生成对抗网络GAN介绍
GAN原理
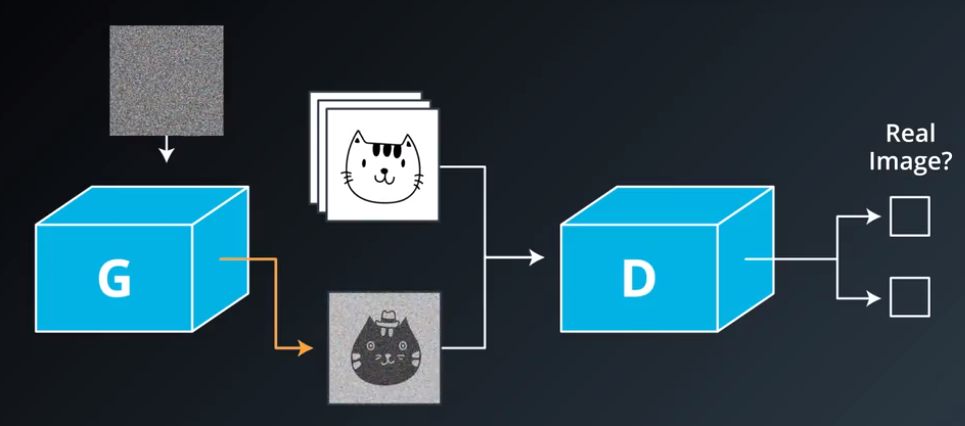
生成对抗网络GAN由生成器和判别器两部分组成:
- 判别器是常规的神经网络分类器,一半时间判别器接收来自训练数据中的真实图像,另一半时间收到来自生成器中的虚假图像。训练判别器使得对于真实图像,它输出的概率值接近1,而对于虚假图像则接近0
- 生成器与判别器正好相反,通过训练,它输出判别器赋值概率接近1的图像。生成器需要产生更加真实的输出,从而欺骗判别器
- 在GAN中要同时使用两个优化器,分别用来最小化判别器和生成器的损失
Batch Normalization
Batch Normalization是DCGAN(Deep Covolutional GAN)中常用的技术,它可以使网络训练得更快,允许更大的学习率,使更多的激活函数变得有效,并且使得参数更易初始化,BN一般用于激活函数使用之前。以图片数据为例,这里简单介绍一下BN的计算过程(参照Tensorflow和Keras中的API)。记训练数据$X$的维数为($N_{batch}$, $N_{height}$, $N_{width}$, $N_{channel}$),批次均值和批次方差分别为$$\mu_{c}=\frac{1}{N_bN_hN_w} \sum_{i=1}^{N_b} \sum_{j=1}^{N_h}\sum_{k=1}^{N_w}X_{ijkc}\text{ },\text{ }\sigma_{c}^{2}=\frac{1}{N_bN_hN_w} \sum_{i=1}^{N_b} \sum_{j=1}^{N_h}\sum_{k=1}^{N_w}\left(X_{ijkc}-\mu_{c}\right)^{2}\text{ },\text{其中}c=1,2,\cdots,N_c$$则BN的输出为$$Y_{ijkc}=\gamma \hat{X}_{ijkc}+\beta,\text{ where }\hat{X}_{ijkc}=\frac{X_{ijkc}-\mu_{c}}{\sqrt{\sigma_{c}^{2}+\epsilon}}$$其中$\epsilon$是一个很小的正值(例如0.001),$\gamma$和$\beta$均为可训练参数。最后用$\mu_{c}$和$\sigma_{c}^{2}$更新总体的均值和方差,总体均值和方差在检验网络和进行预测时使用:$$\hat{\mu}_c=\tau \hat{\mu}_{c}+(1-\tau) \mu_{c}\text{ },\text{ }\hat{\sigma}_{c}^{2}=\tau\hat{\sigma}_{c}^{2}+(1-\tau) \sigma_{c}^{2}\text{ },\text{其中}c=1,2,\cdots,N_c$$其中$\hat{\mu}_c$和$\hat{\sigma}_{c}^{2}$的初始值为0和1,$\tau$可取为0.99
DCGAN应用示例
使用的数据集为the Street View House Numbers(SVHN) dataset,目标是由虚假图像(随机噪音)生成数字图像,具体代码如下所示:
- 数据处理


import pickle as pkl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.io import loadmat
import tensorflow as tf
### 读取数据
data_dir = 'data/'
trainset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntrain_32x32.mat')
testset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntest_32x32.mat')
#the same scale as tanh activation function
def scale(x, feature_range=(-1, 1)):
# scale to (0, 1)
x = ((x - x.min())/(255 - x.min()))
# scale to feature_range
min, max = feature_range
x = x * (max - min) + min
return x
### 数据准备
class Dataset:
def __init__(self, train, test, val_frac=0.5, shuffle=False, scale_func=None):
split_idx = int(len(test['y'])*(1 - val_frac))
self.test_x, self.valid_x = test['X'][:,:,:,:split_idx], test['X'][:,:,:,split_idx:]
self.test_y, self.valid_y = test['y'][:split_idx], test['y'][split_idx:]
self.train_x, self.train_y = train['X'], train['y']
###(32,32,3,:) to (:,32,32,3)
self.train_x = np.rollaxis(self.train_x, 3)
self.valid_x = np.rollaxis(self.valid_x, 3)
self.test_x = np.rollaxis(self.test_x, 3)
if scale_func is None:
self.scaler = scale
else:
self.scaler = scale_func
self.shuffle = shuffle
def batches(self, batch_size):
if self.shuffle:
idx = np.arange(len(self.train_x))
np.random.shuffle(idx)
self.train_x = self.train_x[idx]
self.train_y = self.train_y[idx]
n_batches = len(self.train_y)//batch_size
for ii in range(0, len(self.train_y), batch_size):
x = self.train_x[ii:ii+batch_size]
y = self.train_y[ii:ii+batch_size]
yield self.scaler(x), y
### 创建数据集
dataset = Dataset(trainset, testset) - 搭建网络
- 模型输入


def model_inputs(real_dim, z_dim):
inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, *real_dim), name='input_real')
inputs_z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, z_dim), name='input_z')
return inputs_real, inputs_z - 搭建生成器Generator


### Generator
def generator(z, output_dim, reuse=False, alpha=0.2, training=True):
with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=reuse):
x1 = tf.layers.dense(z, 4*4*512) #First fully connected layer
x1 = tf.reshape(x1, (-1, 4, 4, 512)) #Reshape it to start the convolutional stack
x1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x1, training=training)
x1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1) #leaky relu, 4x4x512 now
# transpose convolution > batch norm > leaky ReLU
x2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x1, 256, 5, strides=2, padding='same') #with zero padding
x2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training)
x2 = tf.maximum(alpha * x2, x2) #8x8x256 now
# transpose convolution > batch norm > leaky ReLU
x3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x2, 128, 5, strides=2, padding='same')
x3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training)
x3 = tf.maximum(alpha * x3, x3) #16x16x128 now
# output layer
logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x3, output_dim, 5, strides=2, padding='same') #32x32x3 now
out = tf.tanh(logits)
return out - 搭建判别器Discriminator


### Discriminator
def discriminator(x, reuse=False, training=True, alpha=0.2):
with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse):
x1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, 64, 5, strides=2, padding='same') #Input layer is 32x32x3
relu1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1) #16x16x64
# convolution > batch norm > leaky ReLU
x2 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu1, 128, 5, strides=2, padding='same')
bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training)
relu2 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn2, bn2) #8x8x128
# convolution > batch norm > leaky ReLU
x3 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu2, 256, 5, strides=2, padding='same')
bn3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training)
relu3 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn3, bn3) #4x4x256
# Flatten it
flat = tf.reshape(relu3, (-1, 4*4*256))
logits = tf.layers.dense(flat, 1)
out = tf.sigmoid(logits)
return out, logits - 搭建GAN并计算损失函数


### Create GAN and Compute Model Loss
### input_real: Images from the real dataset
### input_z: Z input(noise)
### output_dim: The number of channels in the output image
def model_loss(input_real, input_z, output_dim, training=True, alpha=0.2, smooth=0.1):
g_model = generator(input_z, output_dim, alpha=alpha, training=training)
d_model_real, d_logits_real = discriminator(input_real, training=training, alpha=alpha)
# reuse=True: reuse the variables instead of creating new ones if we build the graph again
d_model_fake, d_logits_fake = discriminator(g_model, reuse=True, training=training, alpha=alpha)
# real and fake loss
d_loss_real = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_real, labels=tf.ones_like(d_model_real)*(1-smooth)) #label smoothing
d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_real)
d_loss_fake = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake, labels=tf.zeros_like(d_model_fake))
d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_fake)
### discriminator and generator loss
d_loss = d_loss_real + d_loss_fake
g_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=d_logits_fake, labels=tf.ones_like(d_model_fake))
g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(g_loss)
return d_loss, g_loss, g_model - 优化器


### Optimizer
### beta1: The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment in the optimizer
def model_opt(d_loss, g_loss, learning_rate, beta1):
# Get weights and bias to update
t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('discriminator')]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('generator')]
# Optimize
with tf.control_dependencies(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)): #update population mean and variance
d_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(d_loss, var_list=d_vars)
g_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(g_loss, var_list=g_vars)
return d_train_opt, g_train_opt - 封装GAN


### Final GAN
class GAN:
def __init__(self, real_size, z_size, learning_rate, alpha=0.2, smooth=0.1, beta1=0.5):
tf.reset_default_graph()
self.input_real, self.input_z = model_inputs(real_size, z_size)
self.training = tf.placeholder_with_default(True, (), "train_status")
self.d_loss, self.g_loss, self.samples = model_loss(self.input_real, self.input_z, real_size[2], \
training=self.training, alpha=alpha, smooth=smooth)
self.d_opt, self.g_opt = model_opt(self.d_loss, self.g_loss, learning_rate, beta1)
- 模型输入
- 训练网络


def train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size, print_every=10, show_every=100):
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sample_z = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=(72, z_size)) #samples for generator to generate(for plotting)
samples, losses = [], []
steps = 0
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for e in range(epochs):
for x, y in dataset.batches(batch_size):
steps += 1
### sample random noise for Generator
batch_z = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=(batch_size, z_size))
### run optimizers
_, _ = sess.run([net.d_opt, net.g_opt], feed_dict={net.input_real:x, net.input_z:batch_z})
### get the losses and print them out
if steps % print_every == 0:
train_loss_d = net.d_loss.eval({net.input_z: batch_z, net.input_real: x})
train_loss_g = net.g_loss.eval({net.input_z: batch_z})
print("Epoch {}/{}...".format(e+1, epochs), \
"Discriminator Loss: {:.4f}...".format(train_loss_d), \
"Generator Loss: {:.4f}".format(train_loss_g))
losses.append((train_loss_d, train_loss_g)) #save losses to view after training
### save generated samples
if steps % show_every == 0:
# training=False: the batch normalization layers will use the population statistics rather than the batch statistics
gen_samples = sess.run(net.samples, feed_dict={net.input_z: sample_z, net.training: False})
samples.append(gen_samples)
saver.save(sess, './checkpoints/generator.ckpt')
with open('samples.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pkl.dump(samples, f)
return losses, samples ### Hyperparameters
real_size = (32,32,3)
z_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.0002
batch_size = 128
epochs = 25
alpha = 0.2
smooth = 0.1
beta1 = 0.5 ### Create and Train the network
net = GAN(real_size, z_size, learning_rate, alpha=alpha, smooth=smooth, beta1=beta1)
losses, samples = train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size) - 最终结果可视化


### Visualize
def view_samples(sample, nrows, ncols, figsize=(5,5)): #the number of the sample=nrows*ncols
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize, nrows=nrows, ncols=ncols, sharey=True, sharex=True)
for ax, img in zip(axes.flatten(), sample):
ax.axis('off')
img = ((img - img.min())*255 / (img.max() - img.min())).astype(np.uint8)
ax.set_adjustable('box-forced')
im = ax.imshow(img, aspect='equal')
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0)
return fig, axes
view_samples(samples[-1], 6, 12, figsize=(10,5))
最终生成的图像如下图所示

GAN应用于半监督学习
使用的数据集同上,为了建立一个半监督学习的情景,这里仅使用前1000个训练数据的标签,并且将GAN的判别器由二分类变为多分类,针对此数据,共分为11类(10个真实数字和虚假图像)。代码的整体结构和上一部分相同,这里仅注释有改动的部分,针对该网络更为细节的改进参考文章Improved Techniques for Training GANs以及对应的github仓库。
- 数据处理


import pickle as pkl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.io import loadmat
import tensorflow as tf
data_dir = 'data/'
trainset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntrain_32x32.mat')
testset = loadmat(data_dir + 'svhntest_32x32.mat')
def scale(x, feature_range=(-1, 1)):
x = ((x - x.min())/(255 - x.min()))
min, max = feature_range
x = x * (max - min) + min
return x
class Dataset:
def __init__(self, train, test, val_frac=0.5, shuffle=True, scale_func=None):
split_idx = int(len(test['y'])*(1 - val_frac))
self.test_x, self.valid_x = test['X'][:,:,:,:split_idx], test['X'][:,:,:,split_idx:]
self.test_y, self.valid_y = test['y'][:split_idx], test['y'][split_idx:]
self.train_x, self.train_y = train['X'], train['y']
###################
# For the purpose of semi-supervised learn, pretend that there are only 1000 labels
# Use this mask to say which labels will allow to use
self.label_mask = np.zeros_like(self.train_y)
self.label_mask[0:1000] = 1
###################
self.train_x = np.rollaxis(self.train_x, 3)
self.valid_x = np.rollaxis(self.valid_x, 3)
self.test_x = np.rollaxis(self.test_x, 3)
if scale_func is None:
self.scaler = scale
else:
self.scaler = scale_func
self.train_x = self.scaler(self.train_x)
self.valid_x = self.scaler(self.valid_x)
self.test_x = self.scaler(self.test_x)
self.shuffle = shuffle
def batches(self, batch_size, which_set="train"):
###################
# Semi-supervised learn need both train data and validation(test) data
# Semi-supervised learn need both images and labels
###################
x_name = which_set + "_x"
y_name = which_set + "_y"
num_examples = len(getattr(self, y_name))
if self.shuffle:
idx = np.arange(num_examples)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
setattr(self, x_name, getattr(self, x_name)[idx])
setattr(self, y_name, getattr(self, y_name)[idx])
if which_set == "train":
self.label_mask = self.label_mask[idx]
dataset_x = getattr(self, x_name)
dataset_y = getattr(self, y_name)
for ii in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
x = dataset_x[ii:ii+batch_size]
y = dataset_y[ii:ii+batch_size]
if which_set == "train":
###################
# When use the data for training, need to include the label mask
# Pretend don't have access to some of the labels
yield x, y, self.label_mask[ii:ii+batch_size]
###################
else:
yield x, y
dataset = Dataset(trainset, testset) - 搭建网络
- 模型输入


def model_inputs(real_dim, z_dim):
inputs_real = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, *real_dim), name='input_real')
inputs_z = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (None, z_dim), name='input_z')
###################
# Add placeholders for labels and label masks
y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None), name='y')
label_mask = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (None), name='label_mask')
###################
return inputs_real, inputs_z, y, label_mask - 搭建生成器Generator


### Generator
def generator(z, output_dim, reuse=False, alpha=0.2, training=True, size_mult=128):
with tf.variable_scope('generator', reuse=reuse):
x1 = tf.layers.dense(z, 4 * 4 * size_mult * 4)
x1 = tf.reshape(x1, (-1, 4, 4, size_mult * 4))
x1 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x1, training=training)
x1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1) #(:,4,4,4*size_mult)
x2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x1, size_mult * 2, 5, strides=2, padding='same')
x2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training)
x2 = tf.maximum(alpha * x2, x2) #(:,8,8,2*size_mult)
x3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x2, size_mult, 5, strides=2, padding='same')
x3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training)
x3 = tf.maximum(alpha * x3, x3) #(:,16,16,size_mult)
logits = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(x3, output_dim, 5, strides=2, padding='same') #(:,32,32,3)
out = tf.tanh(logits)
return out - 搭建判别器Discriminator


### Discriminator
###################
### Add dropout layer to reduce overfitting since only 1000 labelled samples exist
### 10 class classification(10 digits) and set [fake logit=0]
###################
def discriminator(x, reuse=False, training=True, alpha=0.2, drop_rate=0., num_classes=10, size_mult=64):
with tf.variable_scope('discriminator', reuse=reuse):
# Add dropout layer
x = tf.layers.dropout(x, rate=drop_rate/2.5) #Input layer (:,32,32,3)
###################
x1 = tf.layers.conv2d(x, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
relu1 = tf.maximum(alpha * x1, x1)
# Add dropout layer
relu1 = tf.layers.dropout(relu1, rate=drop_rate) #(:,16,16,size_mult)
###################
x2 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu1, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
bn2 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x2, training=training)
relu2 = tf.maximum(alpha * x2, x2) #(:,8,8,size_mult)
###################
x3 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu2, size_mult, 3, strides=2, padding='same')
bn3 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x3, training=training)
relu3 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn3, bn3)
# Add dropout layer
relu3 = tf.layers.dropout(relu3, rate=drop_rate) #(:,4,4,size_mult)
###################
x4 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu3, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='same')
bn4 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x4, training=training)
relu4 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn4, bn4) #(:,4,4,2*size_mult)
###################
x5 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu4, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='same')
bn5 = tf.layers.batch_normalization(x5, training=training)
relu5 = tf.maximum(alpha * bn5, bn5) #(:,4,4,2*size_mult)
###################
x6 = tf.layers.conv2d(relu5, 2 * size_mult, 3, strides=1, padding='valid')
# This layer is used for the feature matching loss, don't use batch normalization on this layer
# See the function model_loss for the feature matching loss
relu6 = tf.maximum(alpha * x6, x6) #(:,2,2,2*size_mult)
###################
# Flatten by global average pooling
features = tf.reduce_mean(relu6, (1, 2)) #(:,2*size_mult)
# Multi-classification
class_logits = tf.layers.dense(features, num_classes) #(:,10)
out = tf.nn.softmax(class_logits)
###################
# Split real and fake logits for classifying real and fake
real_class_logits = class_logits
fake_class_logits = 0.
# Set gan_logits such that P(input is real | input) = sigmoid(gan_logits)
# For Numerical stability, use this trick: log sum_i exp a_i = m + log sum_i exp(a_i - m), m = max_i a_i
mx = tf.reduce_max(real_class_logits, 1, keepdims=True) #(:,1)
stable_real_class_logits = real_class_logits - mx #minus the largest real logit for each sample, (:,10)
gan_logits = tf.log(tf.reduce_sum(tf.exp(stable_real_class_logits), 1)) + tf.squeeze(mx) - fake_class_logits #(number of samples,)
###################
return out, class_logits, gan_logits, features - 搭建GAN并计算损失函数


### Create GAN and Compute Model Loss
def model_loss(input_real, input_z, output_dim, y, num_classes, label_mask, g_size_mult, d_size_mult, \
training=True, alpha=0.2, drop_rate=0.):
g_model = generator(input_z, output_dim, alpha=alpha, size_mult=g_size_mult, training=training)
d_on_real = discriminator(input_real, alpha=alpha, drop_rate=drop_rate, size_mult=d_size_mult, training=training)
d_on_fake = discriminator(g_model, reuse=True, alpha=alpha, drop_rate=drop_rate, size_mult=d_size_mult, training=training)
out_real, class_logits_real, gan_logits_real, features_real = d_on_real
out_fake, class_logits_fake, gan_logits_fake, features_fake = d_on_fake
###################
# Compute the loss for the discriminator
# 1. The loss for the GAN problem, minimize the cross-entropy for the binary
# real-vs-fake classification problem
# 2. The loss for the SVHN digit classification problem, where minimize the
# cross-entropy(use the labels) for the multi-class softmax
d_loss_real = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=gan_logits_real, labels=tf.ones_like(gan_logits_real)*0.9) # label smoothing
d_loss_real = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_real)
d_loss_fake = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=gan_logits_fake, labels=tf.zeros_like(gan_logits_fake))
d_loss_fake = tf.reduce_mean(d_loss_fake)
y = tf.squeeze(y) #labels
class_cross_entropy = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=class_logits_real, \
labels=tf.one_hot(y, class_logits_real.get_shape()[1], dtype=tf.float32))
# Use label_mask to ignore the examples pretending unlabeled for the semi-supervised problem
class_cross_entropy = tf.squeeze(class_cross_entropy)
label_mask = tf.squeeze(tf.to_float(label_mask))
d_loss_class = tf.reduce_sum(label_mask * class_cross_entropy) / tf.maximum(1., tf.reduce_sum(label_mask))
d_loss = d_loss_class + d_loss_real + d_loss_fake
###################
# Compute the loss for the generator
# Set the loss to the "feature matching" loss invented by Tim Salimans at OpenAI
# This loss is the mean absolute difference between the real features and the fake features
# This loss works better for semi-supervised learnings than the traditional generator loss
real_moments = tf.reduce_mean(features_real, axis=0)
fake_moments = tf.reduce_mean(features_fake, axis=0)
g_loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(real_moments - fake_moments))
###################
pred_class = tf.cast(tf.argmax(class_logits_real, 1), tf.int32)
eq = tf.equal(y, pred_class)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(tf.to_float(eq))
masked_correct = tf.reduce_sum(label_mask * tf.to_float(eq))
return d_loss, g_loss, correct, masked_correct, g_model - 优化器


### Optimizer
def model_opt(d_loss, g_loss, learning_rate, beta1):
t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('discriminator')]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if var.name.startswith('generator')]
with tf.control_dependencies(tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)):
d_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(d_loss, var_list=d_vars)
g_train_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate, beta1=beta1).minimize(g_loss, var_list=g_vars)
return d_train_opt, g_train_opt - 封装GAN


### Final GAN
class GAN:
def __init__(self, real_size, z_size, g_size_mult=32, d_size_mult=64, num_classes=10, alpha=0.2, beta1=0.5):
tf.reset_default_graph()
###################
# The dropout rate and learning rate
self.drop_rate = tf.placeholder_with_default(.6, (), "drop_rate")
self.learning_rate = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, None, "learning_rate")
###################
self.input_real, self.input_z, self.y, self.label_mask = model_inputs(real_size, z_size)
self.training = tf.placeholder_with_default(True, (), "train_status")
loss_results = model_loss(self.input_real, self.input_z, real_size[2], self.y, num_classes, self.label_mask, \
g_size_mult, d_size_mult, self.training, alpha, self.drop_rate)
self.d_loss, self.g_loss, self.correct, self.masked_correct, self.samples = loss_results
self.d_opt, self.g_opt = model_opt(self.d_loss, self.g_loss, self.learning_rate, beta1)
- 模型输入
- 训练网络


def train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size, learning_rate):
saver = tf.train.Saver()
sample_z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(50, z_size))
samples, train_accuracies, test_accuracies = [], [], []
steps = 0
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for e in range(epochs):
print("Epoch",e)
num_examples = 0
num_correct = 0
for x, y, label_mask in dataset.batches(batch_size):
steps += 1
num_examples += label_mask.sum()
batch_z = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(batch_size, z_size))
_, _, correct = sess.run([net.d_opt, net.g_opt, net.masked_correct], \
feed_dict={net.input_real: x, net.input_z: batch_z, net.y: y, \
net.label_mask: label_mask, net.learning_rate: learning_rate})
num_correct += correct
###################
# At the end of the epoch:
# compute train accuracy(only for labeled[masked] images)
# shrink learning rate
train_accuracy = num_correct / float(num_examples)
print("\t\tClassifier train accuracy: ", train_accuracy)
learning_rate *= 0.9
###################
# At the end of the epoch: compute test accuracy
num_examples = 0
num_correct = 0
for x, y in dataset.batches(batch_size, which_set="test"):
num_examples += x.shape[0]
correct = sess.run(net.correct, feed_dict={net.input_real: x, net.y: y, net.drop_rate: 0., net.training: False})
num_correct += correct
test_accuracy = num_correct / float(num_examples)
print("\t\tClassifier test accuracy", test_accuracy)
###################
# Save history of accuracies to view after training
train_accuracies.append(train_accuracy)
test_accuracies.append(test_accuracy)
###################
gen_samples = sess.run(net.samples, feed_dict={net.input_z: sample_z, net.training: False})
samples.append(gen_samples)
saver.save(sess, './checkpoints/generator.ckpt')
with open('samples.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pkl.dump(samples, f)
return train_accuracies, test_accuracies, samples real_size = (32,32,3)
z_size = 100
learning_rate = 0.0003
batch_size = 128
epochs = 20
net = GAN(real_size, z_size)
train_accuracies, test_accuracies, samples = train(net, dataset, epochs, batch_size, learning_rate) - 最终结果


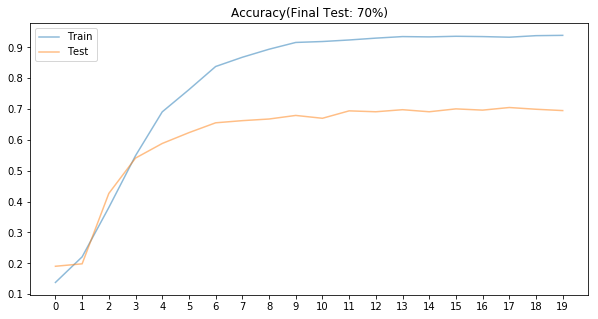
# Plot accuracies
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(train_accuracies, label='Train', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(test_accuracies, label='Test', alpha=0.5)
ax.set_xticks(range(epochs))
plt.title("Accuracy(Final Test: {0}%)".format(int(round(test_accuracies[-1]*100))))
plt.legend()
生成对抗网络GAN介绍的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow从1到2(十二)生成对抗网络GAN和图片自动生成
生成对抗网络的概念 上一篇中介绍的VAE自动编码器具备了一定程度的创造特征,能够"无中生有"的由一组随机数向量生成手写字符的图片. 这个"创造能力"我们在模型中 ...
- 人工智能中小样本问题相关的系列模型演变及学习笔记(二):生成对抗网络 GAN
[说在前面]本人博客新手一枚,象牙塔的老白,职业场的小白.以下内容仅为个人见解,欢迎批评指正,不喜勿喷![握手][握手] [再啰嗦一下]本文衔接上一个随笔:人工智能中小样本问题相关的系列模型演变及学习 ...
- 用MXNet实现mnist的生成对抗网络(GAN)
用MXNet实现mnist的生成对抗网络(GAN) 生成式对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Network,简称GAN)由一个生成网络与一个判别网络组成.生成网络从潜在空间(la ...
- 科普 | 生成对抗网络(GAN)的发展史
来源:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edmond_de_Belamy 五年前,Generative Adversarial Networks(GANs)在深度学习领域掀起 ...
- 生成对抗网络(GAN)
基本思想 GAN全称生成对抗网络,是生成模型的一种,而他的训练则是处于一种对抗博弈状态中的. 譬如:我要升职加薪,你领导力还不行,我现在领导力有了要升职加薪,你执行力还不行,我现在执行力有了要升职加薪 ...
- 深度学习-生成对抗网络GAN笔记
生成对抗网络(GAN)由2个重要的部分构成: 生成器G(Generator):通过机器生成数据(大部分情况下是图像),目的是“骗过”判别器 判别器D(Discriminator):判断这张图像是真实的 ...
- 深度学习框架PyTorch一书的学习-第七章-生成对抗网络(GAN)
参考:https://github.com/chenyuntc/pytorch-book/tree/v1.0/chapter7-GAN生成动漫头像 GAN解决了非监督学习中的著名问题:给定一批样本,训 ...
- 利用tensorflow训练简单的生成对抗网络GAN
对抗网络是14年Goodfellow Ian在论文Generative Adversarial Nets中提出来的. 原理方面,对抗网络可以简单归纳为一个生成器(generator)和一个判断器(di ...
- 原始的生成对抗网络GAN
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1406.2661.pdf 1.简介: GAN的两个模型 判别模型:就是图中右半部分的网络,直观来看就是一个简单的神经网络结构,输入就是一副图像, ...
随机推荐
- abp vnext 开发快速入门 3 实现权限控制
上篇讲了abp vnext 实现了简单的增加操作的例子.删除更新查询基本类似,这里就不讲了,接下来说下如何实现角色权限控制. 再说之前,先说下如果想更加透彻的理解abp vnext的权限控制,最好是先 ...
- JDBC 连接 MySQL 8.0.15+ 常见错误记录
课后复习 1. No suitable driver found for mysql:jdbc://localhost:3306/test 错误原因: mysql:jdbc://localhost:3 ...
- 把若依管理系统部署到Linux
一.前言 1.非常感谢若依作者为大家提供的非常优质的开源web项目,非常感谢!!! 2.若依官方文档:http://doc.ruoyi.vip/ruoyi/ 3.若依官方链接: 1)若依管理系统官方体 ...
- vue+springboot文件上传
//vue element-ui组件 <el-upload style="position: relative;top: -40px;left: 240px;" ...
- Mybatis(一)Mybatis简介与入门程序
Mybatis简介: MyBatis是一个优秀的持久层框架,它对jdbc的操作数据库的过程进行封装,使开发者只需要关注 SQL 本身,而不需要花费精力去处理例如注册驱动.创建connection.创建 ...
- 初识Http
HTTP是一个用在计算机世界里的协议,它确立了一种计算机之间交流通信的规范,以及相关的各种控制 和错误处理方式. HTTP专门用来在两点之间传输数据,不能用于广播.寻址或路由. HTTP传输的是文 ...
- python学习笔记1 -- 函数式编程之高阶函数 filter
filter 函数用于过滤序列,与map 和reduce函数类似,作为高阶函数,他们也是同样的使用方法,filter(参数1, 参数2),参数1是一个函数,而参数2是一个序列. filter的作用是根 ...
- Kubernetes/K8s架构师实战集训营【中、高级班】-2020
下载地址: [中级班] 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1FWAz2V7BPsObixlZyW93sw提取码:mvu0 [高级班] 链接:https://pan.baidu.co ...
- Day05_vue入门
学于黑马和传智播客联合做的教学项目 感谢 黑马官网 传智播客官网 微信搜索"艺术行者",关注并回复关键词"乐优商城"获取视频和教程资料! b站在线视频 学习目标 ...
- 重置spyder 解决 gbk 编码不能读取问题
重置spyder 解决 gbk 编码不能读取问题 2020-06-18
