Spring 学习记录2 Environment
Environment是什么
environment是什么呢....中文是环境大家都知道但是具体代表什么呢?感觉很抽象....从代码里的解释来看environment代表了profile和properties.
profile就是1组bean的定义.实际用途就是在不同环境比如测试环境和生产环境中加载不同的bean达到根据环境加载bean的用途.(因为测试环境可能有些bean是模拟的,比如接口.调用返回的报文都是自己模拟的,真实的bean在测试环境拿不到).
properties就不用说了.就是配置...
这篇文章我想分享下我对properties的学习,因为profile我感觉只要会配置就行了...可能更偏向于配置运维,而properties主要涉及到类型转化等比较复杂的东西.而我自己也写过一些conveter.所以想特别学习下.
结构
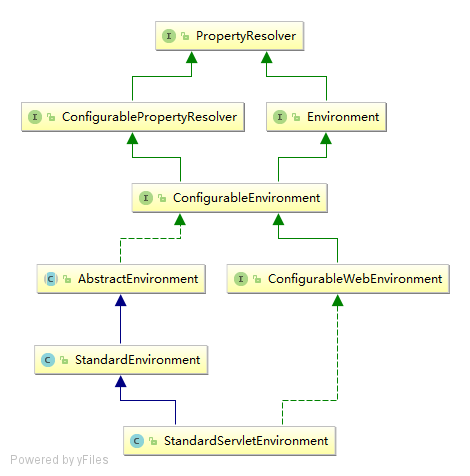
大概就是这样的结构.java web环境下一般都是StandardServletEnvironment环境,而我自己做junit测试的时候是StandardEnvironment 这里主要分析我对StandardEnvironment 的学习(子类可能也就增加了一点点其他功能吧.总的来说应该都是大同小异.估计是把servlet的环境变量也加到properties里了.)
environment的profile的功能是定义在Environment类里的
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* Return the set of profiles explicitly made active for this environment. Profiles
* are used for creating logical groupings of bean definitions to be registered
* conditionally, for example based on deployment environment. Profiles can be
* activated by setting {@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
* "spring.profiles.active"} as a system property or by calling
* {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)}.
* <p>If no profiles have explicitly been specified as active, then any {@linkplain
* #getDefaultProfiles() default profiles} will automatically be activated.
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* Return the set of profiles to be active by default when no active profiles have
* been set explicitly.
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/**
* Return whether one or more of the given profiles is active or, in the case of no
* explicit active profiles, whether one or more of the given profiles is included in
* the set of default profiles. If a profile begins with '!' the logic is inverted,
* i.e. the method will return true if the given profile is <em>not</em> active.
* For example, <pre class="code">env.acceptsProfiles("p1", "!p2")</pre> will
* return {@code true} if profile 'p1' is active or 'p2' is not active.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if called with zero arguments
* or if any profile is {@code null}, empty or whitespace-only
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
}
而properties的功能是定义在PropertyResolver里的
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* Return whether the given property key is available for resolution, i.e.,
* the value for the given key is not {@code null}.
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or {@code null}
* if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @see #getProperty(String, String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
*/
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or
* {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or {@code null}
* if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or
* {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* Convert the property value associated with the given key to a {@code Class}
* of type {@code T} or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved.
* @throws org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionException if class specified
* by property value cannot be found or loaded or if targetType is not assignable
* from class specified by property value
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key (never {@code null}).
* @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* Return the property value associated with the given key, converted to the given
* targetType (never {@code null}).
* @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value are ignored and passed through unchanged.
* @param text the String to resolve
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String)
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown.
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* or if any placeholders are unresolvable
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String, boolean)
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
让我觉得很奇怪的一个地方就是既然Environment代表了profile+properties,那为什么profile相关方法要写在Environment里,而properties相关方法要写在PropertyResolver里呢...都是@since3.1为什么不再弄个ProfileResolver接口然后Environment接口继承这2个接口呢?
PropertyResolver
从前面的接口代码观察.中我觉得这个类主要就是2个作用:
1.给你1个key你要能找到它对应的value.就是解析properties.
2.在properties的基础上增加了placeholder.value中的一部分可能是占位符,要能根据key找到value同时替换占位符为实际的值.
实验1,一个小测试:
ConfigurablePropertyResolver configurablePropertyResolver; // env
1 /**
* getProperty直接写pro的名字
* resolveRequiredPlaceholders用${}替换pro
*/
@Test
public void testPropertiesResolver() {
System.out.println("a= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("a"));//a= b
System.out.println("${a}= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("${a}"));//${a}= null
System.out.println("mmp.a= " + configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty("mmp.a"));//mmp.a= 123
System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("a=${a}"));//a=b
System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("mmp.a=${mmp.a}"));//mmp.a=123
}
加载的配置文件
a=b
mmp.a=123
email=jyzjyz12@163.com
从这个测试中可以看出
1.加载完properties配置以后我想获得value我就只要简简单单的调用getProperty方法就行了.
2.比如在bean定义的applicationContext.XML里数据源相关的bean可能会使用占位符定义,比如datasource的username和password <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" /> 这里的占位符的解析也是通过propertyResolver, resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法或者resolvePlaceholders等相关placeHolder方法来完成.
上面这么多方法其实总结起来就是读取了properties文件,通过key得到value就这么简单...
实验2,再来1个测试:
ConfigurablePropertyResolver configurablePropertyResolver;
/**
* PropertyPlaceholderHelper 在进test之前就已经初始化完成了,所以修改这个placeHolderPrefix没用
*/
@Test
public void testConfigurablePropertyResolver() {
configurablePropertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix("#{");
configurablePropertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix("}");
System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("邮箱地址=${email}")); //可以被替换
System.out.println(configurablePropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders("邮箱地址=#{email}"));//无效
}
前面测试用到了占位符.默认是${},前缀是${后缀是}......那么我们能不能换个占位符呢? 我们来做1个测试 ↑
这个实验结果似乎是不能..但是接口明明提供了setPlaceholderPrefix和suffix方法为什么会不行呢?
我们稍微跟下断点:
AbstractEnvironment.java
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
env里解析placeholder是通过ConfigurablePropertyResolver 来做的.
ConfigurablePropertyResolver 里是用PropertyPlaceholderHelper strictHelper;来做的
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
然后我再加载spring的XML配置.还没进入junit的测试方法的时候,需要加载指定目录下的bean
<context:component-scan base-package="spring">
</context:component-scan>
这样会导致strictHelper被初始化,ConfigurablePropertyResolver默认的placeholder是${}所以设置到strictHelper里的是${}.
后面进入junit的test方法以后尽管我们去修改了ConfigurablePropertyResolver的placeholder为#{}但是因为strictHelper已经被初始化过了,所以我们并不会重新初始化strictHelper.因此test方法里面修改placeholder为#{}无效.
小实验3:
从实验2种我们已经知道placeholder最终是PropertyPlaceholderHelper来解析的.那么我们是不是可以直接使用它来设置我们自己的placeholder呢?
/**
* PropertyPlaceholderHelper 替换字符串
*/
@Test
public void testConfigurablePropertyResolver2() {
PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper = new PropertyPlaceholderHelper("#((", "))");
System.out.println(helper.replacePlaceholders("邮箱地址=#((email))", new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() { //邮箱地址=jyzjyz12@163.com
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) {
return configurablePropertyResolver.getProperty(placeholderName);
}
}));
}
这里我们新建了1个placeholder是#(())的helper..用它去解析#((email)).....从这个实验中我们大概可以观察到.PropertyPlaceholderHelper 得到#((email))这个字符串以后通过匹配前缀和后缀剥离字符串以后肯定会得到email.然后通过email这个key去environment(或者他的委托类的时候)的properties里去getProperties得到对应的value.
我们来稍微跟一下断点:
当我们调用env的resolveRequiredPlaceholders或者类的其他处理placeholder方法的时候,其实都是通过env内部的PropertyResolver去处理的.就是说env实现了PropertyResolver接口.但是他自己不处理,委托其他类来处理
AbstractEnvironment.java
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver是用PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理,这里分为2步,第一步是helper.replacePlaceholders得到剥离了placeholder的key.第二步是通过内部类的resplvePlaceholder方法调用getPropertyAsRawString方法输入key得到value
AbstractPropertyResolver.java
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() {
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) {
return getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);
}
});
}
PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理的时候会一层一层剥离placeholder,因为placeholder可能有N层.
/**
* Replaces all placeholders of format {@code ${name}} with the value returned
* from the supplied {@link PlaceholderResolver}.
* @param value the value containing the placeholders to be replaced
* @param placeholderResolver the {@code PlaceholderResolver} to use for replacement
* @return the supplied value with placeholders replaced inline
*/
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>());
} protected String parseStringValue(
String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(strVal); int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in string value \"" + strVal + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
} return result.toString();
}
29行是个递归调用如果我穿的是${email},29行做完返回的就是email...得到了placeholder中的key以后我们就需要通过内部类PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver中的getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);去通过key得到value.
这个时候的getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);中的placeholderName是email.
这个方法其实就是简单的调用getProperty方法
@Override
protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) {
return getProperty(key, String.class, false);
}
这样就能获得value了.
小结
小结一下environment解决properties和placeholder的方法.
1.如果是properties.直接通过内部PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的getProperty解决
2.如果是placeholder.通过env内部PropertySourcesPropertyResolver相应的resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法(或者其他placeholder方法)来解决.
2.1.这些方法内部会使用helper来解析placeholder....
2.2.PropertyPlaceholderHelper的replacePlaceholders递归调用parseStringValue方法来来剥离placeholder得到key返回给env的PropertySourcesPropertyResolver........
2.3.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver再得到key以后就和查找properties一样了.
所以placeholder相比properties,就是多了一步解析placeholder得到key.利用了PropertyPlaceholderHelper来处理placeholder.
以上便是Environment做为PropertyResolver的用途与原理.
Spring 学习记录2 Environment的更多相关文章
- Spring 学习记录3 ConversionService
ConversionService与Environment的关系 通过之前的学习(Spring 学习记录2 Environment),我已经Environment主要是负责解析properties和p ...
- Spring 学习记录8 初识XmlWebApplicationContext(2)
主题 接上文Spring 学习记录7 初识XmlWebApplicationContext refresh方法 refresh方法是定义在父类AbstractApplicationContext中的. ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(二)
本篇就简单的说一下Bean的装配和AOP 本篇的项目是在上一篇我的Spring学习记录(一) 中项目的基础上进行开发的 1. 使用setter方法和构造方法装配Bean 1.1 前期准备 使用sett ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(四)
虽然Spring管理这我们的Bean很方便,但是,我们需要使用xml配置大量的Bean信息,告诉Spring我们要干嘛,这还是挺烦的,毕竟当我们的Bean随之增多的话,xml的各种配置会让人很头疼. ...
- 我的Spring学习记录(五)
在我的Spring学习记录(四)中使用了注解的方式对前面三篇做了总结.而这次,使用了用户登录及注册来对于本人前面四篇做一个应用案例,希望通过这个来对于我们的Spring的使用有一定的了解. 1. 程序 ...
- Spring 学习记录6 BeanFactory(2)
主题 除了Spring 学习记录5 BeanFactory 里写的几个接口外,BeanFactory的实现类还实现了一些其他接口,这篇文章主要介绍这些接口和实现类. 结构 DefaultListabl ...
- Spring学习记录(九)---通过工厂方法配置bean
1. 使用静态工厂方法创建Bean,用到一个工厂类 例子:一个Car类,有brand和price属性. package com.guigu.spring.factory; public class C ...
- Spring学习记录(七)---表达式语言-SpEL
SpEL---Spring Expression Language:是一个支持运行时查询和操作对象图表达式语言.使用#{...}作为定界符,为bean属性动态赋值提供了便利. ①对于普通的赋值,用Sp ...
- Spring 学习记录5 BeanFactory
主题 记录我对BeanFactor接口的简单的学习. BeanFactory我感觉就是管理bean用的容器,持有一堆的bean,你可以get各种bean.然后也提供一些bean相关的功能比如别名呀之类 ...
随机推荐
- 20155315 2016-2017-2 《Java程序设计》第八周学习总结
教材学习内容总结 第14章 NIO与NIO2 1.认识NIO NIO使用频道(Channel)来衔接数据节点,在处理数据时,NIO可以让你设定缓冲区(Buffer)容量,在缓冲区中对感兴趣的数据区块进 ...
- CH1809 匹配统计
题意 描述 阿轩在纸上写了两个字符串,分别记为A和B.利用在数据结构与算法课上学到的知识,他很容易地求出了"字符串A从任意位置开始的后缀子串"与"字符串B"匹配 ...
- hasura graphql schema 导出
使用的是apollo 的插件 安装apollo npm install -g apollo 基本使用 因为我使用了模式拼接,所以地址有变动,一般是 http://host:port/v1alpha1/ ...
- 3——FFMPEG之解复用器-----AVInputFormat(转)
1. 数据结构: AVInputFormat为FFMPEG的解复用器对象,通过调用av_register_all(),FFMPEG所有的解复用器保存在以first_iformat为链表头的链表中,且还 ...
- BeagleBoneBlack Linux开发相关链接收藏
ubuntu挂载vdi文件 官方linux代码地址 官方devicetree代码地址 [转]使用BBB的device tree和cape(重新整理版) iio: input: ti_am335x_ad ...
- Bootstrap-CL:分页
ylbtech-Bootstrap-CL:分页 1.返回顶部 1. Bootstrap 分页 本章将讲解 Bootstrap 支持的分页特性.分页(Pagination),是一种无序列表,Bootst ...
- Jenkins构建Python项目提示:'python' 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序
问题描述: jenkin集成python项目,立即构建后,发现未执行成功,查看Console Output 提示:'Python' 不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序,如下图: 1.在 Windo ...
- Express详解
express() 创建一个express应用程序 var express = require('express'); var app = express(); app.get('/', functi ...
- C++ 排序总结
原帖地址 http://kongec.blog.sohu.com/85141353.html 附 六分钟演示15中算法 http://www.guokr.com/post/482666/ 一.插入排 ...
- 深度解析Java中的那把锁
锁的本质 我们先来讨论锁的出现是为了解决什么问题,锁要保证的事情其实很好理解,同一件事(一个代码块)在同一时刻只能由一个人(线程)操作. 这里所说的锁为排他锁,暂不考虑读写锁的情况 我们在这里打个比方 ...
