Sched_Boost小结
之前遇到一个耗电问题,最后发现是/proc/sys/kernel/sched_boost节点设置异常,一直处于boost状态。导致所有场景功耗上升。
现在总结一下sched_boost的相关知识。
Sched_Boost
sched_boost主要是通过影响Task placement的方式,来进行boost。它属于QTI EAS中的一部分。
默认task placement policy
计算每个cpu的负载,并将task分配到负载最轻的cpu上。如果有多个cpu的负载相同(一般是都处于idle),那么就会把task分配到系统中capacity最大的cpu上。
设置sched_boost
通过设置节点:/proc/sys/kernel/sched_boost 或者内核调用sched_set_boost()函数,可以进行sched_boost,并且在分配任务时,忽略对energy的消耗。
boost一旦设置之后,就必须显示写0来关闭。同时也支持个应用同时调用设置,设置会选择boost等级最高的生效; 而当所有应用都都关闭boost时,boost才会真正失效。
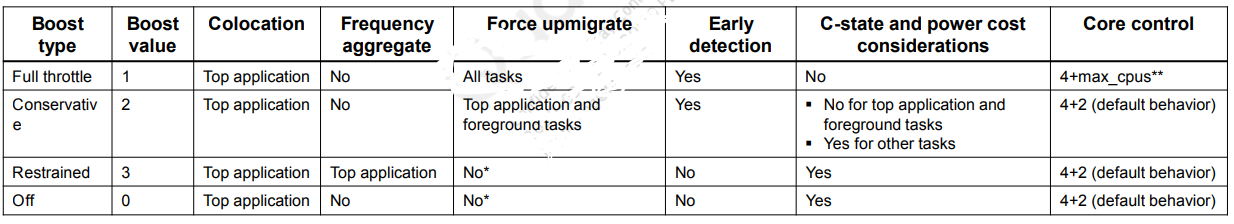
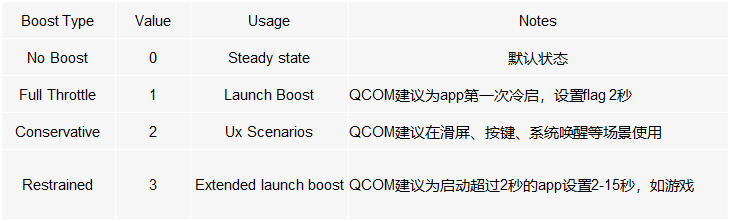
boost等级
sched_boost一共有4个等级,除了0代表关闭boost以外,其他3个等级灵活地控制功耗和性能的不同倾向程度。

在通过节点设置,会调用sched_boost_handler
{
.procname = "sched_boost",
.data = &sysctl_sched_boost,
.maxlen = sizeof(unsigned int),
.mode = ,
.proc_handler = sched_boost_handler,
.extra1 = &neg_three,
.extra2 = &three,
},
经过verify之后,调用_sched_set_boost来设置boost。
int sched_boost_handler(struct ctl_table *table, int write,
void __user *buffer, size_t *lenp,
loff_t *ppos)
{
int ret;
unsigned int *data = (unsigned int *)table->data; mutex_lock(&boost_mutex); ret = proc_dointvec_minmax(table, write, buffer, lenp, ppos); if (ret || !write)
goto done; if (verify_boost_params(*data))
_sched_set_boost(*data);
else
ret = -EINVAL; done:
mutex_unlock(&boost_mutex);
return ret;
而通过内核调用的方式,同样最后也是调用_sched_set_boost来设置boost。
int sched_set_boost(int type)
{
int ret = ; mutex_lock(&boost_mutex);
if (verify_boost_params(type))
_sched_set_boost(type);
else
ret = -EINVAL;
mutex_unlock(&boost_mutex);
return ret;
}
接下来,我们看关键的设置函数_sched_set_boost:
static void _sched_set_boost(int type)
{
if (type == ) //通过type参数判断是否enable/disable boost
sched_boost_disable_all(); //(1)disable all boost
else if (type > )
sched_boost_enable(type); //(2) enable boost
else
sched_boost_disable(-type); //(3) disable boost /*
* sysctl_sched_boost holds the boost request from
* user space which could be different from the
* effectively enabled boost. Update the effective
* boost here.
*/ sched_boost_type = sched_effective_boost();
sysctl_sched_boost = sched_boost_type;
set_boost_policy(sysctl_sched_boost); //(4) 设置boost policy
trace_sched_set_boost(sysctl_sched_boost);
}
首先看一下sched_boost的4个用于控制配置的结构体:
其中refcount来记录设置的次数。enter函数表示切换到该boost配置的动作;exit则是退出该boost配置的动作。
static struct sched_boost_data sched_boosts[] = {
[NO_BOOST] = {
.refcount = ,
.enter = sched_no_boost_nop,
.exit = sched_no_boost_nop,
},
[FULL_THROTTLE_BOOST] = {
.refcount = ,
.enter = sched_full_throttle_boost_enter,
.exit = sched_full_throttle_boost_exit,
},
[CONSERVATIVE_BOOST] = {
.refcount = ,
.enter = sched_conservative_boost_enter,
.exit = sched_conservative_boost_exit,
},
[RESTRAINED_BOOST] = {
.refcount = ,
.enter = sched_restrained_boost_enter,
.exit = sched_restrained_boost_exit,
},
};
(1)disable all boost
调用除no boost外,所有boost配置的exit函数并且将他们的refcount清0。
#define SCHED_BOOST_START FULL_THROTTLE_BOOST
#define SCHED_BOOST_END (RESTRAINED_BOOST + 1 static void sched_boost_disable_all(void)
{
int i; for (i = SCHED_BOOST_START; i < SCHED_BOOST_END; i++) {
if (sched_boosts[i].refcount > ) {
sched_boosts[i].exit();
sched_boosts[i].refcount = ;
}
}
}
(2) enable boost
refcount记录调用次数+;
由于sched+boost支持多应用同时调用的,所以在设置boost之前,要先检查当前有效的boost配置。
优先级是No boost > Full Throttle > Conservative > Restrained。
static void sched_boost_enable(int type)
{
struct sched_boost_data *sb = &sched_boosts[type];
int next_boost, prev_boost = sched_boost_type; sb->refcount++; //refcount记录次数+1 if (sb->refcount != )
return; /*
* This boost enable request did not come before.
* Take this new request and find the next boost
* by aggregating all the enabled boosts. If there
* is a change, disable the previous boost and enable
* the next boost.
*/ next_boost = sched_effective_boost(); //设置boost之前,检查当前有效的boost配置
if (next_boost == prev_boost)
return; sched_boosts[prev_boost].exit(); //调用之前配置的exit,退出之前的boost
sched_boosts[next_boost].enter(); //调用现在配置的enter,进入当前boost状态
通过检查refcount,来确认当前有效的boost。
static int sched_effective_boost(void)
{
int i; /*
* The boosts are sorted in descending order by
* priority.
*/
for (i = SCHED_BOOST_START; i < SCHED_BOOST_END; i++) {
if (sched_boosts[i].refcount >= )
return i;
} return NO_BOOST;
}
(3)disable boost
同样假如是disable boost的话,就会相应的对refcount--,并且调用当前boost类型的exit函数来退出boost。
因为sched_boost支持多种boost同时开启,并按优先级设置。所以当disable一种boost时,最后通过检查当前有效的boost来进入余下优先级高的boost模式。
static void sched_boost_disable(int type)
{
struct sched_boost_data *sb = &sched_boosts[type];
int next_boost; if (sb->refcount <= )
return; sb->refcount--; if (sb->refcount)
return; /*
* This boost's refcount becomes zero, so it must
* be disabled. Disable it first and then apply
* the next boost.
*/
sb->exit(); next_boost = sched_effective_boost();
sched_boosts[next_boost].enter();
}
(4)设置boost policy
在最后一步中,设置policy来体现task是否需要进行up migrate。
如下是sched_boost不同等级对应的up migrate迁移策略。
Full throttle和Conservative:SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG---在进行task placement时,仅考虑capacity最大的cpu core
无:SCHED_BOOST_ON_ALL---在进行task placement时,仅不考虑capacity最小的cpu core
No Boost和Restrained:SCHED_BOOST_NONE---正常EAS
/*
* Scheduler boost type and boost policy might at first seem unrelated,
* however, there exists a connection between them that will allow us
* to use them interchangeably during placement decisions. We'll explain
* the connection here in one possible way so that the implications are
* clear when looking at placement policies.
*
* When policy = SCHED_BOOST_NONE, type is either none or RESTRAINED
* When policy = SCHED_BOOST_ON_ALL or SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG, type can
* neither be none nor RESTRAINED.
*/
static void set_boost_policy(int type)
{
if (type == NO_BOOST || type == RESTRAINED_BOOST) { //conservative和full throttle模式才会进行向上迁移
boost_policy = SCHED_BOOST_NONE;
return;
} if (boost_policy_dt) {
boost_policy = boost_policy_dt;
return;
} if (min_possible_efficiency != max_possible_efficiency) { //左边是cpu中efficiency最小值,右边为最大值。big.LITTLE架构应该恒成立
boost_policy = SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG;
return;
} boost_policy = SCHED_BOOST_ON_ALL;
}
接下来详细分析3种boost设置的原理:
Full Throttle
full throttle(全速)模式下的sched boost,主要有如下2个动作:
(1)core control
(2)freq aggregation
static void sched_full_throttle_boost_enter(void)
{
core_ctl_set_boost(true); //(1)core control
walt_enable_frequency_aggregation(true); //(2)freq aggregation
}
(1)core control:isoloate/unisoloate cpu cores;enable boost时,开所有cpu core
int core_ctl_set_boost(bool boost)
{
unsigned int index = ;
struct cluster_data *cluster;
unsigned long flags;
int ret = ;
bool boost_state_changed = false; if (unlikely(!initialized))
return ; spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, flags);
for_each_cluster(cluster, index) { //修改并记录每个cluster的boost状态
if (boost) {
boost_state_changed = !cluster->boost;
++cluster->boost;
} else {
if (!cluster->boost) {
ret = -EINVAL;
break;
} else {
--cluster->boost;
boost_state_changed = !cluster->boost;
}
}
}
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags); if (boost_state_changed) {
index = ;
for_each_cluster(cluster, index) //针对每个cluster,apply boost设置
apply_need(cluster);
} trace_core_ctl_set_boost(cluster->boost, ret); return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(core_ctl_set_boost);
static void apply_need(struct cluster_data *cluster)
{
if (eval_need(cluster)) //判断是否需要
wake_up_core_ctl_thread(cluster); //唤醒cluster的core control thread
}
具体如何判断的:
enable boost时:判断是否需要unisolate cpu,
disable boost时:判断need_cpus < active_cpus是否成立。
并且与上一次更新的间隔时间满足 > delay time。
static bool eval_need(struct cluster_data *cluster)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct cpu_data *c;
unsigned int need_cpus = , last_need, thres_idx;
int ret = ;
bool need_flag = false;
unsigned int new_need;
s64 now, elapsed; if (unlikely(!cluster->inited))
return ; spin_lock_irqsave(&state_lock, flags); if (cluster->boost || !cluster->enable) {
need_cpus = cluster->max_cpus; //当enable boost时,设置need_cpus为所有cpu
} else {
cluster->active_cpus = get_active_cpu_count(cluster); //当disable boost时,首先获取active的cpu
thres_idx = cluster->active_cpus ? cluster->active_cpus - : ;
list_for_each_entry(c, &cluster->lru, sib) {
bool old_is_busy = c->is_busy; if (c->busy >= cluster->busy_up_thres[thres_idx] ||
sched_cpu_high_irqload(c->cpu))
c->is_busy = true;
else if (c->busy < cluster->busy_down_thres[thres_idx])
c->is_busy = false; trace_core_ctl_set_busy(c->cpu, c->busy, old_is_busy,
c->is_busy);
need_cpus += c->is_busy;
}
need_cpus = apply_task_need(cluster, need_cpus); //根据task需要,计算need_cpus
}
new_need = apply_limits(cluster, need_cpus); //限制need_cpus范围:cluster->min_cpus <= need_cpus <= clusterr->max_cpus
need_flag = adjustment_possible(cluster, new_need); //(*)enable boost时:判断是否需要unisolate cpu; disable boost时:判断need_cpus < active_cpus是否成立 last_need = cluster->need_cpus;
now = ktime_to_ms(ktime_get()); if (new_need > cluster->active_cpus) {
ret = ; //enable boost
} else {
/*
* When there is no change in need and there are no more
* active CPUs than currently needed, just update the
* need time stamp and return. //当需要的cpu没有变化时,只需要更新时间戳,然后return
*/
if (new_need == last_need && new_need == cluster->active_cpus) {
cluster->need_ts = now;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags);
return ;
} elapsed = now - cluster->need_ts;
ret = elapsed >= cluster->offline_delay_ms; //修改need_cpus的时间要大于delay时间,才认为有必要进行更改
} if (ret) {
cluster->need_ts = now; //更新时间戳,need_cpus
cluster->need_cpus = new_need;
}
trace_core_ctl_eval_need(cluster->first_cpu, last_need, new_need,
ret && need_flag);
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&state_lock, flags); return ret && need_flag;
}
满足更新要求的条件后,就会唤醒core control thread
static void wake_up_core_ctl_thread(struct cluster_data *cluster)
{
unsigned long flags; spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags);
cluster->pending = true;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); wake_up_process(cluster->core_ctl_thread);
}
其中会有一个检测pending的防止重入的操作。假如pending标志已经改写,那么就会将当前进程移出rq。
static int __ref try_core_ctl(void *data)
{
struct cluster_data *cluster = data;
unsigned long flags; while () {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); //先退出RUNNING状态,设为TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,后面再调用schedule()。会判断当前task已不处于TASK_RUNNING状态,随后会进行dequeue,并调度其他进程到rq->curr。(典型的出rq操作)
spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags);
if (!cluster->pending) { //检测pending,如果已经core control完成,则直接进行schedule(),并准备退出该thread
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags);
schedule();
if (kthread_should_stop())
break;
spin_lock_irqsave(&cluster->pending_lock, flags);
}
set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
cluster->pending = false;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&cluster->pending_lock, flags); do_core_ctl(cluster); //do work
} return ;
}
static void __ref do_core_ctl(struct cluster_data *cluster)
{
unsigned int need; need = apply_limits(cluster, cluster->need_cpus); //再次check need_cpus是否合法 if (adjustment_possible(cluster, need)) { //再次check是否需要更改
pr_debug("Trying to adjust group %u from %u to %u\n",
cluster->first_cpu, cluster->active_cpus, need); if (cluster->active_cpus > need) //根据need进行cpu un/isolate
try_to_isolate(cluster, need);
else if (cluster->active_cpus < need)
try_to_unisolate(cluster, need);
}
}
(2)freq aggregation:提升cpu freq
设置flag:
static inline void walt_enable_frequency_aggregation(bool enable)
{
sched_freq_aggr_en = enable;
}
后续在以下这一个地方会影响freq选择:
- load freq polcy时,会根据是否开启freq_aggregation的flag而影响load的计算。
开启flag之后,会使用aggr_grp_load替代rq->grp_time.prev_runnable_sum
aggr_grp_load是当前cluster中所有cpu core的rq->grp_time.prev_runnable_sum的总和:sum。
那么开启之后,就会使load变大,从而提升cpu freq或者进行
static inline u64 freq_policy_load(struct rq *rq)
{
。。。
if (sched_freq_aggr_en)
load = rq->prev_runnable_sum + aggr_grp_load;
else
load = rq->prev_runnable_sum + rq->grp_time.prev_runnable_sum;
。。。
}
Conservative
static void sched_conservative_boost_enter(void)
{
update_cgroup_boost_settings(); //(1)更新cgroup boost设置
sched_task_filter_util = sysctl_sched_min_task_util_for_boost; //(2)task util调节
}
(1)遍历group,group一般有以下这些:backgroun,foreground,top-app,rt。
将所有sched_boost_enabled设置为false,除了写了no_override的group。而从init.target.rc中可以看到top-app和foregroung写了该flag(如下),所以最后就会有
write /dev/stune/foreground/schedtune.sched_boost_no_override
write /dev/stune/top-app/schedtune.sched_boost_no_override
void update_cgroup_boost_settings(void)
{
int i; for (i = ; i < BOOSTGROUPS_COUNT; i++) {
if (!allocated_group[i])
break; if (allocated_group[i]->sched_boost_no_override)
continue; allocated_group[i]->sched_boost_enabled = false;
}
}
(2)修改min_task_util的门限
/* 1ms default for 20ms window size scaled to 1024 */
unsigned int sysctl_sched_min_task_util_for_boost = ; //conservative 保守
/* 0.68ms default for 20ms window size scaled to 1024 */
unsigned int sysctl_sched_min_task_util_for_colocation = ; //normal
目前仅发现在如下2处会用到这个值:
1、获取sched_boost_enabled仍然为true的task。过滤task_util较小的task,关闭boost。
下面这个函数是返回task boost policy的,也就是placement boost。函数主要逻辑:
task所在group中打开了sched_boost_endabled,并且sched_boost设置非0:
假如sched_boost=(full throttle),则policy是SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG
假如sched_boost=(Conservative),则还需要判断task util是否超过sched_task_filter_util。超过了,policy=SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG;没超过,policy=SCHED_BOOST_NONE
根据上面看到只有top-app和foreground这2个group是打开了sched_boost_enabled的。
所以,这里就是将top-app和foreground中的task_util较大的task挑选出来,enable了boost;而其他的task,都关闭了boost。
static inline enum sched_boost_policy task_boost_policy(struct task_struct *p)
{
enum sched_boost_policy policy = task_sched_boost(p) ?
sched_boost_policy() :
SCHED_BOOST_NONE;
if (policy == SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG) {
/*
* Filter out tasks less than min task util threshold
* under conservative boost.
*/
if (sched_boost() == CONSERVATIVE_BOOST &&
task_util(p) <= sched_task_filter_util) //修改了这个门限
policy = SCHED_BOOST_NONE;
} return policy;
}
2、在更新walt负载时
更新了unfilter的计数,增大到51,相当于:/* 1ms default for 20ms window size scaled to 1024 */(原先默认为:35,即0.68ms)。也就是当demand_scaled大于这个门限后,会设置一个nr_windows的缓冲时间。缓冲时间每一次update_history就会减1,直到为0。
static void update_history(struct rq *rq, struct task_struct *p,
u32 runtime, int samples, int event)
{
。。。
if (demand_scaled > sched_task_filter_util)
p->unfilter = sysctl_sched_task_unfilter_nr_windows;
else
if (p->unfilter)
p->unfilter = p->unfilter - ;
。。。
}
p->unfilter这个参数又会在如下两个地方用于判断:
首先是在fair.c中,但是由于现在是CONSERVATIVE_BOOST,所以,只会return false。这条暂不分析下去。
static inline bool task_skip_min_cpu(struct task_struct *p)
{
return sched_boost() != CONSERVATIVE_BOOST &&
get_rtg_status(p) && p->unfilter;
}
另外一个地方是如下walt.h中,由于p->unfilter非0,那么就会判断当前cpu是否为小核,如果是小核,那么return true。
static inline bool walt_should_kick_upmigrate(struct task_struct *p, int cpu)
{
struct related_thread_group *rtg = p->grp; if (is_suh_max() && rtg && rtg->id == DEFAULT_CGROUP_COLOC_ID &&
rtg->skip_min && p->unfilter)
return is_min_capacity_cpu(cpu); return false;
}
返回值会影响如下函数的返回值,也是return flase。
所以,会告诉系统当前的task load与当前cpu的capacity不匹配,需要进行迁移。
此外,在进行迁移时,也是调用该函数,用于排除目标cpu为小核。
综上,就是将task从小核迁移到大核。
static inline bool task_fits_max(struct task_struct *p, int cpu)
{
unsigned long capacity = capacity_orig_of(cpu);
unsigned long max_capacity = cpu_rq(cpu)->rd->max_cpu_capacity.val;
unsigned long task_boost = per_task_boost(p); if (capacity == max_capacity)
return true; if (is_min_capacity_cpu(cpu)) {
if (task_boost_policy(p) == SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG ||
task_boost > ||
schedtune_task_boost(p) > ||
walt_should_kick_upmigrate(p, cpu)) //条件为true
return false;
} else { /* mid cap cpu */
if (task_boost > TASK_BOOST_ON_MID)
return false;
} return task_fits_capacity(p, capacity, cpu);
}
Restrained
该模式下,从代码看,仅打开了freq aggregation。与上面全速模式类似,不再赘述。
static void sched_restrained_boost_enter(void)
{
walt_enable_frequency_aggregation(true);
}
总结各个boost的效果
Full throttle:
1、通过core control,将所有cpu都进行unisolation
2、通过freq聚合,将load计算放大。从而触发提升freq,或者迁移等
3、通过设置boost policy= SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG,迁移挑选target cpu时,只会选择大核
最终效果应该尽可能把任务都放在大核运行(除了cpuset中有限制)
Conservative:
1、通过更新group boost配置,仅让top-app和foreground组进行task placement boost
2、提高min_task_util的门限,让进行up migrate的条件更苛刻。只有load较大(>1ms)的task,会进行up migrate。
2、同上,更改min_task_util门限后,会提醒系统task与cpu是misfit,需要进行迁移。
3、通过设置boost policy= SCHED_BOOST_ON_BIG,迁移挑选target cpu时,只会选择大核
最终效果:top-app和foreground的一些task会迁移到大核运行
Restrained:
1、通过freq聚合,将load计算放大。从而触发提升freq,或者迁移等
load放大后,仍遵循基本EAS。提升freq或者迁移,视情况而定。
注意关于early_datection部分简述参考之前文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/lingjiajun/p/12317090.html 中CPU freq调节章节。不过代码中貌似没有看到会影响的地方。由于EAS部分本人还没有仔细学习分析代码,可能还有疏漏或者错误,欢迎交流。
Sched_Boost小结的更多相关文章
- 从零开始编写自己的C#框架(26)——小结
一直想写个总结,不过实在太忙了,所以一直拖啊拖啊,拖到现在,不过也好,有了这段时间的沉淀,发现自己又有了小小的进步.哈哈...... 原想框架开发的相关开发步骤.文档.代码.功能.部署等都简单的讲过了 ...
- Python自然语言处理工具小结
Python自然语言处理工具小结 作者:白宁超 2016年11月21日21:45:26 目录 [Python NLP]干货!详述Python NLTK下如何使用stanford NLP工具包(1) [ ...
- java单向加密算法小结(2)--MD5哈希算法
上一篇文章整理了Base64算法的相关知识,严格来说,Base64只能算是一种编码方式而非加密算法,这一篇要说的MD5,其实也不算是加密算法,而是一种哈希算法,即将目标文本转化为固定长度,不可逆的字符 ...
- iOS--->微信支付小结
iOS--->微信支付小结 说起支付,除了支付宝支付之外,微信支付也是我们三方支付中最重要的方式之一,承接上面总结的支付宝,接下来把微信支付也总结了一下 ***那么首先还是由公司去创建并申请使用 ...
- iOS 之UITextFiled/UITextView小结
一:编辑被键盘遮挡的问题 参考自:http://blog.csdn.net/windkisshao/article/details/21398521 1.自定方法 ,用于移动视图 -(void)mov ...
- K近邻法(KNN)原理小结
K近邻法(k-nearst neighbors,KNN)是一种很基本的机器学习方法了,在我们平常的生活中也会不自主的应用.比如,我们判断一个人的人品,只需要观察他来往最密切的几个人的人品好坏就可以得出 ...
- scikit-learn随机森林调参小结
在Bagging与随机森林算法原理小结中,我们对随机森林(Random Forest, 以下简称RF)的原理做了总结.本文就从实践的角度对RF做一个总结.重点讲述scikit-learn中RF的调参注 ...
- Bagging与随机森林算法原理小结
在集成学习原理小结中,我们讲到了集成学习有两个流派,一个是boosting派系,它的特点是各个弱学习器之间有依赖关系.另一种是bagging流派,它的特点是各个弱学习器之间没有依赖关系,可以并行拟合. ...
- scikit-learn 梯度提升树(GBDT)调参小结
在梯度提升树(GBDT)原理小结中,我们对GBDT的原理做了总结,本文我们就从scikit-learn里GBDT的类库使用方法作一个总结,主要会关注调参中的一些要点. 1. scikit-learn ...
随机推荐
- 基础JS遇到的一些题01
1.两种数组去重方法 const unique = arr =>{ let mySet = new Set(arr); /!* let newArr =[]; for (let i = 0 ;i ...
- 一、Spring的控制反转(IOC)学习
一.控制反转 1.什么是控制反转? 控制反转(Inversion of Control,缩写为IoC),是面向对象中的一种设计原则,可以用来减低计算机代码之间的耦合度.其中最常见的方式叫做依赖注入(D ...
- Openwrt:逆向永久修改Flash中的Mac地址
get mtd device cat /proc/mtd dev: size erasesize name mtd0: 00800000 00010000 "ALL" mtd1: ...
- 初探Redis-基础类型Hash
Redis存在五种基础类型:字符串(String).队列(List).哈希(Hash).集合(Set).有序集合(Sorted Set).本次列举出Hash的常用操作. Redis官网:https:/ ...
- ereg正则%00截断
0x01 <?php $flag = "xxx"; if (isset ($_GET['password'])) { if (ereg ("^[a-zA-Z0-9] ...
- python--集合和文件基本操作
集合 # 集合天生就能去重,集合也是无序的 集合也是{ } 但是空集合定义特殊s=set() #空集合s2 = set('1234445566778')print(s2) s3 = {'1',' ...
- Spring Cloud 系列之 Consul 配置中心
前面我们已经学习过 Spring Cloud Config 了: Spring Cloud 系列之 Config 配置中心(一) Spring Cloud 系列之 Config 配置中心(二) Spr ...
- 复变函数-MINDMAPS-continuous updating
- 我参与 Seata 开源项目的一些感悟
丁老师在他的知识星球邀请我回答以下一个问题: 我觉得这个问题非常有意思,姑且把它贴到公众号这里,与大家分享一下我对这个问题的一些感悟. 感谢丁老师的邀请问答: 在这里我就简单说下,我这段时间参与 Se ...
- zsy后台管理系统-架构设计
Zsy框架总体架构设计 1.Mysql数据库,存储所有表的数据. 2.Zsy-基础项目(Zsy-Model,Zsy-Dao,Zsy-Service,Zsy-Web),基于SSM框架.项目功能包含基本的 ...
