高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-001B-Tree indexes(B+Tree)
一、
1.什么是B-Tree indexes?
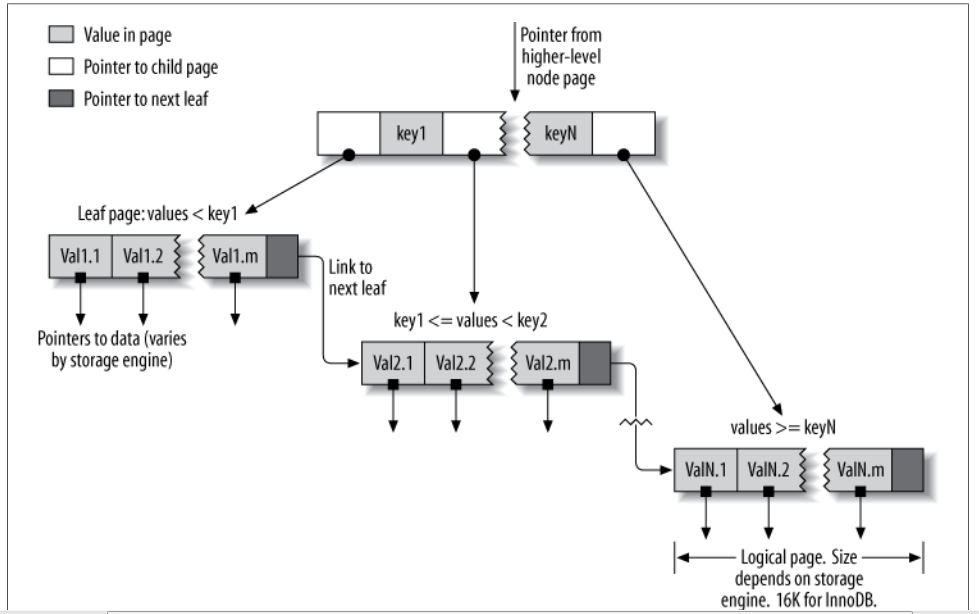
The general idea of a B-Tree is that all the values are stored in order, and each leaf page is the same distance from the root.
A B-Tree index speeds up data access because the storage engine doesn’t have to scan the whole table to find the desired data. Instead, it starts at the root node (not shown in this figure). The slots in the root node hold pointers to child nodes, and the storage engine follows these pointers. It finds the right pointer by looking at the values in the
node pages, which define the upper and lower bounds of the values in the child nodes.Eventually, the storage engine either determines that the desired value doesn’t exist or successfully reaches a leaf page.
Leaf pages are special, because they have pointers to the indexed data instead of pointers to other pages. (Different storage engines have different types of “pointers” to the data.) Our illustration shows only one node page and its leaf pages, but there might be many levels of node pages between the root and the leaves. The tree’s depth depends on how big the table is.
Because B-Trees store the indexed columns in order, they’re useful for searching for ranges of data. For instance, descending the tree for an index on a text field passes through values in alphabetical order, so looking for “everyone whose name begins with I through K” is efficient.
2.例子
CREATE TABLE People (
last_name varchar(50) not null,
first_name varchar(50) not null,
dob date not null,
gender enum('m', 'f')not null,
key(last_name, first_name, dob)
);

3、B-tree index的适用场景
B-Tree indexes work well for lookups by the full key value, a key range, or a key prefix. They are useful only if the lookup uses a leftmost prefix of the index. 3 The index we showed in the previous section will be useful for the
following kinds of queries:
Match the full value
A match on the full key value specifies values for all columns in the index. For example, this index can help you find a person named Cuba Allen who was born on 1960-01-01.
Match a leftmost prefix
This index can help you find all people with the last name Allen. This uses only the first column in the index.
Match a column prefix
You can match on the first part of a column’s value. This index can help you find all people whose last names begin with J. This uses only the first column in the index.
Match a range of values
This index can help you find people whose last names are between Allen and Barrymore. This also uses only the first column.
Match one part exactly and match a range on another part
This index can help you find everyone whose last name is Allen and whose first name starts with the letter K (Kim, Karl, etc.). This is an exact match on last_name and a range query on first_name .
Index-only queries
B-Tree indexes can normally support index-only queries, which are queries that access only the index, not the row storage. We discuss this optimization in “Covering Indexes” on page 177.
Because the tree’s nodes are sorted, they can be used for both lookups (finding values) and ORDER BY queries (finding values in sorted order). In general, if a B-Tree can help you find a row in a particular way, it can help you sort rows by the same criteria. So,our index will be helpful for ORDER BY clauses that match all the types of lookups we just listed.
4.B-tree index的缺点
• They are not useful if the lookup does not start from the leftmost side of the indexed columns. For example, this index won’t help you find all people named Bill or all people born on a certain date, because those columns are not leftmost in the index.Likewise, you can’t use the index to find people whose last name ends with a particular letter.
• You can’t skip columns in the index. That is, you won’t be able to find all people whose last name is Smith and who were born on a particular date. If you don’t specify a value for the first_name column, MySQL can use only the first column of the index.
• The storage engine can’t optimize accesses with any columns to the right of the first range condition. For example, if your query is WHERE last_name="Smith" AND first_name LIKE 'J%' AND dob='1976-12-23' , the index access will use only the first two columns in the index, because the LIKE is a range condition (the server can use the rest of the columns for other purposes, though). For a column that has a limited number of values, you can often work around this by specifying equality conditions instead of range conditions. We show detailed examples of this in the indexing case study later in this chapter.
Now you know why we said the column order is extremely important: these limitations are all related to column ordering. For optimal performance, you might need to create indexes with the same columns in different orders to satisfy your queries.
高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-001B-Tree indexes(B+Tree)的更多相关文章
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-004怎样用索引才高效
一.怎样用索引才高效 1.隔离索引列 MySQL generally can’t use indexes on columns unless the columns are isolated in t ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-002Hash indexes
一. 1.什么是hash index A hash index is built on a hash table and is useful only for exact lookups that u ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-005聚集索引
一.聚集索引介绍 1.什么是聚集索引? InnoDB’s clustered indexes actually store a B-Tree index and the rows together i ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第5章Indexing for High Performance-003索引的作用
一. 1. 1). Indexes reduce the amount of data the server has to examine.2). Indexes help the server av ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记 第6章 查询性能优化
6.1 为什么查询速度会慢 查询的生命周期大致可按照顺序来看:从客户端,到服务器,然后在服务器上进行解析,生成执行计划,执行,并返回结果给客户端.其中“执行”可以认为是整个生命周期中最重要的阶段. ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记 第5章 创建高性能的索引
索引(index),在MySQL中也被叫做键(key),是存储引擎用于快速找到记录的一种数据结构.索引优化是对查询性能优化最有效的手段. 5.1 索引基础 索引的类型 索引是在存储引擎层而 ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记 第4章 Schema与数据类型优化
4.1 选择优化的数据类型 通用原则 更小的通常更好 前提是要确保没有低估需要存储的值范围:因为它占用更少的磁盘.内存.CPU缓存,并且处理时需要的CPU周期也更少. 简单就好 简 ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第1章MySQL Architecture and History-001
1.MySQL架构图 2.事务的隔离性 事务的隔离性是specific rules for which changes are and aren’t visible inside and outsid ...
- 高性能MySQL笔记-第4章Optimizing Schema and Data Types
1.Good schema design is pretty universal, but of course MySQL has special implementation details to ...
随机推荐
- mysql数据库乱码问题
设置如下:SET character_set_client=utf8; SET character_set_results=utf8; SET character_set_connection=utf ...
- nyoj-67-三角形面积(S=(1/2)*(x1y2+x2y3+x3y1-x1y3-x2y1-x3y2))
题目链接 /* Name:nyoj-67-三角形面积 Copyright: Author: Date: 2018/4/26 16:44:47 Description: 三角形的三个顶点坐标求其面积的公 ...
- 利用Fiddler或Charles进行mock数据创造测试环境
使用场景:服务器数据不符合测试条件时,我们可以通过在本地创建虚拟数据来打到测试用例所描述的条件. fiddler使用方法 1.首先在本地创建txt数据:将抓到的response中的json数据拷贝到记 ...
- centos type.h 编译错误问题
# ifndef __int8_t_defined # define __int8_t_defined __intN_t (, __QI__); __intN_t (, __HI__); __intN ...
- 机器学习敲门砖:任何人都能看懂的TensorFlow介绍
机器学习敲门砖:任何人都能看懂的TensorFlow介绍 http://www.jiqizhixin.com/article/1440
- BZOJ - 2588 Spoj 10628. Count on a tree (可持久化线段树+LCA/树链剖分)
题目链接 第一种方法,dfs序上建可持久化线段树,然后询问的时候把两点之间的所有树链扒出来做差. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ...
- Restoring Road Network(Floyd算法的推广)
个人心得:看懂题目花费了不少时间,后面实现确实时间有点仓促了,只是简单的做出了判断是否为真假的情况, 后面看了题解发现其实在判断时候其实能够一起解决的,算了,基础比较差还是慢慢的来吧. 题意概述: 就 ...
- 【LeetCode】028. Implement strStr()
Implement strStr(). Return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle ...
- 数据库使用JDBC连接的方式
下面罗列了各种数据库使用JDBC连接的方式,可以作为一个手册使用. 1.Oracle8/8i/9i/10g/11g数据库(thin模式) Class.forName("oracle.jdbc ...
- Jeesite开垦
1. userIndex里面,$ctx是在哪里定义的? 就是request.context 2. 增加新的包后,扫描配置修改1) spring-context.xml文件中,扫描非@controlle ...
