CS224d 单隐层全连接网络处理英文命名实体识别tensorflow
什么是NER?
命名实体识别(NER)是指识别文本中具有特定意义的实体,主要包括人名、地名、机构名、专有名词等。命名实体识别是信息提取、问答系统、句法分析、机器翻译等应用领域的重要基础工具,作为结构化信息提取的重要步骤。
NER具体任务
1.确定实体位置 2.确定实体类别
给一个单词,我们需要根据上下文判断,它属于下面四类的哪一个,如果都不属于,则类别为0,即不是实体,所以这是一个需要分成 5 类的问题:
• Person (PER)
• Organization (ORG)
• Location (LOC)
• Miscellaneous (MISC)
训练数据有两列,第一列是单词,第二列是标签。
EU ORG
rejects O
German MISC
Peter PER
BRUSSELS LOC
2.模型:
输入层的 x^(t) 为以 x_t 为中心的窗口大小为3的上下文语境,x_t 是 one-hot 向量,x_t 与 L 作用后就是相应的词向量,词向量的长度为 d = 50 :
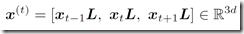
建立一个只有一个隐藏层的神经网络,隐藏层维度是 100,y^ 就是得到的预测值,维度是 5:
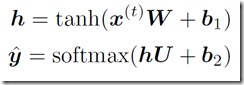
用交叉熵来计算误差:
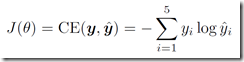
loss(J)对各个参数进行求导:
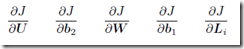

链式法则
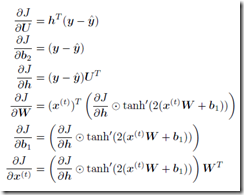
在 TensorFlow 中求导是自动实现的,这里用Adam优化算法更新梯度,不断地迭代,使得loss越来越小直至收敛。
3.具体实现:
在 def test_NER() 中,我们进行 max_epochs 次迭代,每次,用 training data 训练模型 得到一对 train_loss, train_acc,再用这个模型去预测 validation data,得到一对 val_loss, predictions,我们选择最小的 val_loss,并把相应的参数 weights 保存起来,最后我们是要用这些参数去预测 test data 的类别标签:
def test_NER(): config = Config()
with tf.Graph().as_default():
model = NERModel(config) init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
saver = tf.train.Saver() with tf.Session() as session:
# 最好的值时,它的 loss 它的 迭代次数 epoch
best_val_loss = float('inf')
best_val_epoch = 0 session.run(init)
for epoch in xrange(config.max_epochs):
print 'Epoch {}'.format(epoch)
start = time.time()
###
train_loss, train_acc = model.run_epoch(session, model.X_train,
model.y_train)
# 2.用这个model去预测 dev 数据,得到loss 和 prediction
val_loss, predictions = model.predict(session, model.X_dev, model.y_dev)
print 'Training loss: {}'.format(train_loss)
print 'Training acc: {}'.format(train_acc)
print 'Validation loss: {}'.format(val_loss)
if val_loss < best_val_loss:
best_val_loss = val_loss
best_val_epoch = epoch
if not os.path.exists("./weights"):
os.makedirs("./weights") saver.save(session, './weights/ner.weights')
if epoch - best_val_epoch > config.early_stopping:
break
###
# 把 dev 的lable数据放进去,计算prediction的confusion
confusion = calculate_confusion(config, predictions, model.y_dev)
print_confusion(confusion, model.num_to_tag)
print 'Total time: {}'.format(time.time() - start)
# 再次加载保存过的 weights,用 test 数据做预测,得到预测结果
saver.restore(session, './weights/ner.weights')
print 'Test'
print '=-=-='
print 'Writing predictions to q2_test.predicted'
_, predictions = model.predict(session, model.X_test, model.y_test)
save_predictions(predictions, "q2_test.predicted") if __name__ == "__main__":
test_NER()
4.模型训练过程:
- 首先导入数据 training,validation,test:
# Load the training set
docs = du.load_dataset('data/ner/train') # Load the dev set (for tuning hyperparameters)
docs = du.load_dataset('data/ner/dev') # Load the test set (dummy labels only)
docs = du.load_dataset('data/ner/test.masked')
- 把单词转化成 one-hot 向量后,再转化成词向量:
def add_embedding(self):
# The embedding lookup is currently only implemented for the CPU
with tf.device('/cpu:0'): embedding = tf.get_variable('Embedding', [len(self.wv), self.config.embed_size])
# lookup window大小的context的word embedding
window = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, self.input_placeholder)
window = tf.reshape(
window, [-1, self.config.window_size * self.config.embed_size]) return window
- 建立神经层,包括用 xavier 去初始化第一层, L2 正则化和用 dropout 来减小过拟合的处理:
def add_model(self, window):
with tf.variable_scope('Layer1', initializer=xavier_weight_init()) as scope:
W = tf.get_variable(
'W', [self.config.window_size * self.config.embed_size,
self.config.hidden_size])
b1 = tf.get_variable('b1', [self.config.hidden_size])
h = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(window, W) + b1)
if self.config.l2:
tf.add_to_collection('total_loss', 0.5 * self.config.l2 * tf.nn.l2_loss(W))
with tf.variable_scope('Layer2', initializer=xavier_weight_init()) as scope:
U = tf.get_variable('U', [self.config.hidden_size, self.config.label_size])
b2 = tf.get_variable('b2', [self.config.label_size])
y = tf.matmul(h, U) + b2
if self.config.l2:
tf.add_to_collection('total_loss', 0.5 * self.config.l2 * tf.nn.l2_loss(U))
output = tf.nn.dropout(y, self.dropout_placeholder)
return output
- 用 cross entropy 来计算 loss:
def add_loss_op(self, y):
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(y, self.labels_placeholder))
tf.add_to_collection('total_loss', cross_entropy)
loss = tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('total_loss'))
return loss
- 接着用 Adam Optimizer 把loss最小化:
def add_training_op(self, loss):
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(self.config.lr)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
return train_op
每一次训练后,得到了最小化 loss 相应的 weights。
完整程序见:code
CS224d 单隐层全连接网络处理英文命名实体识别tensorflow的更多相关文章
- 基于BERT预训练的中文命名实体识别TensorFlow实现
BERT-BiLSMT-CRF-NERTensorflow solution of NER task Using BiLSTM-CRF model with Google BERT Fine-tuni ...
- NLP入门(八)使用CRF++实现命名实体识别(NER)
CRF与NER简介 CRF,英文全称为conditional random field, 中文名为条件随机场,是给定一组输入随机变量条件下另一组输出随机变量的条件概率分布模型,其特点是假设输出随机 ...
- 实现一个单隐层神经网络python
看过首席科学家NG的深度学习公开课很久了,一直没有时间做课后编程题,做完想把思路总结下来,仅仅记录编程主线. 一 引用工具包 import numpy as np import matplotlib. ...
- cs224d 作业 problem set2 (二) TensorFlow 实现命名实体识别
神经网络在命名实体识别中的应用 所有的这些包括之前的两篇都可以通过tensorflow 模型的托管部署到 google cloud 上面,发布成restful接口,从而与任何的ERP,CRM系统集成. ...
- HMM(隐马尔科夫模型)与分词、词性标注、命名实体识别
转载自 http://www.cnblogs.com/skyme/p/4651331.html HMM(隐马尔可夫模型)是用来描述隐含未知参数的统计模型,举一个经典的例子:一个东京的朋友每天根据天气{ ...
- 基于bert的命名实体识别,pytorch实现,支持中文/英文【源学计划】
声明:为了帮助初学者快速入门和上手,开始源学计划,即通过源代码进行学习.该计划收取少量费用,提供有质量保证的源码,以及详细的使用说明. 第一个项目是基于bert的命名实体识别(name entity ...
- DL4NLP —— 序列标注:BiLSTM-CRF模型做基于字的中文命名实体识别
三个月之前 NLP 课程结课,我们做的是命名实体识别的实验.在MSRA的简体中文NER语料(我是从这里下载的,非官方出品,可能不是SIGHAN 2006 Bakeoff-3评测所使用的原版语料)上训练 ...
- 神经网络结构在命名实体识别(NER)中的应用
神经网络结构在命名实体识别(NER)中的应用 近年来,基于神经网络的深度学习方法在自然语言处理领域已经取得了不少进展.作为NLP领域的基础任务-命名实体识别(Named Entity Recognit ...
- 2. 知识图谱-命名实体识别(NER)详解
1. 通俗易懂解释知识图谱(Knowledge Graph) 2. 知识图谱-命名实体识别(NER)详解 3. 哈工大LTP解析 1. 前言 在解了知识图谱的全貌之后,我们现在慢慢的开始深入的学习知识 ...
随机推荐
- Java编程思想 学习笔记9
九.接口 接口和内部类为我们提供了一种将接口与实现分离的更加结构化的方法. 1.抽象类和抽象方法 抽象类是普通的类与接口之间的一种中庸之道.创建抽象类是希望通过这个通用接口操纵一系列类. Java提 ...
- Centos下新建用户及修改用户目录
Centos下新建用户及修改用户目录 Hillgo 关注 2015.09.22 01:32* 字数 154 阅读 3492评论 0喜欢 3 添加及删除用户 添加用户 test: adduser tes ...
- 攻击WEP加密无线网络
1.介绍 针对客户端环境和无客户端环境下破解WEP的几类方法. 有客户端环境: 一般当前无线网络中存在活动的无线客户端环境,即有用户通过无线连接到无线AP上并正在进行上网等操作时. 无客户端环境: 1 ...
- 20155335俞昆 《java程序设计》第八周总结
2016-2017-2 <Java程序设计>第X周学习总结 ##认识NIO 在java中,输入与输出,基本上是以字节为单位进行的低层次处理,实际上多半是对字节数组中整个区块进行处理,对于d ...
- Java SE之基本程序设计结构
概述: 0.注释 1.基本数据类型(有且仅有8个): 1.1 整型:int,short,long,byte(表示一个字节,[-128,127]) 1.2 ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 徐州赛区网络预赛 G题
题目链接: https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/31459 具体思路: 先顺序输入,然后回溯,假设已经加入了n个点,那么在加入的同时,首先看一下原先x轴上已经有过的点,找到第一个 ...
- 解决ping 127.0.0.1 一般故障 问题
故障如下图: 绕了好一大圈才发现是goupi防火墙搞的鬼,弄得我一些软件一直运行不了!!!!! 废话不多说,关了防火墙就行了:操作步骤如下图示 关闭之后,美滋滋:
- 【Mysql sql inject】POST方法BASE64编码注入write-up
翻到群里的小伙伴发出一道POST型SQL注入题,简单抓包判断出题目需要base64编码后才执行sql语句,为学习下SQL注入出题与闯关的思路+工作不是很忙,所以花点时间玩了一下,哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈 ...
- MySQL— 进阶
目录 一.视图 二.触发器 三.函数 四.存储过程 五.事务 一.视图 视图是一个虚拟表(非真实存在),其本质是[根据SQL语句获取动态的数据集,并为其命名],用户使用时只需使用[名称]即可获取结果集 ...
- oracle查询重复数据方法
SQL重复记录查询方法 2008年08月14日 星期四 21:01 SQL重复记录查询 1.查找表中多余的重复记录,重复记录是根据单个字段(peopleId)来判断select * from peop ...
