2016CCPC长春 - B/D/F/H/I/J/K - (待补)
目录:
F - Harmonic Value Description
B题:HDU 5912 - Fraction - [递归]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5912
Problem Description
Mr. Frog recently studied how to add two fractions up, and he came up with an evil idea to trouble you by asking you to calculate the result of the formula below:
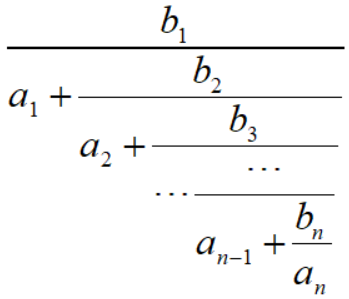
As a talent, can you figure out the answer correctly?
Input
The first line contains only one integer T, which indicates the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains only one integer n (n≤8).
The second line contains n integers: $a_1,a_2,⋯a_n(1\le a_i \le 10)$.
The third line contains n integers: $b_1,b_2,⋯,b_n(1 \le b_i \le 10)$.
Output
For each case, print a line “Case #x: p q”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and p/q indicates the answer.
You should promise that p/q is irreducible.
Sample Input
1
2
1 1
2 3
Sample Output
Case #1: 1 2
Hint
Here are the details for the first sample:
2/(1+3/1) = 1/2
题意:
给出了关于 $a[1:n]$ 和 $b[1:n]$ 的计算式,给你 $a[1:n]$ 和 $b[1:n]$,要求计算式结果。
题解:
由于范围很小,直接递归计算即可。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
const int maxn=; int n;
int a[maxn],b[maxn]; inline int gcd(int m,int n){return n?gcd(n,m%n):m;}
pii dfs(int dist)
{
if(dist==n)
{
int u=b[n];
int d=a[n];
int g=gcd(u,d);
return make_pair(u/g,d/g);
} pii f=dfs(dist+);
int u=b[dist]*f.second;
int d=a[dist]*f.second+f.first;
int g=gcd(u,d);
return make_pair(u/g,d/g);
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) cin>>a[i];
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) cin>>b[i];
pii ans=dfs();
printf("Case #%d: %d %d\n",kase,ans.first,ans.second);
}
}
D题:HDU 5914 - Triangle - [贪心]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5914
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (T≤20), which indicates the number of test cases. For each test case, there is only one line describing the given integer n (1≤n≤20).
Output
For each test case, output one line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1), y is the minimal number of sticks Wallice should steal.
Sample Input
3
4
5
6
Sample Output
Case #1: 1
Case #2: 1
Case #3: 2
题意:
有 $n$ 根棍子,长度分别为 $1,2,3,\cdots,n$,现在要从中取出若干棍子使得剩下的棍子任意三条均不能组成一个三角形,求最少取出多少根棍子。
题解:
首先考虑最开始的 $1,2,3$ 三根木棍都是可以留下来的,而长度为 $4$ 的则需要拿走,因为 $2+3>4$,然后 $5$ 又可以留下, 因为正好 $2+3=5$,依次类推,不难发现就是一个斐波那契数列。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=; int n;
int fibo[maxn];
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
fibo[]=;
fibo[]=;
for(int i=;i<maxn;i++) fibo[i]=fibo[i-]+fibo[i-];
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
cin>>n;
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",kase,n-(upper_bound(fibo+,fibo+maxn,n)-(fibo+)));
}
}
F题:HDU 5916 - Harmonic Value Description - [思维题]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5916
The harmonic value of the permutation $p_1,p_2,⋯,p_n$ is
$\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{n - 1} {\left( {p_i p_{i + 1} } \right)}$
Mr. Frog is wondering about the permutation whose harmonic value is the strictly k-th smallest among all the permutations of [n].
Input
The first line contains only one integer T (1≤T≤100), which indicates the number of test cases.
For each test case, there is only one line describing the given integers n and k (1≤2k≤n≤10000).
Output
For each test case, output one line “Case #x: $p_1$ $p_2$ ⋯ $p_n$”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and $p_1$ $p_2$ ⋯ $p_n$ is the answer.
Sample Input
2
4 1
4 2
Sample Output
Case #1: 4 1 3 2
Case #2: 2 4 1 3
题意:
给出 $[1:n]$ 的一个排列 $p_1$ $p_2$ ⋯ $p_n$,认为其调和值为 $\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{n - 1} {\left( {p_i p_{i + 1} } \right)}$,
现在对于 $[1:n]$ 的所有排列,要求其调和值为第 $k$ 小的排列是哪一个。
题解:
首先 $1,2,3,4,5,6\cdots,n$ 这样的排列,很明显“调和值”最小,为 $n-1$,
若我们把 $2$ 移动至 $3,4$ 之间的位置,就会变成:$1,3,2,4,5,6,\cdots ,n$,不难发现,调和值为 $n$,因为从 $4$ 往后的所有数字都没有变化,gcd值还是 $1$,唯一变化的是 $2,4$ 的gcd值为 $2$,也就是原来多了 $1$,
可以大胆假设:第 $k$ 小调和值的排列,就是把 $1,2,3,4,5,6\cdots,n$ 中的 $k$ 取出来,放到 $2k-1,2k$ 之间。
不妨检验一下 $k=3$,我们先将 $3$ 移至 $5,6$ 之间得到:$1,2,4,5,3,6,7,8,\cdots,n$,发现 $gcd(3,6) = 3$,确实比原来增加了2,
但是,存在问题, 原本 $2,4$ 由 $3$ 隔开,现在并到了一起,gcd值也增加了,那么我们不妨把 $1$ 拿过来填掉这个原来是 $3$ 的坑,得到:$2,1,4,5,3,6,7,8,\cdots,n$,调和值为 $n+1$,就是第 $3$ 小的,完美。
所以,对于任意的 $k$ 满足 $2k \le n$,只要将 $k$ 移动至 $2k$ 之前,将 $1$ 移动至原来 $k$ 的位置,就能得到调和值第 $k$ 小的排列。
(情不自禁就像$%$一下我的神仙队友,这都能想得到,tql(`・ω・´)>)
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=; int n,k;
int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
cin>>n>>k;
printf("Case #%d: ",kase);
if(k==) for(int i=;i<=n;i++) printf("%d%c",i,(i==n)?'\n':' ');
else
{
for(int i=;i<=k-;i++) printf("%d ",i);
printf("1 ");
for(int i=k+;i<=*k-;i++) printf("%d ",i);
printf("%d ",k);
for(int i=*k;i<=n;i++) printf("%d%c",i,(i==n)?'\n':' ');
}
}
}
H题:HDU 5918 - Sequence I - [KMP]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5918
Mr. Frog has two sequences $a_1,a_2,⋯,a_n$ and $b_1,b_2,⋯,b_m$ and a number $p$. He wants to know the number of positions $q$ such that sequence $b_1,b_2,⋯,b_m$ is exactly the sequence $a_q,a_{q+p},a_{q+2p},⋯,a_{q+(m−1)p}$ where $q+(m−1)p \le n$ and $q \ge 1$.
Input
The first line contains only one integer $T \le 100$, which indicates the number of test cases.Each test case contains three lines.
The first line contains three space-separated integers $1 \le n \le 10^6,1 \le m \le 10^6$ and $1 \le p \le 10^6$.
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1,a_2,⋯,a_n(1 \le a_i \le 10^9)$. The third line contains $m$ integers $b_1,b_2,⋯,b_m(1 \le b_i \le 10^9)$.
Output
For each test case, output one line “Case #x: y”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and y is the number of valid q’s.
Sample Input
2
6 3 1
1 2 3 1 2 3
1 2 3
6 3 2
1 3 2 2 3 1
1 2 3
Sample Output
Case #1: 2
Case #2: 1
题意:
给出一个长度为 $n$ 的文本串,一个长度为 $m$ 的模式串,给出跳步长度 $p$,
要求在文本串中,若按照跳步长度 $p$ 来进行遍历,求能找得到多少个模式串。
题解:
特喵的这个就是个KMP模板题,一开始看完题目就想着枚举开头,把所有的跳步长度为 $p$ 的子序列处理出来了,
但是那个时候不知道发什么神经,居然算不清处理出来的若干个子序列的总长是多少!!!以为是 $O(n^2)$ 的总长度就没敢写,后来一看榜单怎么过的人这么多,肯定就是个水题啊!
然后仔细一看,就反应过来了,这若干个子序列的总长就是 $O(n)$ 啊!
假设文本串的编号是 $0$ 到 $n-1$ 的,那么我们只需要开一个表头大小为 $p$ 的邻接表来存这若干个子序列(表头就是 $0,1,2,\cdots,p-1$),对于编号为 $i$ 那个字符,扔进表头为 $i%p$ 的那个链表里去就行了呀!!!每个字符肯定只会出现一次,所以这若干个子序列的总长就是 $O(n)$……
然后就好办了,对邻接表里的每个链表,就当成一个文本串,拿去和模式串KMP匹配一下,求得当前子序列中出现了几次模式串,最后求和一下就是答案了;
总的时间复杂度 $O(n+m)$。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e6+; int n,m,p;
vector<int> str[maxn];
int pat[maxn]; int Next[maxn];
void getNext()
{
int i=, j=-, len=m;
Next[]=-;
while(i<len)
{
if(j == - || pat[i] == pat[j]) Next[++i]=++j;
else j=Next[j];
}
}
int kmp(int p)
{
int i=, j=, len1=str[p].size(), len2=m;
if(len1<len2) return ;
int ans=;
while(i<len1)
{
if(j == - || str[p][i] == pat[j]) i++, j++;
else j=Next[j];
if(j == len2) ans++;
}
return ans;
} int main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
for(int kase=;kase<=T;kase++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&p); for(int i=;i<p;i++) str[i].clear();
for(int i=,a;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
str[i%p].push_back(a);
} for(int i=;i<m;i++) scanf("%d",&pat[i]); pat[m]=;
getNext(); int ans=;
for(int i=;i<p;i++) ans+=kmp(i);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",kase,ans);
}
}
注意:
这里有一个WA点,首先KMP的模板是没错的,但是KMP的模板对应的是char数组的字符串,而我们这里是数字序列;
我们都知道,字符串读入时,位置 $0 \sim n-1$ 存实际字符串,位置 $n$ 存一个 '\0',KMP的模板里是有使用到这个性质的;
而当我们for循环读入数字时,是没有这个 '\0' 终止符的,所以我们应当类似于字符串读入的方式,在位置 $n$ 存一个 $0$(将所有序列可能出现的数字作为一个集合,取该集合范围之外的数字)作为终止符。
I题: HDU 5919 - Sequence II - [主席树]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5919
Mr. Frog has an integer sequence of length n, which can be denoted as $a_1,a_2,⋯,a_n$.
There are m queries. In the i-th query, you are given two integers $l_i$ and $r_i$. Consider the subsequence $a_{l_i},a_{l_{i+1}},a_{l_{i+2}},⋯,a_{r_i}$.
We can denote the positions (the positions according to the original sequence) where an integer appears first in this subsequence as $p_1^{(i)},p_2^{(i)},⋯,p_{k_i}^{(i)}$ (in ascending order, i.e., $p_1^{(i)} < p_2^{(i)} < ⋯ < p_{k_i}^{(i)}$).
Note that $k_i$ is the number of different integers in this subsequence. You should output $p_{\left\lceil {\frac{{k_i }}{2}} \right\rceil }^{(i)}$ for the i-th query.
Input
In the first line of input, there is an integer T (T≤2) denoting the number of test cases.
Each test case starts with two integers n (n≤2e5) and m (m≤2e5).
There are n integers in the next line, which indicate the integers in the sequence(i.e., $a_1,a_2,⋯,a_n$, $0 \le a_i \le 2e5$).
There are two integers $l_i$ and $r_i$ in the following $m$ lines.
However, Mr. Frog thought that this problem was too young too simple so he became angry. He modified each query to $l'_i,r'_i$($1 \le l'_i \le n, 1 \le r'_i \le n$).
As a result, the problem became more exciting. We can denote the answers as $ans_1,ans_2,⋯,ans_m$.
Note that for each test case $ans_0=0$.
You can get the correct input $l_i,r_i$ from what you read (we denote them as $l'_i,r'_i$) by the following formula: $l_i = min{(l'_i+ans_{i−1}) mod n + 1,(r'_i + ans_{i−1}) mod n+1}, r_i = max{(l'_i + ans_{i−1}) mod n + 1, (r'_i+ans_{i−1}) mod n + 1}$
Output
You should output one single line for each test case. For each test case, output one line “Case #x: $ans_1,ans_2,⋯,ans_m$”, where x is the case number (starting from 1) and $ans_1,ans_2,⋯,ans_m$ is the answer.
题意:
给出 $n(n \le 2e5)$ 个数,每个数的大小满足 $0 < a_i \le 2e5$,
给出 $m(m \le 2e5)$ 个询问,对于每个询问输入 $l,r$,序列 $a_l,...,a_r$ 中的每个数,在该序列内第一次出现的位置,合成一个序列 $P$;
若假设这个区间有 $k$ 个不同的数,我们得到的序列 $P$ 就是 $p_1 < p_2 < p_3 < ... <p_k$;
而对应于该查询的答案为:序列中 $P$ 的第 $\left\lceil {\frac{k}{2}} \right\rceil = \left\lfloor {\frac{{k + 1}}{2}} \right\rfloor$ 个数。
例如:
整个序列为:$1,5,2,2,5,1,4,5,1$;
查询区间为 $[1,5]$,即 $1,5,2,2,5$,对应产生的序列 $P$ 即为 $1,2,3$,长度 $k=3$,答案为 $p_{\left\lfloor {\frac{{3 + 1}}{2}} \right\rfloor } = p_2 = 2$;
查询区间为 $[2,7]$,即 $5,2,2,5,1,4$,对应产生的序列 $P$ 即为 $2,3,6,7$,长度 $k=4$,答案为 $p_{\left\lfloor {\frac{{4 + 1}}{2}} \right\rfloor } = p_2 = 3$;
查询区间为 $[6,9]$,即 $1,4,5,1$,对应产生的序列 $P$ 即为 $6,7,8$,长度 $k=3$,答案为 $p_{\left\lfloor {\frac{{3 + 1}}{2}} \right\rfloor } = p_2 = 7$;
(当然,查询的输入那里加了一点小操作,不影响整体大意,第 $i$ 个查询的区间要通过 第 $i-1$ 个查询的答案计算得到)。
题解:
2016CCPC长春 - B/D/F/H/I/J/K - (待补)的更多相关文章
- Gym 101606 - A/B/C/D/E/F/G/H/I/J/K/L - (Undone)
链接:https://codeforces.com/gym/101606 A - Alien Sunset 暴力枚举小时即可. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using ...
- //给定N个整数序列{A1,A2,A3...An},求函数f(i,j)=(k=i~j)Ak的求和
//给定N个整数序列{A1,A2,A3...An},求函数f(i,j)=(k=i~j)Ak的求和 # include<stdio.h> void main() { ,sum1; ]={,- ...
- 2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第七场)E F H I
E Find the median 题意:每次往序列中增加连续的[l,r]的数,每加入一次就询问当前序列的中位数. 解法:此题没有要求在线,那么直接离线+线段树+二分就可以了.求出每个端点之后排序得到 ...
- cometoj(A-D+F+H)代码
A #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> ...
- hdu 5442 (ACM-ICPC2015长春网络赛F题)
题意:给出一个字符串,长度是2*10^4.将它首尾相接形成环,并在环上找一个起始点顺时针或逆时针走一圈,求字典序最大的走法,如果有多个答案则找起始点最小的,若起始点也相同则选择顺时针. 分析:后缀数组 ...
- HDU 4818 RP problem (高斯消元, 2013年长春区域赛F题)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4818 深深地补一个坑~~~ 现场赛坑在这题了,TAT.... 今天把代码改了下,过掉了,TAT 很明显 ...
- HDU 5919 - Sequence II (2016CCPC长春) 主席树 (区间第K小+区间不同值个数)
HDU 5919 题意: 动态处理一个序列的区间问题,对于一个给定序列,每次输入区间的左端点和右端点,输出这个区间中:每个数字第一次出现的位子留下, 输出这些位子中最中间的那个,就是(len+1)/2 ...
- 树链剖分-点的分治(dis[i]+dis[j]==k的点对数量)
poj2114 Boatherds Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 1195 Accepted: 387 ...
- codeforces Gym 100971 A、B、C、F、G、K、L
A题 直接把问号全部变为陆地如果所有陆地连通 那么再逐个把刚才变成陆地的问号变为水如果依旧连通有多种解 为什么我的代码跑不过去,和网上的题解思路一模一样!!?? #include<cst ...
随机推荐
- Android RecyclerView的item大小保持四个半
现在有这么一个需求,实现下图的UI. 我想你应该能想到用RecyclerView实现, 当我唰唰唰几分钟做完之后,UI设计师跟我说,每个item,无论在什么手机上,都要显示四个半,具体看下图 ...
- iScroll的使用
CDN: <script src="//ossweb-img.qq.com/images/js/iscroll_library/iscroll-5.2.0.js">&l ...
- python多线程应用——DB2数据库备份
前言:DB2一个实例下,可以存在多个数据库,之前使用shell备份脚本,但是同一时刻只能备份一个数据库,对于几百G的备份文件,这个速度显然太慢,今天学习了Python多线程,刚好应用一下. 分析:1. ...
- linux服务器ssh防爆破
查看爆破次数记录 # cat /var/log/secure | awk '/Failed/{print $(NF-3)}' | sort | uniq -c | awk '{print $2&quo ...
- 机器学习&深度学习基础(机器学习基础的算法概述及代码)
参考:机器学习&深度学习算法及代码实现 Python3机器学习 传统机器学习算法 决策树.K邻近算法.支持向量机.朴素贝叶斯.神经网络.Logistic回归算法,聚类等. 一.机器学习算法及代 ...
- plsql 通过修改配置文件的方式实现数据库的连接
查看oracle的安装位置: XP系统: 开始>>所有程序>>>Oracle-OraDb10g_home1>>>配置和移植工具>>>右 ...
- You can't specify target table 'ship_product_cat' for update in FROM clause
有时候我们在编辑update时需要select作为条件,在mysql中有时会出现这样的错误:You can't specify target table for update in FROM clau ...
- c 时间转移函数
/* @param date @param formart of date @ ...
- python从FTP下载文件
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ FTP常用操作 """ from ftplib ...
- go语言学习笔记1 Go开发环境
什么是Go?Go是一门并发支持.垃圾回收的编译型系统编程语言,旨在创造一门具有在静态编译语言的高性能和动态语言的高效开发之间拥有良好平衡的一门编程语言. Go的主要特点有哪些?* 类型安全 和 内存安 ...
