Linux的重要子目录
1: 网卡的配置文件
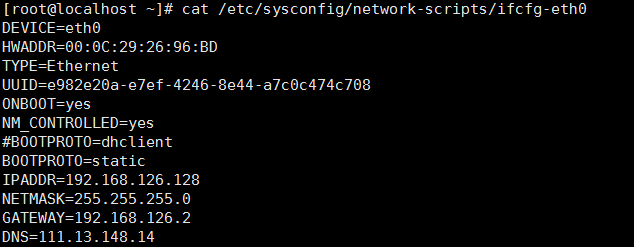 [
[
root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
DEVICE=eth0 #网卡设备名称
HWADDR=:0C::::BD #MAC地址
TYPE=Ethernet #以太网
UUID=e982e20a-e7ef--8e44-a7c0c474c708 #Linux系统内部的标识,唯一
ONBOOT=yes #开机启动
NM_CONTROLLED=yes
#BOOTPROTO=dhclient
BOOTPROTO=static #引导协议,一般为static(静态),dhclient(自动获取)
IPADDR=192.168.126.128 #IP地址
NETMASK=255.255.255.0 #子网掩码
GATEWAY=192.168.126.2 #网关
DNS=111.13.148.14
同样可以使用命令setup来执行网卡参数
2: DNS文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
; generated by /sbin/dhclient-script
search localdomain
nameserver 192.168.126.2
注:网卡的配置文件里面如果配置了DNS,它的优先级是高于这个配置文件的。
3: hosts文件
/etc/hosts 用户IP与名称(域名)的对应解析的配置文件
在实际的生产环境中很有用(一般所有的内网机器hosts文件都保持一致),主要用于服务器迁移

[root@centos6 ~]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
:: localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.197.100 centos6.
[root@centos6 ~]# hostname
centos6.
[root@centos6 ~]# ping centos6.
PING centos6. (192.168.197.100) () bytes of data.
bytes from centos6. (192.168.197.100): icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.051 ms
bytes from centos6. (192.168.197.100): icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.047 ms
bytes from centos6. (192.168.197.100): icmp_seq= ttl= time=0.047 ms
^C
-- centos6. ping statistics --
packets transmitted, received, % packet loss, time 2867ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.047/0.048/0.051/0.006 ms
实际生产环境的作用:
1. 开发、产品、测试人员用于通过正式的域名来测试产品
2. 服务器之间调用可以用域名,方便以后的迁移(各程序之间调用域名,机房迁移之后只需修改相应的hosts文件即可)
4: 主机名文件
/etc/sysconfig/network 修改机器名及网卡启动、网关配置文件
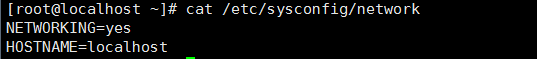
修改上述的HOSTNAME永久生效(修改主机名)
5: fstab文件
/etc/fstab 记录开机要挂载的文件系统文件
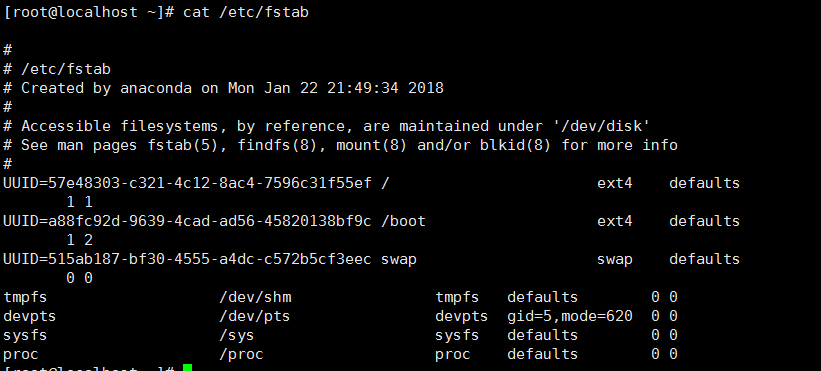
开机自动挂载磁盘,设置文件系统挂载信息的文件
文件信息一共包含六列(具体解析可 man fstab 查看)
第一列: 被挂载的设备名称
第二列: 挂载点位置
第三列: 文件系统类型
第四列: 挂载选项(只读、可写、其他等等)
第五列: 需不需要备份(0就是不备份)
第六列: 需不需要开机检查(0就是不需要,需要设置为1)
6: /etc/rc.local文件
存放开机自启动服务命令(同于windows里面的开始菜单中启动菜单)
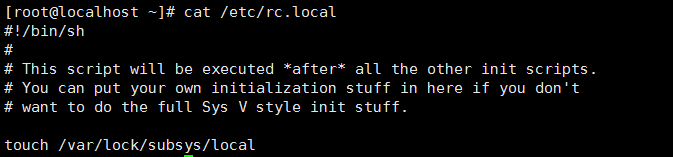
可以将命令直接写入到配置文件的末行
注: 实际生产环境中,一般服务开机自启动都会写入这个配置文件里面,这样只需要查看此配置文件就可以得知服务器运行哪些服务。
7: inittab文件
/etc/inittab 设定系统启动时init进程将把系统设置成什么样的运行级别及加相关的启动文件配置的文件
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/inittab
# inittab is only used by upstart for the default runlevel. #只被用于突然发起的默认运行级别
#
# ADDING OTHER CONFIGURATION HERE WILL HAVE NO EFFECT ON YOUR SYSTEM.
#
# System initialization is started by /etc/init/rcS.conf
#
# Individual runlevels are started by /etc/init/rc.conf
#
# Ctrl-Alt-Delete is handled by /etc/init/control-alt-delete.conf
#
# Terminal gettys are handled by /etc/init/tty.conf and /etc/init/serial.conf,
# with configuration in /etc/sysconfig/init.
#
# For information on how to write upstart event handlers, or how
# upstart works, see init(), init(), and initctl().
#
# Default runlevel. The runlevels used are:
# - halt (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
# - Single user mode
# - Multiuser, without NFS (The same as , if you do not have networking)
# - Full multiuser mode
# - unused
# - X11
# - reboot (Do NOT set initdefault to this)
#
id::initdefault:
注: linux开机启动流程如下:
开机自检----MBR引导程序-----GRUB菜单----加载内核----运行init进程----读取/etc/inittab配置文件----执行/etc/rc.d/rc.sysinit脚本----执行/etc/rc.local脚本(读取运行级别)----启动终端登录进程----登录系统
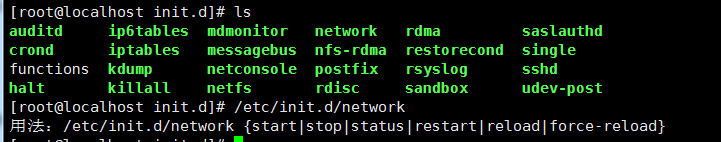
8: 软件启动服务文件
/etc/init.d 安装的软件启动服务(系统的启动服务)所在目录
使用yum、rpm安装的软件启动程序都在这个目录下
9: 全局环境变量文件
/etc/profile 系统全局变量的配置文件
[root@localhost init.d]# cat /etc/profile
# /etc/profile # System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup #系统全局变量和启动程序
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc # It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you #除非你知道你要做什么,否则不要更改
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in #更好的是去创建脚本在/etc/profile.d,去改变
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates. pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$
else
PATH=$:$PATH
fi
esac
} if [ -x /usr/bin/id ]; then
if [ -z "$EUID" ]; then
# ksh workaround
EUID=`id -u`
UID=`id -ru`
fi
USER="`id -un`"
LOGNAME=$USER
MAIL="/var/spool/mail/$USER"
fi # Path manipulation
if [ "$EUID" = "" ]; then
pathmunge /sbin
pathmunge /usr/sbin
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin
else
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin after
pathmunge /usr/sbin after
pathmunge /sbin after
fi HOSTNAME=`/bin/hostname >/dev/null`
HISTSIZE=
if [ "$HISTCONTROL" = "ignorespace" ] ; then
export HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
else
export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
fi export PATH USER LOGNAME MAIL HOSTNAME HISTSIZE HISTCONTROL # By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for login shell
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt ] && [ "`id -gn`" = "`id -un`" ]; then
umask
else
umask
fi for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null 2>&1
fi
fi
done unset i
unset -f pathmunge
export TMOUT=300
HISTSIZE=50
HISTFILESIZE=50
与之关联的还有一个文件/etc/profile.d,可以存放登录后自动执行的脚本
[root@centos6 ~]# cd /etc/profile.d/
[root@centos6 profile.d]# vi welcome.sh
echo "welcome to mingongge's blog"
[root@centos6 profile.d]# chmod +x welcome.sh
[root@centos6 profile.d]# logout
Last login: Thu Dec :: from 192.168.197.1
welcome to mingongge's blog
10: motd文件
/etc/motd 用户登录提示信息
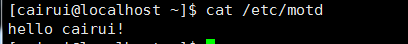

编辑过后,再登录就显示自己编辑的文本。
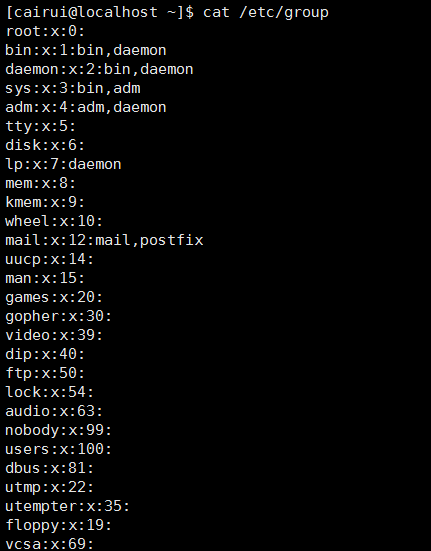
11: group文件
/etc/group 用户的组名与相关信息
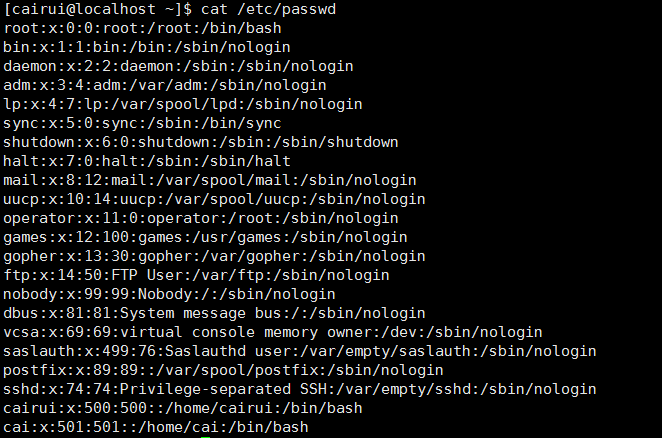
12: 用户账号相关信息
/etc/passwd 系统所有用户账号信息文件
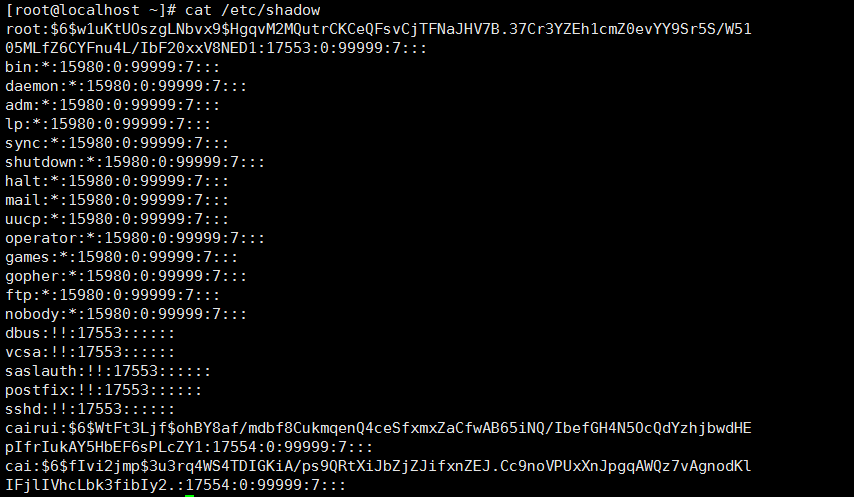
13: 用户密码相关文件
/etc/shadow 系统所有用户密码信息文件
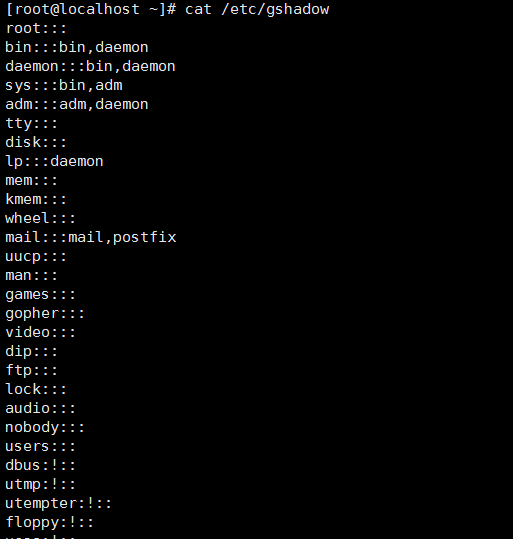
/etc/gshadow 系统所有组密码信息文件
14: 系统信息文件
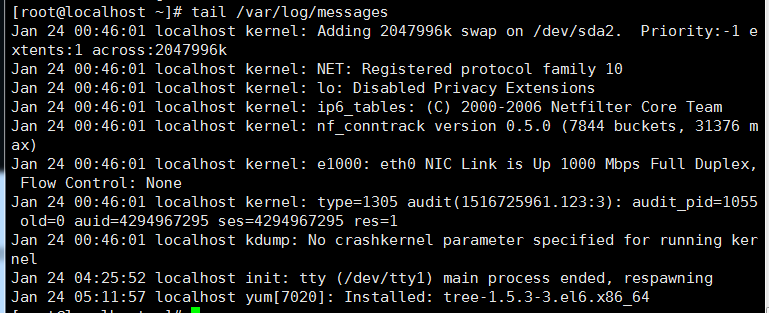
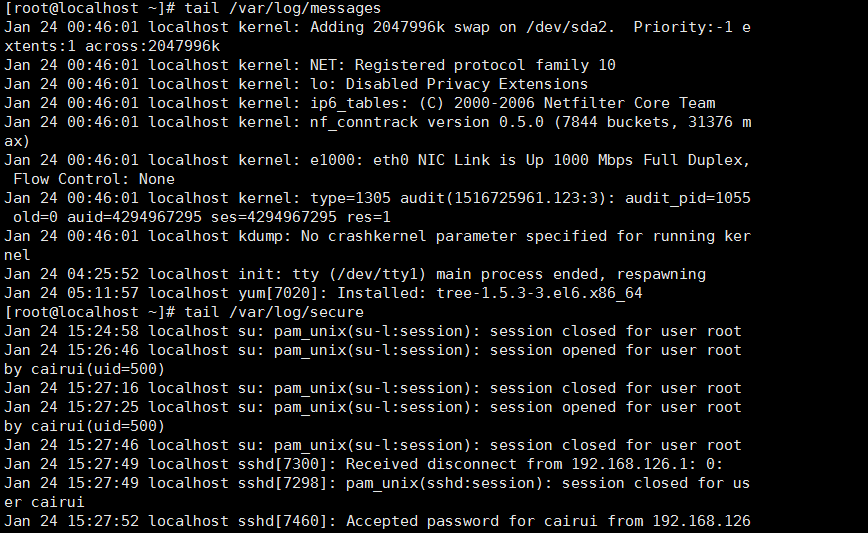
/var/log/messages 系统日志文件
/var/log/secure 登陆系统存取信息文件(系统安全日志文件)
15: 定时任务配置文件
/var/spool/cron/ 定时任务配置文件
DESCRIPTION
Crontab is the program used to install, remove or list the tables #crontab是程序用来安装,移除或者列出一个表去驱动cron进程。
used to drive the cron() daemon. Each user can have their own
crontab, and though these are files in /var/spool/ , they are not #这些定时文件到在/var/spool/cron下
intended to be edited directly. For SELinux in mls mode can be even
more crontabs - for each range. For more see selinux(). The cron jobs could be allow or disallow for different users. For
classical crontab there exists cron.allow and cron.deny files. If
cron.allow file exists, then you must be listed therein in order to
be allowed to use this command. If the cron.allow file does not
exist but the cron.deny file does exist, then you must not be
listed in the cron.deny file in order to use this command. If nei-
ther of these files exists, only the super user will be allowed to
use this command. The second option is using PAM authentication,
where you set up users, which could or couldn’t use crontab and
also system cron jobs from /etc/cron.d/. The temporary directory could be set in enviroment variables. If
it’s not set by user than /tmp is used.
Linux的重要子目录的更多相关文章
- (转)Linux系统重要子目录及内容小结
Linux系统重要子目录及内容小结 原文:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaolong361/article/details/52318834 1.首先来介绍下根目录下的一些重要目录含义 ...
- Linux移植之子目录下的built-in.o生成过程分析
在Linux移植之make uImage编译过程分析中罗列出了最后链接生成vmlinux的过程.可以看到在每个子目录下都有一个built-in.o文件.对于此产生了疑问built-in.o文件是根据什 ...
- Linux C++ 访问子目录以及里面的文件
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <vector> # ...
- 构建LINUX下的入侵检测系统——LIDS 系统管理命令--vlock
构建LINUX下的入侵检测系统——LIDS 系统管理命令--vlock http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-306663-id-2440200.html LIDS官方网站: ...
- Linux命令及架构部署大全
1.Linux系统基础知识 Linux 基础优化配置 Linux系统根目录结构介绍 linux系统重要子目录介绍 Linux基础命令(之一)详解 Linux基础命令(之二)详解 Linux文件系统 L ...
- Linux 驱动开发
linux驱动开发总结(一) 基础性总结 1, linux驱动一般分为3大类: * 字符设备 * 块设备 * 网络设备 2, 开发环境构建: * 交叉工具链构建 * NFS和tftp服务器安装 3, ...
- Linux 目录结构_004
前言 Linux文件系统层次标准,英文全称Filesystem Hierarchy Standard,英文简称FHS. 由于利用Linux来开发产品的团队和个人实在太多了,如果每个人都以自己的想法来配 ...
- Linux移植之make uImage编译过程分析
编译出uboot可以运行的linux内核代码的命令是make uImage,下面详细介绍下生成linux-2.6.22.6/arch/arm/boot/uImage的过程: 1.vmlinux.Ima ...
- linux菜鸟笔记
linux目录的子目录复制 cp -r 要复制的目录+新的目录 cp -r a test 意思就是将a的子目录及文件复制到新的目录test下面 zt@ubuntu:~/Desktop$ mkdir - ...
随机推荐
- zedgraph控件的一些比较有用的属性
(1)zedgraph控件属性具体解释: AxisChange()() ->> This performs an axis change command on the graphPane. ...
- CTF中常见文件的文件头(十六进制)
jpg/jpeg FF D8 FF E0 或 FF D8 FF E1 或 FF D8 FF E8 png 89 50 4E 47 bmp 42 4D 36 5D gif 47 49 46 38 zip ...
- ES6相关实用特性
本文总结ECMAScript6相关实用特性 目录 let和const 箭头函数 class 对象字段 模板字符串 解构赋值 函数参数扩展 迭代器for...of 模块加载 map和weakmap se ...
- Winsock 示例
#include "stdafx.h" #include <Windows.h> #include <iostream> #pragma comment(l ...
- Oracle中REGEXP_SUBSTR函数(字符串转多行)
Oracle中REGEXP_SUBSTR函数 Oracle中REGEXP_SUBSTR函数的使用说明: 题目如下: 在oracle中,使用一条语句实现将'17,20,23'拆分成'17','20',' ...
- 查看hdfs各目录分别占用多少空间
之前在网上搜索到的全部单位好像都是byte的,看起来很麻烦,然后自己看了下 hadoop fs -help [hadoop@slave3 java]$ hadoop fs -help Usage: h ...
- apache2不识别php
sudo apt-get install libapache2-mod-php7.0 sudo a2enmod php7.0 sudo service apache2 restart 注意:Apach ...
- adb pull 和 adb push
1. 操作单个文件 通过adb push,则可将文件添加到SD卡中.如果想在push的时候修改文件名称的话,只需要修改push的第二个参数改成完整路径(目录+文件名),如/sdcard/test-0. ...
- JAVA中string类的split方法
split([separator,[limit]])第一个参数为分隔符,可以是一个正则表达式,第二个参数为返回结果数组的长度
- Hbuilder实用技巧(转)
Hbuilder实用技巧 原创 2016年05月19日 10:25:42 标签: hbuilder 操作 16551 1. Q:怎么实现代码追踪? A:在编辑代码时经常会出现需要跳转到引用文件或者变量 ...
