Fastjson 专题
https://github.com/eishay/jvm-serializers/wiki
TypeReference
1. 基础使用
在fastjson中提供了一个用于处理泛型反序列化的类TypeReference。
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
List<VO> list = JSON.parseObject("...", new TypeReference<List<VO>>() {});
如下写法有更好的性能
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
final static Type type = new TypeReference<List<VO>>() {}.getType();
List<VO> list = JSON.parseObject("...", type);
在这里例子中,通过TypeReference能够解决List中T的类型问题。
@Test
public void TestListGenerics() {
List<UserDO> userDOList = Arrays.asList(new UserDO(1L, "Name1"), new UserDO(2L, "Name2"));
String userListStr = JSON.toJSONString(userDOList);
List<UserDO> userDOS = JSON.parseArray(userListStr, UserDO.class);
assertThat(userDOS.size()).isEqualTo(userDOList.size());
assertThat(userDOS.get(0)).isEqualToComparingFieldByField(userDOList.get(0));
assertThat(userDOS.get(1)).isEqualToComparingFieldByField(userDOList.get(1));
System.out.println(userDOS);
List<UserDO> result = JSON.parseObject(userListStr, new TypeReference<List<UserDO>>() {
}.getType());
assertThat(result.size()).isEqualTo(userDOList.size());
assertThat(result.get(0)).isEqualToComparingFieldByField(userDOList.get(0));
assertThat(result.get(1)).isEqualToComparingFieldByField(userDOList.get(1));
System.out.println(result);
}
2. 带参数使用
在1.2.9 & 1.1.49.android版本中,TypeReference支持泛型参数,方便一些框架实现通用的反序列化类。用法如下:
2.1. 单参数例子
public class Response<T> {
public T data;
}
public static <T> Response<T> parseToMap(String json, Class<T> type) {
return JSON.parseObject(json,
new TypeReference<Response<T>>(type) {});
}
2.2. 双参数例子
public static <K, V> Map<K, V> parseToMap(String json,
Class<K> keyType,
Class<V> valueType) {
return JSON.parseObject(json,
new TypeReference<Map<K, V>>(keyType, valueType) {
});
} // 可以这样使用
String json = "{1:{name:\"ddd\"},2:{name:\"zzz\"}}";
Map<Integer, Model> map = parseToMap(json, Integer.class, Model.class);
assertEquals("ddd", map.get(1).name);
assertEquals("zzz", map.get(2).name);
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/TypeReference
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.junit.Test; import java.lang.reflect.Type; /**
* @Auther: cheng.tang
* @Date: 2019/7/31
* @Description:
*/
public class GsonTest { private static final String source = "{\"code\":500,\"data\":\"\",\"msg\":\"未知异常\",\"success\":false}"; /**
* com.google.gson.JsonSyntaxException: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 21 path $.data
* <p>
* at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$Adapter.read(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:226)
* at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$1.read(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:131)
* at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$Adapter.read(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:222)
* at com.google.gson.Gson.fromJson(Gson.java:922)
* at com.google.gson.Gson.fromJson(Gson.java:887)
* at com.google.gson.Gson.fromJson(Gson.java:836)
* at com.zkh360.gbb.user.utils.GsonTest.gsonDeserializationTest(GsonTest.java:36)
* at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
* at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
* at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
* at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
* at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
* at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
* at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
* at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:325)
* at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:78)
* at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:57)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.run(ParentRunner.java:290)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:71)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:288)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$000(ParentRunner.java:58)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:268)
* at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:363)
* at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
* at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:68)
* at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:47)
* at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:242)
* at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:70)
* Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Expected BEGIN_OBJECT but was STRING at line 1 column 21 path $.data
* at com.google.gson.stream.JsonReader.beginObject(JsonReader.java:385)
* at com.google.gson.internal.bind.ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory$Adapter.read(ReflectiveTypeAdapterFactory.java:215)
* ... 28 more
*/
@Test(expected = JsonSyntaxException.class)
public void gsonDeserializationTest() {
Gson gson = new Gson();
Type type = new TypeToken<ResultDTO<UserIdDTO>>() {
}.getType();
ResultDTO<UserIdDTO> resultDTO = gson.fromJson(source, type);
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(resultDTO));
} @Test
public void fastjsonDeserializationTest() {
ResultDTO<UserIdDTO> userIdDTOResultDTO = JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<ResultDTO<UserIdDTO>>() {
});
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(userIdDTOResultDTO));
} }
fastjson实例化对象时,如果1,true 会转换成true,其它的都为false
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.Data;
import org.junit.Test; import static org.assertj.core.api.Java6Assertions.assertThat; /**
* @author: tangcheng
* @description:
* @since: Created in 2018/08/03 16:31
*/
public class JSONBooleanTypeTest { @Test
public void testFastJson() {
BooleanType booleanType = new BooleanType();
booleanType.setEnable(true);
String output = JSON.toJSONString(booleanType);
assertThat(output).isEqualTo("{\"enable\":true}"); /**
* 字符串的值除了1和true外,都是false
*/
BooleanType serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":true}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isTrue();
serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":1}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isTrue(); serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":false}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isFalse();
serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":2}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isFalse();
serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":0}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isFalse(); serialObj = JSON.parseObject("{\"enable\":-1}", BooleanType.class);
assertThat(serialObj.getEnable()).isFalse();
} @Data
public static class BooleanType {
private Boolean enable;
}
}
JSONObject.toJSONString(Object object, SerializerFeature... features)
SerializerFeature有用的一些枚举值
QuoteFieldNames———-输出key时是否使用双引号,默认为true
WriteMapNullValue——–是否输出值为null的字段,默认为false
WriteNullNumberAsZero—-数值字段如果为null,输出为0,而非null
WriteNullListAsEmpty—–List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null
WriteNullStringAsEmpty—字符类型字段如果为null,输出为”“,而非null
WriteNullBooleanAsFalse–Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null
SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect ,
如果没有设置这个参数会出现的问题【
FastJson如何解决循环引用/重复引用
fastjson支持循环引用/重复引用,并且是缺省打开的。
* 第一个例子序列化后输出结果为:{"1":{},"2":{"$ref":"$.1"}}
第一个对象正常序列化,第二个对象则用引用表示
* 第二个列子序列化后输出结果为:{"1":{"1":{"$ref":".."}}}
】:
如果对象中两个字段存放的是相同的List 对象,则会出现这种情况
http://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/5873277.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35873847/article/details/78850528
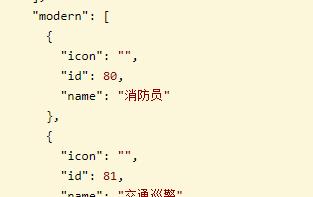
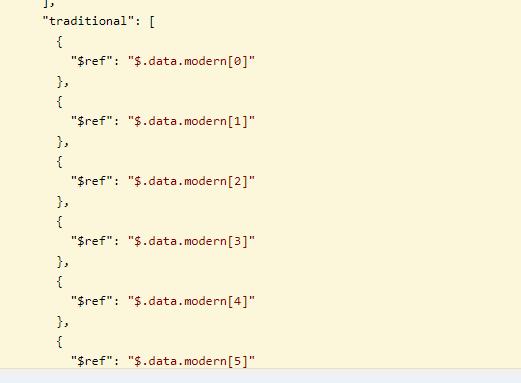
代码:
List<JobResVO> jobs = recommendJobBO.getJobs();
resultResVO.setModern(jobs);
resultResVO.setTraditional(jobs);
Converter中FastJson的配置:
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter httpMessageConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames,
SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString,
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
fastJsonConfig.setSerializeFilters((ValueFilter) (o, s, source) -> {
if (source == null) {
return "";
}
if (source instanceof Date) {
return ((Date) source).getTime();
}
return source;
});
httpMessageConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
converters.add(httpMessageConverter);
}
解决办法:
@Override
public void configureMessageConverters(List<HttpMessageConverter<?>> converters) {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter httpMessageConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig();
fastJsonConfig.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.QuoteFieldNames,
SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString,
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat,
SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect);
fastJsonConfig.setSerializeFilters((ValueFilter) (o, s, source) -> {
if (source == null) {
return "";
}
if (source instanceof Date) {
return ((Date) source).getTime();
}
return source;
});
httpMessageConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig);
converters.add(httpMessageConverter);
}
上面的SerializerFeature主要是针对Object对象序列化转换时的情况(这个时候才能判断参数的类型),而在Map中,你放进入了null就是null,进行序列化时已经没法判断它原来的类型了,所以并没有起作用。要使用SerializerFeature里相关null的参数,应该传入对象进行序列化。
对规则的理解:
SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue 是否输出值为null的字段,默认为false也就是说有null时会输出而不是忽略(默认策略是忽略,所以看不到为null的字段)
WriteNullStringAsEmpty—字符类型字段如果为null,输出为”“,而非null
注意是字段是字段是字段,而不是json.put("key",null),所以用它时,字段为null的可以转换为空字符串。如果让输出的json中所有为null的字符串都变成空字符串,最简单的做法就是加一个值过滤器,这样就避免了有的字段为null,有的字段为空字符的现象。
示例代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.ValueFilter; public class Demo1 { public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private boolean isMale;
private Student gf; public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public int getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public boolean isMale() {
return isMale;
} public void setMale(boolean isMale) {
this.isMale = isMale;
} public Student getGf() {
return gf;
} public void setGf(Student gf) {
this.gf = gf;
}
} private static ValueFilter filter = new ValueFilter() {
@Override
public Object process(Object obj, String s, Object v) {
if (v == null)
return "";
return v;
}
}; public static void main(String[] args) {
new Demo1().foo();
new Demo1().bar();
} private void foo() {
System.out.println("foo()---------------------------");
JSONObject j1 = new JSONObject();
j1.put("name", "zhangsan");
j1.put("age", 13);
j1.put("isMale", true);
j1.put("gf", null);
Map<String, Object> fav = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Set<String> books = new HashSet<String>();
books.add("三国");
books.add("史记");
fav.put("history", books);
String[] arts = new String[] {};
fav.put("arts", arts);
String[] musics = new String[] { "北京欢迎你", "画心" };
fav.put("musics", musics);
List<String> sports = new ArrayList<String>();
fav.put("sports", sports);
j1.put("fav", fav);
List<Student> classmates = new ArrayList<Student>();
classmates.add(new Student());
Student lisi = new Student();
lisi.setMale(false);
lisi.setAge(11);
classmates.add(lisi);
Student zhangsan = new Student();
zhangsan.setAge(13);
zhangsan.setName("张三");
zhangsan.setMale(true);
zhangsan.setGf(lisi);
classmates.add(zhangsan);
j1.put("classmates", classmates);
String str = null;
j1.put("str", str);
System.out.println(j1.toString());
System.out
.println(JSON.toJSONString(j1, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(j1, filter, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(j1, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(j1, filter, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty)); Map<String, JSONObject> m = new HashMap<String, JSONObject>();
m.put("key", j1);
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(m, SerializerFeature.WriteNonStringKeyAsString, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(m, filter, SerializerFeature.WriteNonStringKeyAsString,
SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty)); } private void bar() {
System.out.println("bar()---------------------------");
Student zhangsan = new Student();
zhangsan.setAge(13);
zhangsan.setName("张三");
zhangsan.setMale(true);
Student lisi = new Student();
// lisi.setName("lisi");
lisi.setMale(false);
lisi.setAge(11);
zhangsan.setGf(lisi);
System.out.println(
JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan, SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan, filter));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(zhangsan, filter, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,
SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty));
} }
foo()---------------------------
{"isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"male":false},{"age":11,"male":false},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13}
{"str":null,"isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"gf":null,"male":false,"name":""},{"age":11,"gf":null,"male":false,"name":""},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13,"gf":null}
{"str":"","isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":11,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13,"gf":""}
{"isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"male":false},{"age":11,"male":false},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13}
{"str":"","isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":11,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13,"gf":""}
{"key":{"isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"male":false},{"age":11,"male":false},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.key.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13}}
{"key":{"str":"","isMale":true,"name":"zhangsan","classmates":[{"age":0,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":11,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},{"age":13,"gf":{"$ref":"$.key.classmates[1]"},"male":true,"name":"张三"}],"fav":{"sports":[],"musics":["北京欢迎你","画心"],"history":["史记","三国"],"arts":[]},"age":13,"gf":""}}
bar()---------------------------
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"gf":null,"male":false,"name":""},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"gf":null,"male":false,"name":null},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"male":false},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"male":false},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
{"age":13,"gf":{"age":11,"gf":"","male":false,"name":""},"male":true,"name":"张三"}
JsonPathTestData.json
{
"store": {
"book": [
{
"category": "reference",
"author": "Nigel Rees",
"title": "Sayings of the Century",
"price": 8.95
},
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "Evelyn Waugh",
"title": "Sword of Honour",
"price": 12.99,
"isbn": "0-553-21311-3"
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
@Test
public void testJsonPath() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/JsonPathTestData.json");
String jsonStr = IOUtils.toString(resourceAsStream, "utf-8");
System.out.println(jsonStr); System.out.println(jsonStr);
JSONObject jsonObject = JSON.parseObject(jsonStr); System.out.println("\nBook数目:" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.book.size()"));
System.out.println("第一本书title:" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.book[0].title"));
System.out.println("price大于10元的book:" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.book[price > 10]"));
System.out.println("price大于10元的title:" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.book[price > 10][0].title"));
System.out.println("category(类别)为fiction(小说)的book:" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.book[category = 'fiction']"));
System.out.println("bicycle的所有属性值" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.bicycle.*"));
System.out.println("bicycle的color和price属性值" + JSONPath.eval(jsonObject, "$.store.bicycle['color','price']"));
} @Test
public void testGenerics() {
Result<User> result = new Result<>();
result.setMsg("Success");
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new User(1L, "Name1"));
users.add(new User(2L, "Name2"));
result.setModule(users);
String js = JSON.toJSONString(result);
System.out.println(js);
//java.lang.ClassCastException: com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject cannot be cast to com.tangcheng.learning.json.User
// Result<User> obj = (Result<User>) JSON.parseObject(js, Result.class);
Result<User> userResult = JSON.parseObject(js, new TypeReference<Result<User>>() {
});
System.out.println(userResult);
}
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(Long id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
import java.util.List;
public class Result<T> {
private String msg;
private List<T> module;
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public List<T> getModule() {
return module;
}
public void setModule(List<T> module) {
this.module = module;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Result{" +
"msg='" + msg + '\'' +
", module=" + module +
'}';
}
}
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.util.ParameterizedTypeImpl;
import lombok.Data; @Data
public class Response<T> {
private T data; @Override
public String toString() {
return JSON.toJSONString(this);
} public static void main(String[] args) {
String jsonText = "{\"data\":{\"id\":1,\"name\":\"张三\"}}";
Response<User> response = JSON.parseObject(jsonText, new ParameterizedTypeImpl(new Class[]{User.class}, null, Response.class));
/**
* {"data":{"id":1,"name":"张三"}}
*/
System.out.println(response); response = JSON.parseObject(jsonText, new TypeReference<Response<User>>() {
});
/**
* {"data":{"id":1,"name":"张三"}}
*/
System.out.println(response);
}
} @Data
class User {
private Integer id;
private String name; @Override
public String toString() {
return JSON.toJSONString(this);
}
}
https://www.slideshare.net/randfish/inside-googles-numbers-in-2017?next_slideshow=1
由于json中的key与bean中的属性不能匹配,因此在转换过程中出现了部分属性为null的情况。经过查看官方文档,发现可以使用@JSONField进行解释,但是并没有详细的使用说明。
@JSONField的作用对象:
1. Field
2. Setter 和 Getter方法
注:FastJson在进行操作时,是根据getter和setter的方法进行的,并不是依据Field进行。
一、作用Field
@JSONField作用在Field时,其name不仅定义了输入key的名称,同时也定义了输出的名称。
二、作用在setter和getter方法上
顾名思义,当作用在setter方法上时,就相当于根据 name 到 json中寻找对应的值,并调用该setter对象赋值。
当作用在getter上时,在bean转换为json时,其key值为name定义的值
在fastjson-1.2.12版本中,JSONField支持一个新的配置项jsonDirect,
它的用途是:当你有一个字段是字符串类型,里面是json格式数据,你希望直接输入,而不是经过转义之后再输出。
Model:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;
public static class Model {
public int id;
@JSONField(jsonDirect=true)
public String value;
}
Usage:
Model model = new Model();
model.id = 1001;
model.value = "{}"; String json = JSON.toJSONString(model);
Assert.assertEquals("{\"id\":1001,\"value\":{}}", json);
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONField_jsonDirect_cn
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/issues/1244
http://www.cnblogs.com/softidea/p/5681928.html
fastjson 过滤不需要的字段或者只要某些字段
//第一种:在对象响应字段前加注解,这样生成的json也不包含该字段。
@JSONField(serialize=false)
private String name;
第二种:在对象对应字段前面加transient,表示该字段不用序列化,即在生成json的时候就不会包含该字段了。
private transient String name;
transient使用小结
1)一旦变量被transient修饰,变量将不再是对象持久化的一部分,该变量内容在序列化后无法获得访问。
2)transient关键字只能修饰变量,而不能修饰方法和类。注意,本地变量是不能被transient关键字修饰的。变量如果是用户自定义类变量,则该类需要实现Serializable接口。
3)被transient关键字修饰的变量不再能被序列化,一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化。
第三点可能有些人很迷惑,因为发现在User类中的username字段前加上static关键字后,程序运行结果依然不变,即static类型的username也读出来为“Alexia”了,这不与第三点说的矛盾吗?
实际上是这样的:第三点确实没错(一个静态变量不管是否被transient修饰,均不能被序列化),反序列化后类中static型变量username的值为当前JVM中对应static变量的值,这个值是JVM中的不是反序列化得出的
https://www.cnblogs.com/lanxuezaipiao/p/3369962.html
//第三种:使用fastjson的拦截器
PropertyFilter profilter = new PropertyFilter(){ @Override
public boolean apply(Object object, String name, Object value) {
if(name.equalsIgnoreCase("last")){
//false表示last字段将被排除在外
return false;
}
return true;
} };
json = JSON.toJSONString(user, profilter);
System.out.println(json);
https://blog.csdn.net/stubbornness1219/article/details/52947013
jackson也是一个很优秀的jackson库,但是如果你因为某些理由想迁移到fastjson,这个指南将会为你介绍如何从jackson迁移到fastjson。
Annotions
在fastjson中,有四个Annotation,JSONType、JSONField、JSONCreator、JSONPOJOBuilder,能够完成jackson大多数Annotation对应的功能。
1. JsonView迁移
在fastjson中,提供有一个LabelFilter,能够实现Jackson JsonView的功能,用于定制序列化。详细文档 https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/LabelFilter
2. JsonPOJOBuilder
在Jackson中提供了对Builder模式支持的JsonPOJOBuilder,在fastjson中对应的是JSONPOJOBuilder。详细文档 https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/BuilderSupport
3. JsonAnyGetter & JsonAnySetter & JsonUnwrapped
在fastjson 1.2.32版本中引入JSONField.unwrapped配置,支持类似JsonAnyGetter/JsonAnySetter的功能,详细文档 https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONField_unwrapped_cn
4. JsonPropertyOrder
在fastjson的JSONType.orders提供了同样的功能。例如:
@JSONType(orders={"name", "id"})
public static class VO {
public int id;
public String name;
}
5. JsonRawValue
在fastjson中,通过JSONField.jsonDirect配置能实现同样的功能。
public static class Model {
public int id;
@JSONField(jsonDirect=true)
public String value;
}
6. JsonSerialize
在fastjson中,可以通过使用JSONField.serializeUsing和JSONType.serializer实现同样的功能。
7. JsonCreator
在fastjson中有对应的JSONCreator
8. JsonSetter
在fastjson中,可以用JSONField实现同样的功能。
9. JsonDeserialize
在fastjson中,可以通过使用JSONField.deserializeUsing和JSONType.deserializer实现同样的功能。
10. JsonIgnoreProperties
在fastjson中,可以通过使用JSONType.ignores实现同样的功能
11. JsonIgnore
在fastjson中,可以通过使用JSONField.serilaize=false和JSONField.deserilaize=false和实现同样的功能
12. JsonFormat
在fastjson中,可以通过使用JSONField.format实现同样的功能
13. Jackson Polymorphic Type Handling Annotations
在fastjson中,可以通过JSONType.seeAlso实现类似的功能。详细文档 https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONType_seeAlso_cn
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/guid_to_migrating_from_jackson_to_fastjson_cn
2.4. @JsonRawValue
@JsonRawValue is used to instruct the Jackson to serialize a property exactly as is.
In the following example – we use @JsonRawValue to embed some custom JSON as a value of an entity:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class RawBean { public String name; @JsonRawValue public String json;} |
The output of serializing the entity is:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
{ "name":"My bean", "json":{ "attr":false }} |
And a simple test:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@Testpublic void whenSerializingUsingJsonRawValue_thenCorrect() throws JsonProcessingException { RawBean bean = new RawBean("My bean", "{"attr":false}"); String result = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(bean); assertThat(result, containsString("My bean")); assertThat(result, containsString("{"attr":false}"));} |
http://www.baeldung.com/jackson-annotations
9.4 日期格式处理
Fastjson能识别下面这么多种日期格式的字符串:
1 |
private final static String defaultPatttern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"; |
默认序列化Date输出使用”yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”格式,可以用UseISO8601DateFormat特性换成”yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss”格式。
1 |
JSON.defaultTimeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone("Asia/Shanghai");
|
9.5 常见序列化特性的使用
Fastjson的序列化特性定义在枚举类com\alibaba\fastjson\serializer\SerializerFeature.java中,目前正好有30项。
可以通过设置多个特性到FastjsonConfig中全局使用,也可以在某个具体的JSON.writeJSONString时作为参数使用。
- QuoteFieldNames, //key使用引号
- UseSingleQuotes, //使用单引号
- WriteMapNullValue, //输出Map的null值
- WriteEnumUsingToString, //枚举属性输出toString的结果
- WriteEnumUsingName, //枚举数据输出name
- UseISO8601DateFormat, //使用日期格式
- WriteNullListAsEmpty, //List为空则输出[]
- WriteNullStringAsEmpty, //String为空则输出””
- WriteNullNumberAsZero, //Number类型为空则输出0
- WriteNullBooleanAsFalse, //Boolean类型为空则输出false
- SkipTransientField,
- SortField, //排序字段
- WriteTabAsSpecial,
- PrettyFormat, // 格式化JSON缩进
- WriteClassName, // 输出类名
- DisableCircularReferenceDetect, // 禁止循环引用
- WriteSlashAsSpecial, // 对斜杠’/’进行转义
- BrowserCompatible,
- WriteDateUseDateFormat, // 全局修改日期格式,默认为false。JSON.DEFFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = “yyyy-MM-dd”;JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
- NotWriteRootClassName,
- DisableCheckSpecialChar,
- BeanToArray,
- WriteNonStringKeyAsString,
- NotWriteDefaultValue,
- BrowserSecure,
- IgnoreNonFieldGetter,
- WriteNonStringValueAsString,
- IgnoreErrorGetter,
- WriteBigDecimalAsPlain,
- MapSortField
使用示例如下(可以参见此处):
1 |
Word word = new Word(); |
9.6 Annotation注解的使用
1) JSONField
可以配置在属性(setter、getter)和字段(必须是public field)上。
详情参见此处:JSONField用法
1 |
package com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation;
public @interface JSONField {
|
1 |
@JSONField(name="ID") |
http://kimmking.github.io/2017/06/06/json-best-practice/
7. fastjson序列化的需要像json-lib一样配置java bean的序列化么?
不需要,fastjson的序列化和反序列化都不需要做特别配置,唯一的要求是,你序列化的类符合java bean规范。
8. fastjson如何处理日期
fastjson处理日期的API很简单,例如:
JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(date, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
使用ISO-8601日期格式
JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.UseISO8601DateFormat);
全局修改日期格式
JSON.DEFFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd";
JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
反序列化能够自动识别如下日期格式:
- ISO-8601日期格式
- yyyy-MM-dd
- yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
- yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS
- 毫秒数字
- 毫秒数字字符串
- .NET JSON日期格式
- new Date(198293238)
11. IE 6不支持JSON带中文字符串,要怎么处理?
fastjson提供了BrowserCompatible这个配置,打开之后,所有的中文都会序列化为\uXXXX这种格式,字节数会多一些,但是能兼容IE 6。
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.BrowserCompatible);
10. 当对象存在引用时,序列化后的结果浏览器不支持,怎么办?
使用SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect特性关闭引用检测和生成。
例如:
String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect);
https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/%E5%B8%B8%E8%A7%81%E9%97%AE%E9%A2%98
做个分析 FastJson 在使用 toJSONString 会使用 写入操作,而 我的类里面有这样一个方法 public int getLengthOfByte()
这样FastJson 就会认为 这个类 有一个 lengthOfByte 的属性,于是就出现了异常,解决方法
@JSONType(ignores = "lengthOfByte")
public class DRMessageBody { public int getLengthOfByte(){
String json = toJson();
int num = -1;
num = json.getBytes().length;
if(num==-1){
new RuntimeException("Messagebody of json length is error!");
}
return num;
}
}
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f96e257c7682
Fastjson 专题的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot 企业级核心技术学习专题
专题 专题名称 专题描述 001 Spring Boot 核心技术 讲解SpringBoot一些企业级层面的核心组件 002 Spring Boot 核心技术章节源码 Spring Boot 核心技术 ...
- 2016年中国微信小程序专题研究报告
2016年12月29日,全球领先的移动互联网第三方数据挖掘和分析机构iiMedia Research(艾媒咨询)权威首发<2016年中国微信小程序专题研究报告>. 报告显示,82.6%手机 ...
- [.NET领域驱动设计实战系列]专题二:结合领域驱动设计的面向服务架构来搭建网上书店
一.前言 在前面专题一中,我已经介绍了我写这系列文章的初衷了.由于dax.net中的DDD框架和Byteart Retail案例并没有对其形成过程做一步步分析,而是把整个DDD的实现案例展现给我们,这 ...
- fastjson 混淆注意事项
使用fastjson 注意事项,主要表现: 1.加了符号Annotation 的实体类,一使用就会奔溃 2.当有泛型属性时,一使用就奔溃 在调试的时候不会报错,当你要打包签名混淆包的时候,就会出现上述 ...
- Java的Json解析包FastJson使用
阿里巴巴FastJson是一个Json处理工具包,包括“序列化”和“反序列化”两部分,它具备如下特征:速度最快,测试表明,fastjson具有极快的性能,超越任其他的Java Json parser. ...
- 转载:《.NET 编程结构》专题汇总(C#)
<.NET 编程结构>专题汇总(C#) - M守护神 - 博客园http://www.cnblogs.com/liusuqi/p/3213597.html 前言 掌握一门技术,首要 ...
- fastJson使用
fastjson 是一个性能很好的 Java 语言实现的 JSON 解析器和生成器,由阿里巴巴的工程师开发. 主要特点: 快速FAST (比其它任何基于Java的解析器和生成器更快,包括jackson ...
- FASTJSON
package com.hanqi.test; import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List; impo ...
- Android总结之json解析(FastJson Gson 对比)
前言: 最近为了统一项目中使用的框架,发现项目中用到了两种json解析框架,他们就是当今非常主流的json解析框架:google的Gson 和阿里巴巴的FastJson,为了废除其中一个所以来个性能和 ...
随机推荐
- eclipse-整合struts和spring-maven
maven配置文件 <!-- servlet --> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> < ...
- ThreadPoolExecutor运行机制
最近发现几起对ThreadPoolExecutor的误用,其中包括自己,发现都是因为没有仔细看注释和内部运转机制,想当然的揣测参数导致,先看一下新建一个ThreadPoolExecutor的构建参数: ...
- MOOS学习笔记3——命令行
MOOS学习笔记3--命令行 例程 /** * @code A simple example showing how to use a comms client问问怎么样 */ #include &q ...
- Angular使用总结 --- 模版驱动表单
表单的重要性就不多说了,Angular支持表单的双向数据绑定,校验,状态管理等,总结下. 获取用户输入 <div class="container-fluid login-page&q ...
- JSON 的含义?
JSON 的全称是 JavaScript Object Notation,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.JS ON 与 XML 具有相同的特性,例如易于人编写和阅读,易于机器生成和解析.但是 JSON ...
- 大型B2C网站高性能可伸缩架构技术探秘
大型B2C网站高性能可伸缩架构技术探秘 2010-07-21 08:51 狂放不羁 JavaEye 字号:T | T 向您介绍大型B2C网站高性能的网站架构技术,包括缓存的使用.应用程序和数据库的拆分 ...
- web集群时session同步的3种方法[转]
在做了web集群后,你肯定会首先考虑session同步问题,因为通过负载均衡后,同一个IP访问同一个页面会被分配到不同的服务器上,如果session不同步的话,一个登录用户,一会是登录状态,一会又不是 ...
- Pod install 之后 no such module
官方文档在pod install之后的操作是: open App.xcworkspace 使用pod以后,项目的旧打开方式就不行了,必须到项目目录里面,打开“项目名.xcworkspace”这种方式来 ...
- WebRTC技术调研
相关网址: 协议:https://www.w3.org/TR/webrtc/ https://apprtc.webrtc.org/ https://apprtc.appspot.com/ https: ...
- android解析xml文件方法之一-----DOM
Hello.xml文件 <dict num="219" id="219" name="219"> <key>hell ...
