keras_基本网络层结构(1)_常用层
参考文献:
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_26917383/article/details/72857454
http://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/layers/core_layer/ keras中文文档
keras网络结构
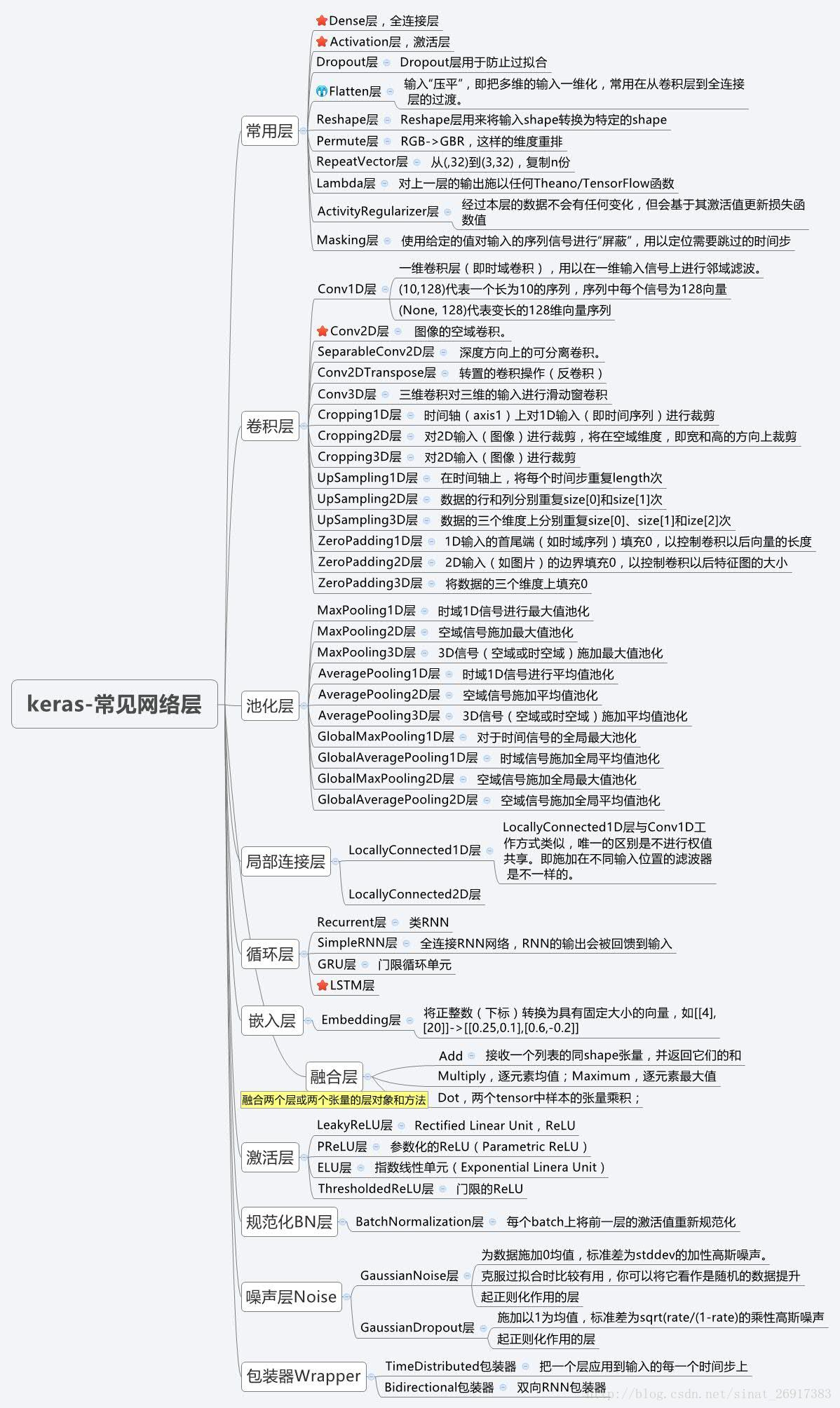
常用层
常用层对应于core模块,core内部定义了一系列常用的网络层,包括全连接层、激活层等。
Dense层
keras.layers.core.Dense(units, activation=None, use_bias=True, kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None)
Dense就是常用的全连接层,所实现的运算是output = activation(dot(input, kernel)+bias)。其中activation是逐元素计算的激活函数,kernel是本层的权值矩阵,bias为偏置向量,只有当use_bias=True才会添加。
如果本层的输入数据的维度大于2,则会先被压为与kernel相匹配的大小。
使用示例:
# as first layer in a sequential model:
# as first layer in a sequential model:
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_shape=(16,)))
# now the model will take as input arrays of shape (*, 16)
# and output arrays of shape (*, 32) # after the first layer, you don't need to specify
# the size of the input anymore:
model.add(Dense(32))
参数:
units:大于0的整数,代表该层的输出维度。
activation:激活函数,为预定义的激活函数名(参考激活函数),或逐元素(element-wise)的Theano函数。如果不指定该参数,将不会使用任何激活函数(即使用线性激活函数:a(x)=x)
use_bias: 布尔值,是否使用偏置项
kernel_initializer:权值初始化方法,为预定义初始化方法名的字符串,或用于初始化权重的初始化器。参考initializers
bias_initializer:偏置向量初始化方法,为预定义初始化方法名的字符串,或用于初始化偏置向量的初始化器。参考initializers
kernel_regularizer:施加在权重上的正则项,为Regularizer对象
bias_regularizer:施加在偏置向量上的正则项,为Regularizer对象
activity_regularizer:施加在输出上的正则项,为Regularizer对象
kernel_constraints:施加在权重上的约束项,为Constraints对象
bias_constraints:施加在偏置上的约束项,为Constraints对象
输入
形如(batch_size, ..., input_dim)的nD张量,最常见的情况为(batch_size, input_dim)的2D张量
输出
形如(batch_size, ..., units)的nD张量,最常见的情况为(batch_size, units)的2D张量
Activation层
keras.layers.core.Activation(activation)
激活层对一个层的输出施加激活函数
参数
- activation:将要使用的激活函数,为预定义激活函数名或一个Tensorflow/Theano的函数。参考激活函数
输入shape
任意,当使用激活层作为第一层时,要指定input_shape
输出shape
与输入shape相同
Dropout层
keras.layers.core.Dropout(rate, noise_shape=None, seed=None)
为输入数据施加Dropout。Dropout将在训练过程中每次更新参数时按一定概率(rate)随机断开输入神经元,Dropout层用于防止过拟合。
参数
rate:0~1的浮点数,控制需要断开的神经元的比例
noise_shape:整数张量,为将要应用在输入上的二值Dropout mask的shape,例如你的输入为(batch_size, timesteps, features),并且你希望在各个时间步上的Dropout mask都相同,则可传入noise_shape=(batch_size, 1, features)。
- seed:整数,使用的随机数种子
Flatten层
keras.layers.core.Flatten()
Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,即把多维的输入一维化,常用在从卷积层到全连接层的过渡。Flatten不影响batch的大小。
使用示例
model = Sequential()
model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3,
border_mode='same',
input_shape=(3, 32, 32)))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 64, 32, 32) model.add(Flatten())
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 65536)
Reshape层
Reshape层用来将输入shape转换为特定的shape
参数
- target_shape:目标shape,为整数的tuple,不包含样本数目的维度(batch大小)
输入shape
任意,但输入的shape必须固定。当使用该层为模型首层时,需要指定input_shape参数
输出shape
(batch_size,)+target_shape
使用示例:
# as first layer in a Sequential model
model = Sequential()
model.add(Reshape((3, 4), input_shape=(12,)))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 3, 4)
# note: `None` is the batch dimension # as intermediate layer in a Sequential model
model.add(Reshape((6, 2)))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 6, 2) # also supports shape inference using `-1` as dimension
model.add(Reshape((-1, 2, 2)))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 3, 2, 2)
Permute层
keras.layers.core.Permute(dims)
Permute层将输入的维度按照给定模式进行重排,例如,当需要将RNN和CNN网络连接时,可能会用到该层。
参数
- dims:整数tuple,指定重排的模式,不包含样本数的维度。重拍模式的下标从1开始。例如(2,1)代表将输入的第二个维度重拍到输出的第一个维度,而将输入的第一个维度重排到第二个维度
使用示例:
model = Sequential()
model.add(Permute((2, 1), input_shape=(10, 64)))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 64, 10)
# note: `None` is the batch dimension
输入shape
任意,当使用激活层作为第一层时,要指定input_shape
输出shape
与输入相同,但是其维度按照指定的模式重新排列
RepeatVector层
keras.layers.core.RepeatVector(n)
RepeatVector层将输入重复n次
参数
- n:整数,重复的次数
输入shape
形如(nb_samples, features)的2D张量
输出shape
形如(nb_samples, n, features)的3D张量
使用示例
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(32, input_dim=32))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 32)
# note: `None` is the batch dimension model.add(RepeatVector(3))
# now: model.output_shape == (None, 3, 32)
Lambda层
keras.layers.core.Lambda(function, output_shape=None, mask=None, arguments=None)
本函数用以对上一层的输出施以任何Theano/TensorFlow表达式
参数
function:要实现的函数,该函数仅接受一个变量,即上一层的输出
output_shape:函数应该返回的值的shape,可以是一个tuple,也可以是一个根据输入shape计算输出shape的函数
mask: 掩膜
arguments:可选,字典,用来记录向函数中传递的其他关键字参数
使用示例:
# add a x -> x^2 layer
model.add(Lambda(lambda x: x ** 2))
# add a layer that returns the concatenation
# of the positive part of the input and
# the opposite of the negative part def antirectifier(x):
x -= K.mean(x, axis=1, keepdims=True)
x = K.l2_normalize(x, axis=1)
pos = K.relu(x)
neg = K.relu(-x)
return K.concatenate([pos, neg], axis=1) def antirectifier_output_shape(input_shape):
shape = list(input_shape)
assert len(shape) == 2 # only valid for 2D tensors
shape[-1] *= 2
return tuple(shape) model.add(Lambda(antirectifier,
output_shape=antirectifier_output_shape))
输入shape
任意,当使用该层作为第一层时,要指定input_shape
输出shape
由output_shape参数指定的输出shape,当使用tensorflow时可自动推断
ActivityRegularizer层
keras.layers.core.ActivityRegularization(l1=0.0, l2=0.0)
经过本层的数据不会有任何变化,但会基于其激活值更新损失函数值
参数
l1:1范数正则因子(正浮点数)
l2:2范数正则因子(正浮点数)
输入shape
任意,当使用该层作为第一层时,要指定input_shape
输出shape
与输入shape相同
Masking层
keras.layers.core.Masking(mask_value=0.0)
使用给定的值对输入的序列信号进行“屏蔽”,用以定位需要跳过的时间步
对于输入张量的时间步,即输入张量的第1维度(维度从0开始算,见例子),如果输入张量在该时间步上都等于mask_value,则该时间步将在模型接下来的所有层(只要支持masking)被跳过(屏蔽)。
如果模型接下来的一些层不支持masking,却接受到masking过的数据,则抛出异常。
使用示例:
考虑输入数据x是一个形如(samples,timesteps,features)的张量,现将其送入LSTM层。因为你缺少时间步为3和5的信号,所以你希望将其掩盖。这时候应该:
赋值
x[:,3,:] = 0.,x[:,5,:] = 0.在LSTM层之前插入
mask_value=0.的Masking层
model = Sequential()
model.add(Masking(mask_value=0., input_shape=(timesteps, features)))
model.add(LSTM(32))
keras_基本网络层结构(1)_常用层的更多相关文章
- keras_基本网络层结构(2)_卷积层
参考文献:http://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/layers/convolutional_layer/ 卷积层 Conv1D层 keras.layers.c ...
- Keras网络层之常用层Core
常用层 常用层对应于core模块,core内部定义了一系列常用的网络层,包括全连接.激活层等 Dense层 keras.layers.core.Dense(units, activation=None ...
- 【转】Caffe初试(七)其它常用层及参数
本文讲解一些其它的常用层,包括:softmax-loss层,Inner Product层,accuracy层,reshape层和dropout层及它们的参数配置. 1.softmax-loss sof ...
- Caffe学习系列(5):其它常用层及参数
本文讲解一些其它的常用层,包括:softmax_loss层,Inner Product层,accuracy层,reshape层和dropout层及其它们的参数配置. 1.softmax-loss so ...
- 转 Caffe学习系列(5):其它常用层及参数
本文讲解一些其它的常用层,包括:softmax_loss层,Inner Product层,accuracy层,reshape层和dropout层及其它们的参数配置. 1.softmax-loss so ...
- 4、Caffe其它常用层及参数
借鉴自:http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/p/5072746.html 本文讲解一些其它的常用层,包括:softmax_loss层,Inner Product层,accu ...
- caffe(5) 其他常用层及参数
本文讲解一些其它的常用层,包括:softmax_loss层,Inner Product层,accuracy层,reshape层和dropout层及其它们的参数配置. 1.softmax-loss so ...
- Linux_用户级_常用命令(4):cp
Linux_用户级_常用命令之cp 开篇语:懒是人类进步的源动力 本文原创,专为光荣之路公众号所有,欢迎转发,但转发请务必写出处! Linux常用命令第二集包含命令:cp 格式 cp [-optio ...
- 1.Python_字符串_常用办法总结
明确:对字符串的操作方法都不会改变原来字符串的值. 1.去掉空格和特殊符号 name.strip() 去掉空格和换行符 name.strip("xx") 去掉某个字符串 name. ...
随机推荐
- 内存记号(Memory Trail)[自定义的名字] --调试方法
即使你把输出导向到文件中,运转记录花费的时间所带来的冲击,仍然足够改变程序的执行结果.如果要改善这种情况,我必须回到一个我所谓的“Memory Trails”(内存记号)的低阶技术中.为了使用 mem ...
- 文字和图片居中的HTML代码怎么写?
HTML 代码 ,怎么将文本/ 图片居中?这是在W3Cschool的编程问答中前端♌蕾儿提出的问题.网友施主同西否给出了详细的解答. html文字居中和html图片居中方法代码,通过在html中实现文 ...
- 机器学习实战python3 K近邻(KNN)算法实现
台大机器技法跟基石都看完了,但是没有编程一直,现在打算结合周志华的<机器学习>,撸一遍机器学习实战, 原书是python2 的,但是本人感觉python3更好用一些,所以打算用python ...
- poj2954 Triangle
地址:http://poj.org/problem?id=2954 题目: Triangle Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submi ...
- flask nginx+uwsgi超时设置
最近使用uwsgi+nginx经常程序执行一般就跳转到nginx报错页面,查看停止时程序日志还在写,nginx报错upstream timeout排查怀疑是超时的问题 设置nginx uwsgi_co ...
- python 解析xml遇到xml.etree.ElementTree.ParseError: not well-formed (invalid token): line 4, column 34
在调试数字驱动用xml文件的方式时,包含读取xml文件的步骤,运行程序报错: d:\test\0629>python XmlUtil.pyTraceback (most recent call ...
- 服务器环境配置nginx / php / php-fpm(一)
登陆,升级应用,查询和关闭selinux yum update getenforce setenforce 0 vi /etc/selinux 添加非root用户 adduser deploy pas ...
- SQL学习笔记二之MySQL的数据库操作
阅读目录 一 系统数据库 二 创建数据库 三 数据库相关操作 一 系统数据库 information_schema: 虚拟库,不占用磁盘空间,存储的是数据库启动后的一些参数,如用户表信息.列信息.权限 ...
- linux内核分析第六周-分析Linux内核创建一个新进程的过程
Linux内核对进程管理是操作系统的重要任务之一. 此次实验就是了解内核创建一个新进程的大致过程. 为了简单,使用fork再用户态创建一个进程.代码如下: 下面是准备工作 cd LinuxKer ...
- 在pom.xml中使用distributionManagement将项目打包上传到nexus私服
本文介绍 如何在pom.xml中使用distributionManagement将项目打包上传到nexus私服 1.pom.xml文件添加distributionManagement节点 <!- ...
