Java的集合(一)
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/hacker_zhidian/article/details/80590428
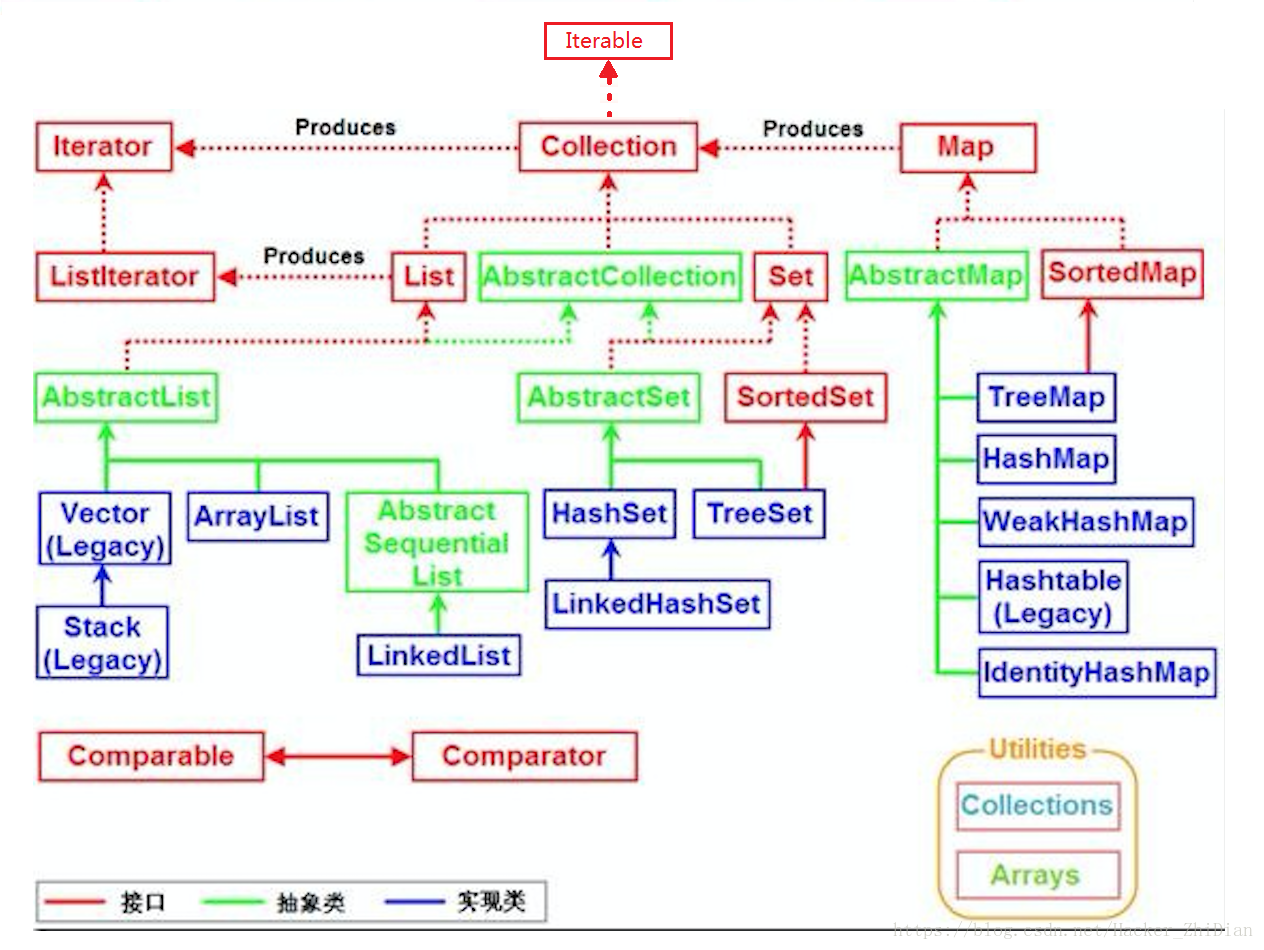
Java集合概况就三个:List、set和map
list(ArrayList、Linkedlist、vector)、set(Treeset、hashset)、map(hashmap、hashtable、treemap)
list接口:
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2014, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/ package java.util; import java.util.function.UnaryOperator; /**
* An ordered collection (also known as a <i>sequence</i>). The user of this
* interface has precise control over where in the list each element is
* inserted. The user can access elements by their integer index (position in
* the list), and search for elements in the list.<p>
*
* Unlike sets, lists typically allow duplicate elements. More formally,
* lists typically allow pairs of elements <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt>
* such that <tt>e1.equals(e2)</tt>, and they typically allow multiple
* null elements if they allow null elements at all. It is not inconceivable
* that someone might wish to implement a list that prohibits duplicates, by
* throwing runtime exceptions when the user attempts to insert them, but we
* expect this usage to be rare.<p>
*
* The <tt>List</tt> interface places additional stipulations, beyond those
* specified in the <tt>Collection</tt> interface, on the contracts of the
* <tt>iterator</tt>, <tt>add</tt>, <tt>remove</tt>, <tt>equals</tt>, and
* <tt>hashCode</tt> methods. Declarations for other inherited methods are
* also included here for convenience.<p>
*
* The <tt>List</tt> interface provides four methods for positional (indexed)
* access to list elements. Lists (like Java arrays) are zero based. Note
* that these operations may execute in time proportional to the index value
* for some implementations (the <tt>LinkedList</tt> class, for
* example). Thus, iterating over the elements in a list is typically
* preferable to indexing through it if the caller does not know the
* implementation.<p>
*
* The <tt>List</tt> interface provides a special iterator, called a
* <tt>ListIterator</tt>, that allows element insertion and replacement, and
* bidirectional access in addition to the normal operations that the
* <tt>Iterator</tt> interface provides. A method is provided to obtain a
* list iterator that starts at a specified position in the list.<p>
*
* The <tt>List</tt> interface provides two methods to search for a specified
* object. From a performance standpoint, these methods should be used with
* caution. In many implementations they will perform costly linear
* searches.<p>
*
* The <tt>List</tt> interface provides two methods to efficiently insert and
* remove multiple elements at an arbitrary point in the list.<p>
*
* Note: While it is permissible for lists to contain themselves as elements,
* extreme caution is advised: the <tt>equals</tt> and <tt>hashCode</tt>
* methods are no longer well defined on such a list.
*
* <p>Some list implementations have restrictions on the elements that
* they may contain. For example, some implementations prohibit null elements,
* and some have restrictions on the types of their elements. Attempting to
* add an ineligible element throws an unchecked exception, typically
* <tt>NullPointerException</tt> or <tt>ClassCastException</tt>. Attempting
* to query the presence of an ineligible element may throw an exception,
* or it may simply return false; some implementations will exhibit the former
* behavior and some will exhibit the latter. More generally, attempting an
* operation on an ineligible element whose completion would not result in
* the insertion of an ineligible element into the list may throw an
* exception or it may succeed, at the option of the implementation.
* Such exceptions are marked as "optional" in the specification for this
* interface.
*
* <p>This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements in this list
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see Set
* @see ArrayList
* @see LinkedList
* @see Vector
* @see Arrays#asList(Object[])
* @see Collections#nCopies(int, Object)
* @see Collections#EMPTY_LIST
* @see AbstractList
* @see AbstractSequentialList
* @since 1.2
*/ public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {
// Query Operations /**
* Returns the number of elements in this list. If this list contains
* more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns
* <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
int size(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements
*/
boolean isEmpty(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains
* at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
boolean contains(Object o); /**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
Iterator<E> iterator(); /**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence (from first to last element).
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must
* allocate a new array even if this list is backed by an array).
* The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper
* sequence
* @see Arrays#asList(Object[])
*/
Object[] toArray(); /**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of
* the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits
* in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new
* array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and
* the size of this list.
*
* <p>If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e.,
* the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array
* immediately following the end of the list is set to <tt>null</tt>.
* (This is useful in determining the length of the list <i>only</i> if
* the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.)
*
* <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* <p>Suppose <tt>x</tt> is a list known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly
* allocated array of <tt>String</tt>:
*
* <pre>{@code
* String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);
* }</pre>
*
* Note that <tt>toArray(new Object[0])</tt> is identical in function to
* <tt>toArray()</tt>.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of this list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of this list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a); // Modification Operations /**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list (optional
* operation).
*
* <p>Lists that support this operation may place limitations on what
* elements may be added to this list. In particular, some
* lists will refuse to add null elements, and others will impose
* restrictions on the type of elements that may be added. List
* classes should clearly specify in their documentation any restrictions
* on what elements may be added.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>add</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this element
* prevents it from being added to this list
*/
boolean add(E e); /**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present (optional operation). If this list does not contain
* the element, it is unchanged. More formally, removes the element with
* the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list changed
* as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
*/
boolean remove(Object o); // Bulk Modification Operations /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection to be checked for containment in this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection
* @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements
* in the specified collection are incompatible with this
* list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator (optional operation). The behavior of this
* operation is undefined if the specified collection is modified while
* the operation is in progress. (Note that this will occur if the
* specified collection is this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>addAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the specified
* collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements, or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @see #add(Object)
*/
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); /**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list at the specified position (optional operation). Shifts the
* element currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent
* elements to the right (increases their indices). The new elements
* will appear in this list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is
* undefined if the specified collection is modified while the
* operation is in progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified
* collection is this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>addAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the specified
* collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this list does not permit null
* elements, or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* (<tt>index < 0 || index > size()</tt>)
*/
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c); /**
* Removes from this list all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation).
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>removeAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Retains only the elements in this list that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation). In other words, removes
* from this list all of its elements that are not contained in the
* specified collection.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>retainAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this list
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this list contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Replaces each element of this list with the result of applying the
* operator to that element. Errors or runtime exceptions thrown by
* the operator are relayed to the caller.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code list}:
* <pre>{@code
* final ListIterator<E> li = list.listIterator();
* while (li.hasNext()) {
* li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
* }
* }</pre>
*
* If the list's list-iterator does not support the {@code set} operation
* then an {@code UnsupportedOperationException} will be thrown when
* replacing the first element.
*
* @param operator the operator to apply to each element
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if this list is unmodifiable.
* Implementations may throw this exception if an element
* cannot be replaced or if, in general, modification is not
* supported
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified operator is null or
* if the operator result is a null value and this list does
* not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {
Objects.requireNonNull(operator);
final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();
while (li.hasNext()) {
li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));
}
} /**
* Sorts this list according to the order induced by the specified
* {@link Comparator}.
*
* <p>All elements in this list must be <i>mutually comparable</i> using the
* specified comparator (that is, {@code c.compare(e1, e2)} must not throw
* a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and {@code e2}
* in the list).
*
* <p>If the specified comparator is {@code null} then all elements in this
* list must implement the {@link Comparable} interface and the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used.
*
* <p>This list must be modifiable, but need not be resizable.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation obtains an array containing all elements in
* this list, sorts the array, and iterates over this list resetting each
* element from the corresponding position in the array. (This avoids the
* n<sup>2</sup> log(n) performance that would result from attempting
* to sort a linked list in place.)
*
* @implNote
* This implementation is a stable, adaptive, iterative mergesort that
* requires far fewer than n lg(n) comparisons when the input array is
* partially sorted, while offering the performance of a traditional
* mergesort when the input array is randomly ordered. If the input array
* is nearly sorted, the implementation requires approximately n
* comparisons. Temporary storage requirements vary from a small constant
* for nearly sorted input arrays to n/2 object references for randomly
* ordered input arrays.
*
* <p>The implementation takes equal advantage of ascending and
* descending order in its input array, and can take advantage of
* ascending and descending order in different parts of the same
* input array. It is well-suited to merging two or more sorted arrays:
* simply concatenate the arrays and sort the resulting array.
*
* <p>The implementation was adapted from Tim Peters's list sort for Python
* (<a href="http://svn.python.org/projects/python/trunk/Objects/listsort.txt">
* TimSort</a>). It uses techniques from Peter McIlroy's "Optimistic
* Sorting and Information Theoretic Complexity", in Proceedings of the
* Fourth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, pp 467-474,
* January 1993.
*
* @param c the {@code Comparator} used to compare list elements.
* A {@code null} value indicates that the elements'
* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used
* @throws ClassCastException if the list contains elements that are not
* <i>mutually comparable</i> using the specified comparator
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the list's list-iterator does
* not support the {@code set} operation
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* if the comparator is found to violate the {@link Comparator}
* contract
* @since 1.8
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
Object[] a = this.toArray();
Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);
ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();
for (Object e : a) {
i.next();
i.set((E) e);
}
} /**
* Removes all of the elements from this list (optional operation).
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>clear</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
*/
void clear(); // Comparison and hashing /**
* Compares the specified object with this list for equality. Returns
* <tt>true</tt> if and only if the specified object is also a list, both
* lists have the same size, and all corresponding pairs of elements in
* the two lists are <i>equal</i>. (Two elements <tt>e1</tt> and
* <tt>e2</tt> are <i>equal</i> if <tt>(e1==null ? e2==null :
* e1.equals(e2))</tt>.) In other words, two lists are defined to be
* equal if they contain the same elements in the same order. This
* definition ensures that the equals method works properly across
* different implementations of the <tt>List</tt> interface.
*
* @param o the object to be compared for equality with this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this list
*/
boolean equals(Object o); /**
* Returns the hash code value for this list. The hash code of a list
* is defined to be the result of the following calculation:
* <pre>{@code
* int hashCode = 1;
* for (E e : list)
* hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
* }</pre>
* This ensures that <tt>list1.equals(list2)</tt> implies that
* <tt>list1.hashCode()==list2.hashCode()</tt> for any two lists,
* <tt>list1</tt> and <tt>list2</tt>, as required by the general
* contract of {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this list
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #equals(Object)
*/
int hashCode(); // Positional Access Operations /**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* (<tt>index < 0 || index >= size()</tt>)
*/
E get(int index); /**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element (optional operation).
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>set</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* (<tt>index < 0 || index >= size()</tt>)
*/
E set(int index, E element); /**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list
* (optional operation). Shifts the element currently at that position
* (if any) and any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their
* indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>add</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and
* this list does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified
* element prevents it from being added to this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* (<tt>index < 0 || index > size()</tt>)
*/
void add(int index, E element); /**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list (optional
* operation). Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one
* from their indices). Returns the element that was removed from the
* list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt> operation
* is not supported by this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* (<tt>index < 0 || index >= size()</tt>)
*/
E remove(int index); // Search Operations /**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
int indexOf(Object o); /**
* Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>,
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this list
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* list does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
int lastIndexOf(Object o); // List Iterators /**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence).
*
* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence)
*/
ListIterator<E> listIterator(); /**
* Returns a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* The specified index indicates the first element that would be
* returned by an initial call to {@link ListIterator#next next}.
* An initial call to {@link ListIterator#previous previous} would
* return the element with the specified index minus one.
*
* @param index index of the first element to be returned from the
* list iterator (by a call to {@link ListIterator#next next})
* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index > size()})
*/
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index); // View /**
* Returns a view of the portion of this list between the specified
* <tt>fromIndex</tt>, inclusive, and <tt>toIndex</tt>, exclusive. (If
* <tt>fromIndex</tt> and <tt>toIndex</tt> are equal, the returned list is
* empty.) The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural
* changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa.
* The returned list supports all of the optional list operations supported
* by this list.<p>
*
* This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of
* the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects
* a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view
* instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom
* removes a range of elements from a list:
* <pre>{@code
* list.subList(from, to).clear();
* }</pre>
* Similar idioms may be constructed for <tt>indexOf</tt> and
* <tt>lastIndexOf</tt>, and all of the algorithms in the
* <tt>Collections</tt> class can be applied to a subList.<p>
*
* The semantics of the list returned by this method become undefined if
* the backing list (i.e., this list) is <i>structurally modified</i> in
* any way other than via the returned list. (Structural modifications are
* those that change the size of this list, or otherwise perturb it in such
* a fashion that iterations in progress may yield incorrect results.)
*
* @param fromIndex low endpoint (inclusive) of the subList
* @param toIndex high endpoint (exclusive) of the subList
* @return a view of the specified range within this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException for an illegal endpoint index value
* (<tt>fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size ||
* fromIndex > toIndex</tt>)
*/
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex); /**
* Creates a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this list.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Implementations should document the
* reporting of additional characteristic values.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation creates a
* <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em> spliterator
* from the list's {@code Iterator}. The spliterator inherits the
* <em>fail-fast</em> properties of the list's iterator.
*
* @implNote
* The created {@code Spliterator} additionally reports
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
}
set代码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/ package java.util; /**
* A collection that contains no duplicate elements. More formally, sets
* contain no pair of elements <code>e1</code> and <code>e2</code> such that
* <code>e1.equals(e2)</code>, and at most one null element. As implied by
* its name, this interface models the mathematical <i>set</i> abstraction.
*
* <p>The <tt>Set</tt> interface places additional stipulations, beyond those
* inherited from the <tt>Collection</tt> interface, on the contracts of all
* constructors and on the contracts of the <tt>add</tt>, <tt>equals</tt> and
* <tt>hashCode</tt> methods. Declarations for other inherited methods are
* also included here for convenience. (The specifications accompanying these
* declarations have been tailored to the <tt>Set</tt> interface, but they do
* not contain any additional stipulations.)
*
* <p>The additional stipulation on constructors is, not surprisingly,
* that all constructors must create a set that contains no duplicate elements
* (as defined above).
*
* <p>Note: Great care must be exercised if mutable objects are used as set
* elements. The behavior of a set is not specified if the value of an object
* is changed in a manner that affects <tt>equals</tt> comparisons while the
* object is an element in the set. A special case of this prohibition is
* that it is not permissible for a set to contain itself as an element.
*
* <p>Some set implementations have restrictions on the elements that
* they may contain. For example, some implementations prohibit null elements,
* and some have restrictions on the types of their elements. Attempting to
* add an ineligible element throws an unchecked exception, typically
* <tt>NullPointerException</tt> or <tt>ClassCastException</tt>. Attempting
* to query the presence of an ineligible element may throw an exception,
* or it may simply return false; some implementations will exhibit the former
* behavior and some will exhibit the latter. More generally, attempting an
* operation on an ineligible element whose completion would not result in
* the insertion of an ineligible element into the set may throw an
* exception or it may succeed, at the option of the implementation.
* Such exceptions are marked as "optional" in the specification for this
* interface.
*
* <p>This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements maintained by this set
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @see Collection
* @see List
* @see SortedSet
* @see HashSet
* @see TreeSet
* @see AbstractSet
* @see Collections#singleton(java.lang.Object)
* @see Collections#EMPTY_SET
* @since 1.2
*/ public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> {
// Query Operations /**
* Returns the number of elements in this set (its cardinality). If this
* set contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns
* <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>.
*
* @return the number of elements in this set (its cardinality)
*/
int size(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains no elements
*/
boolean isEmpty(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this set
* contains an element <tt>e</tt> such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>.
*
* @param o element whose presence in this set is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this set
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* set does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
boolean contains(Object o); /**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set. The elements are
* returned in no particular order (unless this set is an instance of some
* class that provides a guarantee).
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this set
*/
Iterator<E> iterator(); /**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set.
* If this set makes any guarantees as to what order its elements
* are returned by its iterator, this method must return the
* elements in the same order.
*
* <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it
* are maintained by this set. (In other words, this method must
* allocate a new array even if this set is backed by an array).
* The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
* <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all the elements in this set
*/
Object[] toArray(); /**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the
* runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
* If the set fits in the specified array, it is returned therein.
* Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the runtime type of the
* specified array and the size of this set.
*
* <p>If this set fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than this set), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the set is set to
* <tt>null</tt>. (This is useful in determining the length of this
* set <i>only</i> if the caller knows that this set does not contain
* any null elements.)
*
* <p>If this set makes any guarantees as to what order its elements
* are returned by its iterator, this method must return the elements
* in the same order.
*
* <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
* <p>Suppose <tt>x</tt> is a set known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the set into a newly allocated
* array of <tt>String</tt>:
*
* <pre>
* String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);</pre>
*
* Note that <tt>toArray(new Object[0])</tt> is identical in function to
* <tt>toArray()</tt>.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of this set are to be
* stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the same
* runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing all the elements in this set
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in this
* set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a); // Modification Operations /**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present
* (optional operation). More formally, adds the specified element
* <tt>e</tt> to this set if the set contains no element <tt>e2</tt>
* such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns <tt>false</tt>. In combination with the
* restriction on constructors, this ensures that sets never contain
* duplicate elements.
*
* <p>The stipulation above does not imply that sets must accept all
* elements; sets may refuse to add any particular element, including
* <tt>null</tt>, and throw an exception, as described in the
* specification for {@link Collection#add Collection.add}.
* Individual set implementations should clearly document any
* restrictions on the elements that they may contain.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>add</tt> operation
* is not supported by this set
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* set does not permit null elements
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified element
* prevents it from being added to this set
*/
boolean add(E e); /**
* Removes the specified element from this set if it is present
* (optional operation). More formally, removes an element <tt>e</tt>
* such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>, if
* this set contains such an element. Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set
* contained the element (or equivalently, if this set changed as a
* result of the call). (This set will not contain the element once the
* call returns.)
*
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the type of the specified element
* is incompatible with this set
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null and this
* set does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt> operation
* is not supported by this set
*/
boolean remove(Object o); // Bulk Operations /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this set contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection. If the specified collection is also a set, this
* method returns <tt>true</tt> if it is a <i>subset</i> of this set.
*
* @param c collection to be checked for containment in this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains all of the elements of the
* specified collection
* @throws ClassCastException if the types of one or more elements
* in the specified collection are incompatible with this
* set
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this set does not permit null
* elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set if
* they're not already present (optional operation). If the specified
* collection is also a set, the <tt>addAll</tt> operation effectively
* modifies this set so that its value is the <i>union</i> of the two
* sets. The behavior of this operation is undefined if the specified
* collection is modified while the operation is in progress.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set changed as a result of the call
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>addAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this set
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection contains one
* or more null elements and this set does not permit null
* elements, or if the specified collection is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of an element of the
* specified collection prevents it from being added to this set
* @see #add(Object)
*/
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); /**
* Retains only the elements in this set that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation). In other words, removes
* from this set all of its elements that are not contained in the
* specified collection. If the specified collection is also a set, this
* operation effectively modifies this set so that its value is the
* <i>intersection</i> of the two sets.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>retainAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this set
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this set
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this set contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
*/
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the
* specified collection (optional operation). If the specified
* collection is also a set, this operation effectively modifies this
* set so that its value is the <i>asymmetric set difference</i> of
* the two sets.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set changed as a result of the call
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>removeAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this set
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of an element of this set
* is incompatible with the specified collection
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if this set contains a null element and the
* specified collection does not permit null elements
* (<a href="Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>),
* or if the specified collection is null
* @see #remove(Object)
* @see #contains(Object)
*/
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); /**
* Removes all of the elements from this set (optional operation).
* The set will be empty after this call returns.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>clear</tt> method
* is not supported by this set
*/
void clear(); // Comparison and hashing /**
* Compares the specified object with this set for equality. Returns
* <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is also a set, the two sets
* have the same size, and every member of the specified set is
* contained in this set (or equivalently, every member of this set is
* contained in the specified set). This definition ensures that the
* equals method works properly across different implementations of the
* set interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this set
*/
boolean equals(Object o); /**
* Returns the hash code value for this set. The hash code of a set is
* defined to be the sum of the hash codes of the elements in the set,
* where the hash code of a <tt>null</tt> element is defined to be zero.
* This ensures that <tt>s1.equals(s2)</tt> implies that
* <tt>s1.hashCode()==s2.hashCode()</tt> for any two sets <tt>s1</tt>
* and <tt>s2</tt>, as required by the general contract of
* {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this set
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see Set#equals(Object)
*/
int hashCode(); /**
* Creates a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this set.
*
* <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#DISTINCT}.
* Implementations should document the reporting of additional
* characteristic values.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation creates a
* <em><a href="Spliterator.html#binding">late-binding</a></em> spliterator
* from the set's {@code Iterator}. The spliterator inherits the
* <em>fail-fast</em> properties of the set's iterator.
* <p>
* The created {@code Spliterator} additionally reports
* {@link Spliterator#SIZED}.
*
* @implNote
* The created {@code Spliterator} additionally reports
* {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this set
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
default Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.DISTINCT);
}
}
map代码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*/ package java.util; import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.BiFunction;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.io.Serializable; /**
* An object that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys;
* each key can map to at most one value.
*
* <p>This interface takes the place of the <tt>Dictionary</tt> class, which
* was a totally abstract class rather than an interface.
*
* <p>The <tt>Map</tt> interface provides three <i>collection views</i>, which
* allow a map's contents to be viewed as a set of keys, collection of values,
* or set of key-value mappings. The <i>order</i> of a map is defined as
* the order in which the iterators on the map's collection views return their
* elements. Some map implementations, like the <tt>TreeMap</tt> class, make
* specific guarantees as to their order; others, like the <tt>HashMap</tt>
* class, do not.
*
* <p>Note: great care must be exercised if mutable objects are used as map
* keys. The behavior of a map is not specified if the value of an object is
* changed in a manner that affects <tt>equals</tt> comparisons while the
* object is a key in the map. A special case of this prohibition is that it
* is not permissible for a map to contain itself as a key. While it is
* permissible for a map to contain itself as a value, extreme caution is
* advised: the <tt>equals</tt> and <tt>hashCode</tt> methods are no longer
* well defined on such a map.
*
* <p>All general-purpose map implementation classes should provide two
* "standard" constructors: a void (no arguments) constructor which creates an
* empty map, and a constructor with a single argument of type <tt>Map</tt>,
* which creates a new map with the same key-value mappings as its argument.
* In effect, the latter constructor allows the user to copy any map,
* producing an equivalent map of the desired class. There is no way to
* enforce this recommendation (as interfaces cannot contain constructors) but
* all of the general-purpose map implementations in the JDK comply.
*
* <p>The "destructive" methods contained in this interface, that is, the
* methods that modify the map on which they operate, are specified to throw
* <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if this map does not support the
* operation. If this is the case, these methods may, but are not required
* to, throw an <tt>UnsupportedOperationException</tt> if the invocation would
* have no effect on the map. For example, invoking the {@link #putAll(Map)}
* method on an unmodifiable map may, but is not required to, throw the
* exception if the map whose mappings are to be "superimposed" is empty.
*
* <p>Some map implementations have restrictions on the keys and values they
* may contain. For example, some implementations prohibit null keys and
* values, and some have restrictions on the types of their keys. Attempting
* to insert an ineligible key or value throws an unchecked exception,
* typically <tt>NullPointerException</tt> or <tt>ClassCastException</tt>.
* Attempting to query the presence of an ineligible key or value may throw an
* exception, or it may simply return false; some implementations will exhibit
* the former behavior and some will exhibit the latter. More generally,
* attempting an operation on an ineligible key or value whose completion
* would not result in the insertion of an ineligible element into the map may
* throw an exception or it may succeed, at the option of the implementation.
* Such exceptions are marked as "optional" in the specification for this
* interface.
*
* <p>Many methods in Collections Framework interfaces are defined
* in terms of the {@link Object#equals(Object) equals} method. For
* example, the specification for the {@link #containsKey(Object)
* containsKey(Object key)} method says: "returns <tt>true</tt> if and
* only if this map contains a mapping for a key <tt>k</tt> such that
* <tt>(key==null ? k==null : key.equals(k))</tt>." This specification should
* <i>not</i> be construed to imply that invoking <tt>Map.containsKey</tt>
* with a non-null argument <tt>key</tt> will cause <tt>key.equals(k)</tt> to
* be invoked for any key <tt>k</tt>. Implementations are free to
* implement optimizations whereby the <tt>equals</tt> invocation is avoided,
* for example, by first comparing the hash codes of the two keys. (The
* {@link Object#hashCode()} specification guarantees that two objects with
* unequal hash codes cannot be equal.) More generally, implementations of
* the various Collections Framework interfaces are free to take advantage of
* the specified behavior of underlying {@link Object} methods wherever the
* implementor deems it appropriate.
*
* <p>Some map operations which perform recursive traversal of the map may fail
* with an exception for self-referential instances where the map directly or
* indirectly contains itself. This includes the {@code clone()},
* {@code equals()}, {@code hashCode()} and {@code toString()} methods.
* Implementations may optionally handle the self-referential scenario, however
* most current implementations do not do so.
*
* <p>This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @param <K> the type of keys maintained by this map
* @param <V> the type of mapped values
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see HashMap
* @see TreeMap
* @see Hashtable
* @see SortedMap
* @see Collection
* @see Set
* @since 1.2
*/
public interface Map<K,V> {
// Query Operations /**
* Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. If the
* map contains more than <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt> elements, returns
* <tt>Integer.MAX_VALUE</tt>.
*
* @return the number of key-value mappings in this map
*/
int size(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains no key-value mappings
*/
boolean isEmpty(); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified
* key. More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if
* this map contains a mapping for a key <tt>k</tt> such that
* <tt>(key==null ? k==null : key.equals(k))</tt>. (There can be
* at most one such mapping.)
*
* @param key key whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map contains a mapping for the specified
* key
* @throws ClassCastException if the key is of an inappropriate type for
* this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map
* does not permit null keys
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
boolean containsKey(Object key); /**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value. More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if
* this map contains at least one mapping to a value <tt>v</tt> such that
* <tt>(value==null ? v==null : value.equals(v))</tt>. This operation
* will probably require time linear in the map size for most
* implementations of the <tt>Map</tt> interface.
*
* @param value value whose presence in this map is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this map maps one or more keys to the
* specified value
* @throws ClassCastException if the value is of an inappropriate type for
* this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified value is null and this
* map does not permit null values
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
boolean containsValue(Object value); /**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>If this map permits null values, then a return value of
* {@code null} does not <i>necessarily</i> indicate that the map
* contains no mapping for the key; it's also possible that the map
* explicitly maps the key to {@code null}. The {@link #containsKey
* containsKey} operation may be used to distinguish these two cases.
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws ClassCastException if the key is of an inappropriate type for
* this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map
* does not permit null keys
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
V get(Object key); // Modification Operations /**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map
* (optional operation). If the map previously contained a mapping for
* the key, the old value is replaced by the specified value. (A map
* <tt>m</tt> is said to contain a mapping for a key <tt>k</tt> if and only
* if {@link #containsKey(Object) m.containsKey(k)} would return
* <tt>true</tt>.)
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>,
* if the implementation supports <tt>null</tt> values.)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>put</tt> operation
* is not supported by this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified key
* or value prevents it from being stored in this map
*/
V put(K key, V value); /**
* Removes the mapping for a key from this map if it is present
* (optional operation). More formally, if this map contains a mapping
* from key <tt>k</tt> to value <tt>v</tt> such that
* <code>(key==null ? k==null : key.equals(k))</code>, that mapping
* is removed. (The map can contain at most one such mapping.)
*
* <p>Returns the value to which this map previously associated the key,
* or <tt>null</tt> if the map contained no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>If this map permits null values, then a return value of
* <tt>null</tt> does not <i>necessarily</i> indicate that the map
* contained no mapping for the key; it's also possible that the map
* explicitly mapped the key to <tt>null</tt>.
*
* <p>The map will not contain a mapping for the specified key once the
* call returns.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>remove</tt> operation
* is not supported by this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the key is of an inappropriate type for
* this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this
* map does not permit null keys
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
*/
V remove(Object key); // Bulk Operations /**
* Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map
* (optional operation). The effect of this call is equivalent to that
* of calling {@link #put(Object,Object) put(k, v)} on this map once
* for each mapping from key <tt>k</tt> to value <tt>v</tt> in the
* specified map. The behavior of this operation is undefined if the
* specified map is modified while the operation is in progress.
*
* @param m mappings to be stored in this map
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>putAll</tt> operation
* is not supported by this map
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of a key or value in the
* specified map prevents it from being stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null, or if
* this map does not permit null keys or values, and the
* specified map contains null keys or values
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of a key or value in
* the specified map prevents it from being stored in this map
*/
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m); /**
* Removes all of the mappings from this map (optional operation).
* The map will be empty after this call returns.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>clear</tt> operation
* is not supported by this map
*/
void clear(); // Views /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the keys contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of
* the iteration are undefined. The set supports element removal,
* which removes the corresponding mapping from the map, via the
* <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>, <tt>Set.remove</tt>,
* <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt>, and <tt>clear</tt>
* operations. It does not support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt>
* operations.
*
* @return a set view of the keys contained in this map
*/
Set<K> keySet(); /**
* Returns a {@link Collection} view of the values contained in this map.
* The collection is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the collection, and vice-versa. If the map is
* modified while an iteration over the collection is in progress
* (except through the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation),
* the results of the iteration are undefined. The collection
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Collection.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>,
* <tt>retainAll</tt> and <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not
* support the <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @return a collection view of the values contained in this map
*/
Collection<V> values(); /**
* Returns a {@link Set} view of the mappings contained in this map.
* The set is backed by the map, so changes to the map are
* reflected in the set, and vice-versa. If the map is modified
* while an iteration over the set is in progress (except through
* the iterator's own <tt>remove</tt> operation, or through the
* <tt>setValue</tt> operation on a map entry returned by the
* iterator) the results of the iteration are undefined. The set
* supports element removal, which removes the corresponding
* mapping from the map, via the <tt>Iterator.remove</tt>,
* <tt>Set.remove</tt>, <tt>removeAll</tt>, <tt>retainAll</tt> and
* <tt>clear</tt> operations. It does not support the
* <tt>add</tt> or <tt>addAll</tt> operations.
*
* @return a set view of the mappings contained in this map
*/
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet(); /**
* A map entry (key-value pair). The <tt>Map.entrySet</tt> method returns
* a collection-view of the map, whose elements are of this class. The
* <i>only</i> way to obtain a reference to a map entry is from the
* iterator of this collection-view. These <tt>Map.Entry</tt> objects are
* valid <i>only</i> for the duration of the iteration; more formally,
* the behavior of a map entry is undefined if the backing map has been
* modified after the entry was returned by the iterator, except through
* the <tt>setValue</tt> operation on the map entry.
*
* @see Map#entrySet()
* @since 1.2
*/
interface Entry<K,V> {
/**
* Returns the key corresponding to this entry.
*
* @return the key corresponding to this entry
* @throws IllegalStateException implementations may, but are not
* required to, throw this exception if the entry has been
* removed from the backing map.
*/
K getKey(); /**
* Returns the value corresponding to this entry. If the mapping
* has been removed from the backing map (by the iterator's
* <tt>remove</tt> operation), the results of this call are undefined.
*
* @return the value corresponding to this entry
* @throws IllegalStateException implementations may, but are not
* required to, throw this exception if the entry has been
* removed from the backing map.
*/
V getValue(); /**
* Replaces the value corresponding to this entry with the specified
* value (optional operation). (Writes through to the map.) The
* behavior of this call is undefined if the mapping has already been
* removed from the map (by the iterator's <tt>remove</tt> operation).
*
* @param value new value to be stored in this entry
* @return old value corresponding to the entry
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the <tt>put</tt> operation
* is not supported by the backing map
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified value
* prevents it from being stored in the backing map
* @throws NullPointerException if the backing map does not permit
* null values, and the specified value is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of this value
* prevents it from being stored in the backing map
* @throws IllegalStateException implementations may, but are not
* required to, throw this exception if the entry has been
* removed from the backing map.
*/
V setValue(V value); /**
* Compares the specified object with this entry for equality.
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if the given object is also a map entry and
* the two entries represent the same mapping. More formally, two
* entries <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt> represent the same mapping
* if<pre>
* (e1.getKey()==null ?
* e2.getKey()==null : e1.getKey().equals(e2.getKey())) &&
* (e1.getValue()==null ?
* e2.getValue()==null : e1.getValue().equals(e2.getValue()))
* </pre>
* This ensures that the <tt>equals</tt> method works properly across
* different implementations of the <tt>Map.Entry</tt> interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this map entry
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this map
* entry
*/
boolean equals(Object o); /**
* Returns the hash code value for this map entry. The hash code
* of a map entry <tt>e</tt> is defined to be: <pre>
* (e.getKey()==null ? 0 : e.getKey().hashCode()) ^
* (e.getValue()==null ? 0 : e.getValue().hashCode())
* </pre>
* This ensures that <tt>e1.equals(e2)</tt> implies that
* <tt>e1.hashCode()==e2.hashCode()</tt> for any two Entries
* <tt>e1</tt> and <tt>e2</tt>, as required by the general
* contract of <tt>Object.hashCode</tt>.
*
* @return the hash code value for this map entry
* @see Object#hashCode()
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #equals(Object)
*/
int hashCode(); /**
* Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on key.
*
* <p>The returned comparator is serializable and throws {@link
* NullPointerException} when comparing an entry with a null key.
*
* @param <K> the {@link Comparable} type of then map keys
* @param <V> the type of the map values
* @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on key.
* @see Comparable
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <K extends Comparable<? super K>, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByKey() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getKey().compareTo(c2.getKey());
} /**
* Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on value.
*
* <p>The returned comparator is serializable and throws {@link
* NullPointerException} when comparing an entry with null values.
*
* @param <K> the type of the map keys
* @param <V> the {@link Comparable} type of the map values
* @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} in natural order on value.
* @see Comparable
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <K, V extends Comparable<? super V>> Comparator<Map.Entry<K,V>> comparingByValue() {
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> c1.getValue().compareTo(c2.getValue());
} /**
* Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by key using the given
* {@link Comparator}.
*
* <p>The returned comparator is serializable if the specified comparator
* is also serializable.
*
* @param <K> the type of the map keys
* @param <V> the type of the map values
* @param cmp the key {@link Comparator}
* @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by the key.
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByKey(Comparator<? super K> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getKey(), c2.getKey());
} /**
* Returns a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by value using the given
* {@link Comparator}.
*
* <p>The returned comparator is serializable if the specified comparator
* is also serializable.
*
* @param <K> the type of the map keys
* @param <V> the type of the map values
* @param cmp the value {@link Comparator}
* @return a comparator that compares {@link Map.Entry} by the value.
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <K, V> Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> comparingByValue(Comparator<? super V> cmp) {
Objects.requireNonNull(cmp);
return (Comparator<Map.Entry<K, V>> & Serializable)
(c1, c2) -> cmp.compare(c1.getValue(), c2.getValue());
}
} // Comparison and hashing /**
* Compares the specified object with this map for equality. Returns
* <tt>true</tt> if the given object is also a map and the two maps
* represent the same mappings. More formally, two maps <tt>m1</tt> and
* <tt>m2</tt> represent the same mappings if
* <tt>m1.entrySet().equals(m2.entrySet())</tt>. This ensures that the
* <tt>equals</tt> method works properly across different implementations
* of the <tt>Map</tt> interface.
*
* @param o object to be compared for equality with this map
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the specified object is equal to this map
*/
boolean equals(Object o); /**
* Returns the hash code value for this map. The hash code of a map is
* defined to be the sum of the hash codes of each entry in the map's
* <tt>entrySet()</tt> view. This ensures that <tt>m1.equals(m2)</tt>
* implies that <tt>m1.hashCode()==m2.hashCode()</tt> for any two maps
* <tt>m1</tt> and <tt>m2</tt>, as required by the general contract of
* {@link Object#hashCode}.
*
* @return the hash code value for this map
* @see Map.Entry#hashCode()
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #equals(Object)
*/
int hashCode(); // Defaultable methods /**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code defaultValue} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @param defaultValue the default mapping of the key
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code defaultValue} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws ClassCastException if the key is of an inappropriate type for
* this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map
* does not permit null keys
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) {
V v;
return (((v = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key))
? v
: defaultValue;
} /**
* Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries
* have been processed or the action throws an exception. Unless
* otherwise specified by the implementing class, actions are performed in
* the order of entry set iteration (if an iteration order is specified.)
* Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the caller.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code map}:
* <pre> {@code
* for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet())
* action.accept(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
* }</pre>
*
* The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param action The action to be performed for each entry
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified action is null
* @throws ConcurrentModificationException if an entry is found to be
* removed during iteration
* @since 1.8
*/
default void forEach(BiConsumer<? super K, ? super V> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
action.accept(k, v);
}
} /**
* Replaces each entry's value with the result of invoking the given
* function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the
* function throws an exception. Exceptions thrown by the function are
* relayed to the caller.
*
* @implSpec
* <p>The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code map}:
* <pre> {@code
* for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : map.entrySet())
* entry.setValue(function.apply(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param function the function to apply to each entry
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code set} operation
* is not supported by this map's entry set iterator.
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of a replacement value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified function is null, or the
* specified replacement value is null, and this map does not permit null
* values
* @throws ClassCastException if a replacement value is of an inappropriate
* type for this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if function or a replacement value is null,
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of a replacement value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ConcurrentModificationException if an entry is found to be
* removed during iteration
* @since 1.8
*/
default void replaceAll(BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> function) {
Objects.requireNonNull(function);
for (Map.Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
K k;
V v;
try {
k = entry.getKey();
v = entry.getValue();
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
} // ise thrown from function is not a cme.
v = function.apply(k, v); try {
entry.setValue(v);
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) {
// this usually means the entry is no longer in the map.
throw new ConcurrentModificationException(ise);
}
}
} /**
* If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped
* to {@code null}) associates it with the given value and returns
* {@code null}, else returns the current value.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code
* map}:
*
* <pre> {@code
* V v = map.get(key);
* if (v == null)
* v = map.put(key, value);
*
* return v;
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with the specified key, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for the key.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with the key,
* if the implementation supports null values.)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the key or value is of an inappropriate
* type for this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null,
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified key
* or value prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) {
V v = get(key);
if (v == null) {
v = put(key, value);
} return v;
} /**
* Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently
* mapped to the specified value.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code map}:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (map.containsKey(key) && Objects.equals(map.get(key), value)) {
* map.remove(key);
* return true;
* } else
* return false;
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is associated
* @param value value expected to be associated with the specified key
* @return {@code true} if the value was removed
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the key or value is of an inappropriate
* type for this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null,
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default boolean remove(Object key, Object value) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, value) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
remove(key);
return true;
} /**
* Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently
* mapped to the specified value.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code map}:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (map.containsKey(key) && Objects.equals(map.get(key), value)) {
* map.put(key, newValue);
* return true;
* } else
* return false;
* }</pre>
*
* The default implementation does not throw NullPointerException
* for maps that do not support null values if oldValue is null unless
* newValue is also null.
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is associated
* @param oldValue value expected to be associated with the specified key
* @param newValue value to be associated with the specified key
* @return {@code true} if the value was replaced
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of a specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* @throws NullPointerException if a specified key or newValue is null,
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* @throws NullPointerException if oldValue is null and this map does not
* permit null values
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of a specified key
* or value prevents it from being stored in this map
* @since 1.8
*/
default boolean replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {
Object curValue = get(key);
if (!Objects.equals(curValue, oldValue) ||
(curValue == null && !containsKey(key))) {
return false;
}
put(key, newValue);
return true;
} /**
* Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is
* currently mapped to some value.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to, for this {@code map}:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (map.containsKey(key)) {
* return map.put(key, value);
* } else
* return null;
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with the specified key, or
* {@code null} if there was no mapping for the key.
* (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated {@code null} with the key,
* if the implementation supports null values.)
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key or value is null,
* and this map does not permit null keys or values
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if some property of the specified key
* or value prevents it from being stored in this map
* @since 1.8
*/
default V replace(K key, V value) {
V curValue;
if (((curValue = get(key)) != null) || containsKey(key)) {
curValue = put(key, value);
}
return curValue;
} /**
* If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped
* to {@code null}), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping
* function and enters it into this map unless {@code null}.
*
* <p>If the function returns {@code null} no mapping is recorded. If
* the function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the
* exception is rethrown, and no mapping is recorded. The most
* common usage is to construct a new object serving as an initial
* mapped value or memoized result, as in:
*
* <pre> {@code
* map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new Value(f(k)));
* }</pre>
*
* <p>Or to implement a multi-value map, {@code Map<K,Collection<V>>},
* supporting multiple values per key:
*
* <pre> {@code
* map.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new HashSet<V>()).add(v);
* }</pre>
*
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to the following steps for this
* {@code map}, then returning the current value or {@code null} if now
* absent:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (map.get(key) == null) {
* V newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key);
* if (newValue != null)
* map.put(key, newValue);
* }
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties. In particular, all implementations of
* subinterface {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap} must document
* whether the function is applied once atomically only if the value is not
* present.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param mappingFunction the function to compute a value
* @return the current (existing or computed) value associated with
* the specified key, or null if the computed value is null
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and
* this map does not support null keys, or the mappingFunction
* is null
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default V computeIfAbsent(K key,
Function<? super K, ? extends V> mappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(mappingFunction);
V v;
if ((v = get(key)) == null) {
V newValue;
if ((newValue = mappingFunction.apply(key)) != null) {
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
}
} return v;
} /**
* If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to
* compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value.
*
* <p>If the function returns {@code null}, the mapping is removed. If the
* function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the exception is
* rethrown, and the current mapping is left unchanged.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to performing the following
* steps for this {@code map}, then returning the current value or
* {@code null} if now absent:
*
* <pre> {@code
* if (map.get(key) != null) {
* V oldValue = map.get(key);
* V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
* if (newValue != null)
* map.put(key, newValue);
* else
* map.remove(key);
* }
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties. In particular, all implementations of
* subinterface {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap} must document
* whether the function is applied once atomically only if the value is not
* present.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param remappingFunction the function to compute a value
* @return the new value associated with the specified key, or null if none
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and
* this map does not support null keys, or the
* remappingFunction is null
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default V computeIfPresent(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue;
if ((oldValue = get(key)) != null) {
V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (newValue != null) {
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
} else {
remove(key);
return null;
}
} else {
return null;
}
} /**
* Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current
* mapped value (or {@code null} if there is no current mapping). For
* example, to either create or append a {@code String} msg to a value
* mapping:
*
* <pre> {@code
* map.compute(key, (k, v) -> (v == null) ? msg : v.concat(msg))}</pre>
* (Method {@link #merge merge()} is often simpler to use for such purposes.)
*
* <p>If the function returns {@code null}, the mapping is removed (or
* remains absent if initially absent). If the function itself throws an
* (unchecked) exception, the exception is rethrown, and the current mapping
* is left unchanged.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to performing the following
* steps for this {@code map}, then returning the current value or
* {@code null} if absent:
*
* <pre> {@code
* V oldValue = map.get(key);
* V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
* if (oldValue != null ) {
* if (newValue != null)
* map.put(key, newValue);
* else
* map.remove(key);
* } else {
* if (newValue != null)
* map.put(key, newValue);
* else
* return null;
* }
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties. In particular, all implementations of
* subinterface {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap} must document
* whether the function is applied once atomically only if the value is not
* present.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param remappingFunction the function to compute a value
* @return the new value associated with the specified key, or null if none
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and
* this map does not support null keys, or the
* remappingFunction is null
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @since 1.8
*/
default V compute(K key,
BiFunction<? super K, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
V oldValue = get(key); V newValue = remappingFunction.apply(key, oldValue);
if (newValue == null) {
// delete mapping
if (oldValue != null || containsKey(key)) {
// something to remove
remove(key);
return null;
} else {
// nothing to do. Leave things as they were.
return null;
}
} else {
// add or replace old mapping
put(key, newValue);
return newValue;
}
} /**
* If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is
* associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value.
* Otherwise, replaces the associated value with the results of the given
* remapping function, or removes if the result is {@code null}. This
* method may be of use when combining multiple mapped values for a key.
* For example, to either create or append a {@code String msg} to a
* value mapping:
*
* <pre> {@code
* map.merge(key, msg, String::concat)
* }</pre>
*
* <p>If the function returns {@code null} the mapping is removed. If the
* function itself throws an (unchecked) exception, the exception is
* rethrown, and the current mapping is left unchanged.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation is equivalent to performing the following
* steps for this {@code map}, then returning the current value or
* {@code null} if absent:
*
* <pre> {@code
* V oldValue = map.get(key);
* V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value :
* remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);
* if (newValue == null)
* map.remove(key);
* else
* map.put(key, newValue);
* }</pre>
*
* <p>The default implementation makes no guarantees about synchronization
* or atomicity properties of this method. Any implementation providing
* atomicity guarantees must override this method and document its
* concurrency properties. In particular, all implementations of
* subinterface {@link java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap} must document
* whether the function is applied once atomically only if the value is not
* present.
*
* @param key key with which the resulting value is to be associated
* @param value the non-null value to be merged with the existing value
* associated with the key or, if no existing value or a null value
* is associated with the key, to be associated with the key
* @param remappingFunction the function to recompute a value if present
* @return the new value associated with the specified key, or null if no
* value is associated with the key
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code put} operation
* is not supported by this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws ClassCastException if the class of the specified key or value
* prevents it from being stored in this map
* (<a href="{@docRoot}/java/util/Collection.html#optional-restrictions">optional</a>)
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map
* does not support null keys or the value or remappingFunction is
* null
* @since 1.8
*/
default V merge(K key, V value,
BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) {
Objects.requireNonNull(remappingFunction);
Objects.requireNonNull(value);
V oldValue = get(key);
V newValue = (oldValue == null) ? value :
remappingFunction.apply(oldValue, value);
if(newValue == null) {
remove(key);
} else {
put(key, newValue);
}
return newValue;
}
}
总结三大接口:
1、list和set接口直接实现和继承collection接口 这样可以直接用迭代器 map没有继承collection接口 至于实现迭代器需要调用map方法里的entryset()方法
2、有一些方法不一样,
list方法有(
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator);
default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
int hashCode();
E get(int index);
E set(int index, E element);
void add(int index, E element);
E remove(int index);
int indexOf(Object o);
int lastIndexOf(Object o);
ListIterator<E> listIterator();
ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
default Spliterator<E> spliterator();
)、
set方法有(
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object o);
Iterator<E> iterator();
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);
boolean add(E e);
boolean remove(Object o);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);
void clear();
boolean equals(Object o);
int hashCode();
default Spliterator<E> spliterator();
)、
map方法有(
int size();
boolean isEmpty();
boolean containsKey(Object key);
boolean containsValue(Object value);
V get(Object key);
V put(K key, V value);
V remove(Object key);
void putAll(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m);
void clear();
Set<K> keySet();
Collection<V> values();
Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet();
。。。
)
3.实现的类不一样list(
ArrayList(基于数组实现的,动态扩容,扩容方式是将新数组扩大到原来的2倍,旧数组数据拷贝到这个新数组中,性能:查找快、增删慢 不安全(多个线程同时访问就不行了));
vector(基于数组实现的,动态扩容,实现方法带有同步代码块 安全 性能比ArrayList慢);
linkedlist(基于双链表实现的,动态扩容,性能:增删块 查找慢);
)、
set(
hashset(顺序和插入顺序不一致,插入的值可以为null(唯一),插入时是读取对象的hashcode值 并在哈希值数组查找保存该对象,重写equals也要重写hashcode,equals相等 hashcode也相等,不是同步(不安全)
底层:hashmap、哈希表实现的);
Treeset(
TreeSet是SortedSet接口的唯一实现类,TreeSet可以确保集合元素处于排序状态。
TreeSet支持两种排序方式,自然排序 和定制排序,其中自然排序为默认的排序方式。
TreeSet判断两个对象不相等的方式是两个对象通过equals方法返回false,或者通过CompareTo方法比较没有返回0
);
)、
map(
hashmap(
HashMap实现了Map接口,继承AbstractMap,它是基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现(保证键的唯一性),
以key-value的形式存在
HashMap是引用数据类型
HashMap可以允许存在一个为null的key和任意个为null的value
不安全(不同步)
);
Treemap(
基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap实现。该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,
或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
TreeMap 是一个有序的key-value集合,它是通过红黑树实现的
TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,所以它是一个Map,即一个key-value集合
TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法,比如返回有序的key集合
TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,意味着它能被克隆
TreeMap 实现了Java.io.Serializable接口,意味着它支持序列化
);
hashtable(
HashTable基于Dictionary类
HashTable中的key和value都不允许为null
安全(同步)
);
1.这三个都对Map接口进行了实现
2.HashMap是不安全的线程,他允许Key值出现一次null Value值出现无数次的Null
3.Hashtable是安全的线程,他不仅实现了Map接口也实现了Dictionary接口,他的key值与Value值都不允许出现Null
4.treeMap是可以进行排序的,默认按照键的自然顺序进行升序排序,若要进行降序排序则需要在构造集合时候传递一个比较器
)
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/dragon901/article/details/79632397;
https://www.cnblogs.com/sidekick/p/8010522.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39464761/article/details/75137902
Java的集合(一)的更多相关文章
- 【Java】集合_学习笔记
一.集合 1.集合类也称容器类,主要负责保存.盛装其他数据. 2.集合可以保存数量不确定的数据,保存具有映射关系的数据(也称关联数组). 3.Java5后提供一些多线程安全的集合类,放在java.ut ...
- java的集合框架最全详解
java的集合框架最全详解(图) 前言:数据结构对程序设计有着深远的影响,在面向过程的C语言中,数据库结构用struct来描述,而在面向对象的编程中,数据结构是用类来描述的,并且包含有对该数据结构操作 ...
- 谈谈Java的集合组件
让我们一起谈谈Java的集合组件 我们在使用Java的时候,都会遇到并使用到Java的集合.在这里通过自己的理解和网上的资源对Java的集合方面的使用做一个简单的讲解和总结. Java主要分为3个集合 ...
- java.util 集合框架集合
java的集合框架为程序提供了一种处理对象组的标准方式.设计了一系列标准泛型接口: ⑴Collection ()接口,扩展了Iterable接口,位于集合层次结构的顶部,因此所有的集合都实现Colle ...
- Java基础——集合框架
Java的集合框架是Java中很重要的一环,Java平台提供了一个全新的集合框架.“集合框架”主要由一组用来操作对象的接口组成.不同接口描述一组不同数据类型.Java平台的完整集合框架如下图所示: 上 ...
- Java学习-集合(转)
在编写java程序中,我们最常用的除了八种基本数据类型,String对象外还有一个集合类,在我们的的程序中到处充斥着集合类的身影!java中集合大家族的成员实在是太丰富了,有常用的ArrayList. ...
- java的集合框架之一
java是一套很成熟的东西,很多商用的东西都喜欢用它,用的人多,稳定.不过一般也不怎么说起它,因为太常见了,私下里说,写java应用层得就像农民工,每一处都是搭积木,根据设计师的东西如何优雅地搭好积木 ...
- 浅谈Java的集合框架
浅谈Java的集合框架 一. 初识集合 重所周知,Java有四大集合框架群,Set.List.Queue和Map.四种集合的关注点不同,Set 关注事物的唯一性,List 关注事物的索引列表,Q ...
- Java之集合初探(一)
一.集合概述.区别 集合是一种容器,数组也是一种容器 在Java编程中,装各种各样的对象(引用类型)的叫做容器. 为什么出现集合类? 面向对象语言对事物的体现都是以对象的形式,所以为了方便对多个对象的 ...
- Java面向对象 集合(下)
Java面向对象 集合(下) 知识概要: (1)Map集合的体系结构 (2)Map集合的方法 (3)HashMap TreeMap (4)集合框架中的常用工具类 ( ...
随机推荐
- 广深小龙-基于unittest、pytest自动化测试框架之demo来学习啦!!!
基于unittest.pytest自动化测试框架之demo,赶紧用起来,一起学习吧! demo分为两个框架:①pytest ②unittest demo 中 包含 web.api 自动化测试框架 ...
- SpringCloud系列之集成Dubbo应用篇
目录 前言 项目版本 项目说明 集成Dubbo 2.6.x 新项目模块 老项目模块 集成Dubbo 2.7.x 新项目模块 老项目模块 参考资料 系列文章 前言 SpringCloud系列开篇文章就说 ...
- VR全景视图 Google VrPanoramaView
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 一.背景简介 Welcome to VR at Google 进入Google VR主页,发现官方给我们提供了两套解决观看VR ...
- Netty随记之ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter、SimpleChannelInboundHandler
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter是ChannelInboundHandler的一个简单实现,默认情况下不会做任何处理, ...
- Modbus TCP协议说明
协议帧 事物处理标识| 协议标识| 长度| 从机地址| 功能码| 数据 0x00 00| 0x00 00| 0x00 08| 0x01| 0x0F| 0x00 14 0x00 01 0x01 0x01 ...
- JVM调优:GC 参数
2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> JVM调优:GC 参数 博客分类: java jvm 参考: <Memory Management in the Jav ...
- Codeforces Round #622 (Div. 2) 1313 B Different Rules
B. Different Rules Nikolay has only recently started in competitive programming, but already qualifi ...
- 图论--差分约束--POJ 1201 Intervals
Intervals Time Limit: 2000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 30971 Accepted: 11990 Descripti ...
- postman(动态数据获取)
一:返回报文为 json 格式 示例:因为充值记录接口中需要用到登录接口返回报文中的信息如下 1.以获取token(JWT)和uid为例 2.在登录接口的tests中写入代码(因为登录接口报文信息中有 ...
- zabbix日常问题总结
1.connection to database 'zabbix' failed: [1040] Too many connections 问题:数据库连接池太少解决:增加数据库连接池步骤:(1).进 ...
