc 进入服务,查找到MySQL,点击停止服务,然后在控制台cmd进入本地的MySQL文件夹,我的文件名是mysql-8.0.26-winx64,进入后执 ...
- Jmeter-接口测试(二)
鉴权码获取: 1.通过接口获取 appid secret (第三方用户唯一凭证, 第三方用户唯一凭证秘钥) 2.登录之后自动生成 username,password 一.jmeter 接口关联 1. ...
- LOJ数列分块入门九题(中)
#6281. 数列分块入门 5 - 题目 - LibreOJ (loj.ac) 区间开方,区间求和题. 显然,针对区间维护开方操作很难做到,于是考虑其值的性质,显然,int范围内的值最多开方6次就会变 ...
- SVN报错:database is locked
https://blog.csdn.net/k7arm/article/details/81168416 https://www.jianshu.com/p/aa9c67fcc407
- 关于lesscss和颜色梯度(linear-gradient )的一些问题
一.什么是less? 一种 动态 样式 语言. LESS 将 CSS 赋予了动态语言的特性,如 变量, 继承,运算, 函数. LESS 既可以在 客户端 上运行 (支持IE 6+, Webkit, F ...
- Windows10常用快捷键总结
--Windows10常用快捷键总结 1. Window键: 打开或关闭|开始菜单 2. Win + A 打开操作中心 3. Win + D 显示桌面 4. Win + E 打开计算机文件管理器 5. ...
- 【转】【进程管理】Linux进程调度:调度时机
转自:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/163728119 概述: 进程切换分为自愿(voluntary)和强制(involuntary)两种.通常自愿切换是指任务由于等待某种 ...
