关于python中的 take no arguments 的解决方法
针对第四章编写的代码出现的错误做一个总结
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "H:\image\chapter4\p81_chongxie.py", line 160, in <module>
l1 = Linear(X, W1, b1)
TypeError: Linear() takes no arguments
出问题时的init方法的图片
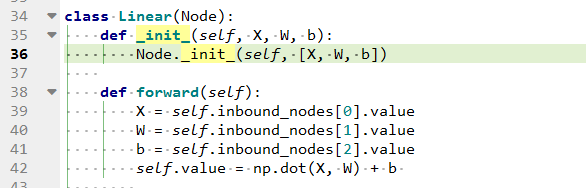
可以看出init两边只有一个下划线 _.
解决办法:把init的两边改成两个下划线 __。即可。

代码运行环境:win7系统 + anaconda3_2020
第四章的代码如下:
- #######################数据结构部分#############################################
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- # %matplotlib inline
- class Node(object):
- def __init__(self, inbound_nodes = []):
- self.inbound_nodes = inbound_nodes
- self.value = None
- self.outbound_nodes = []
- self.gradients = {}
- for node in inbound_nodes:
- node.outbound_nodes.append(self)
- def forward(self):
- raise NotImplementedError
- def backward(self):
- raise NotImplementedError
- class Input(Node):
- def __init__(self):
- Node.__init__(self)
- def forward(self):
- pass
- def backward(self):
- self.gradients = {self : 0}
- for n in self.outbound_nodes:
- self.gradients[self] += n.gradients[self]
- ##################################################################################
- class Linear(Node):
- def __init__(self, X, W, b):
- Node.__init__(self, [X, W, b])
- def forward(self):
- X = self.inbound_nodes[0].value
- W = self.inbound_nodes[1].value
- b = self.inbound_nodes[2].value
- self.value = np.dot(X, W) + b
- def backward(self):
- self.gradients = {n: np.zeros_like(n.value) for n in self.inbound_nodes }
- for n in self.outbound_nodes:
- grad_cost = n.gradients[self]
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] += np.dot(grad_cost, self.inbound_nodes[1].value.T)
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[1]] += np.dot(self.inbound_nodes[0].value.T, grad_cost)
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[2]] += np.sum(grad_cost, axis = 0, keepdims = False)
- ###################################################################################
- class Sigmoid(Node):
- def __init__(self, node):
- Node.__init__(self, [node])
- def _sigmoid(self, x):
- return 1. / (1. + np.exp(-x)) #exp() 方法返回x的指数,e的x次幂
- def forward(self):
- input_value = self.inbound_nodes[0].value
- self.value = self._sigmoid(input_value)
- def backward(self):
- self.gradients = {n: np.zeros_like(n.value) for n in self.inbound_nodes}
- for n in self.outbound_nodes:
- grad_cost = n.gradients[self]
- sigmoid = self.value
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] += sigmoid * (1 - sigmoid) * grad_cost
- class MSE(Node):
- def __init__(self, y, a):
- Node.__init__(self, [y, a])
- def forward(self):
- y = self.inbound_nodes[0].value.reshape(-1, 1)
- a = self.inbound_nodes[1].value.reshape(-1, 1)
- self.m = self.inbound_nodes[0].value.shape[0]
- self.diff = y - a
- self.value = np.mean(self.diff**2)
- def backward(self):
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[0]] = (2 / self.m) * self.diff
- self.gradients[self.inbound_nodes[1]] = (-2 / self.m) * self.diff
- ##########################计算图部分#############################################
- def topological_sort(feed_dict):
- input_nodes = [n for n in feed_dict.keys()]
- G = {}
- nodes = [n for n in input_nodes]
- while len(nodes) > 0:
- n = nodes.pop(0)
- if n not in G:
- G[n] = {'in' : set(), 'out' : set()}
- for m in n.outbound_nodes:
- if m not in G:
- G[m] = {'in' : set(), 'out' : set()}
- G[n]['out'].add(m)
- G[m]['in'].add(n)
- nodes.append(m)
- L = []
- S = set(input_nodes)
- while len(S) > 0 :
- n = S.pop()
- if isinstance(n, Input):
- n.value = feed_dict[n]
- L.append(n)
- for m in n.outbound_nodes:
- G[n]['out'].remove(m)
- G[m]['in'].remove(n)
- if len(G[m]['in']) == 0 :
- S.add(m)
- return L
- #######################使用方法##############################################
- #首先由图的定义执行顺序
- #graph = topological_sort(feed_dict)
- def forward_and_backward(graph):
- for n in graph :
- n.forward()
- for n in graph[:: -1]:
- n.backward()
- #对各个模块进行正向计算和反向求导
- #forward_and_backward(graph)
- #########################介绍梯度下降################
- def sgd_update(trainables, learning_rate = 1e-2):
- for t in trainables :
- t.value = t.value - learning_rate * t.gradients[t]
- ###########使用这个模型#################################
- from sklearn.utils import resample
- from sklearn import datasets
- # %matplotlib inline
- data = datasets.load_iris()
- X_ = data.data
- y_ = data.target
- y_[y_ == 2] = 1 # 0 for virginica, 1 for not virginica
- print(X_.shape, y_.shape) # out (150,4) (150,)
- ########################用写的模块来定义这个神经网络#########################
- np.random.seed(0)
- n_features = X_.shape[1]
- n_class = 1
- n_hidden = 3
- X, y = Input(), Input()
- W1, b1 = Input(), Input()
- W2, b2 = Input(), Input()
- l1 = Linear(X, W1, b1)
- s1 = Sigmoid(l1)
- l2 = Linear(s1, W2, b2)
- t1 = Sigmoid(l2)
- cost = MSE(y, t1)
- ###########训练模型###########################################
- #随即初始化参数值
- W1_0 = np.random.random(X_.shape[1] * n_hidden).reshape([X_.shape[1], n_hidden])
- W2_0 = np.random.random(n_hidden * n_class).reshape([n_hidden, n_class])
- b1_0 = np.random.random(n_hidden)
- b2_0 = np.random.random(n_class)
- #将输入值带入算子
- feed_dict = {
- X: X_, y: y_,
- W1:W1_0, b1: b1_0,
- W2:W2_0, b2: b2_0
- }
- #训练参数
- #这里训练100轮(eprochs),每轮抽4个样本(batch_size),训练150/4次(steps_per_eproch),学习率 0.1
- epochs = 100
- m = X_.shape[0]
- batch_size = 4
- steps_per_eproch = m // batch_size
- lr = 0.1
- graph = topological_sort(feed_dict)
- trainables = [W1, b1,W2, b2]
- l_Mat_W1 = [W1_0]
- l_Mat_W2 = [W2_0]
- l_loss = []
- for i in range(epochs):
- loss = 0
- for j in range(steps_per_eproch):
- X_batch, y_batch = resample(X_, y_, n_samples = batch_size)
- X.value = X_batch
- y.value = y_batch
- forward_and_backward(graph)
- sgd_update(trainables, lr)
- loss += graph[-1].value
- l_loss.append(loss)
- if i % 10 ==9 :
- print("Eproch %d, Loss = %1.5f" % (i, loss))
- #图形化显示
- plt.plot(l_loss)
- plt.title("Cross Entropy value")
- plt.xlabel("Eproch")
- plt.ylabel("Loss")
- plt.show()
- ##########最后用模型预测所有的数据的情况
- X.value = X_
- y.value = y_
- for n in graph:
- n.forward()
- plt.plot(graph[-2].value.ravel())
- plt.title("predict for all 150 Iris data")
- plt.xlabel("Sample ID")
- plt.ylabel("Probability for not a virginica")
- plt.show()
关于python中的 take no arguments 的解决方法的更多相关文章
- Python中pip install MySQL-python报错解决方法
环境 Centos 7(其他Centos或者RHEL一样) 问题 在执行 pip install MySQL-python 时报错如: Command "python setup.py eg ...
- Python中执行系统命令常见的几种方法--转载
Python中执行系统命令常见的几种方法 Python中执行系统命令常见的几种方法有: (1)os.system # 仅仅在一个子终端运行系统命令,而不能获取命令执行后的返回信息 # 如果再命令行下执 ...
- Python中日期和时间格式化输出的方法
本文转自:https://www.jb51.net/article/62518.htm 本文实例总结了python中日期和时间格式化输出的方法.分享给大家供大家参考.具体分析如下: python格式化 ...
- python中readline判断文件读取结束的方法
注:内容来自网络 本文实例讲述了python中readline判断文件读取结束的方法.分享给大家供大家参考.具体分析如下: 大家知道,python中按行读取文件可以使用readline函数,下面现介绍 ...
- python中执行shell命令的几个方法小结(转载)
转载:http://www.jb51.net/article/55327.htm python中执行shell命令的几个方法小结 投稿:junjie 字体:[增加 减小] 类型:转载 时间:2014- ...
- Python中转换角度为弧度的radians()方法
Python中转换角度为弧度的radians()方法 这篇文章主要介绍了Python中转换角度为弧度的radians()方法,是Python入门中的基础知识,需要的朋友可以参考下 radians()方 ...
- Python使用easy-install安装时报UnicodeDecodeError的解决方法
Python使用easy-install安装时报UnicodeDecodeError的解决方法,有需要的朋友可以参考下. 问题描述: 在使用easy-install安装matplotlib.pypar ...
- sql server 还原数据库后,删除用户,提示数据库主体在该数据库中拥有架构,无法删除解决方法
将另一台服务器上的数据库备份文件,在现在用的这台服务器上还原之后,再创建相同的用户名,提示用户已存在 想将之前的用户先删除掉,却提示“数据库主体在该数据库中拥有架构,无法删除解决方法” 在网上找到方法 ...
- jquery中checkbox全选失效的解决方法
这篇文章主要介绍了jquery中checkbox全选失效的解决方法,需要的朋友可以参考下 如果你使用jQuery 1.6 ,代码if ( $(elem).attr(“checked”) ),将 ...
随机推荐
- mac篇---mac安装jupyter
1.Jupyter搭建 pip install --user jupyter 如果是在python3中,则用如下命令: pip3 install --user jupyter 如下图所示: 2. Ju ...
- C++中复杂声明和定义的辨析
0x00 前言 c++中的复杂声明往往令人无法下手,经常使人搞错这到底声明的是一个指针还是指针函数.但其实c++对于复杂声明是遵循一定的规则的,叫做变量名—>右--左-右规则. 0x01 规则解 ...
- day78 作业
目录 1 在作业.html的代码基础上,完成商品数量的加减,注意商品数量如果低于0个,则自动删除当前商品 2 在作业.html的代码基础仧,完成购物车总价格的计算 3 使用ajax获取北京天气,并把昨 ...
- pytest框架使用教程
Pytest框架 一.简介 pytest:基于unittest之上的单元测试框架 有什么特点? 自动发现测试模块和测试方法 断言更加方便,assert + 表达式,例如 assert 1 == 1 灵 ...
- pip install scrapy报错:error: Unable to find vcvarsall.bat解决方法
今天在使用pip install scrapy 命令安装Scrapy爬虫框架时,出现了很让人头疼的错误,错误截图如下: 在网上查找解决方法时,大致知道了问题的原因.是因为缺少C语言的编译环境,其中一种 ...
- 数据可视化之DAX篇(十一)Power BI度量值不能作为坐标轴?这个解决思路送给你
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/79522456 对于PowerBI使用者而言,经常碰到的一个问题是,想把度量值放到坐标轴上,却发现无法实现.尤其是初学者,更是习惯性的想这么 ...
- vue 写h5页面-摇一摇
依赖的第三方的插件 shake.js github地址: https://github.com/alexgibson/shake.js 提供一个摇一摇音效下载地址:http://aspx.sc.chi ...
- Ethical Hacking - Web Penetration Testing(8)
SQL INJECTION WHAT IS SQL? Most websites use a database to store data. Most data stored in it(userna ...
- Vue开发者必会的基础知识盘点
你会Vue吗,你看以下知识点你掌握了多少?实际工作中是否运用的得心应手?如果是,那么恭喜你! Vue中的数据和DOM已经被关联起来,所有的东西都是响应式的.注意我们不再和HTML直接交互.一个Vue应 ...
- nodejs--抓取页面的数据--图
感觉挺有意思,比php好玩 ----做个图留个 纪念
